



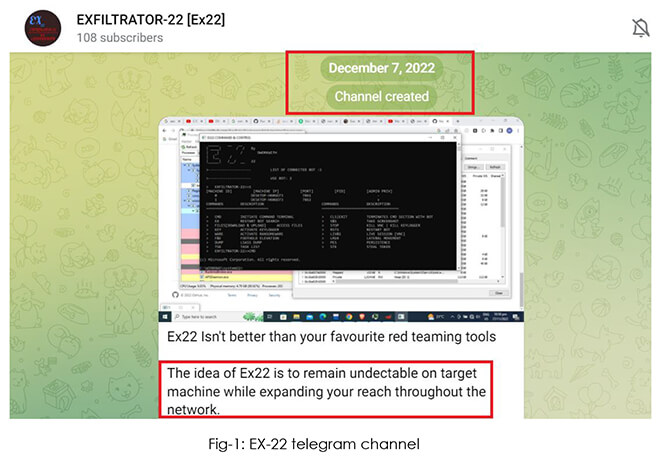
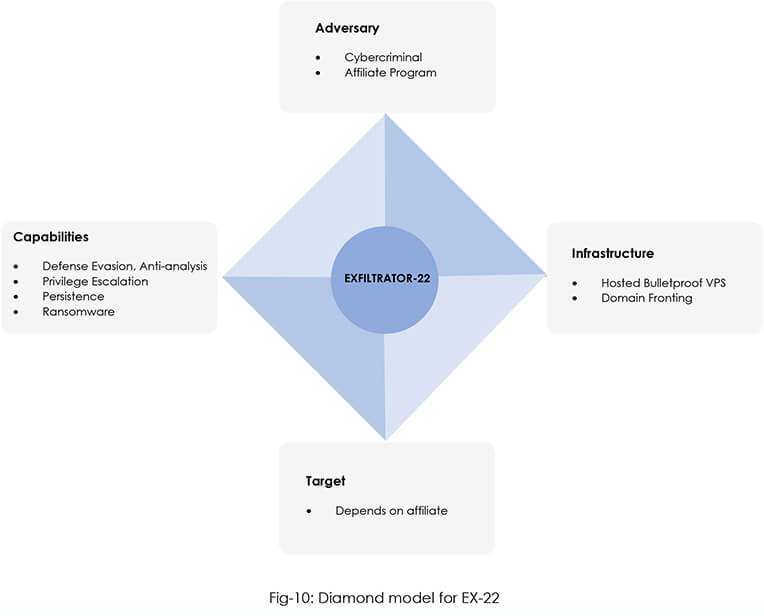
The CYFIRMA Research team has provided a preliminary analysis of a new post- exploitation framework called EXFILTRATOR-22 a.k.a. EX-22. After analyzing the available information, it is moderately certain that the individuals responsible for creating the malware are operating from North, East, or South-East Asia (possible countries include China, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Malaysia, Singapore, Philippines, etc.). These individuals possess a thorough knowledge of defense evasion and anti-analysis techniques. They have utilized leaked source code from post-exploitation frameworks to develop their own post-exploitation-framework-as-a-service model. Likely, ex-affiliates of LockBit, the threat actors are willing to build their own affiliate program and are coming out with an aggressive marketing strategy – claiming to be FUD (fully undetectable) by every Antivirus and EDR vendor.
CYFIRMA research reveals that the development of the first version of EXFILTRATOR-22 was completed on (or before) 27th November 2022. Soon after that, on 7th December 2022, the threat actor created a telegram channel to advertise the malware, in order to attract prospective buyers.
As of 13th February 2023, the malware still has 5/70 detections on Online Sandboxes, even after multiple dynamic scans being performed. This tells us that the threat actors are skilled at anti-analysis and defense evasion techniques.
Towards the end of December 2022, the threat actors stated that a new feature is a work in progress, which will allow users to choose between different agents to help conceal traffic and make it appear normal on the target machine. In January 2023, an official announcement was made on their channel to keep prospective buyers updated on the progress. It was stated that Ex22 is 87% ready for use and the payment model will be subscription based ($1000 for a month and $5000 for lifetime access). Upon purchase, the buyer would be given a login panel to access the Ex22 server, hosted on a bulletproof VPS (Virtual Private Server). A bulletproof VPS allows threat actors to bypass the laws or terms regulating Internet content and used service, in their own country of operation, as many of these bulletproof hosting services are based overseas, relative to the geographical location of the content provider. In this research, we will talk about the attribution of the threat actors behind this malware and the features being advertised by them.
On 10th February 2023, a demonstration video was uploaded to their YouTube channel, showcasing the enhanced features that come with EXFILTRATOR-22.

In a screenshot posted by the threat actors on their telegram channel, we can see that the sample was uploaded to Online Sandboxes for dynamic analysis on 2nd December 2022 at 5:54 PM UTC, which is 3rd December 2022 1:55 AM in the threat actors’ host time- zone.

Please take note that the host timestamp (3rd December 2022 1:55 AM) is 8 hours ahead of the timestamp mentioned in the browser (2nd December 2022 5:54 PM UTC).
Upon taking a closer look at the sample’s activities in the dynamic analysis sandbox, we noted that the sample is a compiled executable, created on 2022-12-02 at 14:08:08 UTC. The malware targets devices with x64 architecture. Furthermore, the C2 infrastructure points to an IP Address, hosted using Akamai (CDN).

Security researchers have identified thousands of domains, served by Akamai’s CDN that can be used for domain fronting. Attackers can use Meek; a publicly available obfuscation plugin for TOR, and an implementation of the domain fronting technique, to hide TOR traffic. By hosting a Meek reflection server in one of these CDNs, Meek can hide TOR traffic in legitimate HTTPS connections to well-known services. As a result, attackers can abuse CDNs to mask malware command and control (C2) traffic using domain fronting.
Similarities with LockBit3.0 samples in the wild
Upon correlating with data from other malware samples, CYFIRMA research has revealed that a LockBit3.0 sample (sha256- d61af007f6c792b8fb6c677143b7d0e2533394e28c50737588e40da475c040ee) and the EXFILTRATOR-22 sample share the same technique (Domain Fronting) and network infrastructure for concealing C2 traffic. A simple lookup on research tools tells us that the above sample has been actively used in LockBit3.0 campaigns.

Upon further investigation, the CYFIRMA research team has identified that the LockBit3.0 sample utilizes the same C2 infrastructure as EX-22.

Ex22 is a tool designed to spread ransomware within corporate networks without being detected. It comes with a wide range of capabilities, making post-exploitation a cakewalk for anyone purchasing the tool. Below are some of the features of the tool that are highly lucrative for buyers:
The buyers of Ex-22 are given an administration panel, along with the subscription. This panel allows threat actors to remotely control the malware, they’ve deployed on infected devices. This allows them to issue commands to the malware and collect information from the infected devices. The panel also enables threat actors to automate tasks, such as deploying new versions of the malware, updating the configuration of the malware, or creating new campaigns. In addition to that, it can help threat actors evade detection. By keeping their operations centralized on a remote server, they can make it more difficult for security researchers to analyze and identify the source of the malware. Let us look at a few interesting features of the administration panel of EX-22:
Ex-22 chooses which UAC bypass method to use, based on the payload and the operating system. All the attacker needs to do is use the “F&E” command.
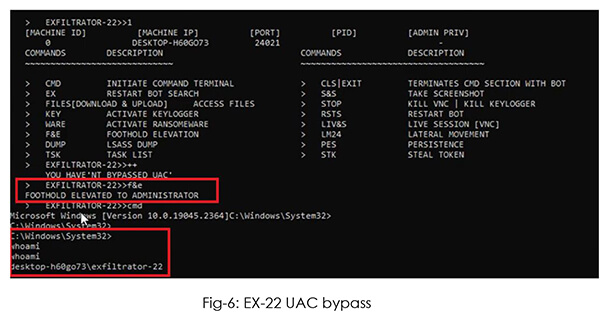
The attacker can check group memberships for the existing user to determine the need for privilege escalation.

In this case, the user is part of the administrator group already, hence the attacker uses “++” to access elevated payloads, based on the victim’s machine ID.

The attacker has the convenience to choose and transfer the payload that needs to run on the target machine. In addition to this, the tool is also capable of creating scheduled tasks with a single command.

It can be concluded with high confidence that the threat actors who created EX-22 are highly sophisticated threat actors that are likely to continue to increase the evasiveness of the malware. With continuous improvements and support, EX-22 becomes a go-to alternative for any threat actors planning to purchase tools for the post exploitation phase but do not want to go with the traditional tools due to high detection rates. The threat actors have come up with their own post-exploitation affiliate model primarily for the below reasons:
| Sr.no | Tactics | Techniques | Procedures |
| 1 | TA0002- Execution | T1129- Shared Modules | Parses PE header Links function at runtime on Windows |
| 2 | TA0003- Persistence | T1547.001- Boot or Logon AutoStart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder | Persists via Run registry key |
| 3 | TA0004- Privilege Escalation | T1055- Process Injection | Spawn processes Creates a process in suspended mode (likely to inject code) |
| T1134- Access Token Manipulation | Acquires debug privileges Modifies access privileges | ||
| 4 | TA0005- Defense Evasion | T1055- Process Injection | Spawn processes Creates a process in suspended mode (likely to inject code) |
| T1497- Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion | Evasive sleep loops hinder dynamic analysis | ||
| T1027- Obfuscated Files or Information | Encrypts data using RC4 PRGA | ||
| T1055.003- Process Injection: Thread Execution Hijacking | Hijacks thread execution | ||
| T1112- Modify Registry | Deletes registry key | ||
| T1134- Access Token Manipulation | Acquires debug privileges Modify access privileges | ||
| T1564.003- Hide Artifacts: Hidden Window | Hides graphical window | ||
| T1620- Reflective Code Loading | Hijacks thread execution | ||
| 5 | TA0006- Credential Access | T1056.001- Input Capture: Keylogging | Logs keystrokes via polling |
| 6 | TA0007- Discovery | T1082- System Information Discovery | Reads software policies |
| T1497- Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion | Evasive sleep loops to hinder dynamic analysis | ||
| T1010- Application Window Discovery | Finds graphical window | ||
| T1057- Process Discovery | Enumerates processes | ||
| T1082- System Information Discovery | Queries environment variable | ||
| T1083- File and Directory Discovery | Checks if the file exists | ||
| T1497.002- Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion: User Activity-Based Checks | Checks for unmoving mouse cursor | ||
| 7 | TA0009- Collection | T1056.001- Input Capture: Keylogging | Logs keystrokes via polling |
| T1113- Screen Capture | Captures screenshots | ||
| 8 | TA0040- Impact | T1486- Data Encrypted for Impact | Modifies user documents Writes a notice file (html or text) to demand a ransom |
| No. | Indicator | Type |
| 1 | 874726830ae6329d3460767970a2f805 | md5 |
| 2 | eca49c8962c55bfb11d4dc612b275daa85cfe8c3 | sha1 |
| 3 | 32746688a23543e674ce6dcf03256d99988a269311bf3a8f0f944016fe3a931d | sha256 |
| 4 | Worm[.]exe | filename |
| 5 | Worm24[.]exe | filename |
| 6 | 23.216.147[.]76 | IPv4 |
| 7 | 20.99.184[.]37 | IPv4 |