



The CYFIRMA research team has discovered a previously unknown financially motivated Threat Actor group, which we had named ‘DEV-0970/Storm-0970’, based on old and new threat actor taxonomy. This group utilizes a ransomware builder, acquired from a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) operator(s), empowering the group to create and deploy multiple ransomware variants and expanding their arsenal of malicious tools. Through vigilant monitoring, valuable insights into their evolving strategies and potential impact on cybersecurity have been gained, the most noteworthy of which is the connection uncovered between Poop69 and BIGHEAD ransomware, both attributed to DEV-0970/Storm-0970. These findings shed light on the group’s methods and emphasize the imperative need for proactive cybersecurity measures to mitigate their threats. The report serves as a call to action for stakeholders to bolster their defenses against the evolving tactics employed by DEV-0970/Storm-0970.
In May 2023, the CYFIRMA research team observed Poop69 ransomware appearing in the wild, and shortly after that, another ransomware named BIG HEAD emerged, thought to originate from the same threat actor, which has become popular recently due to its fake Windows update method. Big head ransomware exempts devices using Russian, Belarusian, Ukrainian, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Armenian, Georgian, Tatar, and Uzbek languages from encryption, hence there is a possibility that the threat actors originate from the CIS.
An interesting correlation between the entities’ contact information emerged, which prompted the deep dive and analysis. This report focuses on the activities of a threat actor, who has been developing and deploying multiple variants of ransomware, demonstrating their ability to create and use different types of ransomware for specific targeted attacks. The following sections will provide a detailed examination of the discoveries, analysis, and suggested approaches to address the risks associated with DEV-0970/Storm-0970.
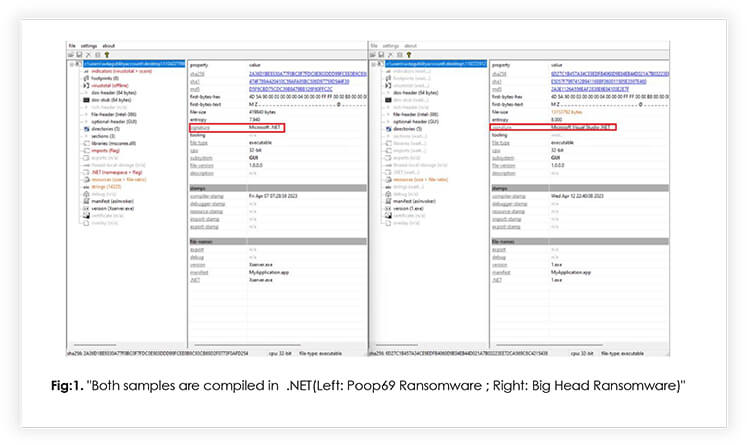
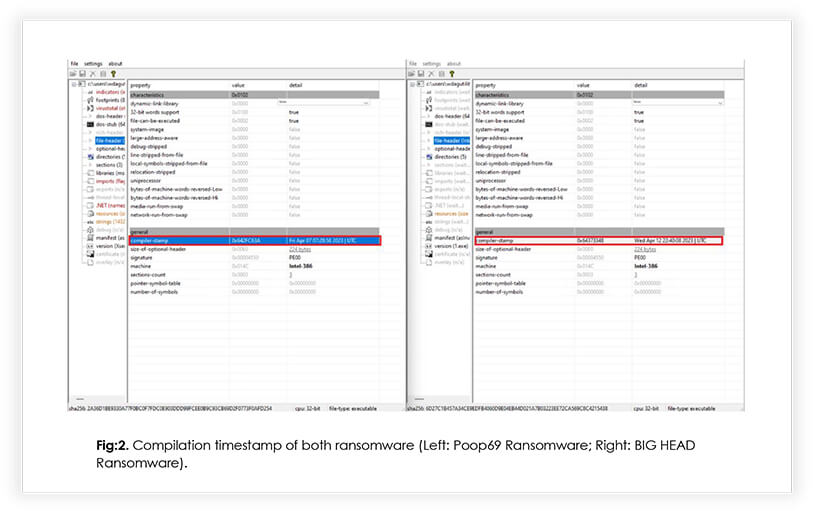
The compilation timestamp in ransomware refers to the date and time, when the ransomware’s code was compiled or built. It represents the moment when the ransomware executable or binary file was created by the attacker.
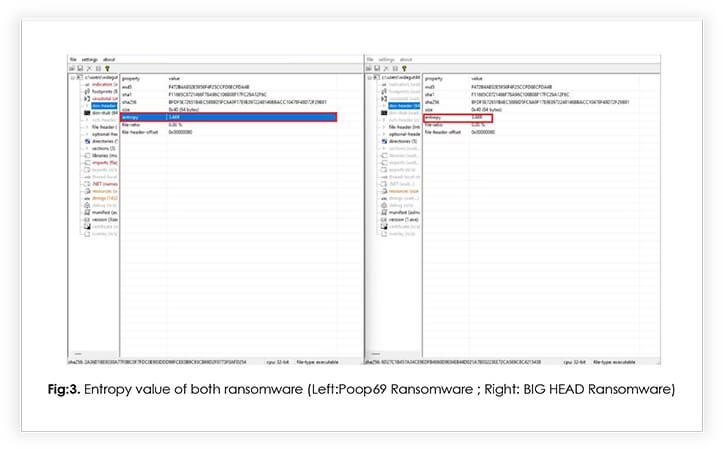
The entropy value in ransomware refers to a measure of the randomness or complexity of the data within the ransomware’s code or encrypted files. Entropy is commonly used as an indicator to analyze the level of encryption or obfuscation techniques used by ransomware.
The entropy value suggests that both samples are lightly packed, and the non-readability of most strings suggests that the sample is lightly obfuscated.
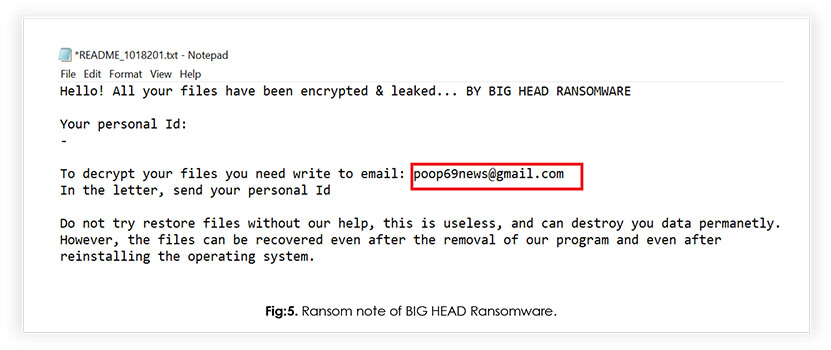
Both ransomware strains share identical contact information for the cybercriminals behind them.
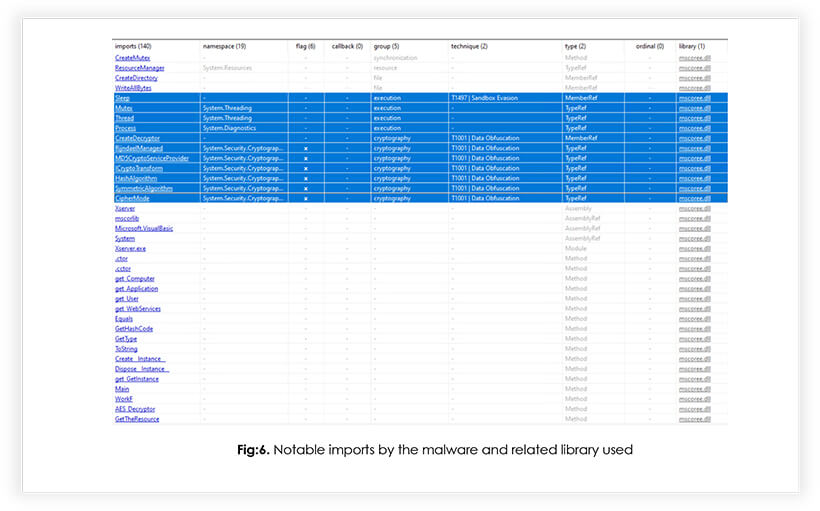
1. Below are the libraries being used by Poop69 Ransomware.
| Sr No | library name | clean/malicious |
| 1 | AES_Decryptor | malicious |
| 2 | GetTheResource | malicious |
2. Libraries used by BIG HEAD Ransomware
| Sr No | library name | clean/malicious |
| 1 | AES_Decryptor | malicious |
| 2 | GetTheResource | malicious |
Upon analyzing both ransomware strains, it appears they utilize identical malicious libraries.
1. AES_Decryptor: This malicious library is likely used by ransomware to decrypt files that have been encrypted using the AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) algorithm. Ransomware typically encrypts victims’ files, making them inaccessible, until a decryption key is obtained, often through payment of a ransom. The AES_Decryptor assists in decryption, enabling the attacker to restore the victims’ files, after receiving the ransom.
2. GetTheResource: This malicious library may be employed by ransomware to retrieve critical resources or information from the compromised system. It could be responsible for collecting system information, network details, login credentials, or other data that could aid the attackers in their extortion tactics or further compromise the victim’s system. This information may be used for future attacks or sold on the dark web for profit.
3. Analysis of Strings of another ransomware used by the DEV-0970/Storm- 0970
| Sr No | library name | clean/malicious |
| 1 | AES_Decryptor | malicious |
| 2 | GetTheResource | malicious |
The other ransomware is also written in .NET, and it’s one of the ransomware variants that have been created using Chaos Builder.
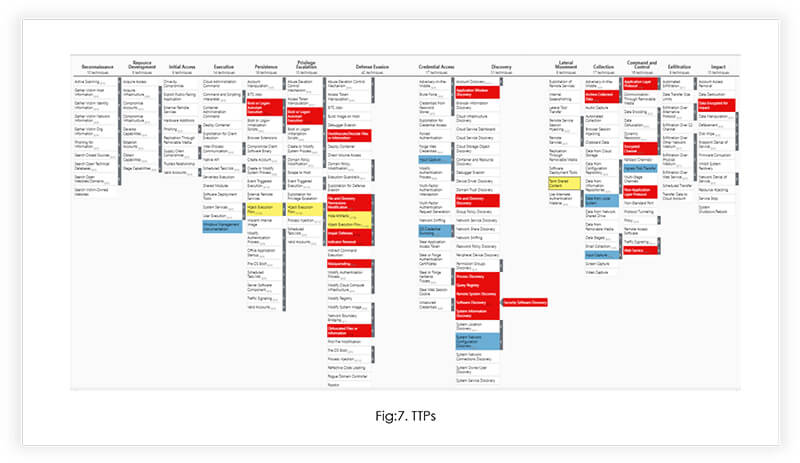
In the above figure, we have marked TTP for both Ransomware Variants in different colors where:

The shared TTPs between the two ransomware strains strongly suggest a common threat actor, who likely utilized a builder from Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) operator(s).
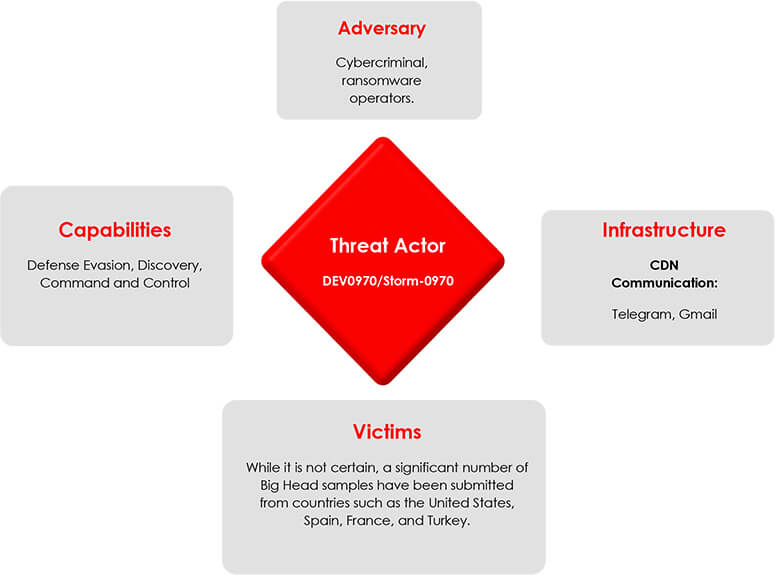
Threat actor Profile: DEV-0970/Storm-0970 is a financially motivated group, specializing in ransomware attacks. They employ multiple variants like BIG HEAD and Poop69.
Threat Landscape: The Ransomware variants target Windows Operating systems, which are widely used by many organizations. There is a possibility of encountering password-stealing trojans and other malware infections along with the ransomware, further complicating the situation.
Victimology: As there are no publicly reported victims, they may have either paid the ransom or the attackers are attempting to sell the stolen data or exploit it for malicious purposes.
Impact: The files have been encrypted, rendering them inaccessible until a ransom is paid. Their activities pose a significant threat to organizations, potentially causing financial losses, data breaches, and operational disruptions.
The rise of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) operators has facilitated the execution of complex ransomware operations by less experienced threat actors. These operators offer easy access to tools and resources, enabling individuals with limited expertise to engage in ransomware attacks. One significant advantage of RaaS is the ability to generate numerous ransomware variants, using a single builder. This approach helps perpetrators evade traditional signature-based detection methods, as each variant possesses unique characteristics. In the case of DEV-0970/Storm-0970, the absence of discussions regarding RaaS affiliate programs on underground forums suggests their reliance on a ransomware builder from MaaS operator(s) to create multiple variants. To effectively defend against such attacks, organization(s) must prioritize the proactive integration of contextual threat intelligence and heuristic-based detections. By staying one step ahead of adversaries, organizations can enhance their ability to detect and mitigate ransomware threats successfully.
Indicators of Compromise
| SHA-256 | Ransomware |
| 2a36d1be9330a77f0bc0f7fdc0e903ddd99fcee0b9c93cb69d2f0773f0afd254 | Poop69 |
| 226bec8acd653ea9f4b7ea4eaa75703696863841853f488b0b7d892a6be3832a | BIG HEAD |
| ff900b9224fde97889d37b81855a976cddf64be50af280e04ce53c587d978840 | BIG HEAD |
| cf9410565f8a06af92d65e118bd2dbaeb146d7e51de2c35ba84b47cfa8e4f53b | BIG HEAD |
| 1c8bc3890f3f202e459fb87acec4602955697eef3b08c93c15ebb0facb019845 | BIG HEAD |
| 64246b9455d76a094376b04a2584d16771cd6164db72287492078719a0c749ab | BIG HEAD |
| 0dbfd3479cfaf0856eb8a75f0ad4fccb5fd6bd17164bcfa6a5a386ed7378958d | BIG HEAD |
| 6698f8ffb7ba04c2496634ff69b0a3de9537716cfc8f76d1cfea419dbd880c94 | BIG HEAD |
| b8e456861a5fb452bcf08d7b37277972a4a06b0a928d57c5ec30afa101d77ead | BIG HEAD |
| 6b3bf710cf4a0806b2c5eaa26d2d91ca57575248ff0298f6dee7180456f37d2e | BIG HEAD |
| 6b771983142c7fa72ce209df8423460189c14ec635d6235bf60386317357428a | BIG HEAD |
| 627b920845683bd7303d33946ff52fb2ea595208452285457aa5ccd9c01c3b0a | BIG HEAD |
| 40d11a20bd5ca039a15a0de0b1cb83814fa9b1d102585db114bba4c5895a8a44 | BIG HEAD |
| 159fbb0d04c1a77d434ce3810d1e2c659fda0a5703c9d06f89ee8dc556783614 | BIG HEAD |
| 9aa38796e0ce4866cff8763b026272eb568fa79d8a147f7d61824752ad6d8f09 | BIG HEAD |
| 39caec2f2e9fda6e6a7ce8f22e29e1c77c8f1b4bde80c91f6f78cc819f031756 | BIG HEAD |
| 1ada91cb860cd3318adbb4b6fd097d31ad39c2718b16c136c16407762251c5db | BIG HEAD |
| be6416218e2b1a879e33e0517bcacaefccab6ad2f511de07eebd88821027f92d | BIG HEAD |
| 9a7889147fa53311ba7ec8166c785f7a935c35eba4a877c1313a8d2e80e3230d | BIG HEAD |
| f6a2ec226c84762458d53f5536f0a19e34b2a9b03d574ae78e89098af20bcaa3 | BIG HEAD |
| f354148b5f0eab5af22e8152438468ae8976db84c65415d3f4a469b35e31710f | BIG HEAD |
| 037f9434e83919506544aa04fecd7f56446a7cc65ee03ac0a11570cf4f607853 | BIG HEAD |
| 980bac6c9afe8efc9c6fe459a5f77213b0d8524eb00de82437288eb96138b9a2 | BIG HEAD |
| 603fcc53fd7848cd300dad85bef9a6b80acaa7984aa9cb9217cdd012ff1ce5f0 | BIG HEAD |
| bcf8464d042171d7ecaada848b5403b6a810a91f7fd8f298b611e94fa7250463 | BIG HEAD |
| 64aac04ffb290a23ab9f537b1143a4556e6893d9ff7685a11c2c0931d978a931 | BIG HEAD |
| f59c45b71eb62326d74e83a87f821603bf277465863bfc9c1dcb38a97b0b359d | BIG HEAD |
| 66bb57338bec9110839dc9a83f85b05362ab53686ff7b864d302a217cafb7531 | BIG HEAD |
| 806f64fda529d92c16fac02e9ddaf468a8cc6cbc710dc0f3be55aec01ed65235 | BIG HEAD |
| 9c1c527a826d16419009a1b7797ed20990b9a04344da9c32deea00378a6eeee2 | BIG HEAD |
| 40e5050b894cb70c93260645bf9804f50580050eb131e24f30cb91eec9ad1a6e | BIG HEAD |
| 25294727f7fa59c49ef0181c2c8929474ae38a47b350f7417513f1bacf8939ff | BIG HEAD |
| dcfa0fca8c1dd710b4f40784d286c39e5d07b87700bdc87a48659c0426ec6cb6 | BIG HEAD |
| 6d27c1b457a34ce9edfb4060d9e04eb44d021a7b03223ee72ca569c8c4215438 | BIG HEAD |
| 1942aac761bc2e21cf303e987ef2a7740a33c388af28ba57787f10b1804ea38e | Another ransomware used by DEV-0970/Storm-0970 |
(Source: Surface Web)