Published On : 2024-11-08
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
October 2024 marked a rise in ransomware incidents, with the RansomHub group leading in impact. Sectors like manufacturing and healthcare faced significant threats, with groups primarily targeting the USA. Groups like Dragon, Fog, and Akira showcased evolution during this period, and the emergence of groups like Hellcat and Playboy highlights an intensifying ransomware landscape with evolving tactics.
INTRODUCTION
Welcome to the October 2024 ransomware report. This report examines the latest ransomware trends, including RansomHub’s high activity and newly emerged groups like Hellcat. With the USA as a primary target, the report highlights ransomware’s growing reach across various industries and highlights the need for heightened cybersecurity measures.
Key Points:
- In October 2024, the RansomHub ransomware group emerged as a significant threat, taking the lead with 85 victims.
- The Manufacturing sector is the primary target of ransomware attacks experiencing 91 incidents.
- The USA was the most targeted geography in October 2024, with more than 50% of ransomware incidents.
- The ransomware groups, Hellcat, Playboy, and Interlock emerged as newly identified threats in October 2024.
RANSOMWARE GROUPS: TREND COMPARISON
Throughout October 2024, there was notable activity from several ransomware groups. Here are the trends regarding the top 5:
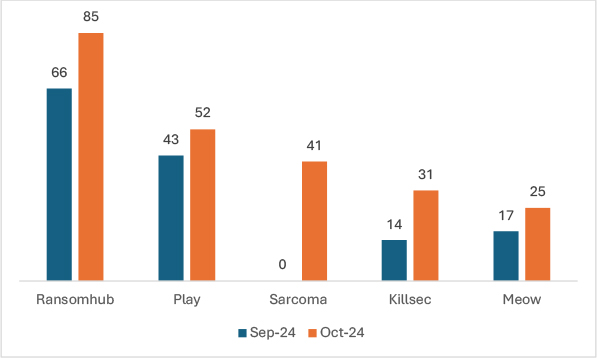
Over this month, ransomware trends exhibited significant shifts, with emerging groups gaining momentum. RansomHub saw a 28.8% increase in victims, Play ransomware group grew by 20.9%, with cases increasing from 43 to 52. Sarcoma emerged in October with 41 reported incidents. Killsec experienced a substantial 121.4% rise in victims, while Meow showed a 47.1% increase. These trends highlight a rapidly evolving ransomware landscape, with both established and newer groups intensifying their reach.
RANSOMWARE OF THE MONTH
RansomHub
RansomHub, a newly emerged ransomware group, debuted its leak site in February 2024. It is likely an updated iteration of the older Knight ransomware, rebranded by new threat actors who possibly acquired Knight’s source code earlier in 2024. Their sophisticated ransomware targets multiple platforms and leverages vulnerabilities for initial access. Employing advanced obfuscation and attack techniques, RansomHub has swiftly become a significant player in the ransomware threat landscape in a very short period.
Below are the observed TTPs of RansomHub
| Tactics |
ID |
Technique |
| Initial Access |
T1190 |
Exploit Public-Facing Application |
| Initial Access |
T1133 |
External Remote Services |
| Resource Development |
T1588.006 |
Obtain Capabilities: Vulnerabilities |
| Resource Development |
T1587.001 |
Develop Capabilities: Malware |
| Persistence |
T1098 |
Account Manipulation |
| Defense Evasion |
T1562.009 |
Impair Defenses: Safe Mode Boot |
| Defense Evasion |
T1562 |
Impair Defenses |
| Defense Evasion |
T1562.001 |
Impair Defenses: Disable or Modify Tools |
| Discovery |
T1016 |
System Network Configuration Discovery |
| Collection |
T1560.001 |
Archive Collected Data: Archive via Utility |
| Command and Control |
T1105 |
Ingress Tool Transfer |
| Command and Control |
T1219 |
Remote Access Software |
| Command and Control |
T1090 |
Proxy |
| Exfiltration |
T1041 |
Exfiltration Over C2 Channel |
| Impact |
T1486 |
Data Encrypted for Impact |
| Impact |
T1657 |
Financial Theft |
INDUSTRIES HIT: SEPTEMBER 2024 Vs OCTOBER 2024
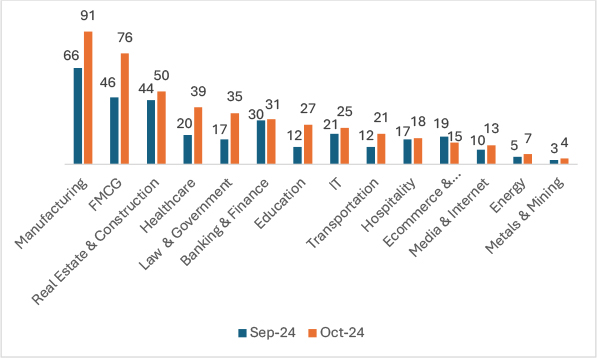
In October 2024, ransomware attacks demonstrated varying trends across industries. Manufacturing saw a notable 37.9% increase, The FMCG sector faced a substantial 65.2% rise. Real Estate and Construction experienced a moderate growth of 13.6%, and Healthcare reported an impressive surge of 95%, escalating from 20 to 39 cases. Law and Government incidents more than doubled, climbing by 105.9%, Banking & Finance showed minimal change with a 3.3% increase, while Education nearly doubled its victim count, rising by 125%. IT, Transportation, and Hospitality witnessed increases of 19%, 75%, and 5.9%, respectively. Conversely, the Ecommerce and Telecommunications sector saw a decline of 21.1%, dropping from 19 to 15 cases. Media & Internet, Energy, and Metals and Mining reported smaller increases, highlighting diverse impacts across sectors in October.
TREND COMPARISON OF RANSOMWARE ATTACKS
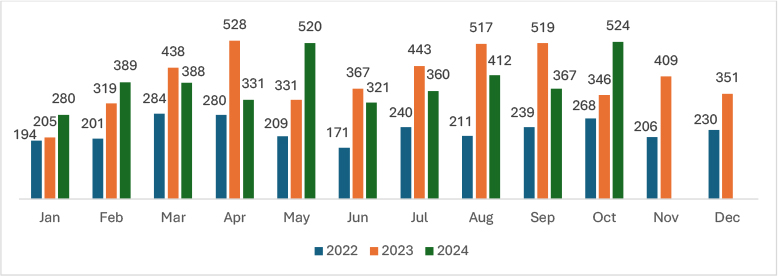
In October 2024, ransomware incidents increased by 42.78% compared to September 2024. With high confidence, this increase can be attributed to the high performance of new players such as Sarcoma, and old prominent players, such as Play, and RansomHub, among others.
GEOGRAPHICAL TARGETS: TOP 5 LOCATIONS
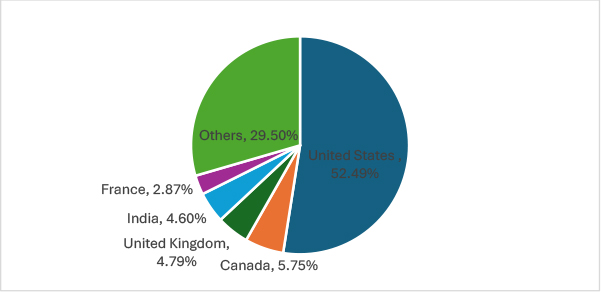
This chart illustrates the geographical distribution of ransomware targets in October 2024. The United States is the most affected, accounting for 274 disclosed incidents of all 524 incidents. Canada follows with 30, while the United Kingdom and India reported 25 and 24 respectively. France is impacted to a lesser extent, representing 15 cases. The remaining 154 encompass other countries, indicating that ransomware operations maintain a significant global reach beyond these primary regions. This distribution highlights the concentration of ransomware attacks in key regions, with developed economies being prime targets for cybercriminals.
EVOLUTION OF RANSOMWARE GROUPS IN OCTOBER 2024
- DragonForce ransomware is evolving by expanding its Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model, targeting global industries, such as manufacturing, real estate, and transportation. The group utilizes two ransomware variants, one based on LockBit 3.0 and another on ContiV3, to conduct double-extortion attacks. Affiliates can customize payloads, adjust encryption parameters, and alter ransom notes for flexibility. DragonForce also employs advanced tactics like “Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver” (BYOVD) and clearing Windows Event Logs to evade detection and hinder investigations. With a significant concentration of attacks in the U.S., the group poses a growing threat worldwide, leveraging advanced techniques for maximum impact.
- Ransomware groups, including those behind Fog and Akira, have been exploiting the critical CVE-2024-40711 vulnerability in Veeam Backup & Replication software. This flaw, rated 9.8 on the CVSS scale, is a deserialization of untrusted data issues that allows attackers to execute remote code without authentication. Exploiting a specific URI on port 8000, the attackers create unauthorized local accounts with administrative and remote access privileges, which they use to deploy ransomware. The Fog and Akira ransomware groups have used this vulnerability to compromise systems, with initial access often gained through compromised VPN gateways that are outdated or lack multifactor authentication (MFA). After breaching the system, attackers have been observed exfiltrating sensitive data, using tools like rclone, and presenting both encryption and data theft threats to their victims. Organizations using this software are urged to update to version 12.2.0.334 or later, secure VPN access with MFA, and apply patches to prevent further exploitation.
- A ransomware threat actor, Storm-0501, has shifted tactics to target hybrid cloud environments, aiming to compromise both on-premises and cloud assets. The group gains initial access by exploiting weak credentials, known vulnerabilities, and using stolen or purchased credentials. After access is obtained, they move laterally through tools like Impacket and Cobalt Strike, exfiltrate data via a custom Rclone binary, and disable security using PowerShell. Storm-0501 leverages stolen Microsoft Entra ID credentials to compromise cloud synchronization accounts and hijack sessions, maintaining persistence by creating new federated domains. This allows the attackers to authenticate as any user whose “Immutableid” property is known. Their attacks involve either deploying Embargo ransomware on both on-premise and cloud environments or maintaining persistent backdoor access for future operations. The ransomware is distributed via compromised privileged accounts, using scheduled tasks or Group Policy Objects (GPOs).
- The Qilin ransomware strain has evolved into a new Rust-based variant, dubbed Qilin.B, with significant enhancements in encryption and evasion techniques. This version employs AES-256-CTR with AESNI support for faster encryption on capable systems while retaining ChaCha20 for older hardware. It also incorporates RSA-4096 for key protection, making decryption without the private key nearly impossible. Qilin.B disrupts data recovery by terminating critical processes, such as backup and security services, wiping volume shadow copies, and clearing event logs. Persistence is ensured by adding autorun keys in the Windows Registry, while its reach is extended by enabling network drive sharing between elevated and non-elevated processes. The ransomware targets both local and network directories, generating ransom notes for each directory with a unique victim ID. Additionally, it deletes its binary post-encryption to hinder detection and analysis. These improvements, when combined, present a formidable threat, particularly in critical infrastructure environments.
- The Beast ransomware platform, operational since 2022, continues to evolve as a flexible RaaS targeting Windows, Linux, and VMware ESXi systems. Its adaptability allows affiliates to customize the malware for specific targets. Beast employs Elliptic-curve cryptography and ChaCha20 encryption for robust file encryption on Windows, with multithreaded capabilities for faster processing and service termination to avoid file interference. Its Linux and ESXi variants further enable attackers to shut down virtual machines before encryption, severely disrupting operations. A key feature is its offline builder, introduced in August 2024, allowing ransomware payload creation without an internet connection, expanding its attack scope. Beast also uses SMB scanning for self-propagation across networked systems, increasing the ransomware’s impact. It avoids targeting systems in CIS countries by checking the system’s language settings and IP address. Additionally, it removes Windows shadow copies to prevent victims from recovering data using system backups.
- The BlackBasta ransomware operation, active since April 2022, has evolved its social engineering tactics by moving to Microsoft Teams for attacks. Initially, the group targeted employees by overwhelming their inboxes with spam emails and posing as IT help desk personnel. This allowed them to gain remote access through tools like AnyDesk and Windows Quick Assist. Recently, Black Basta has shifted to using Microsoft Teams, where attackers impersonate IT help desk accounts, using external user profiles with deceptive display names. By initiating one-on-one chats, they trick employees into installing remote access software or scanning QR codes that lead to malicious domains. Once access is granted, tools like SystemBC and Cobalt Strike are deployed to move laterally and encrypt systems. This evolution highlights Black Basta’s focus on exploiting legitimate communication channels to infiltrate corporate networks and carry out ransomware attacks.
EMERGING GROUPS
Hellcat
A new ransomware group launched its leak site at the end of October 2024, listing one victim so far. Detailed information about the ransomware is still scarce. Stay tuned with CYFIRMA for updates.

Source: Underground forum
Interlock
The emerging Interlock ransomware operation, active since the beginning of October 2024, has been launching attacks on organizations globally with a distinctive approach: deploying an encryptor specifically targeting FreeBSD servers. To date, Interlock has claimed responsibility for attacks on six organizations and subsequently leaked stolen data on its website following unpaid ransom demands.
Source: Underground forum
PlayBoy Locker
PlayBoy Locker, a new ransomware group emerged at the end of October 2024 and listed one victim at the same time as its leak site launch. Stay tuned for CYFIRMA research reports for more updates in the future.
Source: Underground forum
Sarcoma
The group launched its leak site at the beginning of October 2024. The group claimed more than 40 victims in a single month and emerged as a prominent player in the ransomware landscape.
Source: Underground forum
KEY RANSOMWARE EVENTS IN OCTOBER 2024
- The BianLian ransomware group has claimed responsibility for a cyberattack on a pediatric healthcare network, compromising its IT systems. The breach, detected in September 2024, resulted in the exfiltration of sensitive data, including personal and health information of patients, employees, and guarantors. Stolen data includes names, Social Security numbers, medical records, billing, and treatment information. While the group has yet to leak the data, they threaten to do so unless a ransom is paid. The attack did not affect electronic medical records, which are hosted on a separate network. Impacted individuals are being notified and offered credit monitoring services.
- Four members of the REvil ransomware group were sentenced to prison in Russia for charges including hacking, money laundering, and distributing malware. The individuals received sentences ranging from 4.5 to 6 years. This marks a rare instance of Russian cybercriminals being convicted. They were part of a larger group arrested following a major takedown of the REvil operation by Russian authorities. The convictions follow earlier arrests and ongoing prosecutions tied to the dismantled ransomware group, once known for large-scale attacks. Additionally, authorities are investigating other money laundering services linked to cybercriminal activities.
- A ransomware attack on a global tech company led to a data breach, with the 8BASE and Everest ransomware groups stealing and leaking sensitive information after ransom demands were unmet. The attack targeted the company’s Vietnam-based division, though it did not involve file encryption. Over 50,000 files, including internal documents, business contracts, and procurement policies, were stolen. The 8BASE group initially claimed responsibility, followed by Everest, which leaked the data on the dark web. The attackers gained access using valid VPN credentials. The company has since secured the breach, implemented protections, and warned employees of potential phishing risks.
- A recent ransomware attack on Casio, claimed by the Underground ransomware group, resulted in the theft of sensitive data. The breach exposed personal and confidential information of employees, job candidates, business partners, and customers, though no credit card data was compromised. The stolen data includes legal, financial, and human resources documents, while services like CASIO ID and ClassPad.net were unaffected. Casio is working with authorities to investigate and mitigate the impact, advising those affected to be cautious of phishing attempts. The company has also urged the public not to spread leaked information to prevent further harm.
BUSINESS IMPACT ANALYSIS
Based on available public reports, approximately 31% of enterprises are compelled to halt their operations, either temporarily or permanently, in the aftermath of a ransomware onslaught. The ripple effects extend beyond operational disruptions, as detailed by additional metrics:
- A significant 40% of affected organizations are forced into downsizing their workforce due to the financial strain caused by the attack.
- The aftermath sees 35% of businesses experiencing turnover at the executive level, with C-suite members stepping down in the wake of the security breach.
- The financial toll of cyber incidents is staggering, with the average cost burden to companies, irrespective of their size, estimated at around $200,000. This figure underscores the substantial economic impact of cyber threats.
- Alarmingly, 75% of small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) face existential threats, admitting the likelihood of closure should cybercriminals extort them for ransom to avoid malware infection.
- The long-term viability of these entities is also in jeopardy, with 60% of small businesses shutting down within six months post-attack, highlighting the enduring impact of such security breaches.
- Even in instances where ransoms are not conceded to, organizations bear significant financial weight in their recovery and remediation endeavors to restore normality and secure their systems.
EXTERNAL THREAT LANDSCAPE MANAGEMENT (ETLM) OVERVIEW
Impact Assessment
Ransomware continues to pose a significant threat to both organizations and individuals, with attackers encrypting critical data and demanding payment for its release. Beyond the immediate ransom, these attacks lead to substantial financial losses from cybersecurity measures, recovery costs, and operational downtime. Additionally, ransomware incidents erode customer trust, create emotional distress, and may lead to regulatory violations. The resulting damage to reputation and consumer confidence can destabilize markets and disrupt business continuity. It is essential, therefore, for businesses and governments to proactively counter ransomware threats to safeguard financial stability and uphold public trust.
Victimology
Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting businesses that store high-value information, including personal data, financial records, and intellectual property. Industries such as manufacturing, real estate, healthcare, FMCG, e-commerce, finance, and technology are especially at risk due to the large volumes of sensitive data they manage. Focusing on economically strong countries with advanced digital infrastructures, these actors seek to exploit vulnerabilities, encrypt critical data, and demand sizable ransoms to maximize their financial gains.
CONCLUSION
October 2024 saw a marked escalation in ransomware threats across various sectors and geographies, with both new and established groups demonstrating increased sophistication. Organizations are urged to prioritize cybersecurity measures, focusing on resilience and readiness to counteract these evolving threats. Strengthened defenses and awareness are essential to mitigate future ransomware impacts.
STRATEGIC RECOMMENDATIONS:
- Strengthen cybersecurity measures: invest in robust cybersecurity solutions, including advanced threat detection and prevention tools, to proactively defend against evolving ransomware threats.
- Employee training and awareness: conduct regular cybersecurity training for employees to educate them about phishing, social engineering, and safe online practices to minimize the risk of ransomware infections.
- Incident response planning: develop and regularly update comprehensive incident response plans to ensure a swift and effective response in case of a ransomware attack, reducing the potential impact and downtime.
MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS:
- Cyber Insurance: Evaluate and consider cyber insurance policies that cover ransomware incidents to mitigate financial losses and protect the organization against potential extortion demands.
- Security audits: conduct periodic security audits and assessments to identify and address potential weaknesses in the organization’s infrastructure and processes.
- Security governance: establish a strong security governance framework that ensures accountability and clear responsibilities for cybersecurity across the organization.
TACTICAL RECOMMENDATIONS:
- Patch management: regularly update software and systems with the latest security patches to mitigate vulnerabilities that threat actors may exploit.
- Network segmentation: implement network segmentation to limit the lateral movement of ransomware within the network, isolating critical assets from potential infections.
- Multi-Factor authentication (MFA): enable MFA for all privileged accounts and critical systems to add an extra layer of security against unauthorized access.











