



A new phishing campaign by TA578 is uncovered that utilizes thread hijacked emails to deploy the BumbleBee malware which is followed by Cobalt Strike. Earlier, the TA578 threat actor used to deploy Urnsif, IcedID, KPOT Stealer, Buer Loader, and BazaLoader malware. The BumbleBee malware supports commands as listed below.
These features were not present in the earlier malware.
The email sample is part of an email thread that is hijacked by the attacker to bait the user to open the hyperlink.
hxxps[:]//storage[.]googleapis[.]com/urh21265vg2o9x[.]appspot[.]com/g/b/file/d/fZ xgV38APHDew[.]html
EML file MD5: 9f0c4ed7308226d143e214ad43a29711
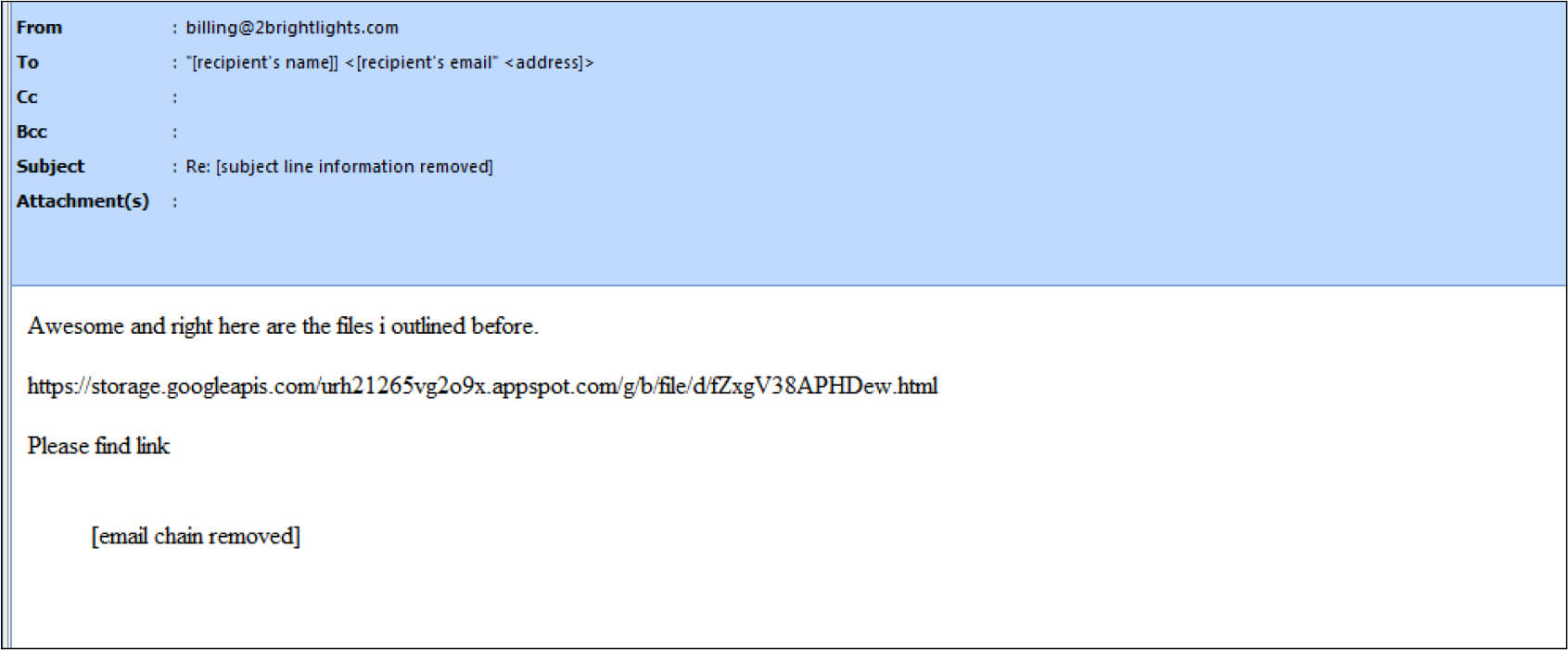
Upon opening the link, an ISO file is downloaded from Google Drive which is a Bumblebee payload.
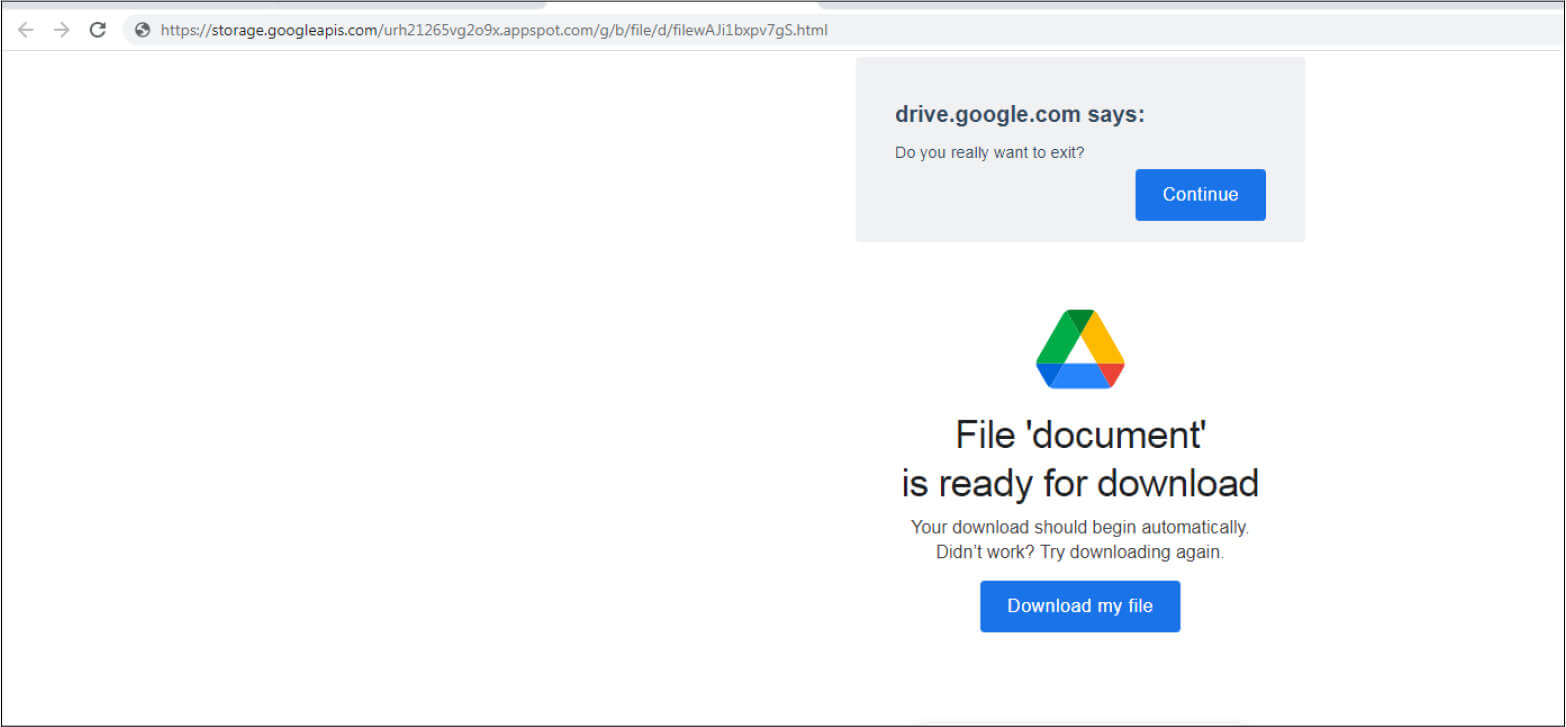
Payload Hash: a0fca5d81252df8623f431b461b0da30
The domain 2brightlights[.]com has been used in other campaigns. This domain was used in one of the Bazarloader campaigns in 2020.
The ISO file is embedded with .lnk file and .DLL file
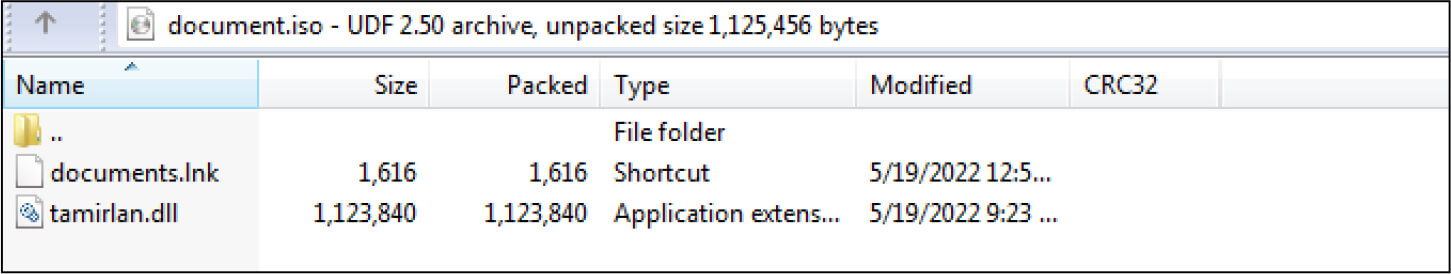
DLL file Hash: bb2f698d6b1aebba2c1d16ef665d3463
When the iso executed the .lnk file, it contains the command: %windir%\system32\rundll32.exe tamirlan.dllEdHVntqdWt, to run the .DLL file
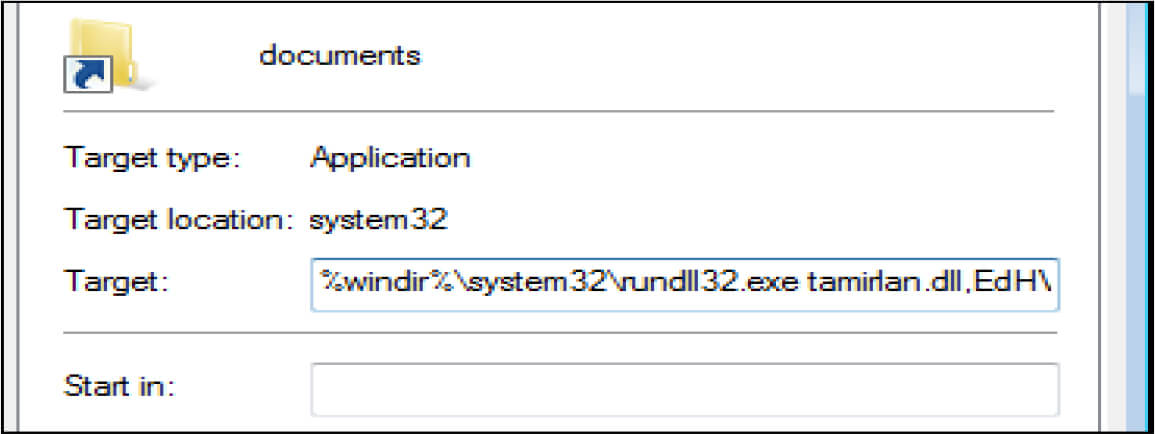
This malware is capable of deploying the ransomware to encrypt the system and exfiltrate the data to the C2 server. Further, it can drop Cobalt Strike, Shellcode, Silver, and other red team tools.
Phishing emails are the primary vector for attackers to get initial access to organizations leading to the deployment of ransomware and other post-exploitation tools to exfiltrate critical data for financial gains. The infamous Conti gang has recently changed their delivery payload malware from BazzarLoader to BumbleBee, signaling continuous innovation and the move to more sophisticated and evasive malware.
| Sr No. | Tactic | Technique |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TA0001: Initial Access | T1566 :Phishing |
| 2 | TA0002: Execution | T1059.007: Command and Scripting Interpreter: JavaScript |
| 3 | TA0003: Persistence | T1547.001: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder |
| 4 | TA0005: Defense Evasion | T1027: Obfuscated Files or Information |
| T1497.003: Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion: Time Based Evasion |
||
| 5 | TA0007: Discovery | T1012: Query Registry |
| T1057: Process Discovery | ||
| 6 | TA0009: Collection | T1056.004: Credential API Hooking |
| T1005: Data from Local System |