



A critical unauthenticated remote code execution vulnerability, denoted as CVE- 2023-3519, has been exposed within the architecture of Citrix ADC and Citrix Gateway products. This flaw enables threat actors to execute arbitrary code on susceptible systems without the need for authentication: this signifies a grave security concern, impacting numerous Citrix instances on a global scale, with the potential to cause data breaches, compromised systems, and unauthorized access. CYFIRMA’s vigilant research underscores the urgency of swift mitigation measures, such as applying provided patches and heightening security protocols to ensure the resilience of digital assets, in the face of this formidable threat.
CVE-2023-3519 represents a grave security threat targeting Citrix ADC and Citrix Gateway devices. These products are widely deployed for load balancing and remote access, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals, seeking to exploit the unauthenticated remote code execution vulnerability. This vulnerability underscores the importance of prompt mitigation to safeguard critical systems and sensitive data.
Key Takeaways:
Acknowledgements:
The CYFIRMA Research team acknowledges the collaborative efforts of cybersecurity professionals and institutions in providing insights and intelligence related to CVE-2023- 3519. The dedication of these individuals contributes to the collective defense against evolving cyber threats.
Vulnerability Type: Remote Code Execution (RCE)
CVE ID: CVE-2023-3519
CVSS Severity Score: 9.8 (Critical)
Affected Products: Citrix ADC and Citrix Gateway
Impact: Remote code execution, unauthorized access, data breaches, network compromise
Severity: Critical Patched Available: Yes
CVE-2023-3519 is a severe security vulnerability affecting Citrix ADC and Gateway products. The flaw allows attackers to execute malicious code remotely without requiring authentication: by exploiting this vulnerability, attackers can compromise the targeted system, gain unauthorized access, and potentially exfiltrate sensitive information. The vulnerability has gained attention due to its potential for widespread impact and the availability of proof-of-concept exploits. CYFIRMA researchers have identified instances of exploitation, underlining the urgency of addressing the issue.
The impact of CVE-2023-3519 is substantial, with potential consequences, including unauthorized access, data breach, and system compromise. Attackers exploiting this vulnerability can execute arbitrary code, potentially leading to a complete compromise of the targeted Citrix ADC and Gateway devices. This could facilitate data theft, lateral movement, and even disruption of critical services, imposing severe financial and reputational repercussions on affected organizations.
The vulnerability impacts various versions of Citrix ADC and Gateway devices. A detailed list of affected versions can be found in the official Citrix security bulletin here.
The exploitation and analysis of the CVE-2023-3519 vulnerability in Citrix NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway involved a thorough examination of the vulnerability’s underlying mechanism, potential exploit vectors, and steps to compromise the affected systems.
While we were researching, we also found that almost 80000 Citrix ADC are publicly available, which may be vulnerable to CVE-2023-3519 vulnerability.
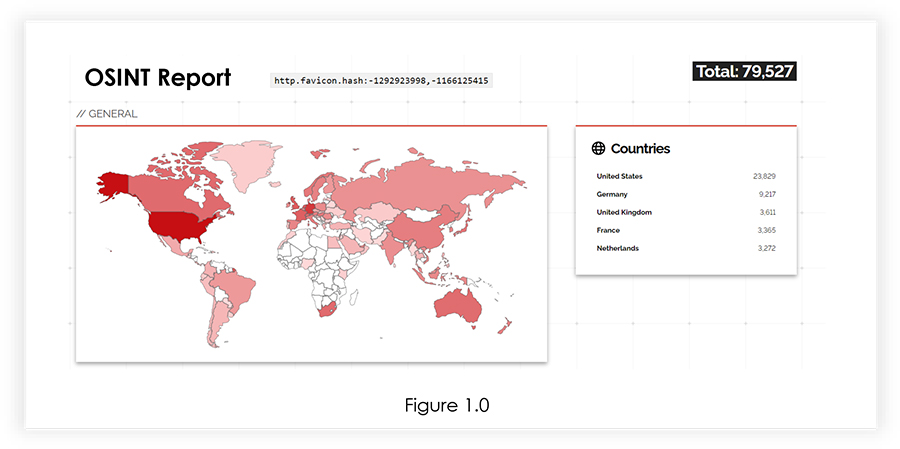
The initial analysis revealed that the root cause of the vulnerability was a stack-based buffer overflow. This flaw allowed unauthenticated attackers to manipulate the system’s memory stack, potentially leading to remote code execution. Among the three vulnerabilities disclosed by Citrix, CVE-2023-3519 stood out as the most severe, actively exploited issue.
In the analysis process, we observed the modifications made to the software, after the introduction of a patch. Our attention was initially drawn to the various functions related to the Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML), in particular ‘ns_aaa_saml_parse_authn_request’. Although, this function initially appeared to be pertinent, it eventually proved to be a misleading trail. Our focus was redirected to the ‘/netscaler/nsppe service’, specifically the NetScaler Packet Parsing Engine, as this is where the actual vulnerability was situated.
One of the analysis points focused on a difference in the vulnerability description provided by Citrix, and the actual exploit scenario. It was discovered that the vulnerability could be triggered without SAML being enabled. Moreover, the function ‘ns_aaa_gwtest_get_event_and_target_names’ emerged as the crux of the vulnerability.
Exploitation was initiated by meticulously crafting a malicious request, designed to trigger a stack overflow. Leveraging tools like the GNU Debugger (gdb) for debugging, breakpoints were strategically set to gain insight into the system compromise process. This debugging phase was integral in knowing the exact moment the vulnerability would activate, as well as understanding the mechanisms through which an attacker could manipulate the system’s operations.
Further investigation delved into the prospect of an attacker overwriting the return address to facilitate the execution of arbitrary code. This exploration entailed creating payloads and dispatching requests intended to overwrite stack data, thereby enabling manipulation of the program’s execution sequence.
To validate these findings, various payloads were deployed, commencing with rudimentary payloads involving debug breakpoints. This stage substantiated successful control over the execution flow. Subsequently, the focus shifted towards more intricate payloads, such as crafting shellcode using tools like msfvenom. The shellcode facilitated command execution within the compromised system. This progression demonstrated the attacker’s potential to generate files and issue arbitrary commands as part of the exploitation effort.
It’s important to recognize that this analysis transpired within an environment devoid of key security safeguards, including Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) and Data Execution Prevention (DEP). ASLR and DEP are prominent features within contemporary systems, serving to thwart memory manipulation-based exploitation techniques. However, the absence of these measures in the context of the specific vulnerability rendered the exploitation process relatively straightforward.
To mitigate CVE-2023-3519, organizations must promptly apply the provided security patches by Citrix. Timely patching and updates are crucial to forestall potential exploitation. Implementing network segmentation, robust firewall rules, and intrusion detection systems bolster defence mechanisms. Continuous monitoring and threat intelligence gathering are recommended to detect and respond to any suspicious activity promptly.
Target Geography:
Based on the available information regarding the CVE-2023-3519 vulnerability in Citrix ADC and Gateway devices, organizations worldwide that utilize these products with the affected versions could potentially be impacted. Citrix ADC and Gateway devices are widely deployed across the globe, making the vulnerability relevant to organizations in various geographical regions.
Attackers may focus their attention on targeting regions where Citrix products are extensively used. This could encompass regions such as North America, Europe, Asia- Pacific, and other areas with a significant presence of Citrix infrastructure. The widespread adoption of Citrix products in these regions increases the potential attack surface and raises the likelihood of identifying vulnerable systems.
Target Industry:
The CVE-2023-3519 vulnerability in Citrix ADC and Gateway devices can affect organizations across a range of industries that rely on Citrix’s networking solutions. Namely: healthcare, finance, government, telecommunications, and other sectors.
Threat actors may selectively target industries that handle sensitive data or have a higher reliance on Citrix’s products. Given the potential impacts of successful exploitation, such as unauthorized code execution and compromise of systems, these industries become attractive targets for attackers seeking to take advantage of the vulnerability.
Target Technology:
The CVE-2023-3519 vulnerability specifically affects Citrix ADC and Gateway devices, which are integral components of Citrix’s networking infrastructure. As Citrix is a major provider of networking and application delivery solutions, the vulnerability is limited to organizations utilizing Citrix’s products for load balancing, security, and remote access.
It is important to note that the potential consequences of the vulnerability go beyond Citrix’s products: a successful exploitation could lead to unauthorized code execution and potential compromise of an organization’s broader technological environment, including servers, applications, and other interconnected systems.
Understanding the specific target geography, industries, and technologies impacted by the CVE-2023-3519 vulnerability helps organizations prioritize their security efforts. This includes promptly applying patches, implementing proactive security measures, and staying vigilant to mitigate the risk of exploitation.
From underground forums, CYFIRMA Research team has observed that unknown hackers are selling CITRIX Exploits.
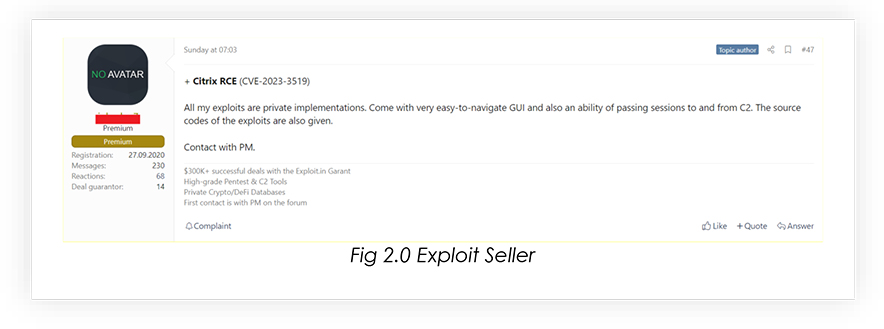
Organizations and individuals utilizing Citrix ADC and Gateway products are strongly advised to exercise heightened vigilance and proactively secure their systems against potential threats, stemming from the CVE-2023-3519 vulnerability. Swift and strategic actions are essential to safeguard digital assets and sensitive data from compromise.
In conclusion, the critical nature of the CVE-2023-3519 vulnerability calls for immediate and comprehensive action by organizations and individuals relying on Citrix ADC and Gateway products. Timely application of provided security patches, system updates, and vigilant network monitoring are imperative to mitigate potential risks. Collaboration within the cybersecurity community and continuous threat intelligence sharing play a crucial role in staying ahead of emerging threats. By adopting these proactive measures and acknowledging the potential severity of the vulnerability, stakeholders can bolster their defenses and safeguard against unauthorized access, data breaches, and network compromise. The CYFIRMA Research team remains dedicated to contributing to the collective effort to enhance cybersecurity resilience and protect digital assets in the face of evolving cyber threats.