



Vulnerabilities are a critical component of cyber-attacks, providing attackers with an avenue to gain unauthorized entry into computer systems, networks, and software. Among these vulnerabilities, zero-day vulnerabilities are of particular interest to attackers, since they are previously unknown and unpatched, making them highly desirable targets for exploitation. Cybercriminals utilize specialized attack techniques like spear phishing, watering hole attacks, or drive-by downloads that leverage zero-day vulnerabilities to gain access to vulnerable systems or confidential data. These attacks are designed to exploit the vulnerability and gain unauthorized access, exfiltrate data, or install malware while avoiding detection.
Once a zero-day vulnerability has been exploited, attackers may employ a variety of techniques to maintain persistence within the system. For example, they may install a backdoor that provides them with covert access to the system even after the vulnerability has been patched. The backdoor may be disguised as a benign-looking file or presented as a legitimate system process.
The CYFIRMA research team has extensively analyzed a long list of reported vulnerabilities and highlighted the most frequently exploited vulnerabilities and zero-day flaws in 2022, in a research report, along with key observations. The report sheds light on the most critical vulnerabilities that cybercriminals are targeting and provides insights to help organizations take proactive measures to mitigate their risk of cyber-attacks.
The external threat landscape associated with zero-day vulnerabilities and the most exploited vulnerabilities is constantly evolving, presenting a significant challenge for organizations of all types. Attackers can exploit these vulnerabilities through various means, and any entity that uses software or connected devices can be a potential target. Especially big tech companies, technology products, and service providers are top targets in vulnerability exploration, which can provide access to large attack surfaces and open opportunities for supply chain attacks. To mitigate the risk, organizations must implement a comprehensive security strategy, that includes regular updates, vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and employee training, while adopting a proactive approach to threat intelligence.
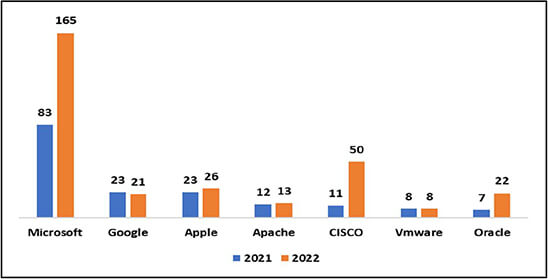
CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities – Top Contributor Trend
Based on CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities list, big tech companies like Microsoft, Google, Apple, CISCO, VMware, and Oracle are the top contributors to the vulnerability list, through their products and services. This trend clearly tells the story that threat actors target widely used technologies, applications, and services to compromise the large attack surface. This trend also continued in most exploited and zero-day vulnerabilities.
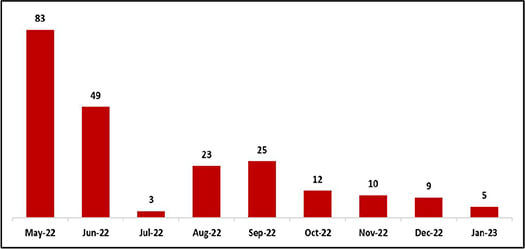
CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities – Monthly Trend
Zero-day vulnerability – Yearly Trend
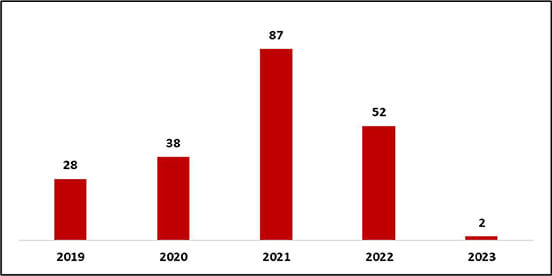
From 2019 to 2021, the trend of zero-day vulnerabilities has remained a major concern for organizations. During this period, the discovery of zero-day vulnerabilities has become increasingly frequent, with many of them being found in widely-used software, such as web browsers, operating systems, and other critical infrastructure. This trend has been driven by the increasing sophistication of attackers, who are constantly seeking new and creative ways to exploit vulnerabilities for their own gain.
In response to this trend, many organizations have increased their investment in security research and development and have also implemented measures such as bug bounty programs, to encourage responsible disclosure of zero-day vulnerabilities, this is one of the reasons for the decrease in zero-day numbers in 2022. We observed major tech giants; Google ($10 billion), and Microsoft ($20 billion), committing billions of dollars to strengthen cybersecurity after several high-profile cyberattacks, including on government software contractor SolarWinds and Colonial Pipeline attack, that has brought added urgency to the security issues. However, the increasing use of complex software and hardware systems means that zero-day vulnerabilities will likely continue to be a significant challenge in the coming years.
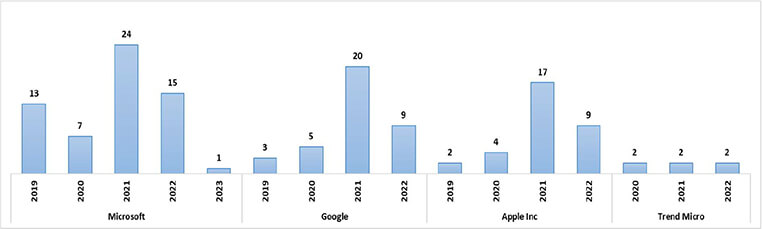
It is important to note that finding zero-day vulnerabilities is a time-consuming and complex process, that requires a deep understanding of software and computer systems. This also opens the opportunity to identify zero days and sell in underground forums for a high price. Here are some high-profile zeroday conversations observed by our research team in the underground forum.
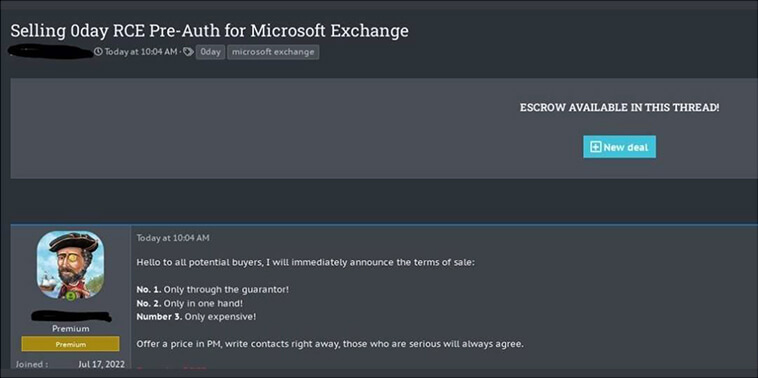
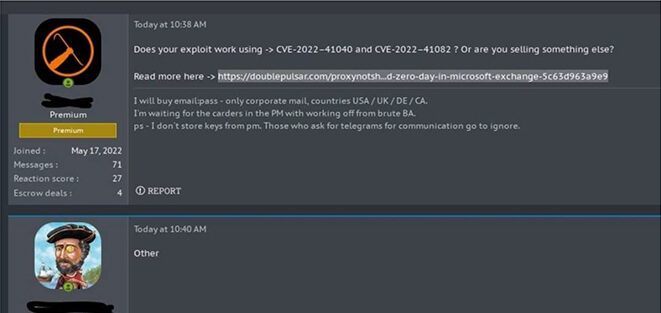
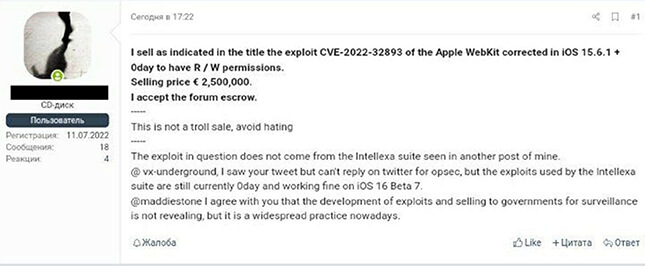
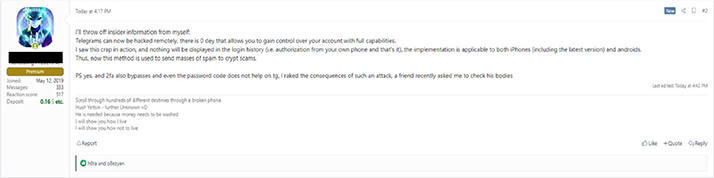
1. Vulnerability: CVE-2022-27518
Description: Unauthenticated remote arbitrary code execution vulnerability found in Citrix.
CVSS: 9.8
Vendor: Citrix Systems, Inc.
Product: Citrix ADC and Citrix Gateway
Update: Available
Exploitation: Observed China-linked threat actors actively exploiting this vulnerability.
Threat Actor: China-linked threat actors possibly APT5
2. Vulnerability: CVE-2022-42475
Description: FortiOS SSL-VPN and FortiProxy SSL-VPN have a heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability that could allow a remote, unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code or commands through carefully crafted requests.
CVSS: 9.8
Vendor: Fortinet, Inc.
Product: FortiOS SSL-VPN 7.2.0 through 7.2.2, 7.0.0 through 7.0.8, 6.4.0 through 6.4.10, 6.2.0 through 6.2.11, 6.0.15 and prior versions and FortiProxy SSL-VPN 7.2.0 through 7.2.1, 7.0.7 and prior versions.
Update: Available
Exploitation: Exploited by attackers to compromise governmental or government-related targets. Chinese threat actors are suspected to use this vulnerability in their cyber espionage operations.
Threat Actor: Chinese threat actors and others
3. Vulnerability: CVE-2022-42458
Description: Authentication bypass, using an alternative path or channel vulnerability in bingo!CMS version 1.7.4.1 and the prior version allow a remote unauthenticated attacker to upload an arbitrary file. As a result, an arbitrary script may be executed, and/or a file may be modified.
CVSS: 9.8
Vendor: Shift Tech Inc.
Product: bingo!CMS
Update: Available
Exploitation: Shift Tech Inc. observed exploration of this vulnerability in the wild.
4. Vulnerability: CVE-2022-3236
Description: In Sophos Firewall versions v19.0 MR1 and earlier, a code injection vulnerability was found in the User Portal and Webadmin, enabling a remote attacker to execute code.
CVSS: 9.8
Vendor: Sophos Limited
Product: Sophos Firewall
Update: Available
Exploitation: The vendor observed active exploitation of this vulnerability in a small set of organizations in the South Asia region.
Threat Actor: Chinese APT Group possibly exploiting this vulnerability
5. Vulnerability: CVE-2022-3180
Description: A remote attacker may be able to access the system with elevated privileges, using the WPGateway plugin for WordPress. This vulnerability could be used by an attacker to add malicious administrators.
CVSS: 9.8
Vendor: WordPress
Product: WPGateway
Update: There is no update yet that fixes the vulnerability.
Exploitation: The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild. The firewall rule is made available to block the exploit by researchers.
6. Vulnerability: CVE-2022-29499
Description: A vulnerability has been observed in the Mitel Service Appliance component of MiVoice Connect (Mitel Service Appliances – SA 100, SA 400, and Virtual SA), which could allow a malicious actor to perform remote code execution.
CVSS: 9.8
Vendor: Mitel Networks Corp.
Product: MiVoice Connect
Update: Available
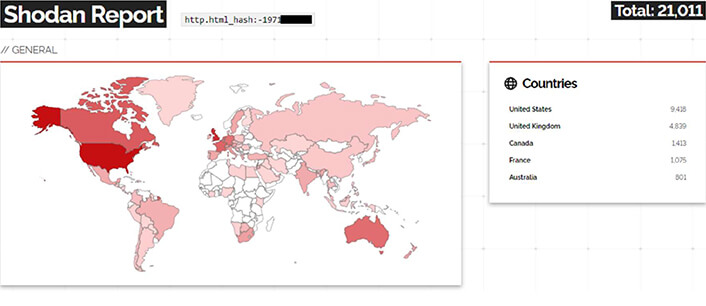
Exploitation: The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild. Shodan’s analysis revealed that 21,011 Mitel appliances that are accessible to the general public have this vulnerability as of 15th Feb 2023.
7. Vulnerability: CVE-2022-26134
Description: An OGNL injection vulnerability found in Confluence Server and Data Center, which allows an unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code on a Server or Data Center instance.
CVSS: 9.8
Vendor: Atlassian
Product: Atlassian Confluence Server
Update: Available
Exploitation: The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
Threat Actor: Researchers observed Kinsing and the Dark.IoT malware abusing this vulnerability.
8. Vulnerability: CVE-2022-26871
Description: An arbitrary file upload vulnerability was found in Trend Micro Apex Central, which can allow an unauthenticated remote attacker to upload an arbitrary file, allowing remote code execution.
CVSS: 9.8
Vendor: Trend Micro
Product: Trend Micro Apex Central and Apex Central SaaS
Update: Available
Exploitation: The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
9. Vulnerability: CVE-2022-22965
Description: A Spring MVC or Spring WebFlux application running on JDK 9+ is vulnerable to remote code execution (RCE) via data binding. The specific exploit requires the application to run on Tomcat as a WAR deployment. The vulnerability allows a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on the target system. The vulnerability exists due to improper input validation. A remote attacker can send a specially crafted HTTP request to the affected application and execute arbitrary code on the target system. Successful exploitation of this vulnerability may result in the complete compromise of the vulnerable system.
VSS: 9.8
Vendor: Java
Product: Pivotal Spring Framework
Update: Available
Exploitation: The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
10.Vulnerability: CVE-2022-22587
Description: A memory corruption issue was observed in iOS 15.3 and iPadOS 15.3, macOS Big Sur 11.6.3, and macOS Monterey 12.2 earlier versions, which allow arbitrary code execution with kernel privileges.
CVSS: 9.8
Vendor: Apple Inc.
Product: Apple iOS and macOS
Update: Available
Exploitation: The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
1. Vulnerability: CVE-2022-40684
Description: A critical Authentication Bypass Vulnerability in Fortinet Appliances traced as CVE-2022-40684 has been found to be actively exploited in the wild. An authentication bypass using an alternate path or channel vulnerability [CWE-288] in FortiOS, FortiProxy, and FortiSwitchManager could permit an unauthenticated attacker to perform administrative interface operations, using specially crafted HTTP or HTTPS requests.
VSS: 9.8
Vendor: Fortinet, Inc.
Product: FortiOS and FortiSwitchManager
Update: Available
Exploitation: The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
Threat Actor: Our intelligence research community observed Iranian and Chinese threat actors abusing the vulnerabilities of Fortinet products. The suspected threat actors are US17IRGCorp aka APT34, HAFNIUM, and its affiliates in the ongoing campaign” عقب درب” translating to “Tailgate”. Also, darkweb forum discussions indicated ransomware groups’ attention on the CVE.
2. Vulnerability: CVE-2022-1388
Description: Authentication bypass vulnerability observed in F5 BIG-IP. This vulnerability allows an unauthenticated attacker with network access to the BIG-IP system, through the management port and/or self IP addresses to execute arbitrary system commands, create or delete files, or disable services.
CVSS: 9.8
Vendor: F5 Networks
Product: BIG-IP
Update: Available
Exploitation: The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
Threat Actor: BlackTech and others
3. Vulnerability: CVE-2022-35405
Description: Remote code execution vulnerability observed in the following ManageEngine products,
• Unauthenticated remote code execution in ManageEngine Password Manager Pro and PAM360.
• Authenticated remote code execution in ManageEngine Access Manager Plus.
CVSS: 9.8
Vendor: Zoho Corp.
Product: ManageEngine Products
Update: Available
Exploitation: The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
4. Vulnerability: CVE-2022-41082
Description: CVE-2022-41082 is Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability. This vulnerability allows Remote Code Execution (RCE) when PowerShell is accessible to the attacker.
CVSS: 9.8
Vendor: Microsoft
Product: Microsoft Exchange Server
Update: Available
Exploitation: The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
Threat Actor: Researchers observed the Play ransomware group using this vulnerability to exploit the victim’s network.
5. Vulnerability: CVE-2022-41352
Description: A vulnerability was observed in Zimbra Collaboration (ZCS) 8.8.15 and 9.0. An attacker can upload arbitrary files through amavisd via a cpio loophole (extraction to /opt/zimbra/jetty/webapps/zimbra/public) that can lead to inaccurate access to any other user accounts.
CVSS: 9.8
Vendor: Zimbra, Inc.
Product: Zimbra Collaboration software
Update: Available
Exploitation: The vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild. CVE-2022-27518 (Citrix), CVE-2022-26134 (Confluence), CVE-2022-42475 (Fortinet), and CVE-2022-3236 (Sophos) are also part of the most exploited vulnerability in the 2022 list, along with being zero-days, which was detailed under ‘Top 10 Critical Zero-days Vulnerabilities Exploited In 2022’.
Zero-day and most exploited vulnerabilities remain a significant threat to cybersecurity. The increasing sophistication of attacks targeting vulnerabilities highlights the need for organizations to take proactive steps to protect their systems and data. This includes implementing strong security measures such as regular software updates, network segmentation, and access controls, as well as training employees on cybersecurity best practices. Furthermore, the trend of exploiting vulnerabilities is likely to continue in the coming years, so it’s essential for organizations to remain vigilant, invest in cybersecurity, and be prepared to respond quickly and effectively to any potential attacks.