


This research report explores CVE-2024-27198, a critical vulnerability discovered in JetBrains TeamCity. This flaw enables remote, unauthenticated attackers to bypass authentication measures, potentially resulting in unauthorized control over servers. With a CVSS base score of 9.8, its severity is significant, potentially leading to complete system compromise, including unauthenticated Remote Code Execution (RCE) capabilities.
Our investigation highlights the active targeting of CVE-2024-27198 by the North Korean threat actor Kimsuki. Open-source intelligence (OSINT) gathering also indicates other threat actors scanning for and potentially exploiting this vulnerability. Notably, JetBrains TeamCity vulnerabilities are frequently targeted by nation-state threat actors. Previous incidents, such as the exploitation of CVE-2023-42793 by APT 29 and the threat posed by NOBELIUM/Midnight Blizzard, emphasize the serious risks involved. Of particular concern is the potential for supply chain attacks, as compromise could grant access to sensitive assets.
CVE-2024-27198 is a critical vulnerability discovered in JetBrains TeamCity versions before 2023.11.4. This flaw enables remote attackers to bypass authentication and seize control of vulnerable servers. JetBrains TeamCity functions as a CI/CD server, automating tasks like building, testing, and deploying code changes, while seamlessly integrating with version control systems and supporting various testing frameworks. Its robust reporting and analytics capabilities enhance development workflows. Exploitation of this vulnerability has been observed, with threat actors distributing Jasmin ransomware and creating unauthorized user accounts. Notably, CI/CD vulnerabilities are frequently targeted by nation-state threat actors due to their extensive attack surface, presenting opportunities for supply chain attacks.
Key Takeaways:
Acknowledgements:
The CYFIRMA Research team acknowledges security researchers who responsibly disclosed this vulnerability.
Vulnerability Type: Authentication bypass
CVE ID: CVE-2024-27198
CVSS Severity Score: 9.8 (Critical)
Application: JetBrains TeamCity
Impact: Allowing to perform admin actions
Severity: Critical
Affected Versions: JetBrains TeamCity versions before 2023.11.4.
Patch Available: Yes
CVE-2024-27198 is a critical authentication bypass vulnerability identified within the web component of JetBrains TeamCity versions before 2023.11.4. This vulnerability enables remote unauthenticated attackers to circumvent authentication checks by crafting specific URLs. By exploiting this flaw, attackers can directly access endpoints that are typically protected by authentication mechanisms, thereby gaining unauthorized control over vulnerable TeamCity servers. With a CVSS base score of 9.8 (Critical), the severity of this vulnerability is heightened due to its potential to facilitate complete compromise of affected systems.
CVE-2024-27198 poses a significant threat by enabling remote, unauthenticated attackers to fully compromise vulnerable TeamCity servers. This vulnerability grants adversaries unrestricted control over all aspects of the TeamCity infrastructure, comprising projects, builds, agents, and artifacts. Exploiting this unauthorized access, attackers can leverage compromised TeamCity servers as a launch pad for executing supply chain attacks.
JetBrains TeamCity versions before 2023.11.4 are vulnerable to CVE-2024-27198.
Is there already an exploit tool to attack this vulnerability?
As of the latest available information, there is a known public exploit tool for CVE-2024-27198 targeting JetBrains TeamCity. The availability of a publicly available exploit tool provides a limited opportunity for organizations to address and remediate the vulnerability before potential malicious actors can capitalize on it. With proof-of-concept exploit code readily accessible, there is an increased risk of widespread compromise of TeamCity servers, emphasizing the urgency for organizations to take proactive measures to mitigate the threat.
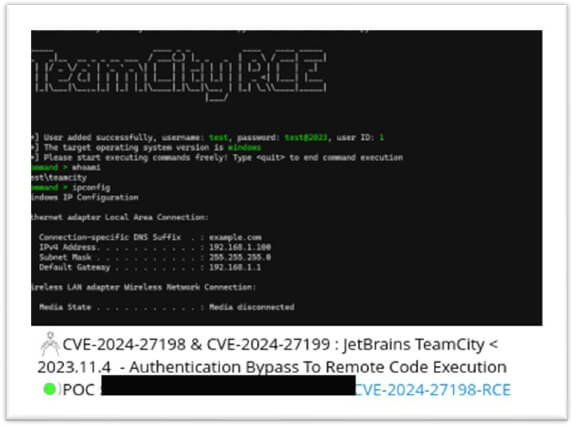
Has this vulnerability already been used in an attack?
Previous incidents, including the exploitation of CVE-2023-42793 by APT 29 and the threat posed by NOBELIUM/Midnight Blizzard, underscore the vulnerability of JetBrains TeamCity to exploitation by nation-state threat actors. Our investigation further uncovered active targeting of CVE-2024-27198 by the North Korean threat actor Kimsuki. Moreover, open-source intelligence (OSINT) gathering revealed additional threat actors scanning for and potentially exploiting this vulnerability.
Furthermore, CVE-2024-27198 in JetBrains TeamCity has been actively exploited by threat actors to deliver Jasmin ransomware and create unauthorized user accounts. The Shadowserver Foundation has observed attempted exploitation, while actors associated with the BianLian and Jasmin ransomware families have weaponized the vulnerability to distribute payloads such as the XMRig cryptocurrency miner and Spark RAT.
What is the attack complexity level?
The attack complexity level for CVE-2024-27198 in JetBrains TeamCity is assessed as Critical.
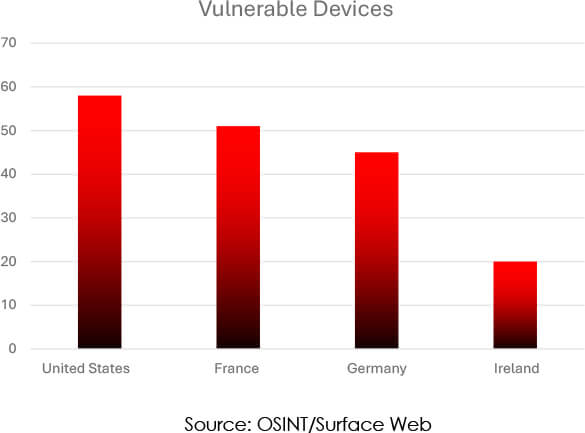
Our investigation has unveiled a critical vulnerability impacting JetBrains TeamCity servers. Through our research, we have identified a concerning 241 publicly accessible instances of JetBrains TeamCity that may be vulnerable to this flaw.
Researchers have discovered that by exploiting CVE-2024-27198 within JetBrains TeamCity, attackers can exploit a specific endpoint, such as /app/rest/server, typically requiring authentication. Unauthenticated access to this endpoint is possible by fulfilling three specific requirements during an HTTP(S) request.
Firstly, attackers need to request an unauthenticated resource generating a 404 response, achievable by requesting a non-existent resource like /hax. Secondly, they must pass an HTTP query parameter named “jsp” containing the value of an authenticated URI path, appending an HTTP query string such as ?jsp=/app/rest/server. Lastly, ensuring the arbitrary URI path concludes with “.jsp” by appending an HTTP path parameter segment like;.jsp is essential.
By amalgamating these conditions, the attacker crafts a URI path like /hax?jsp=/app/rest/server;.jsp. This manipulation exploits the authentication bypass vulnerability, enabling successful access to the authenticated endpoint devoid of authentication.
This vulnerability poses severe risks as attackers can exploit it in varied ways to seize control of vulnerable TeamCity servers, thereby gaining control over all associated projects, builds, agents, and artifacts. Such unauthorized access significantly compromises the integrity and confidentiality of the compromised systems and their stored data.
To mitigate the exploitation of CVE-2024-27198 in JetBrains TeamCity, organizations should promptly apply security patches and update affected systems. Additionally, implementing robust network security measures, monitoring systems for suspicious activity, and conducting regular security audits are essential. Restricting access to critical systems and educating employees on cybersecurity best practices further strengthens defences against potential exploits.
Target Geography:
Organizations worldwide rely on JetBrains TeamCity, those using affected versions are susceptible to the vulnerability and are at risk. This vulnerability carries broad geographical implications, impacting regions such as the United States, France, the United Kingdom, South Africa, Ukraine, and Poland. Regardless of their location, organizations globally may face exploitation risks, if they utilize the affected server.
Target Industry:
The CVE-2024-27198 vulnerability poses a significant threat to organizations across various sectors, including banking, healthcare, software manufacturing, and more. These industries heavily depend on JetBrains TeamCity for their automation requirements. Malicious actors with the knowledge of this vulnerability may strategically target specific sectors, taking into account the perceived value of the data or services facilitated by JetBrains TeamCity. Industries dealing with sensitive information or relying extensively on JetBrains TeamCity for automation could become prime targets for exploitation.
Target Technology:
The authentication bypass vulnerability (CVE-2024-27198) in JetBrains TeamCity poses a severe threat to CI/CD pipelines, allowing attackers to gain unauthenticated access to critical endpoints and compromise the integrity of automated software development processes. This vulnerability is particularly concerning for organizations relying on TeamCity, as it could enable attackers to assume control of servers and manipulate build processes.
The past exploits of vulnerabilities akin to JetBrains TeamCity CVE-2023-42793 underscore the persistent threat posed by sophisticated threat actors. Notorious incidents like the SolarWinds supply chain attack highlight the potential impact of such exploits. These actors, often associated with nation-state groups like North Korea, have leveraged vulnerabilities to achieve remote code execution, facilitating malicious activities, such as privilege escalation and lateral movement within networks. Threat actors affiliated with APT29 and other nation-state groups have consistently demonstrated their capability to exploit vulnerabilities for malicious purposes, emphasizing the importance of robust security measures and proactive vulnerability management practices to safeguard CI/CD pipelines and critical infrastructure.
We’ve identified malicious IP addresses associated with attacks targeting JetBrains TeamCity vulnerabilities:
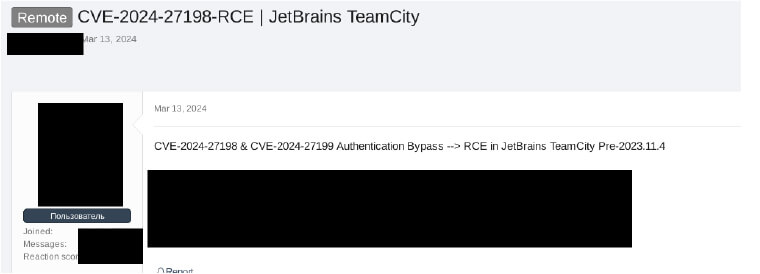
Presently, discussions surrounding the vulnerability in JetBrains TeamCity are ongoing, with some participants discussing the possibility of offering exploits for sale on forums. Additionally, there are conversations regarding how the proof-of-concept (PoC) works and its potential implications.
The CVE-2024-27198 vulnerability in JetBrains TeamCity poses a significant threat to organizations across various sectors, including banking, healthcare, software manufacturers, and more, that rely heavily on JetBrains TeamCity for automation purposes. Malicious actors, armed with the knowledge of this vulnerability, may strategically target specific industries, prioritizing those with perceived valuable data or services facilitated by JetBrains TeamCity. Industries handling sensitive information or extensively relying on JetBrains TeamCity for automation are at heightened risk of exploitation. Therefore, organizations must prioritize patching and implementing security measures to mitigate the potential impact of this critical vulnerability.