



Date: 04-April-22
Author: Manoj Kumar (Cyfirma-Malware Research Team)
Suspected Malware: Doublezero wiper Malware
Function: Destructor
Risk Score: 8
Confidence Level: High
Threat actor Associations: Unknown
First Seen: March 2022
DeCyfir presence: Yes
Doublezero is a data wiper malware, which destroys files, registry keys, and trees on the Victim machine. On March 17, 2022, the computer emergency Response team of Ukraine discovered malware dubbed “DoubleZero” that targeted Ukrainian enterprises during Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. This malware deletes registry hives (HKCU, HKU, HKLM) , terminate the “lsass” process, get full access control to wipe out non-system and system files.
Sample Details:
File Type: Windows PE
Architecture: 32 Bit
MD5: B4F0CA61AB0C55A542F32BD4E66A7DC2
SHA256: 30B3CBE8817ED75D8221059E4BE35D5624BD6B5DC921D4991A7ADC4C3EB5DE4A
Subsystem: Console
It is still unclear on the initial access for the malware. It is believed that the targeted systems were already compromised, and the malware was executed during the invasion of Ukraine by Russians.
This malware was written in .net programing language. This date wiper malware has customized obfuscation and a huge amount of junk code that makes malware reverse engineering harder to analyze these codes fully. This malware binary shows a compile-time is 12 Oct 2093.
This malware has a method, which enumerates the list of domain controllers connected to the infected host. When the malware is executed, it first checks if the compromised machine is one of the domain controllers. If this host is one of the domain controllers, the malware will not be executed. Threat actor added a large junk of unwanted code across this malware codes.
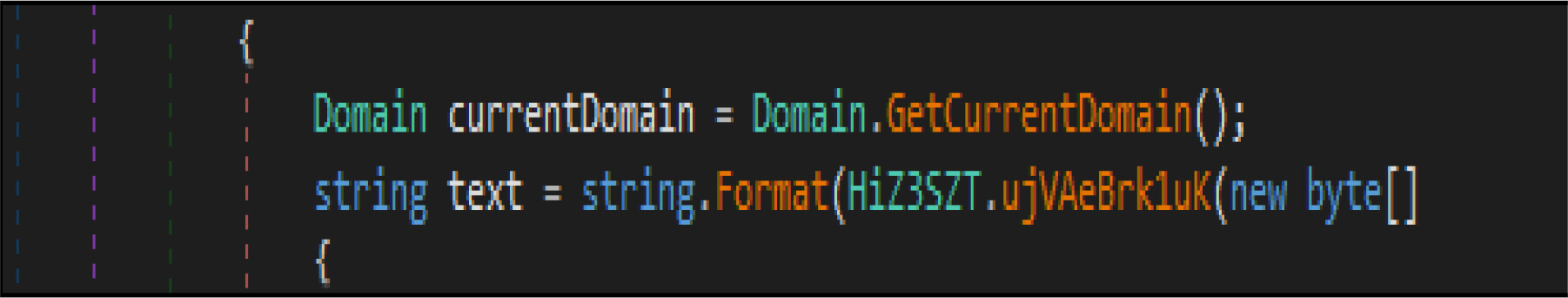
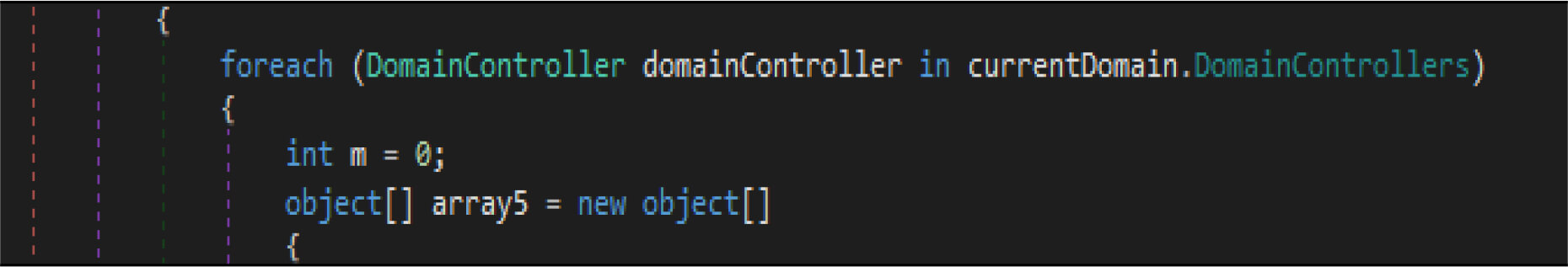
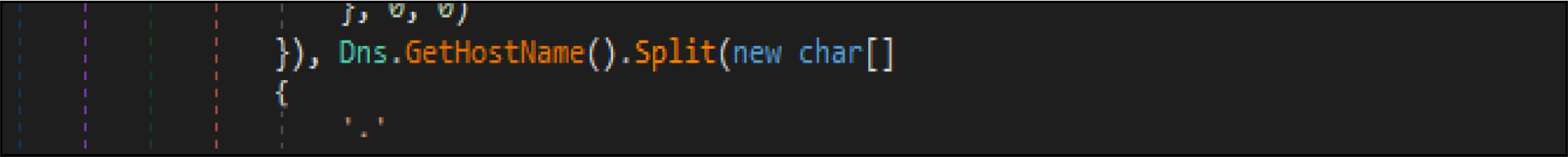
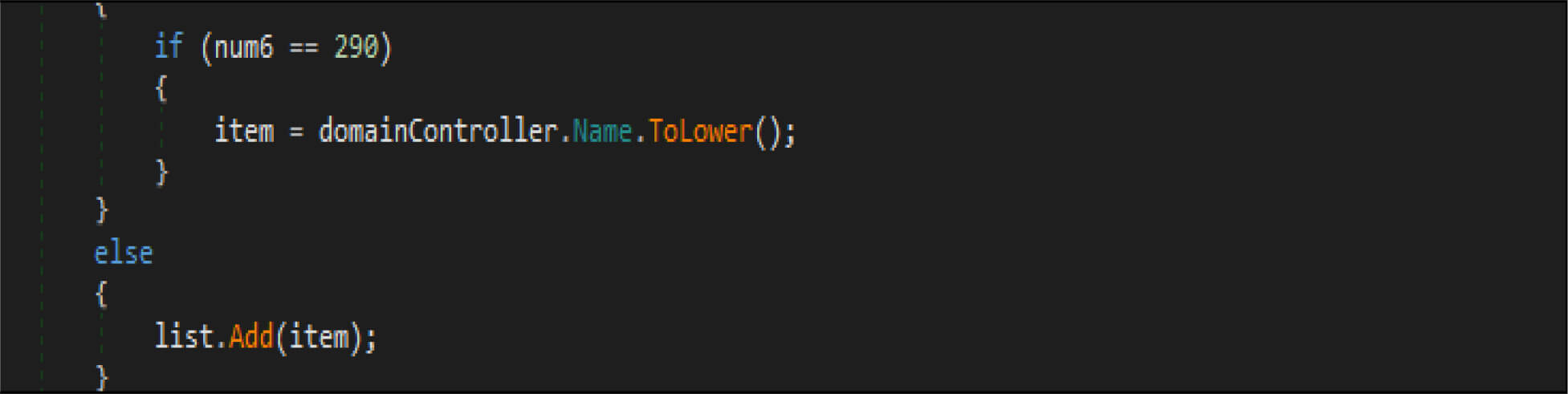
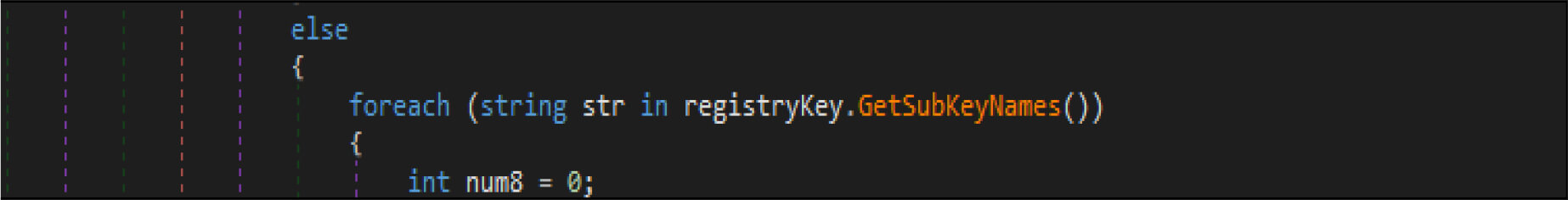
This malware first destroys non-system files, after that it will overwrite system-related files. This wiper malware hardcoded a specific list of the file location in their code as shown in the below figure. This malware before executing the destructive routine, it will list several directory names and paths where it will look for files it will wipe out.
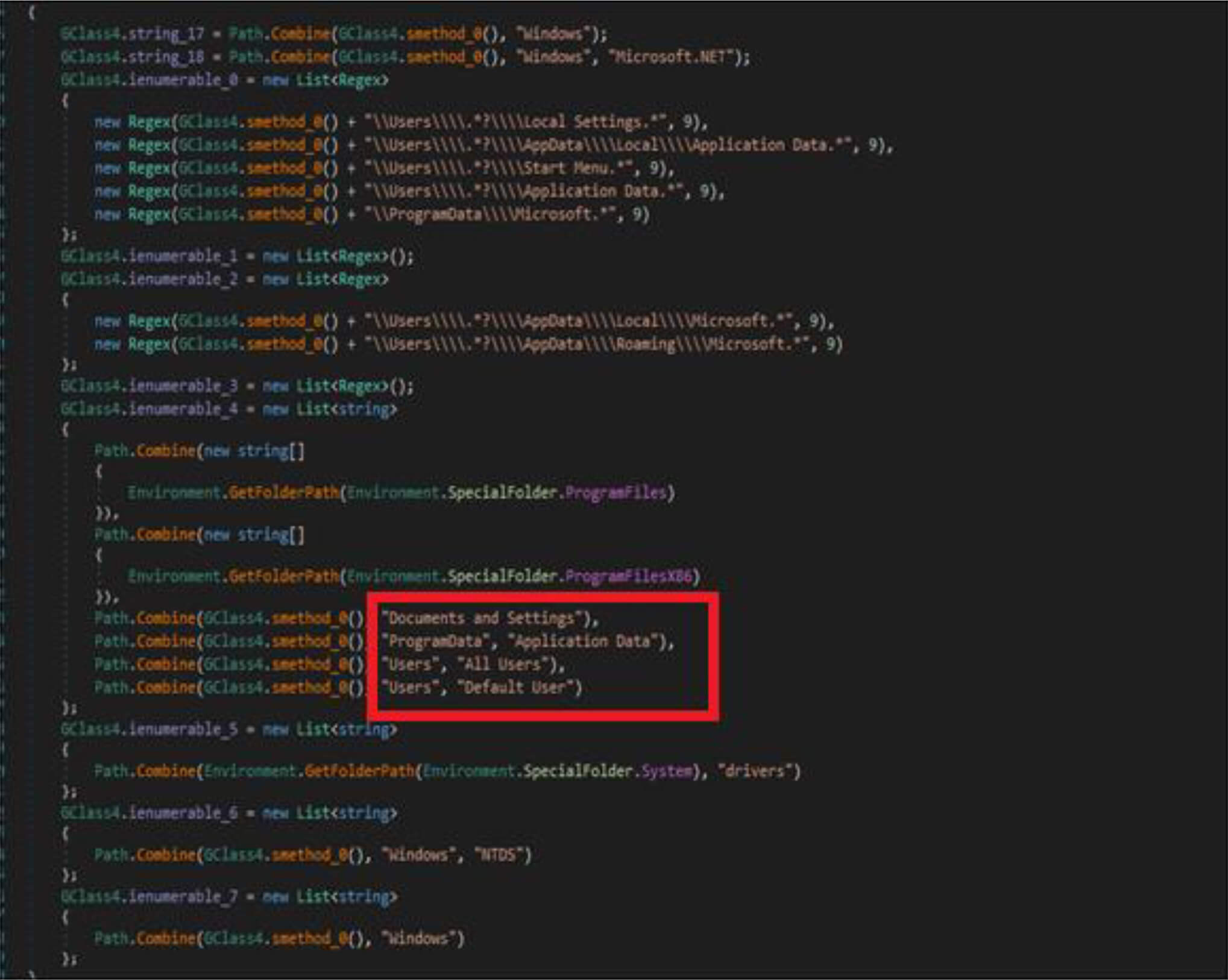
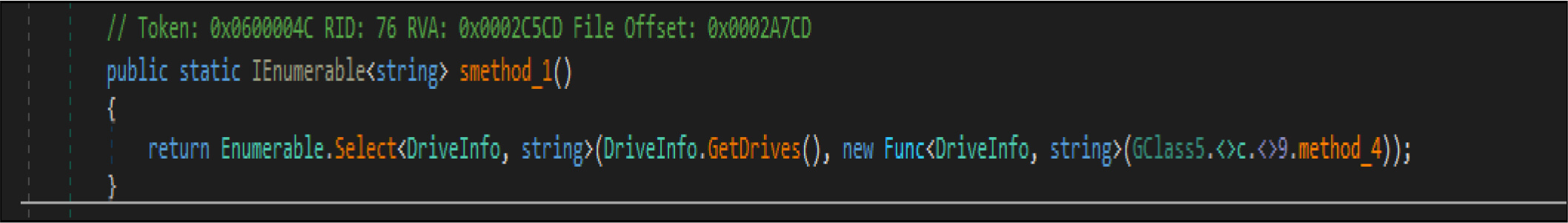
Apart From the above-listed directory, this wiper malware gets all the available (mounted) drivers to the compromised host by the below code snippets.
Doublezero wiper malware adjusts the privileges on the compromised system by RtlAdjustPrivilege API.
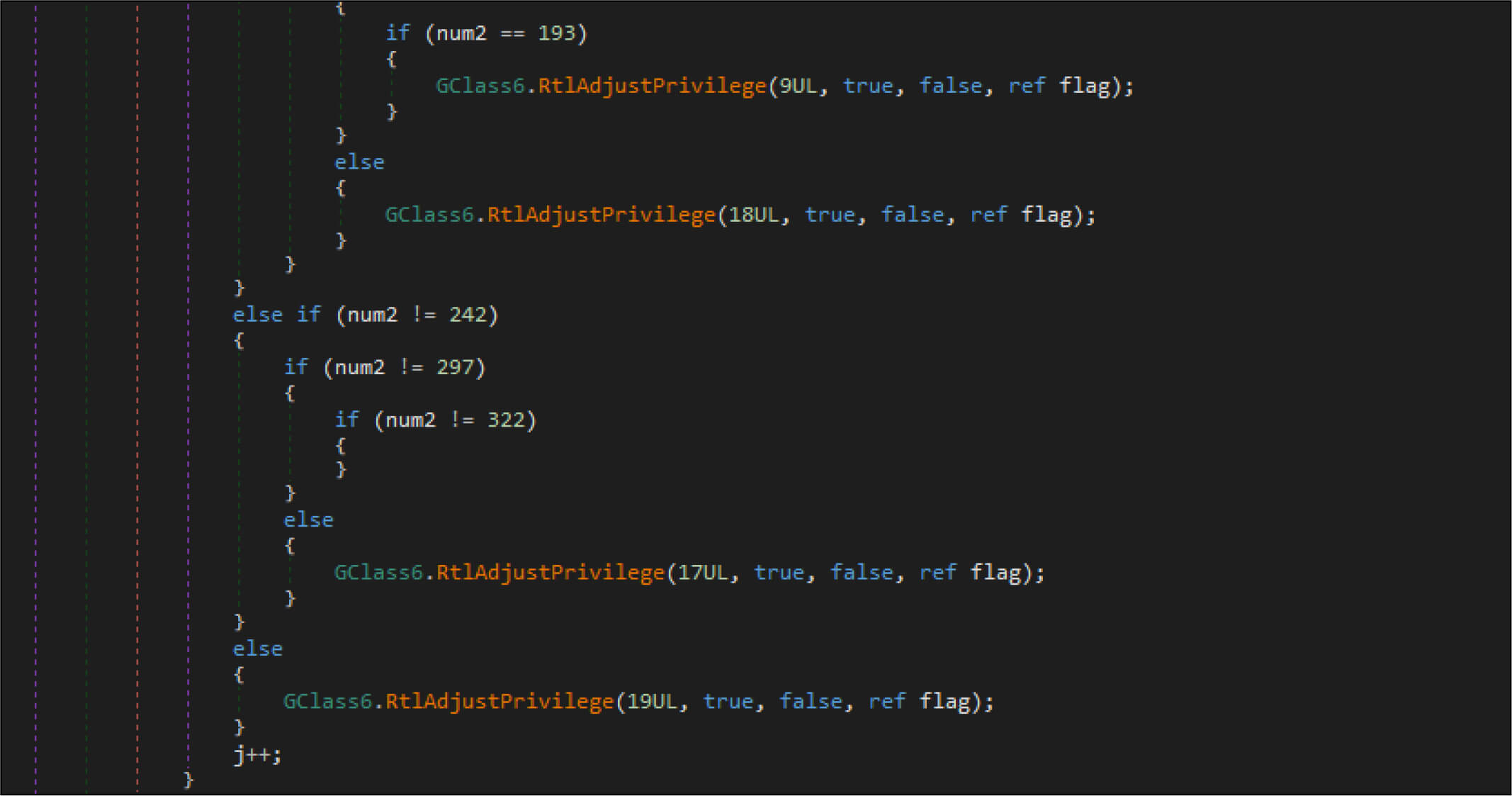
| SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege | 9UL |
| SeRestorePrivilege | 18UL |
| SeBackupPrivilege | 17UL |
| SeShutdownPrivilege | 19UL |
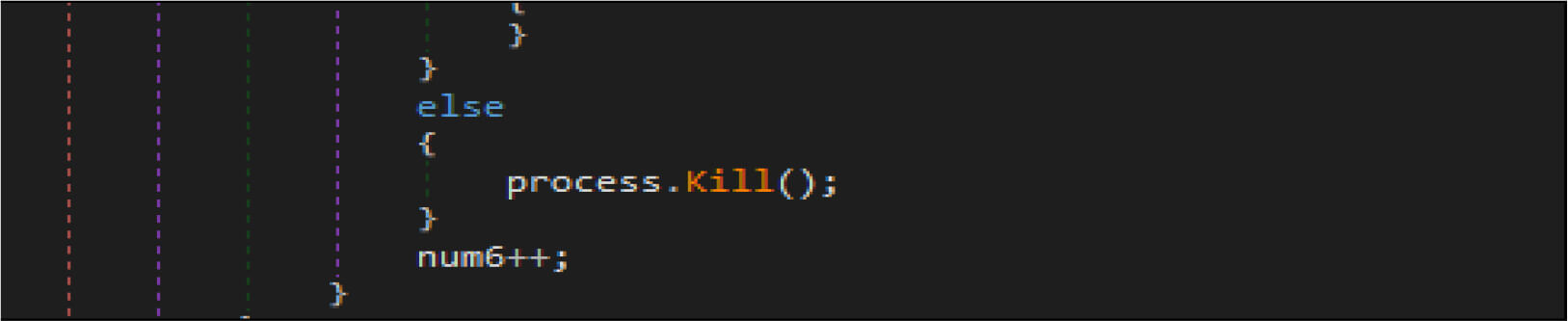
This wiper malware enumerated the running process and look the process name with the name “lsass “, then terminate that process(“lsass”).
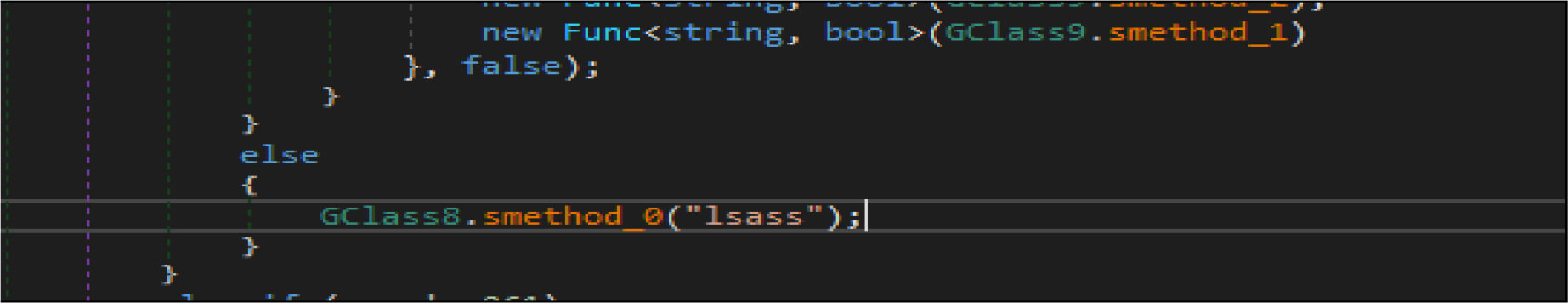
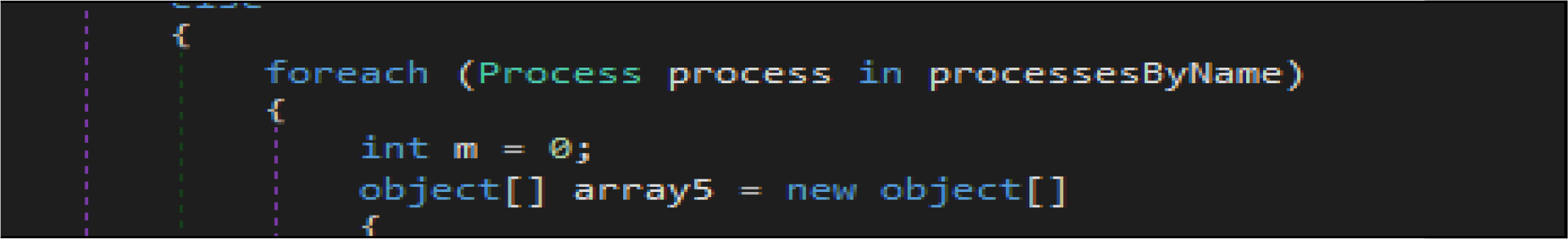
This wiper malware changes the current logon user as an owner of this registry hives then modifies access control to full access control to delete the following entries from the registry.

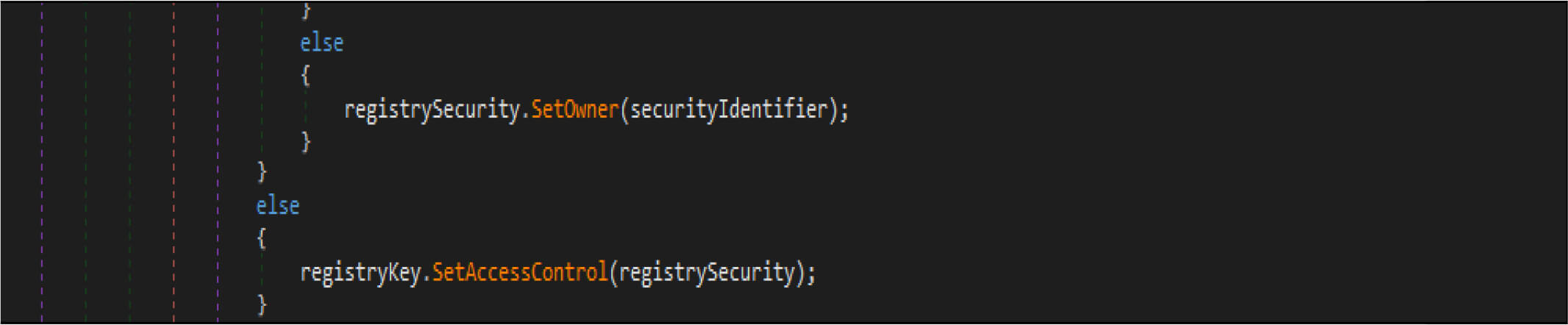

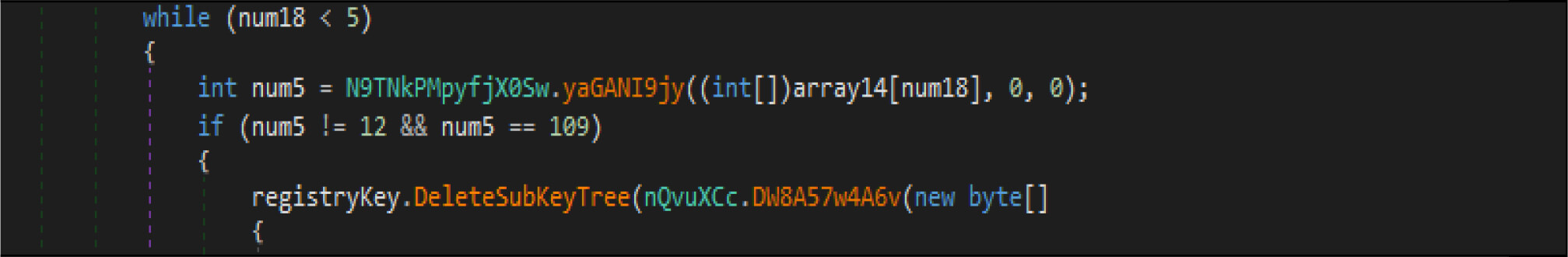
This malware also adjusts the security identifier of its process to obtain full control of file system rights to avoid being denied while overwriting the files.
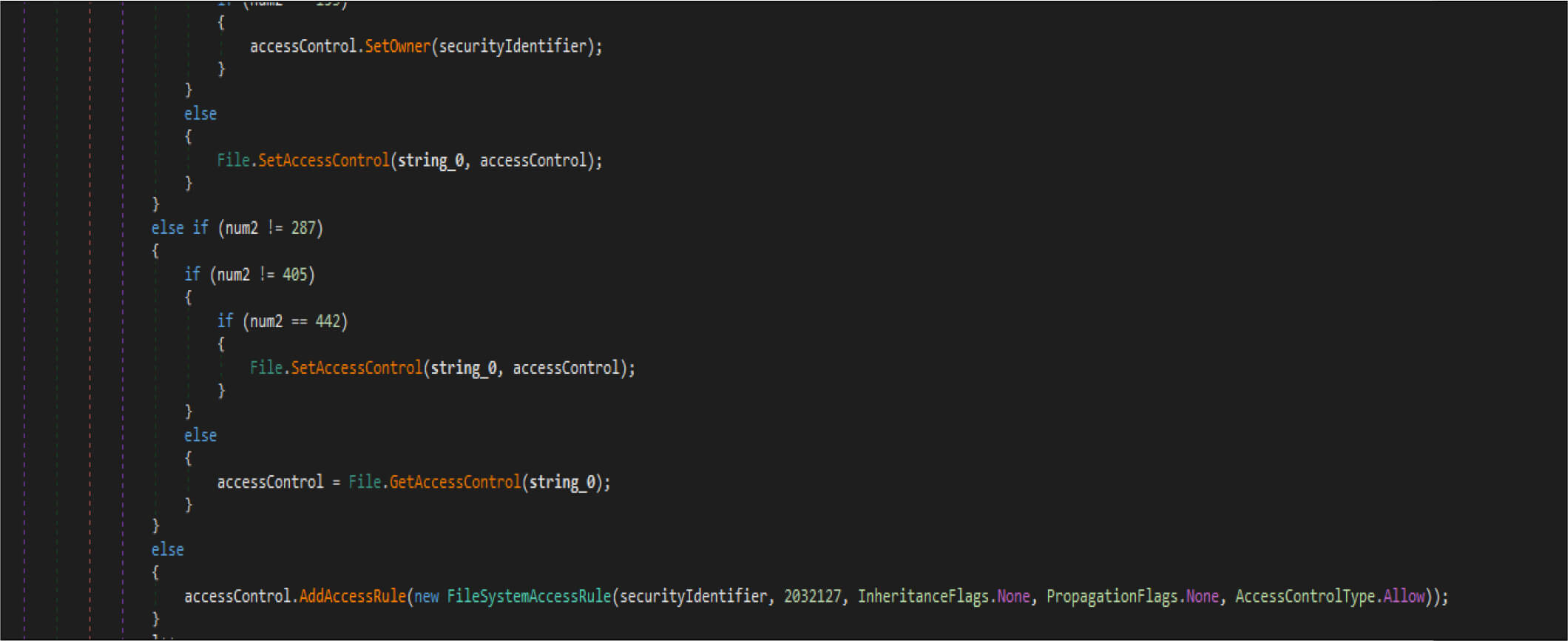
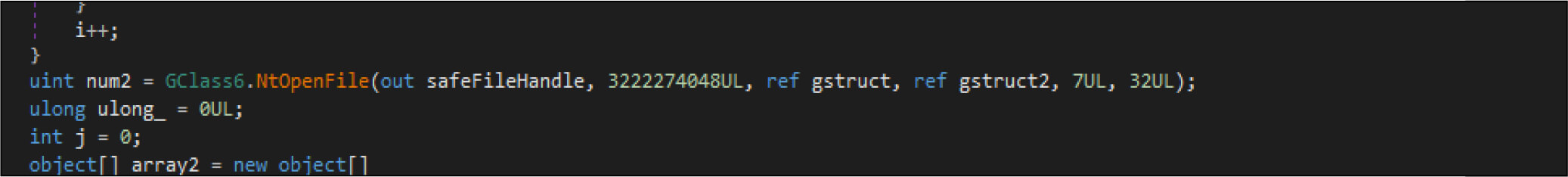
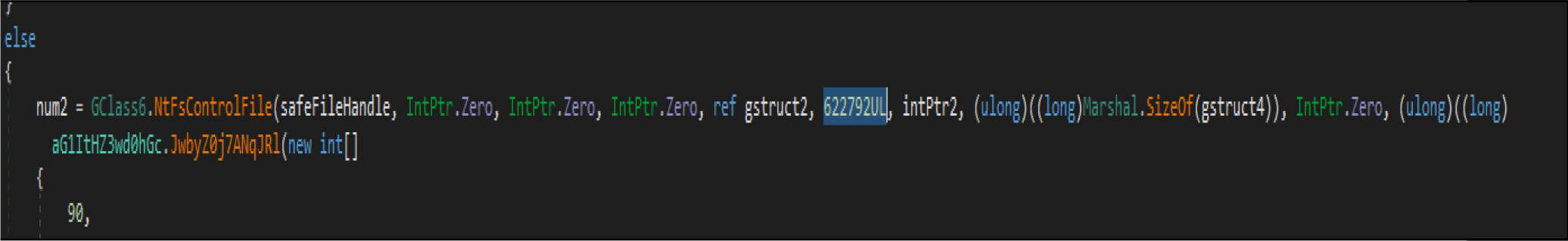
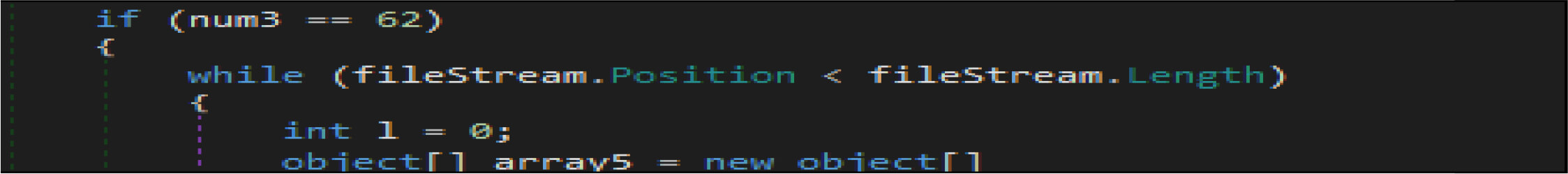
Then it opens the target files by native API NtOpenFile, after that it is calling native API NtFsControlFile with a control code of FSCTL_SET_ZERO_DATA , which overwrites files with zero bytes. This malware has two wiping routines. This is one the routine
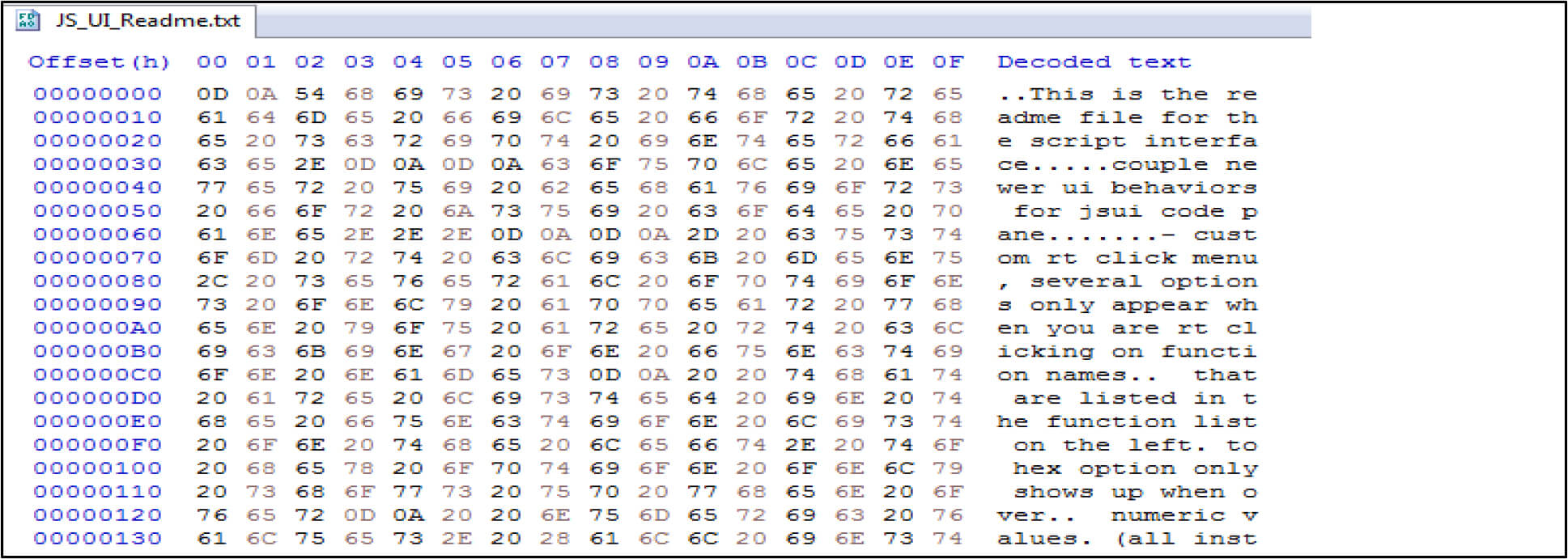
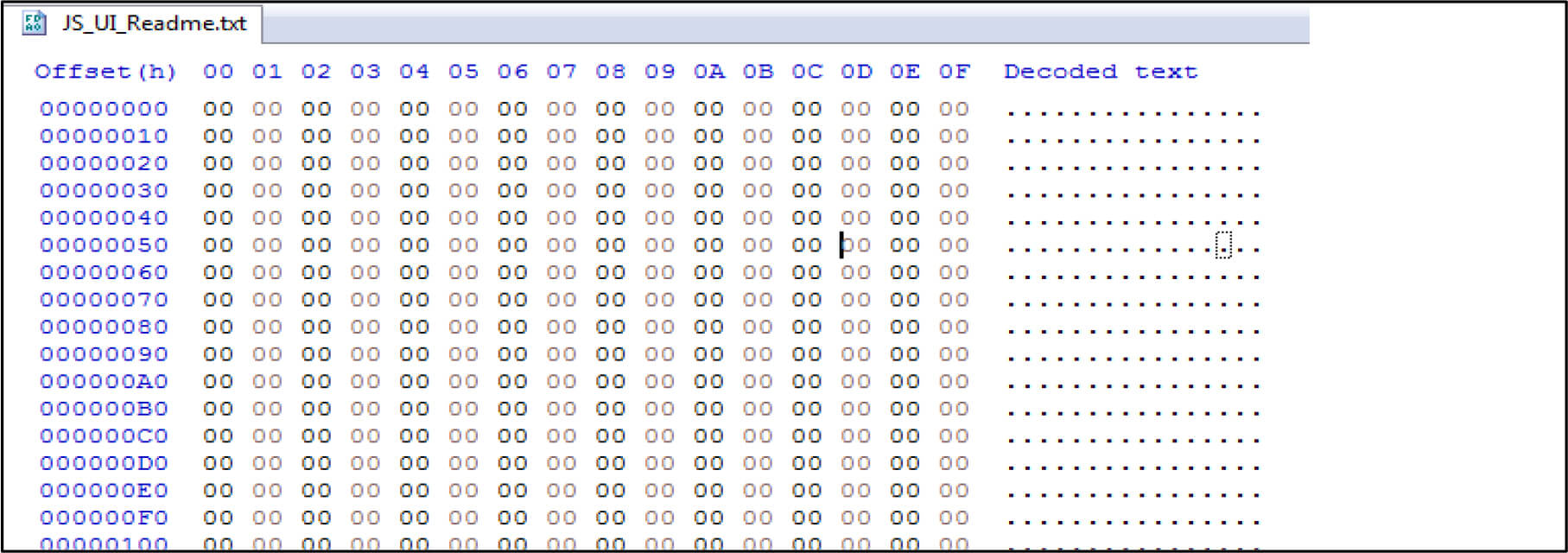
For example, the below screenshot showing after executing the file contents zero out by this malware.
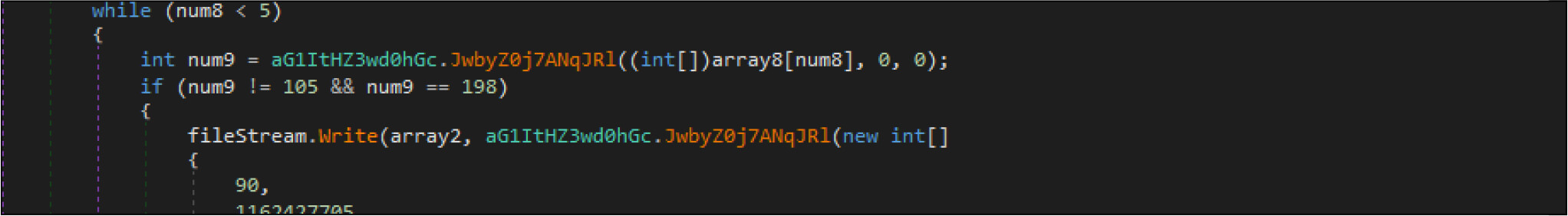
The second routine, the wiper malware use file. FileStream.Write () a method to fill up the file with all zero bytes.

This malware will shut down the system by ExitWindowsEx API call, once the destructive activity is completed.

While geopolitical issues between Russian and Ukrainian, the unknown cyber threat actors targeted Ukrainian enterprises by Doublezero wiper malware, which is 4th data wiper malware attack has been seen over the past two months against Ukrainian such as “CaddyWiper” ,”HermeticWiper” and “WhisperGate. Threat actors spread this malware by spear-phishing attacks(zip files name was” Virus … extremely dangerous !!!. Zip). This malware has the capability to wipe out system and non-system files and reboot the infected system. This data wiper malware modifies the full access rights to delete registry hives (HKCU, HKU, HKLM) and wipe out files.
| Sr No. | Indicator | Type | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | B4F0CA61AB0C55A542F32BD4E66A7DC2 | MD5 Hash | Sample File |
| 2 | 30B3CBE8817ED75D8221059E4BE35D5624BD6B5DC921D4991A7ADC4C3EB5DE4A | SHA256 Hash | Sample File |
| Sr No. | Tactic | Technique |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Initial Access (TA0001) | T1566.001:Spearphishing Attachment |
| 2 | Execution (TA0002) | T1204.002: Malicious File |
| 3 | Privilege Escalation (TA0004) | T1543:Create or Modify System Process |
| 4 | Defense Evasion (TA0005) | T1562.001: Disable or Modify Tools T1222:File and Directory Permissions Modification T1112: Modify Registry T1027: Obfuscated Files or Information |
| 5 | Discovery (TA0007) | T1083: File and Directory Discovery T1057: Process Discovery |
| 6 | Impact (TA0040) | T1561.001:Disk Content Wipe T1529: System Shutdown/Reboot |