



This CYFIRMA Monthly Ransomware Report thoroughly analyses ransomware activity in November 2023, covering significant attacks, the top five ransomware families, geographical distribution, targeted industries, evolution of attacks, vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware groups, and trends. Organizations can leverage these insights to enhance their cybersecurity strategies and mitigate ransomware risks.
Welcome to the November 2023 Ransomware Report. This report offers a detailed analysis of significant ransomware events during this period. We explore the top 5 ransomware groups responsible for the highest number of victims and the industries they targeted. Additionally, we investigate the geographical locations that experienced the most ransomware attacks in November 2023. Furthermore, we discuss the evolution of ransomware groups during this month and vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware groups in November 2023. The report aims to equip organizations with crucial insights to bolster their cybersecurity measures and combat the evolving ransomware threat landscape effectively.
• In November 2023, the LockBit ransomware group emerged as a significant threat, taking the lead on the chart with 108 victims.
• The Manufacturing sector is the primary target of ransomware attacks, experiencing 80 incidents.
• The USA was the most targeted geography in November 2023, with 187 ransomware incidents.
• The GhostLocker emerged as a newly identified threat in November 2023.
• The number of ransomware victims increased by approximately 18.21% from October to November 2023.
In November 2023, multiple ransomware groups were active. Below are the trends of the top 5 ransomware groups with the highest number of victims in November 2023 compared with October 2023.
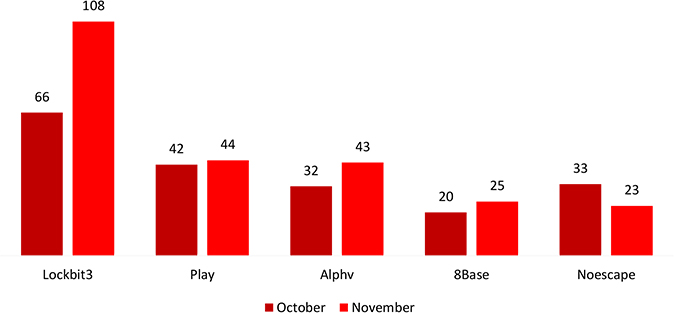
Analyzing the data, there’s a notable increase in activity related to LockBit, Play, Alphv, and 8Base, possibly due to failures in ransom negotiations or increased attacks by these threat actors. Conversely, Noescape has reduced, indicating a potential downturn in their respective ransomware operations or successful ransom negotiations among known victims.
Manufacturing stands out as the primary industry targeted, with the United States being the most focused nation for LockBit.
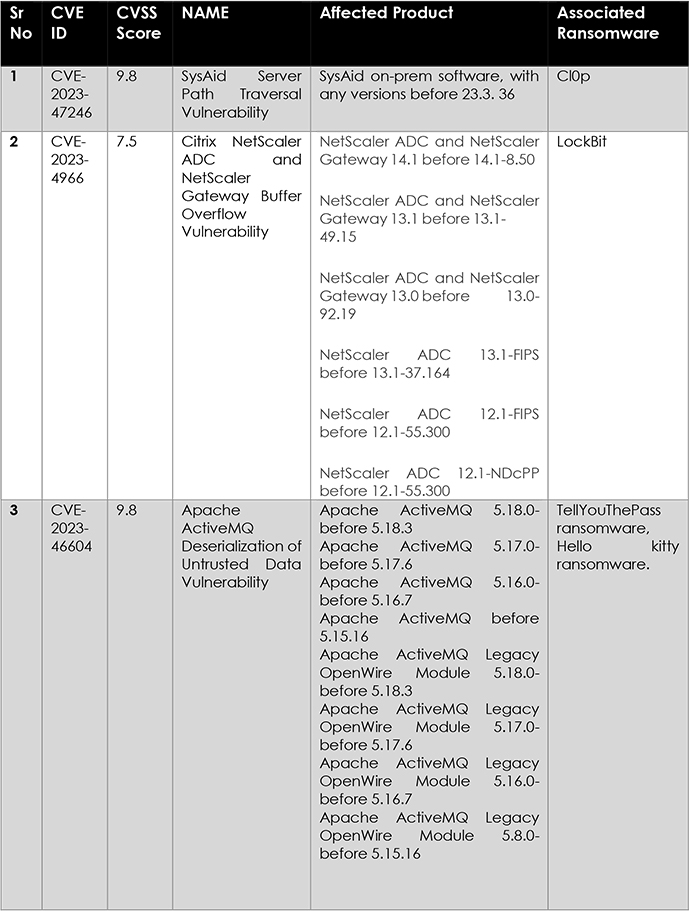
The ransomware capitalized on a critical vulnerability in Citrix Bleed, leading to unauthorized access. This exploit is believed to be a key factor contributing to the significant ransomware incidents.
As per the information available, LockBit disclosed victim organizations with revenue ranging from less than $5 million to $19.3 billion. This implies that the attackers did not focus solely on specific financial tiers but instead impacted organizations across a wide spectrum of revenue scales.
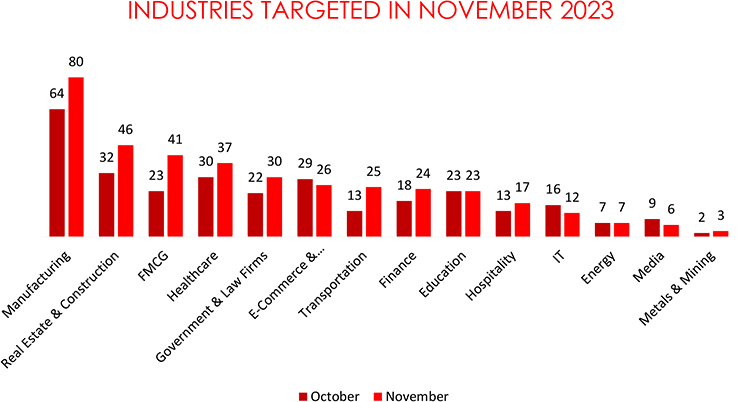
In November 2023, cyber threats targeted various industries, revealing significant shifts from October. Manufacturing witnessed a substantial 25% increase, possibly due to a growing reliance on digital systems. Real Estate & Construction surged by 43.8%, and FMCG saw a 78.3% rise, indicating an increased focus on consumer-centric sectors. Healthcare experienced a 23.3% uptick, likely due to the sensitive nature of patient data. Government & Law Firms increased by 36.4%, while E-Commerce & Telecommunication faced a 10.3% decline. Transportation, Finance, and Education also saw increases, emphasizing the diverse and evolving nature of cyber threats across sectors.
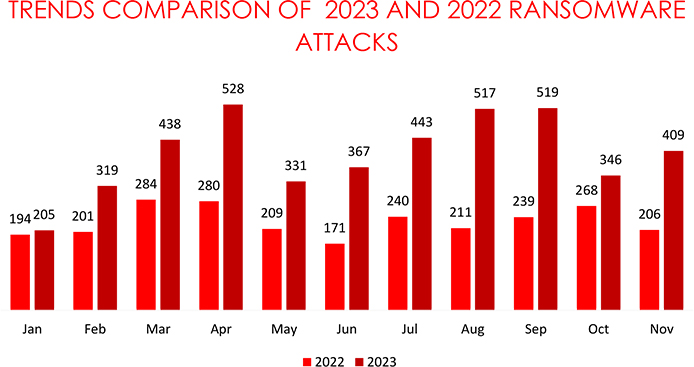
There was an increase of approximately 18.21% in the number of ransomware victims from October 2023(346 Victims) to November 2023(409 Victims).
From January 2023 to November 2023, the globally known ransomware incidents are 76% higher than the 2022 data, suggesting an alarming escalation in global cybersecurity threats.
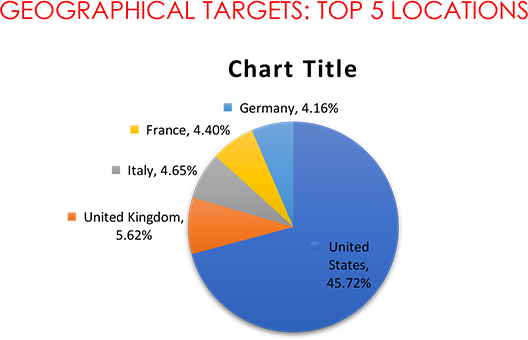
The continued trend of targeting these nations persists due to their economic prosperity, robust technological infrastructure, and possession of high-value data, creating lucrative opportunities for extortion and ransom payments.
DJVU evolved with a new variant.
A new variant of the DJVU ransomware, named Xaro, is distributed through deceptive freeware sites. Users unknowingly download an archive file, executing a disguised installer that is, in fact, PrivateLoader, a pay-per-install downloader. PrivateLoader communicates with servers, leading to the download of various malware, including Xaro, RedLine Stealer, and Vidar. Xaro exhibits complex execution flows, involving process hollowing, file encryption using AES-256, and the creation of scheduled tasks.
Phobos came up with a new variant.
The Vx-underground ransomware, a variant of the Phobos ransomware family, encrypts files and appends the “.id[[unique_id].[[email protected]].VXUG” extension. Notably, it is distinct from the vx-underground online repository. The ransomware generates playful and customized ransom notes, excluding critical files to avoid system disruption. It employs various strategies, including process closure and Firewall disablement, ensuring persistence by copying itself and extracting geolocation data for assessing target value.
BlackCat Ransomware with Scattered Spider strikes using Malicious Google Ads and alerts.
The notorious ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware gang has adopted new tactics, using Google Ads laced with malware to attack corporations and public entities. Russian-speaking affiliates of the gang, named Scattered Spider, collaborate in these attacks. They exploit malvertising to distribute the Nitrogen malware, ultimately leading to ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware infections.
Prolific Threat Actor Farnetwork exposed for Ransomware-as-a-Service operations.
Farnetwork, a prolific threat actor, has been exposed for its involvement in five ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) programs, including JSWORM, Nefilim, Karma, Nemty, and Nokoyawa. Operating since 2019, farnetwork launched its own RaaS program based on Nokoyawa and developed a botnet service in 2022. The RaaS model involves affiliates receiving 65% of the ransom amount, enhancing efficiency by leveraging pre-established network access. Nokoyawa ceased operations in October 2023, but there’s a high probability of farnetwork resurfacing with a new RaaS program under a different name.
C3RB3R; a new variant of Cerber ransomware.
C3RB3R; a new variant of the Cerber ransomware, exploits a Confluence server vulnerability (CVE-2023-22518) to establish control. Linux compromise involves command injection, while Windows activation employs remote scripts. The ransomware encrypts files, targeting Volume Shadow Copies and appending the .L0CK3D extension. A “read-me3.txt” ransom note follows, demanding payment for decryption.
GhostSec came up with GhostLocker.
Hacktivist group GhostSec has launched GhostLocker Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) on Telegram, starting at $999 and increasing to $4999. GhostLocker provides customization for encryption, process termination, service disruption, ransom amounts, session ID, and delays. The ransomware, compiled with Python compiler Nuitka, encrypts files with a “.ghost” extension and places “readme.html” ransom notes. GhostSec, initially focused on counterterrorism, has targeted multiple countries, engaging in cyber activities such as water pump assaults and a sustained offensive on Israel.
Qilin ransomware strikes at automotive giant Yanfeng.
Qilin ransomware targets Yanfeng Automotive, one of the world’s largest automotive parts suppliers in a cyberattack, posing risks to global automakers’ supply chain. Yanfeng, unresponsive to inquiries, faces data exposure threats as Qilin claims responsibility, leaking financial and technical documents.
The British Library got hit by Rhysida.
The Rhysida ransomware gang claims responsibility for the ransomware attack on the British Library. The library confirms the ransomware attack and advises password resets. The incident has impacted online systems and services, affecting millions of annual visitors to the renowned collection of over 150 million items.
Cogdell Memorial fell victim to Lorenz.
The Lorenz extortion group has disclosed data stolen from Cogdell Memorial Hospital in Texas. The hospital faced a computer network incident in early November, prompting the suspension of some systems.
E-payment provider trapped by LockBit.
The LockBit ransomware attacked Fawry; an Egyptian e-payment provider, encrypting files and allegedly stealing customer data. Fawry confirmed the leak of personal details, including addresses and phone numbers, but made assurances the incident would not affect financial transactions.
ALPHV Group targeted Insurance providers.
Fortune 500 insurance company Fidelity National Financial (FNF) experienced a ransomware attack, forcing the shutdown of key systems, and impacting services. Ransomware group ALPHV/BlackCat claimed responsibility, prompting FNF to assess the incident’s impact.
Impact Assessment:
Ransomware poses a serious threat, casting a dark cloud over both organizations and individuals in the outside world. Its harmful impact unfolds by encrypting data and demanding ransom payments relentlessly. The aftermath is severe, leading to financial losses, expenses for data recovery, and business disruptions, causing downtime and reduced productivity. Beyond the immediate consequences, these attacks can expose sensitive information and customer data, triggering regulatory compliance issues and legal problems. The ripple effect extends to reputation, as organizations deal with public scrutiny, weakened customer trust, and a decline in market confidence. A steadfast commitment to staying vigilant and reinforcing strong cybersecurity measures is crucial to combat this growing menace.
Victimology:
Hackers now target businesses with valuable data like personal info, finances, and intellectual property. Industries such as Manufacturing, Real Estate, Health Care, FMCG, E-commerce, Finance, and Technology are at risk due to their data richness. Cybercriminals pick countries with strong economies and digital setups for bigger ransom returns. Their goal is simple: find weaknesses, lock data, and demand hefty ransoms for its release, all for the promise of big profits.
The surge in ransomware attacks from January to November 2023, a 76% increase compared to 2022, underscores a concerning global cybersecurity threat. Trends in November reveal intensified activities from LockBit, Play, ALPHV, and 8Base, potentially linked to failed negotiations or heightened attacks. The emergence of new ransomware variants like Xaro, Vx-underground, and C3RB3R, coupled with the exploitation of vulnerabilities like CVE-2023-4966, and more, underscores the adaptability and sophistication of threat actors. Robust cybersecurity measures must address these evolving tactics to mitigate risks and protect diverse sectors effectively.
During the drafting of this report a notable incident took place.
Through the involvement of a confidential source (CHS), the FBI managed to infiltrate the ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware operation’s affiliate system. This access allowed the FBI to gain access to the ransomware’s backend panel, where they acquired private decryption keys. These keys were then utilized to develop a decryptor, which effectively aided over 400 victims in restoring their data. Moreover, the FBI obtained 946 Tor key pairs associated with various aspects of the ransomware’s infrastructure, including negotiation sites, data leak portals, and URL control panels. Following this disruption, the ransomware group regained control of their data leak site and responded by accusing the FBI of accessing their decryption keys for the past 1.5 months, impacting 400 companies. They also stated that 3,000 additional victims would lose access to decryption keys and that they were removing any restrictions placed on their affiliates.
Strengthen Cybersecurity Measures: Invest in robust cybersecurity solutions, including advanced threat detection and prevention tools, to proactively defend against evolving ransomware threats.
Employee Training and Awareness: Conduct regular cybersecurity training for employees to educate them about phishing, social engineering, and safe online practices to minimize the risk of ransomware infections.
Incident Response Planning: Develop and regularly update a comprehensive incident response plan to ensure a swift and effective response in case of a ransomware attack, reducing the potential impact and downtime.
Cyber Insurance: Evaluate and consider cyber insurance policies that cover ransomware incidents to mitigate financial losses and protect the organization against potential extortion demands.
Security Audits: Conduct periodic security audits and assessments to identify and address potential weaknesses in the organization’s infrastructure and processes.
Security Governance: Establish a strong security governance framework that ensures accountability and clear responsibilities for cybersecurity across the organization.
Patch Management: Regularly update software and systems with the latest security patches to mitigate vulnerabilities that threat actors may exploit.
Network Segmentation: Implement network segmentation to limit lateral movement of ransomware within the network, isolating critical assets from potential infections.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enable MFA for all privileged accounts and critical systems to add an extra layer of security against unauthorized access.