



June 2024 saw varied ransomware activity, with ‘Play’ and ‘RansomHub’ having decreased incidents, while ‘Akira’ and ‘Qilin’ increasing theirs. Industry targeting fell across the board, and total victims reduced by 38.27% from May. The US, UK, Canada, Italy, and Germany were primary targets. Emerging threats included El Dorado, Cicada3301, SenSayQ, and Trinity. Key events featured significant breaches and a notable arrest. The ransomware landscape continues to evolve, with fluctuating activities and shifting tactics.
This report analyses ransomware trends in June 2024. It highlights the targeting of specific industries and regions, vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware groups are also covered, emerging ransomware groups, and significant incidents. The findings emphasize the evolving threat landscape and the necessity for enhanced cybersecurity strategies to mitigate financial and operational risks.
Throughout June 2024, there was notable activity from several ransomware groups. Here are the trends regarding the top 5 among them.
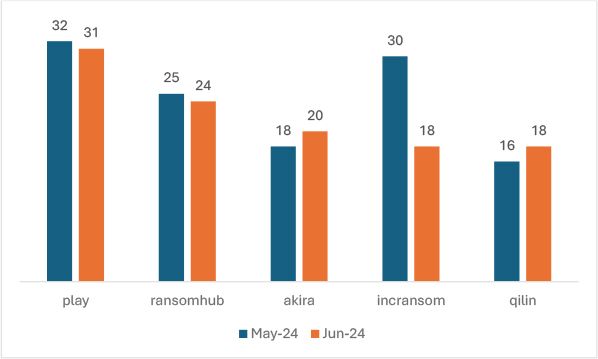
In June 2024, the activity of the top five ransomware groups showed varying trends compared to May 2024. The ‘Play’ group experienced a slight decrease in incidents by 3.13%. Similarly, ‘RansomHub’ saw a minor decline of 4%. Conversely, ‘Akira’ increased its activity by 11.11%. ‘IncRansom’ experienced a significant reduction in incidents, decreasing by 40%. Lastly, ‘Qilin’ saw an increased activity, with incidents rising by 12.5%. This comparison highlights a mixed trend among these ransomware groups, with some intensifying their operations while others reduced their activities.
Play
Play ransomware, also known as PlayCrypt, emerged in 2022 as a sophisticated and evolving threat, employing a double-extortion model where it encrypts systems after exfiltrating sensitive data. This ransomware group has expanded its targets globally, utilizing intermittent encryption to evade detection and transforming into a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) operation. The ransomware targets all-sized businesses in finance, legal, software, shipping, law enforcement, and logistics sectors including other sectors. It employs diverse initial access methods, including leveraging valid accounts and exploiting vulnerabilities in RDP servers and Fortinet SSL VPNs. Execution involves scheduled tasks, PsExec, and wmic, while persistence is maintained through valid accounts and strategic placement of executables in crucial Domain Controller shared folders. Privilege escalation is achieved using Mimikatz to extract high-privilege credentials. Credential access and discovery are conducted using Mimikatz, Empire, ADFind, Microsoft Nltest, and Bloodhound. Lateral movement is enabled by Cobalt Strike SMB beacon, SystemBC, Empire, and Mimikatz. Before deploying the ransomware, Play ensures the exfiltration of sensitive data using WinRAR and WinSCP. The impact culminates in the encryption of files with the “.play” extension and the delivery of a ransom note named ReadMe.txt, providing instructions for victims to contact the attackers for the ransom payment.
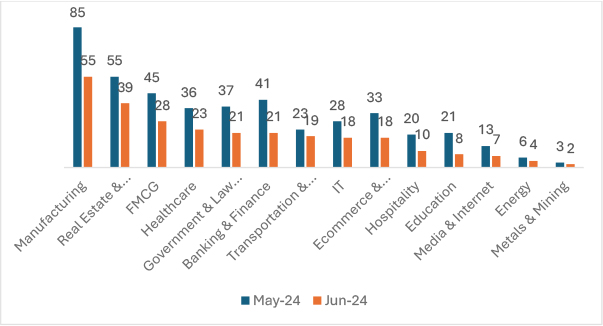
In June 2024, the targeting of various industries by ransomware groups showed significant changes compared to May 2024. The Manufacturing sector experienced a decrease of 35.29%, while Real Estate & Construction saw a reduction of 29.09%. The FMCG sector had a 37.78% decline, and Healthcare witnessed a 36.11% drop. Government & Law Firms were targeted 43.24% less, and the Banking & Finance sector saw a 48.78% decrease. Transportation & Logistics experienced a reduction of 17.39%, and IT saw a 35.71% decrease. Ecommerce & Telecommunications were targeted 45.45% less, and the Hospitality industry experienced a 50% reduction. Education saw a significant decrease of 61.90%, while Media & Internet experienced a 46.15% drop. The Energy sector had a 33.33% decrease, and Metals & Mining saw a 33.33% reduction as well. This comparison highlights a general downward trend in ransomware targeting across most industries in June 2024, also we can anticipate a kickback of ransomware groups as they did in previous years.
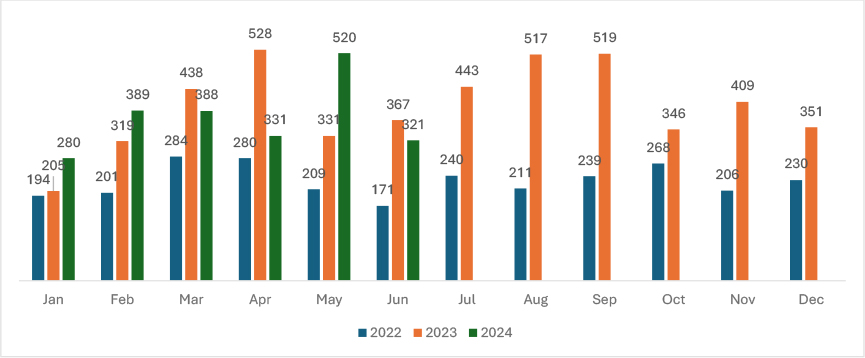
From May 2024 to June 2024, the number of ransomware victims saw a reduction of approximately 38.27%.
Overall, the trend shows a substantial increase in ransomware victims from 2022 to 2023. In 2024, the data displays significant monthly fluctuations, indicating a variable ransomware activity throughout the year.
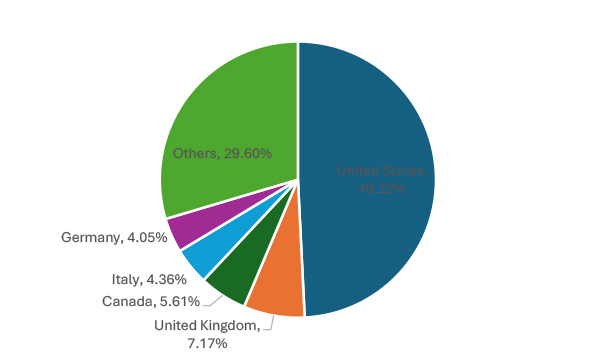
Ransomware groups have primarily targeted the following top five geographies: the United States (158), the United Kingdom (23), Canada (18), Italy (14), and Germany (13). This data highlights the concentration of ransomware attacks in these regions, emphasizing the need for enhanced cybersecurity measures.
Ransomhub is now seen targeting VMware ESXi VMs with Linux Version.
RansomHub, a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operation launched in February 2024, has been seen targeting VMware ESXi environments with a specialized Linux encryptor derived from Knight ransomware. This ESXi variant, written in C++, has been in use since April 2024 and features a bug that defenders can exploit to send it into an endless loop, thereby evading encryption.
Targetcompany Ransomware now targets VMware ESXi environments
Researchers have identified a new Linux variant of TargetCompany ransomware, targeting VMware ESXi environments with a custom shell script. Active since June 2021 and also known as Mallox, FARGO, and Tohnichi, it primarily attacks databases in East and Southeast Asia. This new variant ensures admin privileges, exfiltrates data, encrypts VM-related files, and deletes traces. Attributed to an affiliate named “vampire,” the shift to Linux indicates evolving tactics.
| Sr.No | CVE | CVSS | Vulnerability Name | Associated Threat actor |
| 1 | CVE-2024-4577 | 9.8 | PHP-CGI OS Command Injection Vulnerability | TellYouThePass ransomware |
| 2 | CVE-2024-26169 | 7.8 | Microsoft Windows Error Reporting Service Improper Privilege Management Vulnerability | Blackbasta |
El Dorado Ransomware
By the mid of June 2024 researchers discovered a new ransomware group called El Dorado, this is a ransomware variant originating from the LostTrust ransomware. It encrypts files, appends the “.00000001” extension to the filenames, and generates a ransom note titled “HOW_RETURN_YOUR_DATA.TXT”.

Cicada3301
Cicada3301 has recently emerged as a formidable cyber threat, targeting organizations globally. Known for their sophisticated attack vectors, they have been involved in numerous high-profile ransomware incidents. Their operations typically involve thorough reconnaissance and exploiting network vulnerabilities, especially those overlooked in the IT security protocols of their targets.
During the writing of this report, the group has had 4 victims listed and interestingly all the company’s data was leaked on the leak site.
SenSayQ
SenSayQ is an emerging ransomware actor recently observed in the threat landscape. Their exact methods remain unclear, but they are known to use double-extortion tactics, which involve exfiltrating data from company environments and encrypting files. SenSayQ employs a variant of LockBit ransomware for encryption, leaving ransom notes in most folders.
During the writing of this report, the group has had 2 victims listed on its leak site.
Trinity
Trinity is a newly identified ransomware variant believed to be an updated version of the “2023Lock” ransomware. This malware encrypts user files, appending the “.trinitylock” extension to them. Trinity shares some of its code base with another ransomware variant known as Venus. The threat actors behind Trinity employ double extortion techniques, exfiltrating confidential files and threatening to release them publicly if their demands are not met.
CYFIRMA has observed that initially in the middle of June, the group listed 5 victims, but during the writing of this report our research team could notice only 3 victims, so there is a high possibility of ransom payment or data sold to third parties.
A Conti and LockBit ransomware crypter specialist got caught
The Ukraine cyber police arrested a 28-year-old Russian in Kyiv for aiding Conti and LockBit ransomware operations by making their malware undetectable and conducting a ransomware attack himself. The arrest, part of ‘Operation Endgame,’ followed a Dutch police investigation. The suspect faces up to 15 years imprisonment.
Qilin hits the Healthcare sector hard
Multiple London hospitals faced significant disruptions after a ransomware attack by Qilin targeted Synnovis (formerly Viapath), impacting operations at Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. Over 800 operations and 700 appointments were rescheduled, with ongoing IT system restoration expected to take months. The attack prompted shortages in blood reserves, particularly O-positive and O-negative types, prompting urgent donor appeals from NHS Blood and Transplant.
Black Basta Strikes on Keytronic
Keytronic, a prominent PCBA manufacturer, recently experienced a significant data breach attributed to the Black Basta ransomware gang. The cyberattack disrupted operations in the U.S. and Mexico for two weeks. Black Basta subsequently leaked 530GB of stolen data, including personal information and corporate documents. Keytronic disclosed in an SEC filing that the breach would materially impact their financial condition for the fourth quarter, with incurred expenses of approximately $600,000 for external cybersecurity experts. The company is notifying affected parties and regulatory agencies as per legal requirements.
Ransomhub making headlines
British auction house Christie’s experienced a data breach by the RansomHub ransomware group, leading to the theft of sensitive client information. Christie’s took immediate measures to secure their network, engaged external cybersecurity experts, and notified law enforcement. The breach involved unauthorized access to customer files, affecting potentially 500,000 clients. Christie’s is offering a free twelve-month subscription to an identity theft and fraud monitoring service for impacted individuals. RansomHub, known for its data-theft extortion tactics, claimed responsibility and later claimed to have sold the stolen data on their dark web auction platform.
Australian mining company discloses breach
Northern Minerals, an Australian rare earth exploration company, disclosed a security breach where data was stolen and subsequently surfaced on the dark web. The stolen information includes corporate, operational, and financial data, as well as details of personnel and shareholders. The company notified authorities and affected individuals. Despite the breach, its mining operations remain unaffected. BianLian ransomware group claimed responsibility and published the data after Northern Minerals reportedly refused to pay ransom.
Based on available public reports approximately 31% of enterprises are compelled to halt their operations, either temporarily or permanently, in the aftermath of a ransomware onslaught. The ripple effects extend beyond operational disruptions, as detailed by additional metrics:
Impact Assessment
Ransomware poses a significant threat to organizations and individuals by seizing critical data and demanding ransoms for its release. These attacks often result in substantial financial losses, including the costs of ransom payments and investments in cybersecurity for recovery. The impact also includes operational disruptions, diminished customer trust, and emotional distress for those affected. Moreover, ransomware incidents can lead to breaches of data regulations, damaging reputations, eroding consumer confidence, and destabilizing markets. Therefore, combating ransomware is crucial for businesses and government bodies to safeguard financial security and uphold public trust.
Victimology
Currently, cybercriminals are focusing on businesses that store valuable data, such as personal details, financial information, and intellectual property. Industries like manufacturing, real estate, healthcare, FMCG, e-commerce, finance, and technology are particularly vulnerable due to their extensive data resources. These criminals target countries with strong economies and advanced digital infrastructures to maximize their ransom demands. Their strategy is straightforward: find weaknesses, encrypt the data, and demand hefty ransoms, all with the goal of making substantial profits.
The ransomware landscape in June 2024 exhibited mixed trends among the top five ransomware groups. While ‘Play’ and ‘RansomHub’ saw minor declines in activity, ‘Akira’ and ‘Qilin’ experienced increased incidents, and ‘IncRansom’ faced a substantial reduction. The targeting of various industries significantly decreased, with sectors like Healthcare, Education, and Banking & Finance experiencing notable declines in attacks. Geographically, the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Italy, and Germany remained primary targets. Emerging ransomware groups, such as El Dorado, Cicada3301, SenSayQ, and Trinity, posed new threats with evolving tactics. Key events included significant disruptions in the healthcare sector by Qilin, the arrest of a Conti and LockBit specialist, and major breaches involving RansomHub and Black Basta. These developments underscore the need for heightened cybersecurity measures and vigilance across industries and regions.