


CYFIRMA has identified an active and evolving Telegram phishing operation that abuses Telegram’s native authentication workflows to obtain fully authorized user sessions. Unlike traditional phishing attacks that rely solely on credential harvesting or token replay, this campaign leverages attacker-controlled Telegram API credentials and integrates directly with Telegram’s legitimate login and authorization infrastructure. By inducing victims to approve in-app authorization prompts under false pretenses, the attackers achieve complete session compromise while minimizing technical anomalies and user suspicion. This assessment details the technical mechanics, social-engineering components, and infrastructure design of the observed campaign, and places it within the broader historical context of Telegram-focused threat activity tracked by CYFIRMA. The findings highlight a continued shift toward the abuse of legitimate platform features as a primary attack vector, increasing the difficulty of detection, prevention, and user awareness.
CYFIRMA has identified an active Telegram account takeover campaign that demonstrates clear indicators of global targeting and operational scalability. The operation abuses Telegram’s legitimate authentication and in-app authorization workflows to obtain fully authorized user sessions, allowing attackers to compromise accounts without relying on malware, exploit-based access, or direct credential replay.
The campaign supports multiple authentication paths, including QR-code–based login and manual credential submission, both of which ultimately trigger a legitimate Telegram authorization prompt on the victim’s mobile device. By framing these prompts as routine security or verification checks, the attackers shift the decisive action into Telegram’s trusted application interface, significantly increasing victim compliance while reducing detectable anomalies.
Technical analysis indicates the phishing infrastructure is centrally managed and configuration-driven, enabling rapid deployment across numerous domains and consistent reuse of authentication logic. This design supports high-volume operations and facilitates rapid domain rotation, a tactic commonly observed in globally distributed phishing campaigns seeking to evade takedowns and blocklisting.
Based on historical intelligence and observed tradecraft, CYFIRMA assesses with high confidence that this campaign is designed for broad international reach rather than localized targeting. The use of compromised Telegram accounts as secondary delivery mechanisms further amplifies global exposure, allowing the operation to propagate quickly across geographic boundaries and trusted user networks. The campaign reflects a continued evolution toward the abuse of legitimate platform features, underscoring the growing challenge of detecting and mitigating large-scale account takeover activity in globally connected environments.
QR-Code Login Flow
Manual Login Flow (Phone Number & Password)
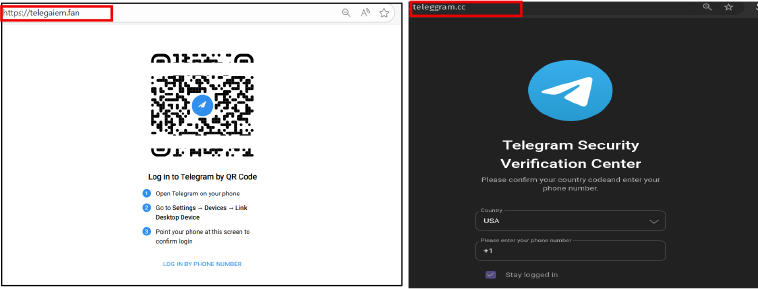
This triggers an in-app authorization prompt on the victim’s mobile device, prompting the user to confirm the action by selecting options such as “This is me” or “Yes.” Once approved, the attacker gains immediate and full session access without requiring the victim to scan a QR code or manually enter credentials. The phishing pages reinforce compliance by presenting misleading system messages, such as:

This messaging:
Captured network traffic indicates that the phishing frontend dynamically retrieves its runtime configuration from a centralized backend via a cross-origin API request. The JSON response supplies attacker-controlled Telegram application credentials (api_id and api_hash) along with structured localization data used to render the login interface, handle validation states, and deliver social-engineering prompts that instruct victims to approve an in-app Telegram authorization request. This confirms direct integration between the phishing frontend and Telegram’s native authentication workflow.

The presence of an explicit Simplified Chinese language setting (zh-CN) and fully localized UI messaging demonstrates deliberate multilingual support implemented at the framework level. This configuration-driven design enables rapid reuse of identical phishing workflows across multiple domains while maintaining centralized control over authentication logic, language content, and Telegram API parameters.

CYFIRMA’s assessment indicates that Telegram account takeover operations have remained an active and evolving threat vector over the past several years, with multiple campaigns leveraging phishing, session hijacking, and social engineering to compromise user accounts at scale. Prior waves of Telegram-focused attacks have resulted in the compromise of large numbers of accounts globally, particularly through credential-harvesting pages, malicious Telegram Web QR-code abuse, and reuse of stolen session tokens to propagate further phishing activity through trusted contact networks. These campaigns have demonstrated a clear pattern of using compromised accounts as secondary delivery mechanisms, significantly amplifying reach and success rates.
The activity observed in the current campaign aligns with these previously documented trends but reflects a notable evolution in tradecraft. Rather than relying solely on credential theft or QR token replay, this operation leverages attacker-registered Telegram API credentials and abuses Telegram’s built-in login confirmation workflow to obtain legitimate, fully authorized sessions. This approach reduces friction for the attacker, bypasses traditional indicators of compromise, and increases victim compliance by shifting the decisive action into Telegram’s official application interface.
Threat intelligence monitoring has also consistently shown that Telegram phishing infrastructure is highly transient, with operators frequently registering new domains that closely resemble legitimate Telegram branding and rapidly cycling them to evade takedowns and blocklists. The present campaign follows this pattern, with newly registered domains resurfacing repeatedly while maintaining identical backend logic, configuration structures, and social engineering content. This behavior is indicative of a centralized, reusable phishing framework rather than isolated or opportunistic activity.
Based on historical campaign behavior and current infrastructure characteristics, it is assessed with high confidence that this operation will continue to iterate rather than cease. Short-term predictions include continued domain churn, expansion into additional language localizations, and increased use of compromised Telegram accounts to deliver phishing links directly within chats and groups. Over the medium term, similar techniques are likely to be adapted to impersonate other Telegram trust signals, such as account recovery, device management, or premium feature verification, further blurring the line between legitimate and malicious authentication requests.
Overall, the campaign represents a continuation and refinement of established Telegram account takeover activity, underscoring a broader threat landscape in which attackers increasingly favor abuse of legitimate platform features over exploit-based compromise, making detection and user awareness significantly more challenging.
| Tactic | Technique ID | Technique Name |
| Initial Access | T1566.002 | Phishing: Spearphishing Link |
| Initial Access | T1078 | Valid Accounts |
| Credential Access | T1556 | Modify Authentication Process |
| Credential Access | T1528 | Steal Application Access Token |
| Defense Evasion | T1036 | Masquerading |
| Defense Evasion | T1078 | Valid Accounts |
| Persistence | T1098 | Account Manipulation |
The Telegram phishing activity analyzed in this assessment reflects a recurring campaign pattern rather than a standalone or novel operation. The observed infrastructure, authentication flows, and social-engineering mechanics closely align with techniques commonly associated with earlier Telegram phishing waves, with newly registered domains reproducing the same login workflows, authorization prompts, and backend integration. The appearance of new domains implementing identical functionality is consistent with a campaign restart model, in which previously used infrastructure is replaced while core operational logic remains unchanged. This approach enables continued activity without redesigning tooling and results in multiple, short-lived phishing sites that are functionally indistinguishable from one another. The consistency of behavior across these domains indicates continuity of an established framework rather than isolated or opportunistic phishing attempts.
Overall, the campaign demonstrates the persistence of abuse-of-function tactics within Telegram phishing activity, where legitimate platform authentication mechanisms are repeatedly leveraged to obtain authorized account access. This repeated redeployment model underscores the ongoing challenge of addressing account takeover activity that blends into normal platform behavior and relies on user approval rather than technical exploitation.