Published On : 2024-10-10
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
September 2024 witnessed a 10.92% decline in ransomware incidents compared to the previous month, primarily due to a reduction in victim count from prominent groups such as LockBit. Ransomware groups like Medusa and Play saw dramatic increases, highlighting the ever-changing nature of the threat landscape. Despite a slight decline in victim count, RansomHub remained a dominant player. Sectors like FMCG and IT saw an increase in attacks, while others, including healthcare and hospitality, experienced a decrease. Geographically, the United States continued to be the most targeted region.
INTRODUCTION
Welcome to the September 2024 ransomware report, offering an in-depth analysis of the evolving threat landscape. This report compares ransomware activity levels between August and September 2024, highlighting key shifts and the strategies of prominent ransomware groups. It also identifies the most targeted industries and regions, providing insights into how attacks are adapting and evolving. By examining these trends, the report aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the changing tactics and focus areas of ransomware actors throughout the month.
Key Points:
- In September 2024, the RansomHub ransomware group emerged as a significant threat, taking the lead with 66 victims.
- The Manufacturing sector is the primary target of ransomware attacks, experiencing 66 incidents.
- The USA was the most targeted geography in September 2024, with more than 50% of ransomware incidents.
- The ransomware groups, Nitrogen, Orca, and Kransom, emerged as newly identified threats in September 2024.
TREND COMPARISON OF SEPTEMBER 2024’s TOP 5 RANSOMWARE GROUPS WITH AUGUST 2024.
Throughout September 2024, there was notable activity from several ransomware groups. Here are the trends regarding the top 5:
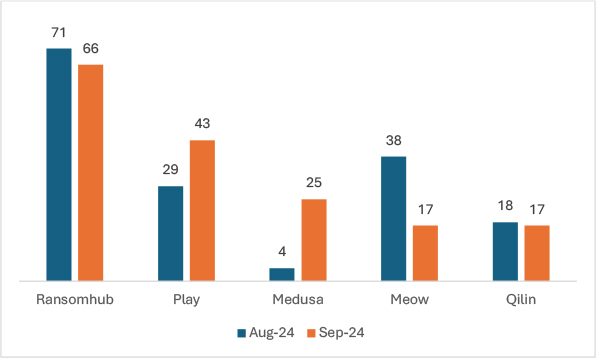
In September 2024, ransomware trends exhibited significant shifts, with emerging groups gaining momentum. Notably, the Play ransomware group saw a sharp increase in activity, with a 48.3% rise in victims compared to August. Medusa displayed the most dramatic growth, recording a staggering 525% increase in its victim count. On the other hand, RansomHub experienced a slight decrease, with a 7% decline, dropping from 71 to 66 victims. Meanwhile, the Meow ransomware witnessed a significant drop in activity, with a 55.3% decrease. Lastly, Qilin ransomware remained consistent, with minor changes in victim numbers. These shifts highlight the volatile nature of ransomware activity, where certain groups are rapidly expanding while others see diminished operations.
RANSOMWARE OF THE MONTH
RansomHub
Despite the reduction in the victims count, RansomHub retains the highest number of victims in September 2024.
RansomHub, a newly emerged ransomware group, debuted its leak site in February 2024. It is likely an updated iteration of the older Knight ransomware, rebranded by new actors who possibly acquired Knight’s source code earlier in 2024, and their sophisticated ransomware targets multiple platforms and leverages vulnerabilities for initial access. Employing advanced obfuscation and attack techniques, RansomHub has swiftly become a significant player in the ransomware threat landscape in a very short period.
Below are the observed TTPs of RansomHub
| Tactics |
ID |
Technique |
| Initial Access |
T1190 |
Exploit Public-Facing Application |
| Initial Access |
T1133 |
External Remote Services |
| Resource Development |
T1588.006 |
Obtain Capabilities: Vulnerabilities |
| Resource Development |
T1587.001 |
Develop Capabilities: Malware |
| Persistence |
T1098 |
Account Manipulation |
| Defense Evasion |
T1562.009 |
Impair Defenses: Safe Mode Boot |
| Defense Evasion |
T1562 |
Impair Defenses |
| Defense Evasion |
T1562.001 |
Impair Defenses: Disable or Modify Tools |
| Discovery |
T1016 |
System Network Configuration Discovery |
| Collection |
T1560.001 |
Archive Collected Data: Archive via Utility |
| Command and Control |
T1105 |
Ingress Tool Transfer |
| Command and Control |
T1219 |
Remote Access Software |
| Command and Control |
T1090 |
Proxy |
| Exfiltration |
T1041 |
Exfiltration Over C2 Channel |
| Impact |
T1486 |
Data Encrypted for Impact |
| Impact |
T1657 |
Financial Theft |
INDUSTRIES HIT: SEPTEMBER 2024 Vs AUGUST 2024
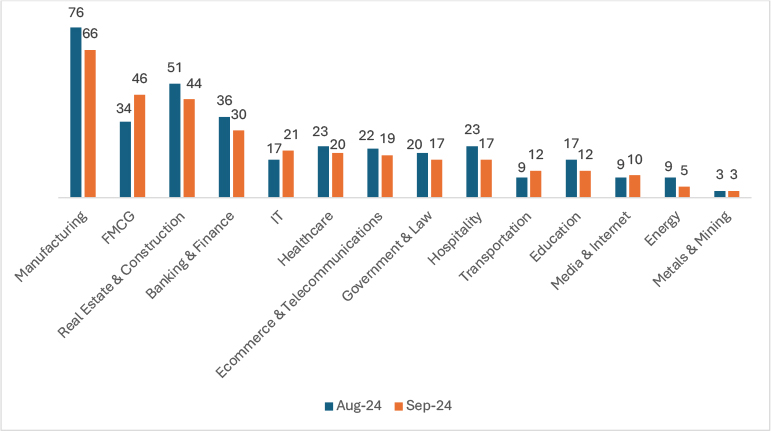
In September 2024, ransomware attacks demonstrated varying trends across industries. Manufacturing saw a 13.2% decrease in its victims, while FMCG recorded a 35.3% rise, increasing from 34 to 46 attacks. Real estate and construction experienced a 13.7% decline, while banking and finance saw a 16.7% drop. The IT sector observed a 23.5% increase in its incidents. Healthcare saw a 13% decline, and e-commerce & telecommunications recorded a 13.6% drop. Government and law were down by 15%, and hospitality saw the sharpest decline, at 26.1%. Transportation, on the other hand, rose by 33.3%, while education saw a 29.4% drop. Media and internet experienced a slight 11.1% increase, while the energy sector dropped by 44.4%. Metals and mining remained constant with no change. These fluctuations reflect the dynamic nature of ransomware attacks across sectors.
TREND COMPARISON OF RANSOMWARE ATTACKS
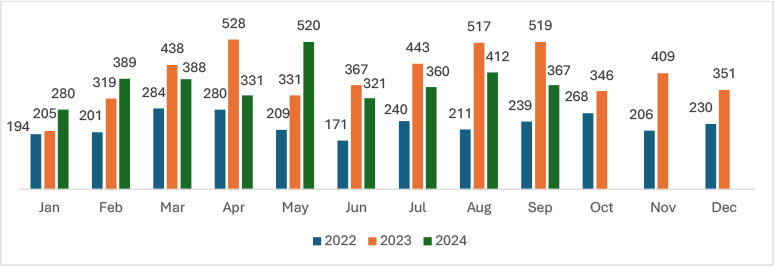
In September 2024, ransomware incidents decreased by 10.92% compared to August 2024. With medium confidence, this decline can be attributed to the weakened influence of prominent ransomware groups like LockBit. This shift in the threat landscape likely resulted from law enforcement takedowns targeting these groups.
GEOGRAPHICAL TARGETS: TOP 5 LOCATIONS
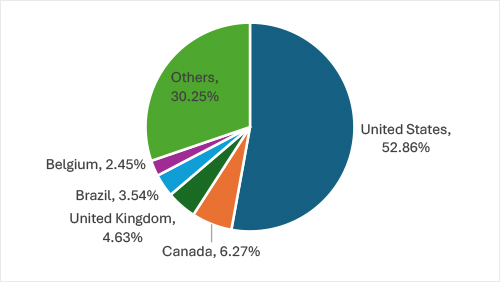
This chart illustrates the geographical distribution of ransomware targets, with the United States being the most affected, accounting for 52.86% of attacks. Canada follows with 6.27%, and the United Kingdom at 4.63%. Other countries collectively represent 30.25% of the total. Notable targets also include Brazil at 3.54% and Belgium at 2.45%. This distribution underscores the concentration of ransomware attacks in key regions, with developed economies being prime targets for cybercriminals.
EVOLUTION OF RANSOMWARE GROUPS IN SEPTEMBER 2024
- A Mallox ransomware affiliate has repurposed the Kryptina ransomware code to create a Linux-targeted variant, “Mallox Linux 1.0.” This version retains Kryptina’s core components, including AES-256-CBC encryption, decryption routines, and command-line builder, while making minor changes in ransom notes and simplifying documentation. Additionally, the affiliate’s infrastructure includes tools, such as a Kaspersky password reset utility, a privilege escalation exploit, PowerShell scripts, and Java-based payload droppers. This technical evolution reflects Mallox’s shift from targeting Windows systems to expanding attacks on Linux and VMWare ESXi, capitalizing on leaked source code to enhance multi-platform capabilities.
- The NoName ransomware group, active for over three years, has shifted its tactics, now deploying RansomHub malware, potentially indicating an affiliate partnership. NoName previously used its ScRansom malware, part of the Spacecolon malware family, but faced issues with complex decryption due to its AES-CTR-128 and RSA-1024 encryption scheme. The group has leveraged brute-force techniques and exploits older vulnerabilities, such as EternalBlue (CVE-2017-0144), ZeroLogon (CVE-2020-1472), and others, to gain access to networks. NoName began mimicking larger ransomware operations, creating a clone of the LockBit data leak site and using LockBit-branded ransom notes in attacks. Recently, NoName employed RansomHub’s advanced tools, including an EDR killer for disabling security defences. This, coupled with the use of RansomHub’s ransomware in later attacks, points to NoName likely becoming a RansomHub affiliate, aiming to enhance its operational sophistication and effectiveness.
- The Cicada3301 ransomware operation emerged in mid-2024, evolving into a significant threat. Initially observed in June 2024, the group targets organizations worldwide using Rust-based encryptors for both Windows and VMware ESXi systems, indicating its focus on enterprise environments. It uses the ChaCha20 stream cipher for encryption, with RSA securing the symmetric keys. For larger files, intermittent encryption is applied to hinder decryption efforts. Cicada3301 disrupts virtual machines by shutting them down and deleting snapshots using ESXi management commands. A feature also enables VM encryption without shutdown, adding flexibility. Notably, the group utilizes the Brutus botnet to brute-force VPNs, providing initial access to networks. This botnet activity, linked with former ALPHV operations, suggests a rebrand or evolution involving previous ALPHV members, highlighting the group’s advanced capabilities and strategic approach.
- Ransomware groups like BianLian and Rhysida are increasingly leveraging Microsoft’s Azure Storage Explorer and AzCopy tools to exfiltrate stolen data from breached networks into Azure Blob storage. These tools, typically used for legitimate cloud management and data transfers, offer scalability and ease of use, making them attractive for ransomware operations. Azure’s trusted status within enterprises allows attackers to bypass security filters and firewalls, facilitating undetected data transfers. Attackers must first install dependencies and upgrade .NET to version 8 for these tools to function. Multiple instances of Storage Explorer are used to accelerate the upload process, maximizing the speed of data exfiltration. Logging capabilities in AzCopy can provide valuable insights for incident responders, aiding them in identifying stolen files and potential payloads through log files. Ransomware actors exploit Azure’s enterprise-level features to expedite data theft and extortion attempts.
VULNERABILITIES EXPLOITED IN SEPTEMBER 2024 BY RANSOMWARE GROUPS
| Sr.No |
CVE |
CVSS |
Vulnerability Name |
Associated Threat Actor |
Vulnerable Software Versions |
Patch |
| 1 |
CVE-2024-40766 |
9.8 |
SonicWall SonicOS Improper Access Control Vulnerability |
Akira |
SonicWall Gen 5 running SonicOS version 5.9.2.14-12o and older
SonicWall Gen 6 running SonicOS version 6.5.4.14-109n and older
SonicWall Gen 7 running SonicOS version 7.0.1-5035 and older |
YES |
EMERGING GROUPS
Kransom ransomware disguises itself as the legitimate StarRail game, utilizing DLL side-loading to execute its malicious payload. It stores a malicious DLL file alongside the game, which the executable loads, allowing the ransomware to hijack the execution flow. By employing a valid certificate, the malware evades detection, appearing harmless to security measures. The encrypted ransomware code within the DLL is obfuscated using XOR, complicating detection efforts. When activated, the ransomware displays a message prompting users to contact the game’s developers for assistance, masking its true intent and exploiting the game’s structure to execute its attack.
A new ransomware group launched its dark web leak site this week. They go by the name Nitrogen and have currently listed more than 6 victims on the site, during the writing of this report.

Source: Underground forum
Orca Ransomware is identified as a variant of the Zeppelin malware family, known for its potent encryption capabilities. Once it infiltrates a system, Orca encrypts files and modifies their names by appending the extension .ORCA followed by a unique victim ID. The group has claimed 3 victims during the writing of this report.
Source: Underground forum
KEY RANSOMWARE EVENTS IN SEPTEMBER 2024
- Access Sports, an orthopedic service provider, suffered a ransomware attack by the Inc Ransom group, compromising the sensitive data of 88,000 individuals, including SSNs and medical records. Although no misuse has been reported, the company offered fraud protection. Inc Ransom claims to have leaked confidential company data online.
- The Port of Seattle confirmed that the Rhysida ransomware group was responsible for the recent cyberattack, which affected websites, email, phone systems, and operations at Seattle-Tacoma International Airport. The attack disrupted key services, including baggage handling and check-in kiosks. The Port isolated systems to contain the breach, and there has been no further unauthorized activity reported since August. The investigation is ongoing, and the Port continues efforts to restore affected systems fully.
- RansomHub ransomware group has claimed responsibility for breaching Intermountain Planned Parenthood in Montana, stealing 93GB of sensitive data. The group posted a sample of the stolen data on its dark web leak site and is demanding a ransom. Planned Parenthood has acknowledged the cyberattack and is investigating the breach.
- The U.S. Treasury’s OFAC has sanctioned two cryptocurrency exchanges, Cryptex and PM2BTC, for laundering funds linked to Russian ransomware groups. Cryptex laundered over $51 million and facilitated $720 million in transactions involving cybercriminal services. PM2BTC, now seized, processed illegal currency conversions for Russian actors. Both exchanges are connected to Russian money launderer Sergey Sergeevich Ivanov, who is linked to various cybercrime operations. The sanctions aim to disrupt Russian cybercrime networks and prevent U.S. entities from engaging with these exchanges. Previous sanctions targeted other exchanges and mixing services tied to Russian and North Korean cybercriminals.
BUSINESS IMPACT ANALYSIS
Based on available public reports, approximately 31% of enterprises are compelled to halt their operations, either temporarily or permanently, in the aftermath of a ransomware onslaught. The ripple effects extend beyond operational disruptions, as detailed by additional metrics:
- A significant 40% of affected organizations are forced into downsizing their workforce due to the financial strain caused by the attack.
- The aftermath sees 35% of businesses experiencing turnover at the executive level, with C-suite members stepping down in the wake of the security breach.
- The financial toll of cyber incidents is staggering, with the average cost burden to companies, irrespective of their size, estimated at around $200,000. This figure underscores the substantial economic impact of cyber threats.
- Alarmingly, 75% of small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) face existential threats, admitting the likelihood of closure should cybercriminals extort them for ransom to avoid malware infection.
- The long-term viability of these entities is also in jeopardy, with 60% of small businesses shutting down within six months post-attack, highlighting the enduring impact of such security breaches.
- Even in instances where ransoms are not conceded to, organizations bear significant financial weight in their recovery and remediation endeavors to restore normality and secure their systems.
EXTERNAL THREAT LANDSCAPE MANAGEMENT (ETLM) OVERVIEW
Impact Assessment
Ransomware remains a major threat to organizations and individuals, encrypting critical data and demanding payment for its release. The impact extends beyond ransom demands, leading to financial losses from cybersecurity measures, recovery efforts, and operational disruptions. These attacks also erode customer trust, cause emotional distress, and result in potential regulatory violations. The damage to reputation and consumer confidence can destabilize markets and disrupt business operations. As such, it is crucial for businesses and governments to proactively address ransomware threats to protect financial stability and maintain public trust.
Victimology
Cybercriminals are intensifying their focus on businesses that store sensitive information, such as personal data, financial records, and intellectual property. Sectors like manufacturing, real estate, healthcare, FMCG, e-commerce, finance, and technology are especially vulnerable due to their extensive data assets. Targeting countries with strong economies and advanced digital systems, these criminals aim to maximize their ransom demands. Their approach involves exploiting vulnerabilities, encrypting essential data, and demanding substantial ransoms to achieve significant financial gains.
CONCLUSION
September 2024 demonstrated that the threat landscape remains highly adaptable and dynamic. The significant rise in attacks by groups like Medusa and the persistent influence of RansomHub emphasizes the need for continuous vigilance and proactive defence strategies. The diverse impact across industries and regions indicates that ransomware operators are constantly shifting their targets and tactics to exploit vulnerabilities. New and evolving groups, such as Mallox and Cicada3301, highlight a trend toward more sophisticated multi-platform attacks. As groups increasingly leverage advanced tools and exploit critical vulnerabilities, the importance of robust cybersecurity measures and timely patching remains paramount. Ongoing monitoring and analysis will be essential to counter these evolving threats effectively.
STRATEGIC RECOMMENDATIONS:
- Strengthen cybersecurity measures: invest in robust cybersecurity solutions, including advanced threat detection and prevention tools, to proactively defend against evolving ransomware threats.
- Employee training and awareness: conduct regular cybersecurity training for employees to educate them about phishing, social engineering, and safe online practices to minimize the risk of ransomware infections.
- Incident response planning: develop and regularly update a comprehensive incident response plan to ensure a swift and effective response in case of a ransomware attack, reducing the potential impact and downtime.
MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS:
- Cyber Insurance: Evaluate and consider cyber insurance policies that cover ransomware incidents to mitigate financial losses and protect the organization against potential extortion demands.
- Security audits: conduct periodic security audits and assessments to identify and address potential weaknesses in the organization’s infrastructure and processes.
- Security governance: establish a strong security governance framework that ensures accountability and clear responsibilities for cybersecurity across the organization.
TACTICAL RECOMMENDATIONS:
- Patch management: regularly update software and systems with the latest security patches to mitigate vulnerabilities that threat actors may exploit.
- Network segmentation: implement network segmentation to limit the lateral movement of ransomware within the network, isolating critical assets from potential infections.
- Multi-Factor authentication (MFA): enable MFA for all privileged accounts and critical systems to add an extra layer of security against unauthorized access.



![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()