



CYFIRMA’s Research team present this extensive analysis, a critical vulnerability, CVE-2023-46747, analyzed within F5 BIG-IP Traffic Management User Interface (TMUI). This security flaw allows unauthenticated remote code execution via AJP smuggling, enabling threat actors to bypass authentication and execute arbitrary commands. The discovery poses a severe risk to affected systems’ confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Given its impact on multiple versions of F5 BIG-IP, organizations are urged to promptly implement mitigation strategies to prevent potential exploitation.
A critical security loophole, CVE-2023-46747, was identified in F5 BIG-IP’s TMUI, enabling unauthenticated remote code execution through AJP smuggling.
This flaw stems from inadequate handling of AJP (Apache JServ Protocol) requests, providing a gateway for attackers to manipulate requests and execute unauthorized commands. Its impact extends across multiple versions of F5 BIG-IP, posing a severe threat to enterprises, data centers, and essential infrastructure.
This widespread vulnerability requires immediate attention and proactive mitigation measures.
Key Takeaways:
Acknowledgements:
CYFIRMA Research acknowledges the collaborative efforts of security researchers and the cybersecurity community in identifying and addressing CVE-2023-46747 within F5 BIG-IP TMUI. F5’s swift response in releasing patches highlights the vital role of coordinated security efforts in fortifying digital infrastructure against evolving threats.
Vulnerability Type: Unauthenticated Remote Code Execution (RCE) via AJP Smuggling
CVE ID: CVE-2023-46747
CVSS Severity Score: 9.8 (Critical)
Application: F5 BIG-IP Traffic Management User Interface (TMUI)
Impact: Allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code
Severity: Critical
Affected Versions: Multiple versions of F5 BIG-IP TMUI are affected, check here.
Patch Available: Yes
CVE-2023-46747 represents a critical vulnerability found in F5 BIG-IP’s TMUI, enabling unauthenticated attackers to execute remote code arbitrarily. This security loophole emerges from inadequate AJP request handling, permitting threat actors to bypass authentication and execute malicious commands. AJP smuggling facilitates the injection and execution of arbitrary code within the system, granting unauthorized access and potentially compromising affected systems.
The vulnerability’s exploitation poses severe risks, including unauthorized system access, data breaches, manipulation of systems, and service disruptions. Successful exploitation could compromise sensitive information, severely impacting business operations and exposing organizations to significant financial and reputational harm.
Multiple instances of F5 BIG-IP Traffic Management User Interface (TMUI) are affected by CVE-2023-46747; a critical vulnerability. For detailed information and affected versions, check here.
Is there already an exploit tool to attack this vulnerability?
According to the latest available information, there is a known public exploit tool for CVE-2023-46747 targeting the F5 BIG-IP Traffic Management User Interface (TMUI).
Has this vulnerability already been used in an attack?
Specific information confirming exploitation of CVE-2023-46747 is not available. Monitoring reports or observations of exploitation attempts in the last 30 days are inconclusive.
Are hackers discussing this vulnerability in the Deep/Dark Web?
As per CYFIRMA’s observations, discussions, or potential exploitation of CVE-2023-46747 in the Deep/Dark Web were identified. Continuous monitoring of underground forums and channels remains crucial to detect emerging discussions or potential threats.
What is the attack complexity level?
The attack complexity level for CVE-2023-46747 in F5 BIG-IP TMUI is assessed as LOW.
Historical Trends and Known Exploits:
Historically, threat actors have targeted vulnerabilities in various software products. While there are known exploits for CVE-2023-46747 that have surfaced, organizations should remain vigilant as threat actors might attempt exploitation, leading to unauthorized access, data breaches, or network compromise.
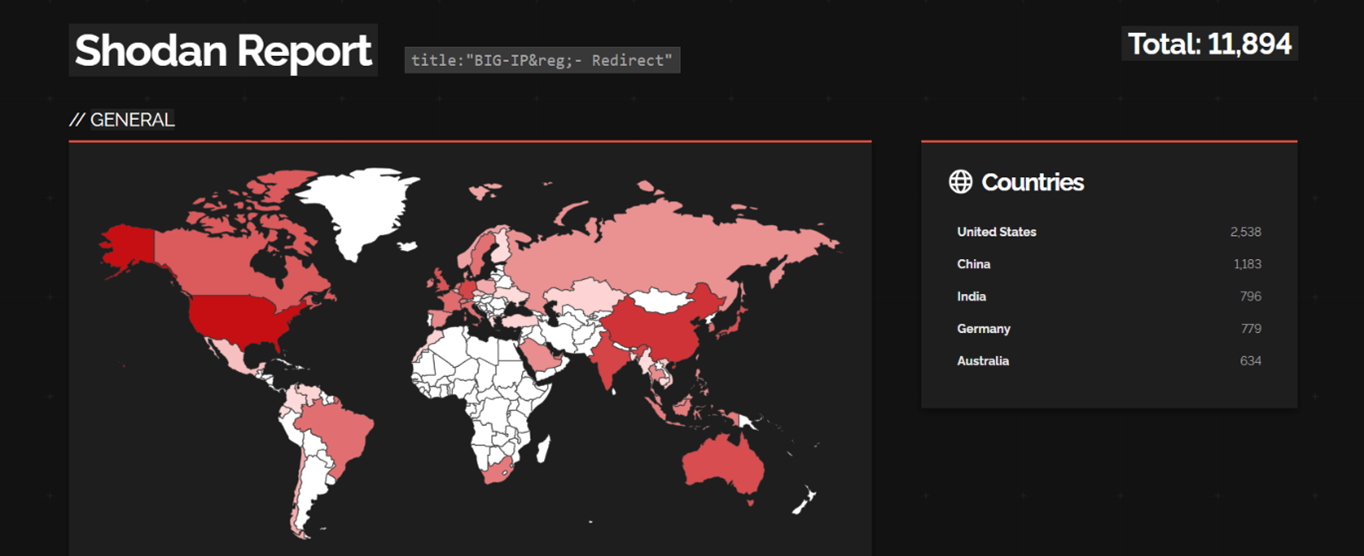
Our analysis found that more than 11000+ F5 BIG-IP Traffic Management User Interface (TMUI) are public, and which can be vulnerable to CVE-2023-46747.
The exploitation of the vulnerability in F5 BIG-IP TMUI involves a multi-step process to bypass authentication and execute unauthorized commands. Initially, the attack leverages a flaw within the TMUI interface, allowing the creation of a user account without proper authentication or authorization mechanisms.
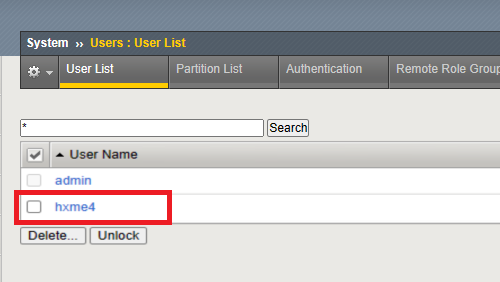
This flaw provides unauthorized access, granting the attacker entry into the system. Upon successful unauthorized user creation, the attacker then proceeds to exploit another vulnerability to obtain an authentication token.
This token serves as a cryptographic key, granting access to protected resources within the TMUI interface. With the acquired authentication token in hand, the attacker crafts HTTP requests specifically designed to execute arbitrary system commands on the targeted F5 BIG-IP device. These crafted requests take advantage of the system’s functionality to execute unauthorized commands, potentially leading to the compromise of the device.
To ensure a higher success rate in executing commands, the exploit includes a retry mechanism. If initial attempts fail due to network instability or other factors, the exploit retries the command execution process multiple times before signaling a failure. The attacker interacts with the system via an interface that prompts for command inputs. This interactive mode allows the attacker to input commands directly, facilitating their execution on the vulnerable F5 BIG-IP device.
Moreover, there’s a precautionary step implemented to identify specific proxies, such as Burp Suite, known to potentially interfere with the exploitation process. This check warns against using these proxies due to their potential disruption, ensuring a smoother exploitation experience. This sequence of steps showcases the severity of the vulnerability, demonstrating the potential for unauthorized access and arbitrary command execution, highlighting the critical need for mitigation, and patching to prevent exploitation.
To mitigate CVE-2023-46747, organizations should immediately update F5 BIG-IP systems to the latest patched versions. Implementing stringent network-level controls, restricting TMUI access, and deploying robust firewall rules can aid in mitigating the risk of exploitation. Continuous monitoring and auditing of network traffic for suspicious activities are essential for early threat detection and response. It’s imperative for cybersecurity teams to remain vigilant, promptly apply security patches, and continually reinforce defences to thwart potential exploitation attempts.
Target Geography: Organizations worldwide deploying F5 BIG-IP Traffic Management User Interface (TMUI) falling within the affected versions may potentially be at risk. The impact of CVE-2023-46747 is not restricted by geography but extends to any region where F5 BIG-IP TMUI is utilized. Therefore, organizations in regions like North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and other areas with significant F5 BIG-IP deployments might be exposed to the risk of exploitation.
Target Industry: The vulnerability CVE-2023-46747 in F5 BIG-IP TMUI has the potential to impact organizations across diverse industries. This encompasses sectors such as healthcare, finance, government, telecommunications, and other industries relying on F5 BIG-IP TMUI for traffic management and network security.
Threat actors knowledgeable about this vulnerability may selectively target industries based on the perceived value of the data or services handled by F5 BIG-IP instances. Organizations dealing with sensitive information or heavily reliant on F5 BIG-IP TMUI for network security may become specific targets.
Target Technology: The CVE-2023-46747 vulnerability specifically affects F5 BIG-IP Traffic Management User Interface (TMUI); a crucial component for network traffic handling and security. While the immediate impact is on TMUI instances, successful exploitation may extend beyond, compromising interconnected systems, applications, and servers linked with F5 BIG-IP TMUI. This amplifies the potential impact on an organization’s technological infrastructure.
Understanding the potential impact across different geographic regions, industries, and technologies is crucial for organizations to evaluate their exposure to CVE-2023-46747. It emphasizes the urgent need for addressing the issue through patching, proactive security measures, and continuous monitoring to mitigate the risks associated with this critical vulnerability.
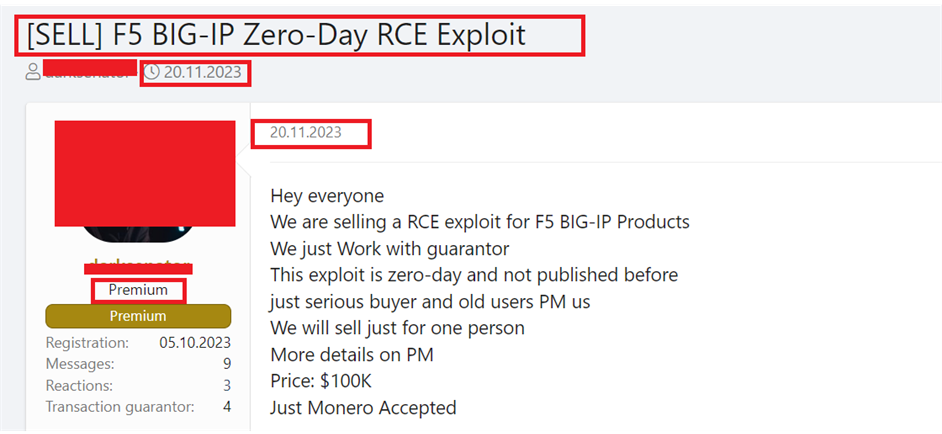
From underground forums, CYFIRMA’s Research team has observed that unknown hackers are selling this exploit to organizations compromised using F5 BIG-IP Exploits. We can expect to see the use of double-extortion tactics by ransomware groups after gaining foothold on target organisations using this vulnerability.
In conclusion, the discovery of CVE-2023-46747 exposes a critical vulnerability within F5 BIG-IP Traffic Management User Interface (TMUI), underscoring the immediate need for organizations to address this issue urgently.
The severity of CVE-2023-46747 demands immediate attention to safeguard the ongoing integrity and confidentiality of digital infrastructure.