



The Russian threat actors have been observed to be very active and have targeted multiple organizations in the past. The primary objective of these hacker groups in targeting foreign organizations appears to be to exfiltrate sensitive details to be sold in the grey market or potential competitors for financial gains. Russian threat actors have potential collaboration with other nation threat actors and it is suspected Russian groups could be offering Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS model) to them.
Recently, CYFIRMA analyzed a malicious sample in DeCYFIR and secondary OSINT tools for validation and suspect it to be leveraged by Russian threat actors Nobelium and Wizard Spider.
The threat actor is a well-resourced, highly dedicated and organized cyberespionage group that is believed to be working for the Russian Federation since at least 2008 to collect intelligence in support of foreign and security policy decision-making. It uses various tools such as PinchDuke , CozyCar , POSHSPY , PowerDuke , OnionDuke , GeminiDuke , MiniDuke , CosmicDuke , HAMMERTOSS , CloudDuke , SeaDuke.
Motivation: Espionage, Financial Gains, Political Motives
The threat actor is a sophisticated eCrime group that has been operating the Ryuk ransomware since August 2018, targeting large organizations for a high-ransom return. Wizard Spider, known as the Russia-based operator of the TrickBot banking malware, had focused primarily on wire fraud in the past.
Motivation: Financial crime, Financial gains
Following are some of the hypotheses based on which Russian threat actors are suspected to have leveraged this malicious sample:
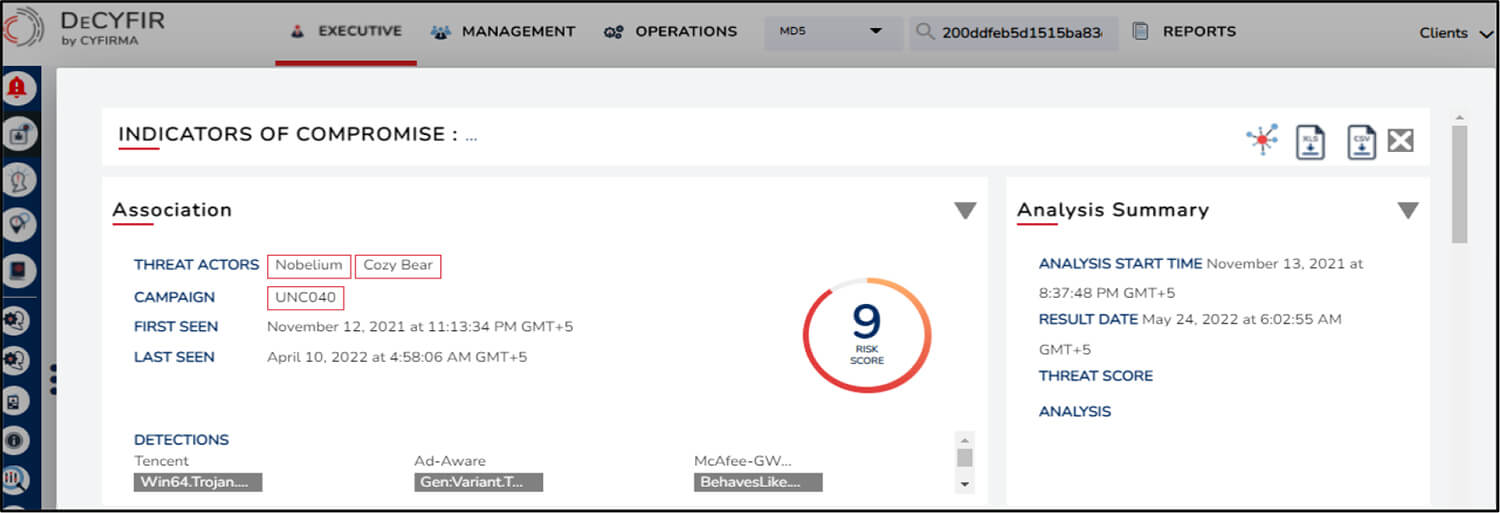
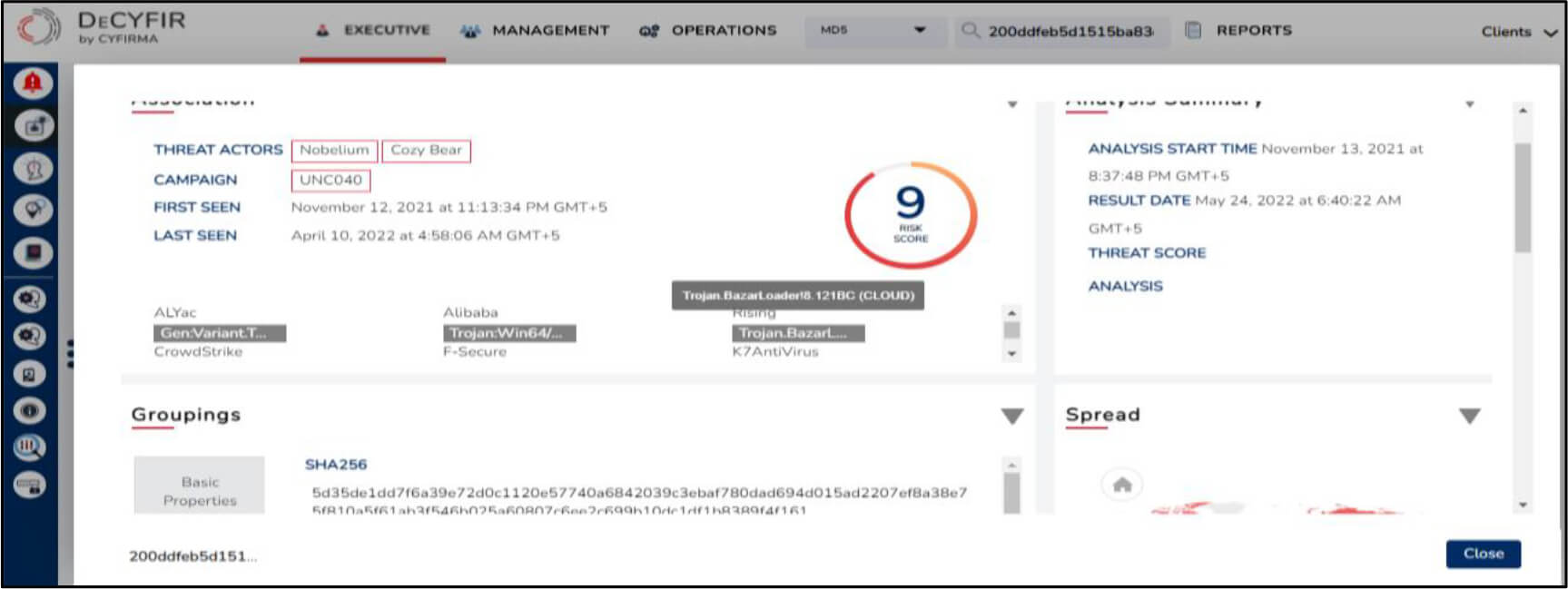
The campaign is suspected to be active since 24 January 2022.
For validation, the sample was analyzed in secondary OSINT tools which indicated that it was potentially used by Nobelium based on a similar tactic i.e. ISO disk image -> LNK link file -> DLL implant in a phishing campaign that seemed to target multiple victims based in the United States, Great Britain, and Europe.
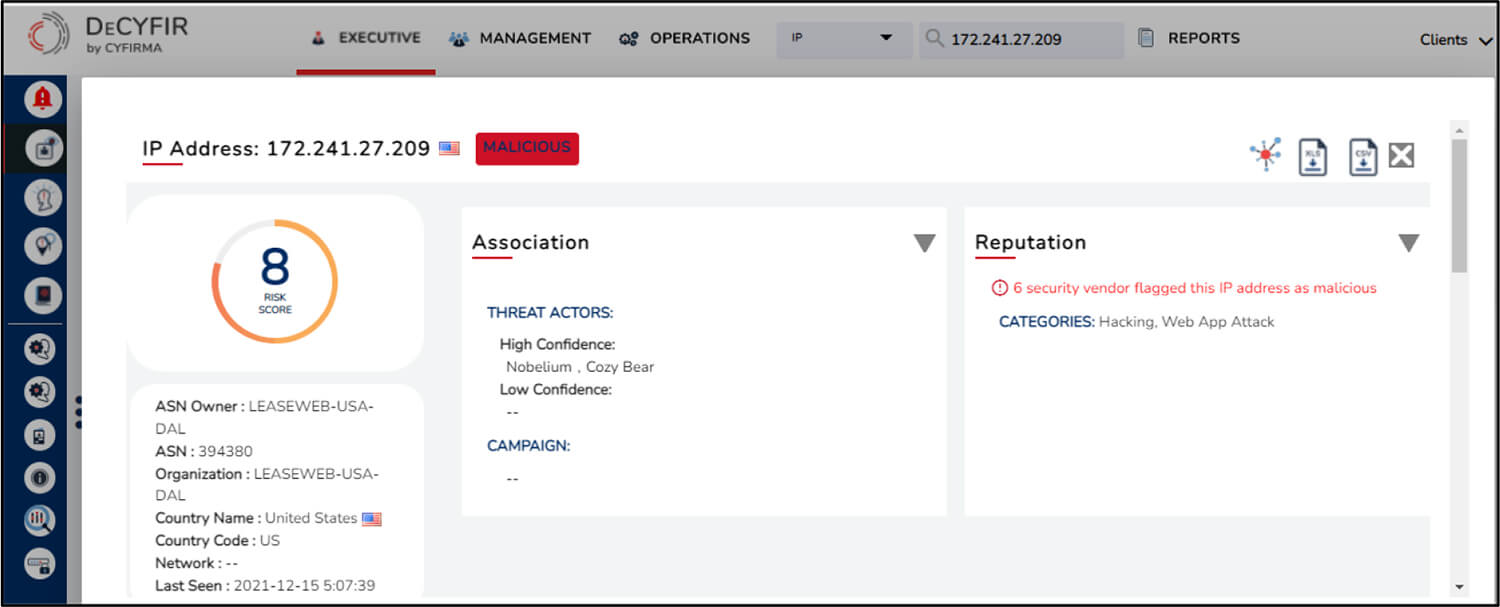
Following are some of the other campaigns tracked by CYFIRMA that are found to be potentially carried out by Nobelium threat actor, found through DeCYFIR’s AI & ML engines on the dark web:
The following CYFIRMA tracked campaign was potentially carried out by Wizard Spider. In addition, Fin11 and Oceanlotus were also suspected to possibly have perpetrated this campaign:
The Russian threat actors have been observed to be very active and have targeted multiple organizations in the past. The primary objective of these hacker groups in targeting foreign organizations appears to be to exfiltrate sensitive details to be sold in the grey market or to potential competitors for financial gains. Russian threat actors are assumed to have potential collaborations with other nations’ threat actors, and it is suspected that Russian groups could be offering Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS model) to them.
MITRE ATT&CK TTPs
| Sr No. | Tactic | Technique |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TA0043: Reconnaissance |
T1595: Active Scanning T1589: Gather Victim Identity Information |
| 2 | TA0042: Resource Development |
T1583: Acquire Infrastructure T1586: Compromise Accounts T1584: Compromise Infrastructure T1587: Develop Capabilities T1588: Obtain Capabilities |
| 3 | TA0001: Initial Access |
T1190: Exploit Public-Facing Application T1133: External Remote Services T1566: Phishing T1195: Supply Chain Compromise T1199: Trusted Relationship T1078: Valid Accounts |
| 4 | TA0002: Execution |
T1059: Command and Scripting Interpreter T1203: Exploitation for Client Execution T1053: Scheduled Task/Job T1204: User Execution T1047: Windows Management Instrumentation |
| 5 | TA0003: Persistence |
T1098: Account Manipulation T1547: Boot or Logon Autostart Execution T1136: Create Account T1546: Event Triggered Execution T1133: External Remote Services T1053: Scheduled Task/Job T1505: Server Software Component T1078: Valid Accounts |
| 6 | TA0004: Privilege Escalation |
T1548: Abuse Elevation Control Mechanism T1547: Boot or Logon Autostart Execution T1484: Domain Policy Modification T1546: Event Triggered Execution T1068: Exploitation for Privilege Escalation T1053: Scheduled Task/Job T1078: Valid Accounts |
| 7 | TA0005: Defense Evasion |
T1548: Abuse Elevation Control Mechanism T1140: Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information T1484: Domain Policy Modification T1562: Impair Defenses T1070: Indicator Removal on Host T1036: Masquerading T1027: Obfuscated Files or Information T1553: Subvert Trust Controls T1218: System Binary Proxy Execution T1550: Use Alternate Authentication Material T1078: Valid Accounts |
| 8 | TA0006: Credential Access |
T1110: Brute Force T1555: Credentials from Password Stores T1606: Forge Web Credentials T1621: Multi-Factor Authentication Request Generation T1003: OS Credential Dumping T1558: Steal or Forge Kerberos Tickets T1539: Steal Web Session Cookie T1552: Unsecured Credentials |
| 9 | TA0007: Discovery |
T1087: Account Discovery T1482: Domain Trust Discovery T1083: File and Directory Discovery T1069: Permission Groups Discovery T1057: Process Discovery T1018: Remote System Discovery T1082: System Information Discovery T1016: System Network Configuration Discovery |
| 10 | TA0008: Lateral Movement |
T1021: Remote Services T1550: Use Alternate Authentication Material |
| 11 | TA0009: Collection |
T1560: Archive Collected Data T1213: Data from Information Repositories T1005: Data from Local System T1074: Data Staged T1114: Email Collection |
| 12 | TA0011: Command and Control |
T1071: Application Layer Protocol T1001: Data Obfuscation T1568: Dynamic Resolution T1573: Encrypted Channel T1105: Ingress Tool Transfer T1095: Non-Application Layer Protocol T1090: Proxy T1102: Web Service |
| 13 | TA0010: Exfiltration | T1048: Exfiltration Over Alternative Protocol |
| Sr No. | Tactic | Technique |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TA0042: Resource Development | T1588: Obtain Capabilities |
| 2 | TA0001: Initial Access | T1133: External Remote Services T1566: Phishing T1078: Valid Accounts |
| 3 | TA0002: Execution | T1059: Command and Scripting Interpreter T1053: Scheduled Task/Job T1569: System Services T1204: User Execution T1047: Windows Management Instrumentation |
| 4 | TA0003: Persistence | T1547: Boot or Logon Autostart Execution T1543: Create or Modify System Process T1133: External Remote Services T1053: Scheduled Task/Job T1078: Valid Accounts |
| 5 | TA0004: Privilege Escalation | T1547: Boot or Logon Autostart Execution T1543: Create or Modify System Process T1055: Process Injection T1053: Scheduled Task/Job T1078: Valid Accounts |
| 6 | TA0005: Defense Evasion | T1222: File and Directory Permissions Modification T1562: Impair Defenses T1070: Indicator Removal on Host T1036: Masquerading T1112: Modify Registry T1027: Obfuscated Files or Information T1055: Process Injection T1553: Subvert Trust Controls T1078: Valid Accounts |
| 7 | TA0006: Credential Access | T1557: Adversary-in-the-Middle T1003: OS Credential Dumping T1558: Steal or Forge Kerberos Tickets |
| 8 | TA0007: Discovery | T1087: Account Discovery T1135: Network Share Discovery T1018: Remote System Discovery T1082: System Information Discovery T1016: System Network Configuration Discovery T1033: System Owner/User Discovery |
| 9 | TA0008: Lateral Movement | T1210: Exploitation of Remote Services T1570: Lateral Tool Transfer T1021: Remote Services |
| 10 | TA0009: Collection | T1557: Adversary-in-the-Middle T1074: Data Staged |
| 11 | TA0011: Command and Control | T1071: Application Layer Protocol |
| 12 | TA0010: Exfiltration |
T1048: Exfiltration Over Alternative Protocol T1041: Exfiltration Over C2 Channel |
| 13 | TA0040: Impact | T1489: Service Stop |
Rule 1:
title: Suspicious Call by Ordinal
id: e79a9e79-eb72-4e78-a628-0e7e8f59e89c
description: Detects suspicious calls of DLLs in rundll32.dll exports by ordinal
status: stable
tags:
– attack.defense_evasion
– attack.t1218.011
logsource:
category: process_creation
product: windows
detection:
selection:
Image|endswith: ‘\rundll32.exe’
CommandLine|contains:
– ‘,#’
– ‘, #’
– ‘.dll #’ # Sysmon removes , in its log
– ‘.ocx #’ # HermeticWizard
filter:
CommandLine|contains|all:
– ‘EDGEHTML.dll’
– ‘#141’
condition: selection and not filter
falsepositives:
– False positives depend on scripts and administrative tools used in the monitored environment
– Windows control panel elements have been identified as source (mmc)
level: high
Rule 2:
title: LOLBAS rundll32 without expected arguments (via cmdline)
description: Detects use of rundll32 as a LOLBAS binary where rundll32 is passed unexpected arguments such as a .iso instead of .dll (i.e. rundll32.exe test.iso, evilexport).
tags:
– attack.defense_evasion
– attack.execution
– attack.t1036
– attack.t1085
logsource:
category: process_creation
product: windows
detection:
selection_image:
Image|endswith: ‘\rundll32.exe’
filter:
CommandLine|contains:
– ‘.dll’
– ‘.cpl’
– ‘-localserver’
filter_re:
CommandLine|re: ‘.*[Mm][Ss][Ii][0-9A-Z]{4}\.[Tt][Mm][Pp].*’
condition: selection_image AND NOT (filter or filter_re)
falsepositives:
– none
level: medium
Rule 3:
title: Net.exe Execution
id: 183e7ea8-ac4b-4c23-9aec-b3dac4e401ac
status: experimental
description: Detects execution of Net.exe, whether suspicious or benign.
tags:
– attack.discovery
– attack.t1049
– attack.t1018
– attack.t1135
– attack.t1201
– attack.t1069.001
– attack.t1069.002
– attack.t1087.001
– attack.t1087.002
– attack.lateral_movement
– attack.t1021.002
– attack.t1077 # an old one
– attack.s0039
logsource:
category: process_creation
product: windows
detection:
selection:
Image|endswith:
– ‘\net.exe’
– ‘\net1.exe’
cmdline:
CommandLine|contains:
– ‘ group’
– ‘ localgroup’
– ‘ user’
– ‘ view’
– ‘ share’
– ‘ accounts’
– ‘ stop ‘
condition: selection and cmdline
fields:
– ComputerName
– User
– CommandLine
– ParentCommandLine
falsepositives:
– Will need to be tuned. If using Splunk, I recommend | stats count by Computer,CommandLine following the search for easy hunting by computer/CommandLine.
level: low
Rule 4:
title: Stop Windows Service
id: eb87818d-db5d-49cc-a987-d5da331fbd90
description: Detects a windows service to be stopped
status: experimental
tags:
– attack.impact
– attack.t1489
logsource:
category: process_creation
product: windows
detection:
selection:
Image|endswith:
– ‘\sc.exe’
– ‘\net.exe’
– ‘\net1.exe’
CommandLine|contains: ‘stop’
filter:
CommandLine: ‘sc stop KSCWebConsoleMessageQueue’ # kaspersky Security Center Web Console double space between sc and stop
User|startswith:
– ‘NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM’
– ‘AUTORITE NT\Sys’ # French language settings
condition: selection and not filter
fields:
– ComputerName
– User
– CommandLine
falsepositives:
– Administrator shutting down the service due to upgrade or removal purposes
level: low
Source: Surface Web