



Inside the World of Initial Access Broker (IAB): Insights and Trends
Initial Access Brokers (IABs) are rapidly evolving as an essential component of cybercrime and especially the Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) supply chain. IABs’ dedicated focus on the Initial Access stage of the kill chain allows them to evolve and advance their techniques and crack open doors of even well- protected large organizations. CYFIRMA constantly monitors the IABs eco- system, and this report aims to provide insight into the activity of 3 more prominent brokers.
“Prevention is better than cure” – It is better to identify and stop the intrusion in the kill chain’s initial phase than do firefighting when the intrusion reached the exploitation stage. This is where understanding IAB is crucial because they can aid in early intrusion detection to prevent operational, financial, and reputational disruption. IABs enable Threat Actors (TAs) to create maximum damage with less dwell time. It is the best example of how TAs collaborates to the tune of greater profits for all except, the victims.
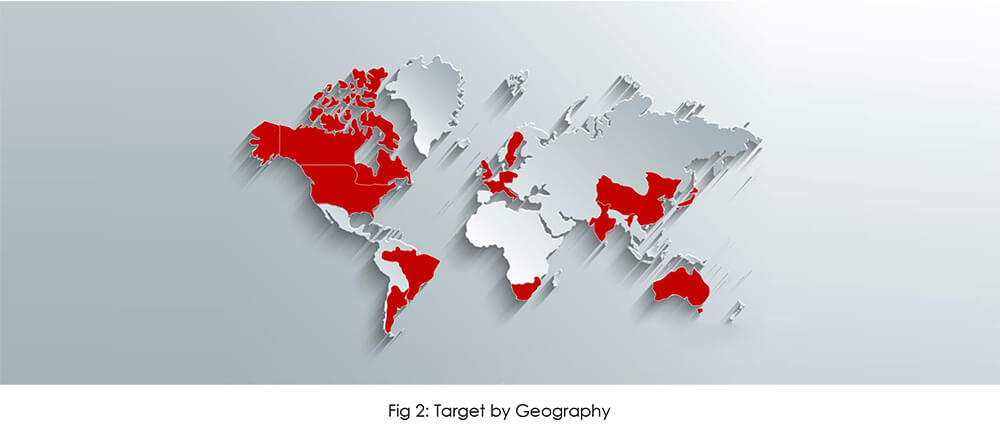
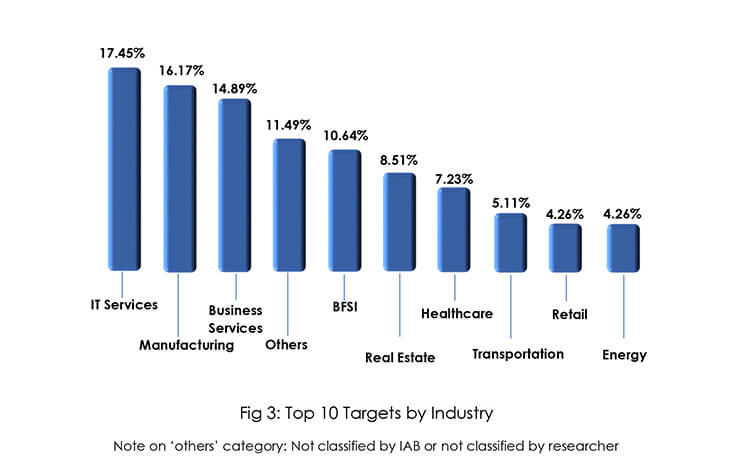
Initial Access Brokers specialize in advanced social engineering, spamming, and exploiting vulnerable remote access tools to gain initial access to victims’ networks. After gaining initial access to victims’ systems IABs fear losing access and hence aim to monetize the access as soon as possible resulting in selling network access to any actor – financially motivated APTs such as multiple FIN Groups, ransomware actors, data brokers, nation-state actors combing the cybercrime underground for leads, or essentially any threat actor with a way to monetize said access. IABs target organizations across the globe, the top target countries are the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Germany, India, France, Japan, and Australia. The top target industries are IT Services, Manufacturing, Business Services, BFSI, Real Estate, Healthcare, Transportation, Retail, and the Energy sector.
Initial access brokers are generally lower-tier, opportunistic threat actors supplying the affiliates with access-as-a-service. They obtain initial access to organizations and then offer it for sale on the underground forums to RaaS affiliates. Affiliates then buy these initial accesses, pivot, and move laterally until enough control is obtained so the ransomware can be spread and computers are locked.
Ransomware affiliates face constant scrutiny from the ransomware developers and commission-based salary that’s dependent on successful network intrusions, the affiliates need to constantly gain more network access to stay active which is one of the basic requirements of the affiliate program. This is where the initial access broker comes to rescue affiliates and make money for everyone involved except victims.
Our sample data analysis of the IAB ecosystem revealed that nearly half of victim organizations’ revenue is up to USD 10 million. Indicating that it is easier to compromise small organizations with limited budgets to implement strong cyber defenses than it is to compromise larger organizations with more revenue. Data from compromised victims of financially strong organizations demonstrate the sophistication of IABs as well as the fact that money alone cannot protect an organization from cyber-attacks.
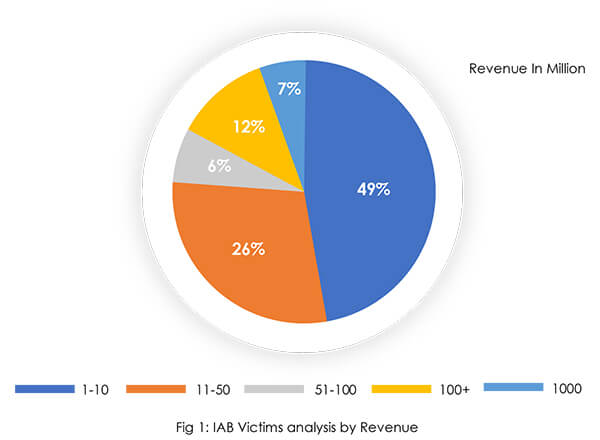
The United States is the most popular choice among initial access brokers, followed by countries in the European Union. Stringent data protection laws and regulations in the United States and Europe, as well as the consequences of violating data protection laws, are possibly driving IABs to target organizations in the region rather than other countries. Furthermore, both regions are regarded as developed, with a plethora of strong revenue- generating organizations that can provide large attack surfaces for IAB operations. Demand for access to the organization residing in the USA and European Union countries is more than in other countries by access buyers. Access for USA-based organizations is offered at a minimum of USD 3,000 – USD 5,000 whereas for other region organizations access is offered at USD 1,500 or less.
The Broker1 joined forums for cybercrime in July 2019 but did not start selling network access until June 2022. The RCE vulnerability CVE-2022-22954 (CVSS:9.8), which affects VMware Workspace One Access & Identity Manager, is one of the vulnerabilities that the actor exploits. The actor is still active on the well-known forum despite being barred from the Exploit forum.

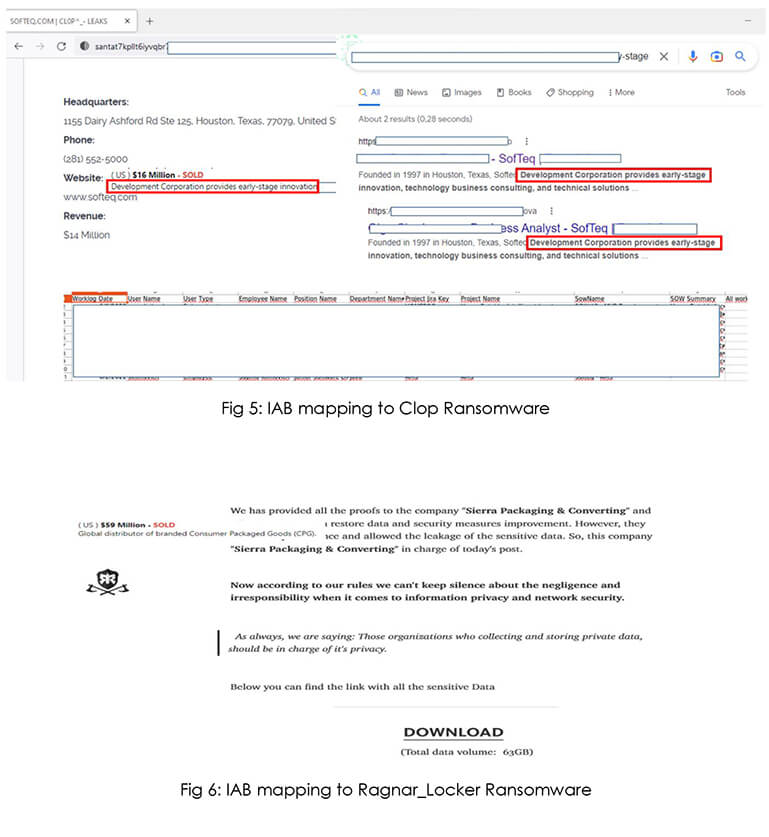
Based on our research, Broker1 is working together with a ransomware affiliate to grant initial access. The Clop ransomware group compromised the SofTeq Development Corporation, and we believe with high confidence that access was sold by Broker1 to the ransomware group. In another example, we observed with medium confidence that IAB (Broker1) sold access to Sierra Packaging & Converting, and later the organization was compromised by Ragnar_Locker ransomware group evidencing the hypothesis that IABs are an integral part of the ransomware access supply chain.
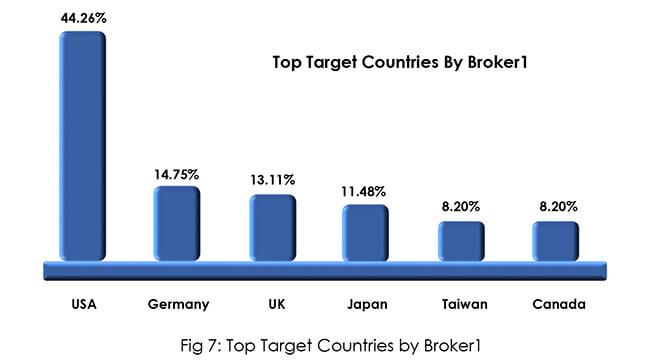
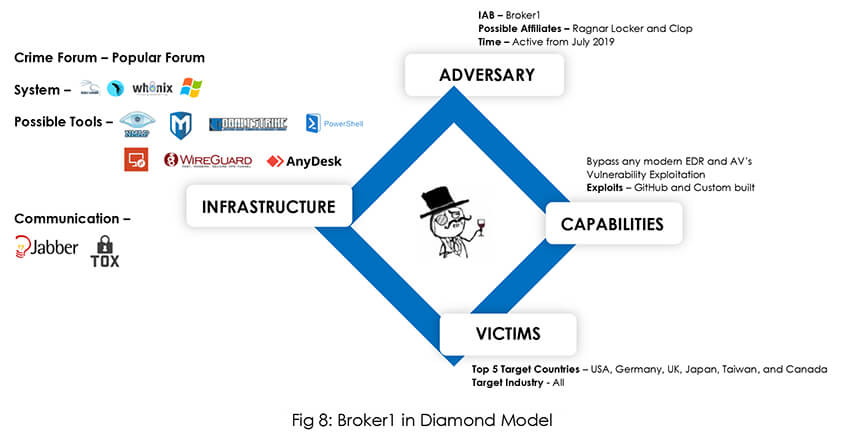
After being a quiet observer in the forum during the initial days Broker1 started selling network access for further exploitation in June 2022. As previously mentioned, sold access was subsequently used by ransomware groups, demonstrating IAB’s affiliation with related ransomware groups. IAB maintained a credible reputation for its offerings on the forum. In recent activities along with network access, IAB started selling tools for exploitation and crypt service to bypass AVs. IAB’s signature on numerous services and technical abilities, as described in the profiling, show that he has progressed from initially being a passive observer to a prolific threat actor.
Initial Access Broker – Broker2 joined forums for cybercrime in June 2020, after almost a year of observing period Broker2 started selling network access to the organization for further exploitation in May 2021. Broker2 offerings received positive feedback from threat actors on the forum, including the well-regarded and prominent Russian-speaking threat actor ‘stallman’.

Tracking back IAB’s footprint to its initial days, interestingly Broker2 started his operation as an access buyer (M&T Bank business accounts) than a seller. Probably wanted to resell later for a profit. IAB initially started selling WordPress Admin user id and passwords followed by bank account details and leaked DL and SSN cards before moving to the organizations’ network access in May 2021. Thereafter Broker2 only engaged in selling the organizations’ network access.
Broker2’s top victims are from IT Services, Manufacturing, BFSI, Business Services, and Real Estate industries. Victim organizations belong to 23 different countries spread across America, European Union, Asia, and Africa.
Initial Access Broker – Broker3 has been active since September 2021 and usually offers VPN-RDP access. IAB offerings received positive feedback from threat actors on the forum. In March 2022 IAB started selling VPN access in bulk for some time. We also noticed some other IABs selling access in bulk, this seems to be an attractive offer for buyers (threat actors) who will be getting access to multiple networks for a cheap price.

Based on our observation of Broker3 activities we believe IAB is possibly exploiting known Fortinet vulnerabilities to gain access to victims’ VPNs. Also, believe IAB is using python-based exploits to compromise the systems or network.
Broker3’s top victims are from Business Services, Manufacturing, Real Estate, BFSI, and Healthcare industries. Victim organizations belong to 31 different countries. The United States, United Kingdom, Canada, India, and France are the top 5 victims countries.
In a competitive cybercrime space, access is ‘King’ and IABs are ‘King Makers’. Especially for ransomware affiliates, it’s important to have a regular supply of access to the organization network for them to exploit further to maintain their operations and existence. This is where Initial Access Brokers come to rescue operators by supplying access to the operators. The existence of IAB in the whole cybercrime ecosystem becomes a necessity over a period as the number of ransomware groups increases day by day. Association with good and trustable IABs is a path to success for ransomware affiliates and other threat actors.