



The CVE-2023-49606 vulnerability in Tinyproxy exposes servers to remote code execution (RCE). Exploitation could lead to severe consequences, compromising network integrity and confidentiality. Immediate action is necessary to mitigate the risk posed by this critical flaw.
A critical vulnerability has been discovered in Tinyproxy, an open-source HTTP/HTTPS proxy server designed for Unix-like operating systems. Tracked as CVE-2023-49606, this flaw allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected systems. The vulnerability stems from a memory safety issue, potentially triggered by processing HTTP connection headers. This discovery raises concerns due to the widespread use of Tinyproxy across various network infrastructures. Over 1,680,355 servers may be potentially affected. The vulnerability poses a significant threat to organizations relying on Tinyproxy for network communication.
Key Takeaways:
Acknowledgements:
CYFIRMA Research acknowledges the collaborative efforts of security researchers and the cybersecurity community in identifying and addressing the CVE-2023-49606, vulnerability.
Vulnerability Type: Unauthenticated Remote Code Execution (RCE)
CVE ID: CVE-2023-49606
CVSS Severity Score: 9.8 (Critical)
Application: Tinyproxy
Impact: Allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code, posing a significant risk of remote code execution.
Severity: Critical
Affected Versions: All versions of Tinyproxy are affected. Check here
Patch Available: Yes
Mitigation: Organizations are strongly advised to apply the latest security updates and patches promptly to mitigate the risk of exploitation.
CVE-2023-49606 arises from a memory safety issue within Tinyproxy’s handling of HTTP connection headers. By exploiting this flaw, attackers can send crafted requests to the proxy server, triggering the memory corruption condition. This could result in arbitrary code execution, enabling attackers to take control of the affected system remotely. Additionally, the vulnerability could be leveraged to launch denial of service attacks, disrupting network operations, and potentially causing service outages.
The impact of CVE-2023-49606 is significant, posing a serious threat to the security and stability of networks relying on Tinyproxy. Exploitation of this vulnerability could lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and service disruptions, with potentially severe consequences for affected organizations. The widespread use of Tinyproxy exacerbates the risk, amplifying the potential impact across various industries and sectors.
All versions of Tinyproxy are affected by CVE-2023-49606, amplifying the urgency for organizations to apply patches and implement mitigations promptly.
Check here.
Is there already an exploit tool to attack this vulnerability?
As of the latest information available, there is a known public exploit tool targeting CVE-2023-49606, affecting Tinyproxy installations.
Has this vulnerability already been used in an attack?
Regarding exploitation, while CVE-2023-49606 poses a critical risk, there is no specific information confirming the active exploitation of this vulnerability at present.
Are hackers discussing this vulnerability in the Deep/Dark Web?
Discussions related to potential exploitation or proof-of-concept demonstrations may be observed in the Deep/Dark Web.
What is the attack complexity level?
The attack complexity level for CVE-2023-49606 in Tinyproxy is assessed as LOW.
Historical Trends and Known Exploits:
There is a known public exploit tool targeting CVE-2023-49606 affecting Tinyproxy installations. However, discussions related to potential exploitation or proof-of-concept demonstrations may be observed in the Deep/Dark Web, indicating the potential for malicious actors to exploit the vulnerability.
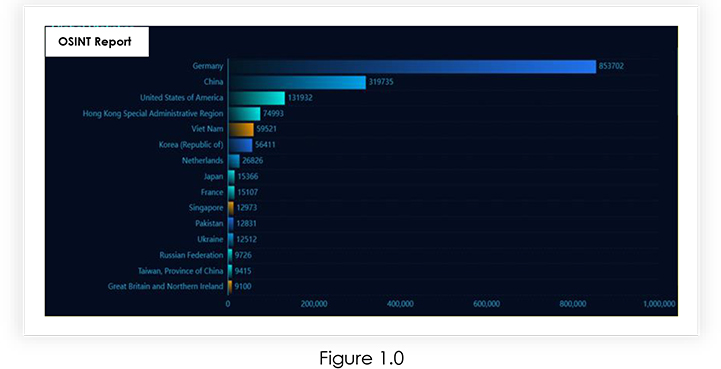
Our analysis found that more than 1,680,355+ Tinyproxy instances are public, which can be vulnerable to CVE-2023-49606.
The exploitation of a use-after-free vulnerability often begins with an understanding of the vulnerable software’s memory management behaviour. When memory is allocated for an object or task, it’s marked as in use. However, if that memory is later freed or deallocated and accessed by the program, a use-after-free scenario occurs. Attackers exploit this scenario by carefully crafting inputs that trigger the vulnerability.
In this case, attackers can exploit the vulnerability by sending specially crafted HTTP requests containing headers designed to trigger the use-after-free condition. By carefully constructing the payload within HTTP headers, such as the User-Agent header, attackers can execute arbitrary commands or code on the vulnerable system.
For instance, an attacker might include a malicious command within the User-Agent header, such as a bash command to establish a reverse shell connection to their controlled server. When this vulnerable software processes the HTTP request, it may inadvertently access or execute the freed memory, leading to the execution of the attacker’s command.
Once the use-after-free condition is triggered, attackers can gain unauthorized access to the system, execute arbitrary code with elevated privileges, or manipulate system resources for malicious purposes. This exploitation can have severe consequences, ranging from data breaches to system compromise and further exploitation of other vulnerabilities.
To mitigate the risk posed by CVE-2023-49606, organizations are advised to:
Target Geography:
The impact of CVE-2023-49606 extends globally, affecting organizations worldwide utilizing Tinyproxy for HTTP/HTTPS proxy services. Geographically, the vulnerability affects regions across North America, Europe, Asia, and beyond, where Tinyproxy is widely deployed. Organizations in diverse geographical locations, regardless of their specific region, are susceptible to potential exploitation of this critical security flaw.
Target Industry:
CVE-2023-49606 poses a threat across various industries, including but not limited to technology, finance, healthcare, government, and education, relying on Tinyproxy for proxy server functionality. Threat actors may target industries based on the value of the data or services hosted on vulnerable Tinyproxy instances. Industries handling sensitive information or those heavily reliant on secure network communication may face heightened risks.
Target Technology:
This vulnerability affects all versions of Tinyproxy, an open-source HTTP/HTTPS proxy server utilized by organizations for network communication. Exploitation of CVE-2023-49606 can lead to remote code execution, potentially compromising the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical data and systems. Given the widespread adoption of Tinyproxy across various technological ecosystems, the impact of this vulnerability can extend to interconnected systems, applications, and services, emphasizing the need for comprehensive mitigation strategies.
Understanding the global reach, cross-industry implications, and technological dependencies of CVE-2023-49606 is crucial for organizations to accurately assess their risk exposure. Swift action, including patching, implementing security controls, and monitoring for suspicious activities, is essential to mitigate the potential risks associated with this critical vulnerability.
There are some active discussions regarding this vulnerability, however, we have not observed any mention of this exploit being sold.
CVE-2023-49606 presents a critical risk to organizations utilizing Tinyproxy, necessitating immediate attention and remediation efforts. Addressing this vulnerability promptly is crucial to safeguarding network infrastructure and preventing potential exploitation by threat actors.