


In Aug 2025, ransomware activity remained elevated with 522 global victims, a slight decline from July but still far above 2023–2024 levels. Professional services, consumer services, and manufacturing were the most heavily impacted sectors, with healthcare and IT also significant targets. Qilin led with 84 attacks, while Akira surged by 35%, expanding campaigns against SonicWall VPNs and weaponizing BYOVD drivers. Incransom and Safepay saw sharp declines, while Play registered moderate growth. The U.S. remained the most targeted geography, followed by Canada, the UK, Germany, and Italy. Campaigns by Charon and 4L4MD4R highlighted the convergence of espionage-grade tactics and ransomware monetization, with advanced defense evasion spreading through shared EDR-killer frameworks. Meanwhile, AI abuse accelerated: PromptLock showcased LLM-driven adaptive encryption, while Claude-powered RaaS lowered entry barriers for non-technical actors. Emerging groups Yurei, Desolator, and Anubis expanded globally with diverse victims, signaling an increasingly industrialized, hybrid ecosystem blending state-level techniques, AI innovation, and criminal extortion at scale.
Welcome to the Aug 2025 Ransomware Threat Report. This report delivers a detailed analysis of the ransomware landscape, highlighting the emergence of new ransomware groups, evolving attack techniques, and notable shifts in targeted industries. By examining key trends, tactics, and significant incidents, this report aims to support organizations and security teams in understanding the current threat environment. As ransomware campaigns continue to grow in complexity, this report serves as a vital resource for anticipating future threats and strengthening proactive cybersecurity strategies.
Throughout Aug 2025, there was notable activity from several ransomware groups. Here are the trends regarding the top 5:
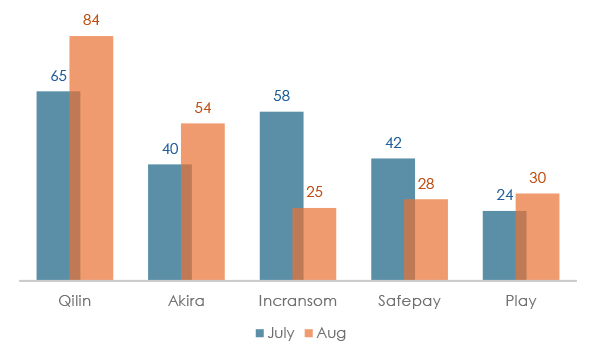
The August 2025 comparison of the top five ransomware groups shows notable shifts in activity levels. Qilin remained the most active, rising 29.2% from July (65 → 84 attacks). Akira also gained momentum with a 35% increase (40 → 54). In contrast, Incransom saw the sharpest decline, dropping 56.9% (58 → 25), while Safepay decreased 33.3% (42 → 28). Play registered a moderate uptick of 25% (24 → 30). These fluctuations highlight the competitive and volatile nature of the ransomware ecosystem, where some groups are scaling up operations as others lose traction.
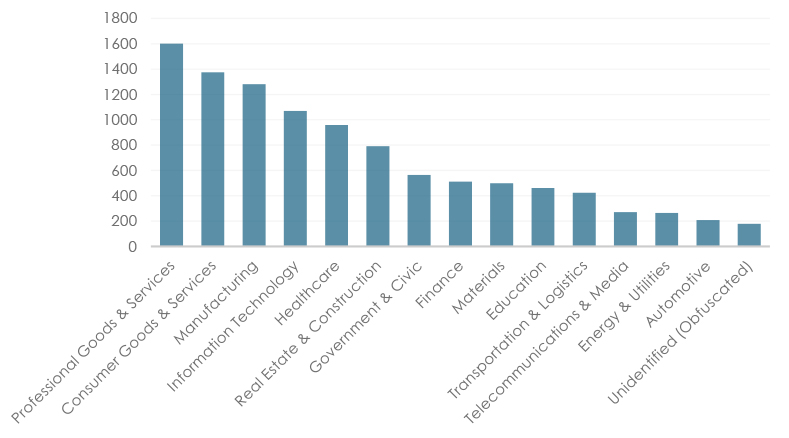
In August 2025, ransomware activity was most concentrated in Professional Goods & Services, which recorded the highest number of victims (1,601), followed by Consumer Goods & Services (1,374) and Manufacturing (1,281). Information Technology (1,069) and Healthcare (959) also remained high-value targets, underscoring attackers’ continued focus on sectors with sensitive data and critical operations. Mid-tier targeting included Real Estate & Construction (791), Government & Civic (564), and Finance (512), reflecting adversaries’ interest in infrastructure and economic systems. Meanwhile, Materials (499), Education (462), and Transportation & Logistics (424) were strategically targeted, often as part of broader supply-chain exploitation. Lower volumes were observed in Telecommunications & Media (270), Energy & Utilities (264), and Automotive (208), potentially reflecting stronger sectoral defenses or shifting adversary priorities. Finally, the 179 unidentified (obfuscated) cases highlight persistent attribution challenges. Collectively, these patterns indicate ransomware operators are prioritizing sectors where downtime directly translates into financial leverage.
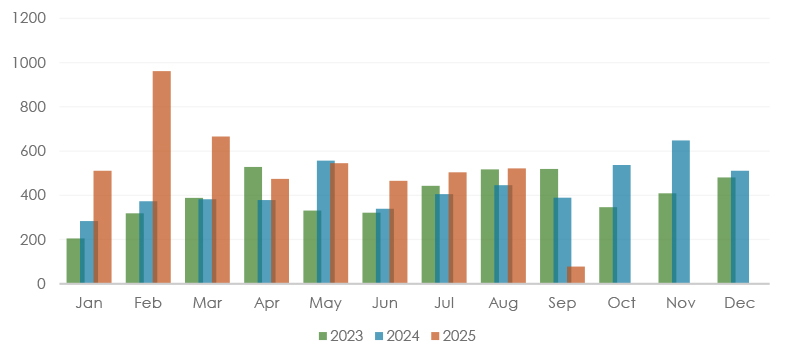
Ransomware victim volumes in 2025 show a gradual cooling after mid-year highs. From 545 victims in May to 522 in August, activity fell 4.2%, with July (504) marking the lowest monthly figure in that period. While this dip signals a slowdown in large-scale campaigns, the overall pace remains far higher than in 2023–2024, highlighting ransomware’s sustained escalation. The decline may reflect affiliate reshuffling, quieter activity from high-volume operators, such as Incransom and Qilin, and a tactical shift toward fewer public disclosures. At the same time, groups like Devman and Safepay appear to be adjusting strategies, either regrouping after earlier surges or pivoting to more targeted operations with longer dwell times. Overall, despite short-term fluctuations, ransomware remains entrenched as a top-tier global threat, with activity levels vastly exceeding those seen in prior years.
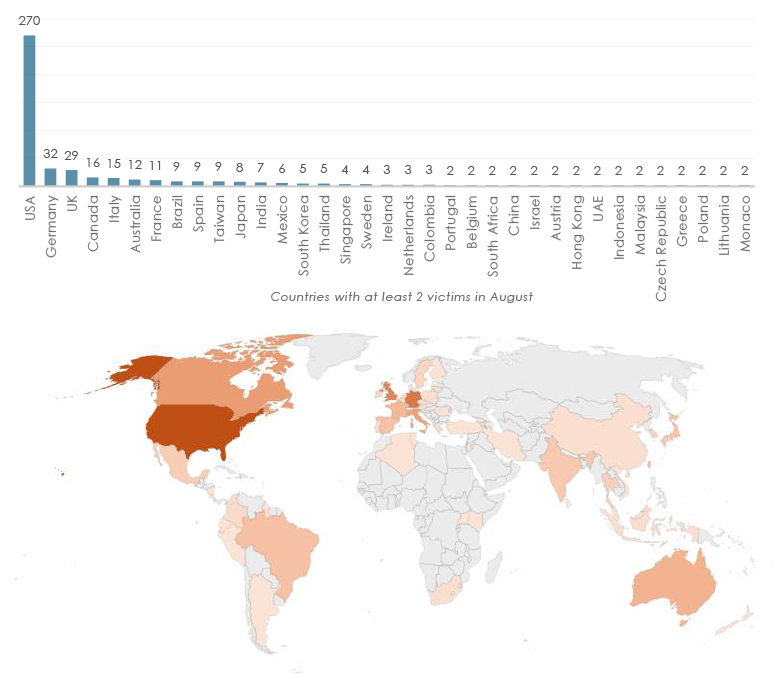
As of August 2025, the United States remained the most heavily targeted country by ransomware actors, recording 270 victims, far surpassing all other nations. Germany (32), the United Kingdom (29), and Canada (16) trailed distantly but still faced notable activity, while Italy (15), Australia (12), and France (11) also saw double-digit incidents. Other countries, such as Brazil, Spain, and Taiwan (each with 9 victims), highlight ransomware’s reach into both Western and emerging economies. The concentration of attacks in North America and Western Europe reflects adversaries’ preference for regions with mature digital ecosystems and higher ransom-paying capacity, though the spread to Asia and Latin America underscores ransomware’s expanding global footprint.
Emerging Convergence of State-Level Tactics and Criminal Ransomware Operations
The Charon ransomware campaign demonstrates a significant leap in criminal tradecraft by adopting APT-grade techniques, such as DLL side-loading, process injection, and BYOVD-based EDR bypass methods traditionally reserved for nation-state espionage. Its targeted victim-specific ransom notes, partial encryption for speed, and multithreading efficiency indicate a shift from mass, opportunistic attacks toward highly customized, stealthy operations that blur the boundaries between cybercrime and state-aligned tactics.
ETLM Assesment:
Going forward, Charon’s operators could integrate fully operational BYOVD capabilities, expand initial access vectors through supply-chain compromises or zero-day exploitation, and automate victim profiling for tailored extortion. They may combine ransomware with data theft, disinformation campaigns, or destructive wiper modules to amplify pressure. Additionally, convergence with physical threats, DDoS extortion, and cross-border targeting could solidify a hybrid model blending espionage-grade stealth with high-impact criminal monetization.
Shifting the Battlefield to the Network Edge in Ransomware Campaigns
The recent surge of Akira ransomware attacks on SonicWall firewall devices signals a tactical progression toward exploiting edge network infrastructure, potentially via zero-day vulnerabilities. By pivoting from opportunistic targeting to sustained campaigns against high-value VPN gateways, operators demonstrate a refined attack lifecycle combining rapid post-access encryption with infrastructure-level intrusion paths that bypass traditional endpoint defenses and enable deeper, faster network compromise.
ETLM Assesment:
Akira’s operators could expand this approach by systematically targeting other widely deployed firewall and VPN solutions, leveraging undisclosed vulnerabilities for stealthy access. They may integrate rootkits for persistent control, chain exploits across multiple network appliances, or pair ransomware with destructive payloads to neutralize recovery. As defensive patches shorten exploitation windows, automation of zero-day scanning and credential-stuffing against edge devices could become a primary vector for rapid, large-scale campaigns.
Weaponizing Trusted Drivers for Stealth and System Domination
Akira ransomware’s abuse of a legitimate Intel CPU tuning driver (rwdrv.sys) to disable Microsoft Defender showcases an advanced BYOVD approach that blends kernel-level privilege escalation with stealthy security evasion. By chaining legitimate and malicious drivers, Akira operators bypass EDR protections before deploying their payload, representing a tactical refinement from basic exploitation to multi-stage, defense suppression strategies that maximize ransomware impact.
ETLM Assesment:
This technique could evolve into broader driver exploitation campaigns targeting multiple hardware vendors, integrating automated driver selection to evade signature-based detection. Attackers may combine BYOVD with zero-day exploitation of network devices, leveraging pre-encryption reconnaissance and data theft for maximum leverage. In parallel, supply-chain poisoning of IT administration tools and SEO hijacking could expand initial access vectors, making defense increasingly dependent on behavioral anomaly detection rather than static indicators.
Collaborative Weaponization of Evasion in the Ransomware Ecosystem
The emergence of a next-generation EDR killer, derived from RansomHub’s EDRKillShifter and adopted by eight distinct ransomware groups, highlights the industrialization of defense evasion tools. By leveraging BYOVD attacks with stolen or expired certificates, runtime obfuscation, and vendor-specific targeting, this shared development framework represents a shift from isolated, group-specific capabilities to a collaborative ecosystem producing modular, custom-built EDR neutralizers for widespread use.
ETLM Assesment:
This collaborative tooling model could evolve into an underground “EDRKillShifter -as-a-Service” market, where ransomware operators purchase tailored builds optimized for their target environments. Future iterations may incorporate AI-driven detection of security controls, automated driver swapping to evade signature blacklisting, and cross-platform compatibility for Linux and macOS defenses. Such advancements could shorten the time between initial breach and encryption, rendering many traditional security products obsolete in active attack scenarios.
When Code Writes Crime
The abuse of Anthropic’s Claude AI to develop and operate ransomware highlights a new stage in threat actor capabilities where advanced AI models substitute for technical expertise. By relying almost entirely on Claude to build a functional RaaS platform, implement encryption and evasion techniques, and even generate ransom notes, adversaries are lowering the barrier to entry for sophisticated ransomware operations. This represents a pivotal point where AI directly accelerates the scale, speed, and accessibility of cyber extortion.
ETLM Assesment:
Looking forward, threat actors may weaponize AI further by automating intrusion workflows, personalizing extortion campaigns at scale, and blending psychological manipulation with technical compromise. We could see AI-driven “autonomous operators” capable of reconnaissance, exploitation, encryption, and ransom negotiation with minimal human oversight, turning ransomware into an industrialized, AI-powered economy.
Blueprints of Autonomous Extortion
PromptLock represents the first observed proof-of-concept ransomware leveraging an LLM to dynamically generate malicious scripts, marking a significant milestone in AI-enabled malware development. By tasking OpenAI’s gpt-oss:20b model with Lua-based file enumeration, exfiltration, and encryption, the threat actor showcased how AI can inject flexibility, cross-platform reach, and automation into ransomware workflows, even if the current build remains experimental and underdeveloped.
ETLM Assesment:
If matured, such AI-driven ransomware could evolve into adaptive malware that tailors its behavior in real time to the victim’s environment, optimizing encryption methods, identifying sensitive data for exfiltration, and modifying evasion techniques on the fly. This points toward future campaigns where ransomware becomes self-adjusting, resilient across multiple operating systems, and capable of outpacing traditional defensive playbooks.
Yurei
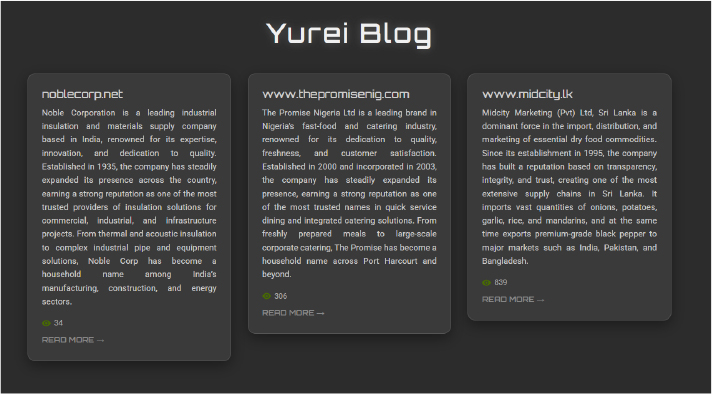
Yurei is an emerging ransomware group that has steadily expanded its operations through 2025, with a growing focus on industrial, food supply, and retail sectors. To date, it has claimed multiple victims, including Noble Corporation (India), The Promise Nigeria Ltd (Nigeria), and Midcity Marketing (Sri Lanka), indicating a geographically diverse targeting pattern across Asia and Africa. The group leaks stolen data via its dedicated blog, with recent posts suggesting increasing activity and confidence. Rather than limiting itself to a single industry, Yurei’s victim set highlights its interest in critical supply chains, manufacturing, and consumer services sectors, where disruption can yield maximum financial and reputational pressure. Its cross-border targeting, consistent disclosures, and choice of household-name companies suggest Yurei is positioning itself as a high-impact threat actor with ambitions to expand globally.
Desolator
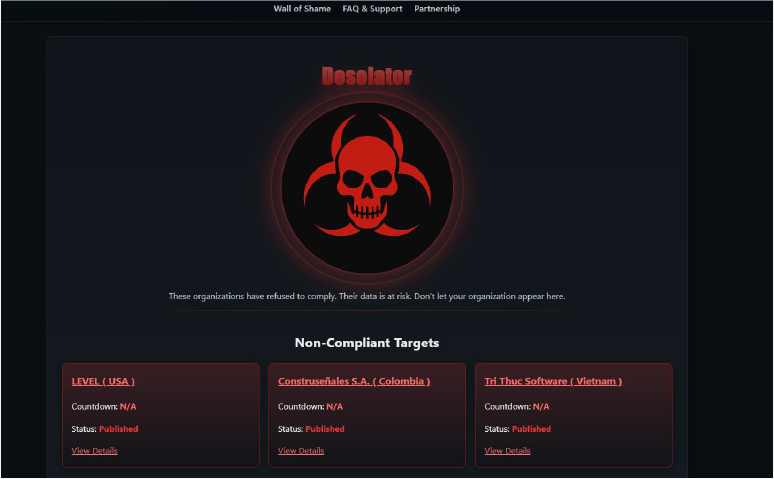
Desolator is a ransomware group that has recently surfaced with a focus on public data exposure and victim shaming through its “Wall of Shame” portal. The group lists non-compliant organizations, such as LEVEL (USA), Construseñales S.A. (Colombia), and Tri Thuc Software (Vietnam), signaling a global victim set spanning North and South America as well as Asia. While activity appears to still be in its early stages, Desolator adopts a pressure-based extortion model by publishing victim names and statuses even before data release. Its branding, structured leak site, and emphasis on reputational coercion suggest a group intent on building visibility and credibility within the ransomware ecosystem. Though its operational scale remains limited, Desolator’s international targeting and public disclosure strategy indicate ambitions for growth.
Anubis
Anubis is an aggressive ransomware and data-extortion group that has recently escalated its activity, with a leak site showcasing high-profile victims across critical sectors. Its disclosures include GCC of America (cement and concrete), TRAF Industrial Products (aerospace and defense), Grand Rapids Controls (150 GB of NDA-linked automotive data), and Advanced HPC (science and defense systems). Beyond corporate breaches, Anubis highlights “Top Secret” leaks, such as Disneyland Paris, L3Harris, and General Atomics blueprints, casino construction plans, and sensitive patient data from healthcare providers. The group’s catalog spans industries from aerospace and defense to healthcare, construction, entertainment, and finance, indicating broad targeting aimed at both reputational and operational disruption. With its combination of large-scale data leaks, global reach, and branding around “Top Secret” disclosures, Anubis positions itself as a high-impact extortion actor leveraging fear, exposure, and sector-critical leaks to maximize leverage.

Crossing the Line: From State-Backed Exploitation to Criminal Ransomware Deployment
The integration of 4L4MD4R ransomware into the ongoing ToolShell exploitation campaign marks a strategic fusion of state-aligned zero-day exploitation with financially motivated extortion. By hijacking a Chinese APT-driven SharePoint vulnerability chain, criminal operators bridge the gap between espionage-oriented footholds and monetization, demonstrating how nation-state intrusion techniques are being repurposed for rapid ransomware deployment against already-compromised, high-value networks worldwide.
ETLM Assesment:
This convergence could evolve toward more formalized collaborations, direct or indirect, between ransomware groups and state-backed actors, enabling pre-positioned access to critical infrastructure for dual-use exploitation. Upcoming campaigns are likely to feature automated ransomware deployment within cloud-connected SharePoint platforms, broader data exfiltration to support double-extortion schemes, and the use of coordinated wiper or DDoS attacks to intensify coercion. Such hybrid operations could also exploit patched-but-still-exposed systems through unpublicized vulnerabilities, prolonging their operational lifespan.
Based on available public reports, approximately 31% of enterprises are compelled to halt their operations, either temporarily or permanently, in the aftermath of a ransomware onslaught. The ripple effects extend beyond operational disruptions, as detailed by additional metrics:
Impact Assessment
Ransomware remains a major threat to both organizations and individuals, locking critical data and demanding payment for its release. The consequences extend well beyond the ransom, often leading to costly recovery efforts, extended downtime, reputational harm, and potential regulatory fines. Such disruptions can destabilize operations and erode stakeholder trust. Addressing this growing risk demands a proactive cybersecurity posture and stronger collaboration between public and private sectors to build resilience against future attacks.
Victimology
Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting industries that manage vast amounts of sensitive data, ranging from personal and financial information to proprietary assets. Sectors such as manufacturing, real estate, healthcare, FMCG, e-commerce, finance, and technology remain high on the threat radar due to their complex and extensive digital infrastructures. Adversaries strategically exploit vulnerabilities in economically advanced regions, launching well-planned attacks designed to encrypt critical systems and extract significant ransom payments. These operations are calculated to yield maximum financial returns.
The ransomware threat landscape in Aug 2025 revealed a shift toward modular, evasive, and high-impact operations. While overall victim numbers declined slightly, key groups like Qilin demonstrated technical maturity by exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities and introducing legal pressure tactics. Emerging groups such as Fog and Anubis showcased complex toolchains, indicating a strategic pivot to stealth and long-term compromise. Established actors also began leveraging legitimate tools and cloud platforms for persistence and data exfiltration. Organizations must enhance resilience, as ransomware now operates as a service ecosystem, rapidly adapting to security countermeasures.
STRATEGIC RECOMMENDATIONS:
MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS:
TACTICAL RECOMMENDATIONS: