


This CYFIRMA Monthly Ransomware report thoroughly analyses ransomware activity in March 2024, covering significant attacks, the top five ransomware families, geographical distribution, targeted industries, evolution of attacks, and trends. Organizations can leverage these insights to enhance their cybersecurity strategies and mitigate ransomware risks.
Welcome to the March 2024 Ransomware Report. This report provides a comprehensive analysis of ransomware events during this period. We highlight activities of the top 5 most active ransomware groups and the industries they targeted, along with the geographies that faced the highest number of attacks. Additionally, we examine the evolution of ransomware groups and the vulnerabilities they exploit. We aim to furnish organizations with essential insights to enhance their cybersecurity measures and effectively combat the ever-evolving threat landscape.
In March 2024, several ransomware groups were actively operating. Below, we outline trends regarding the top 5 ransomware groups.
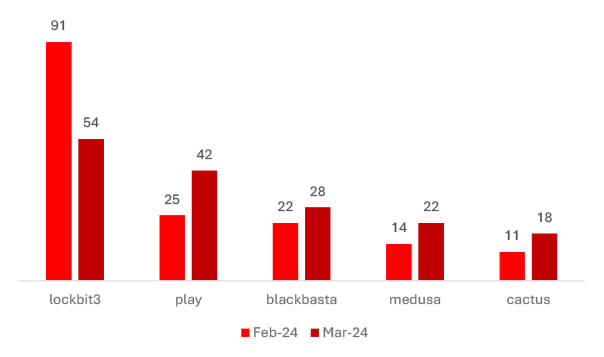
Comparing February to March 2024, LockBit3 infections decreased by 40.66%, while Play ransomware cases surged by 68%. BlackBasta experienced a slight uptick of 27.27%, Medusa infections saw a notable 57.14% increase, and Cactus ransomware incidents rose by 63.64%. These shifts imply that the rise in counts may stem from unsuccessful ransom negotiations.
But in the case of LockBit, it seems that affiliates are shifting to other RaaS, possibly in response to increased law enforcement scrutiny.
LockBit:
Despite leading the victim’s chart LockBit failed to increase the victim’s number when compared to last month.
Manufacturing emerged as the primary target, with the United States being LockBit’s focal nation.
Notably, the impacted companies had revenues ranging from $5 million to $1.8 billion, hence the group affected a wide range of businesses, not just specific financial tiers.
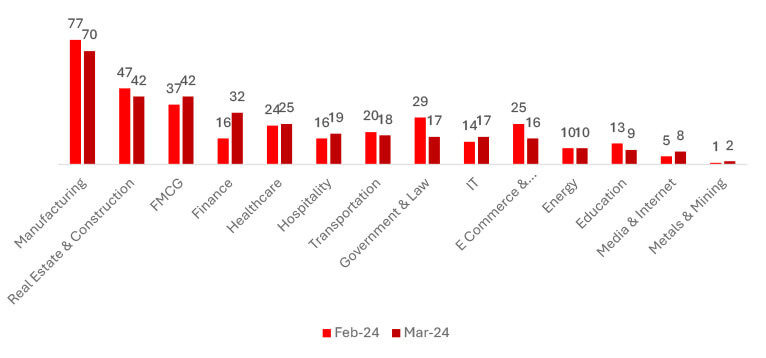
Comparing February to March 2024, notable trends emerged across various sectors. Manufacturing experienced a slight decline of 9.09%, while Real Estate & Construction also decreased by 10.64%. FMCG witnessed a modest increase of 13.51%, and Finance saw a substantial surge of 100%. Healthcare observed a marginal increase of 4.17%, whereas Hospitality experienced a 15.63% uptick. Government & Law encountered a significant decrease of 41.38%, while IT witnessed slight growth. Transportation faced a 10% decrease, and Energy remained stable. Education observed a decline of 30.77%. This trend suggests that ransomware poses a threat to every sector.
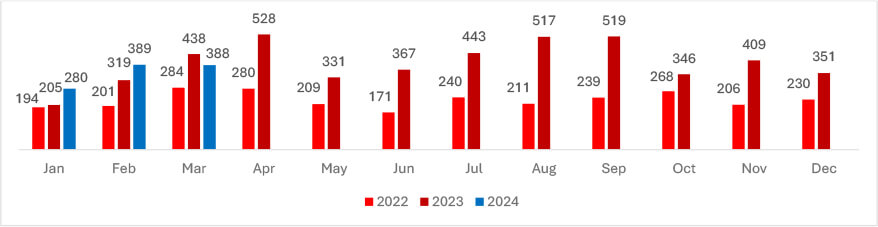
Despite many law enforcement events and takedowns, Ransomware still made a significant impact on Businesses globally. In March, the number of victims remained almost the same compared to February, highlighting a consistency in incidents within that period.
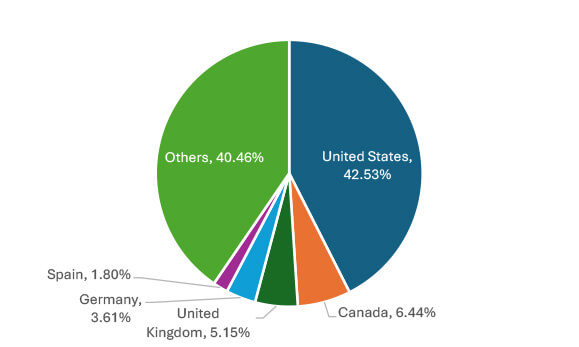
The top 5 nations with the highest number of victims are the United States (165), Canada (25), the United Kingdom (20), Germany (14), and Spain (7). These countries are likely targeted due to their economic significance, advanced technological infrastructure, and high internet connectivity, offering lucrative targets for cybercriminals.
| Sr No | CVE ID | CVSS Score | Name | Affected Product | Associated Ransomware |
| 1 | CVE-2024-27198 | 9.8 | JetBrains TeamCity Authentication Bypass Vulnerability | JetBrains TeamCity CI/CD server products up to 2023.11.4 | BianLian and Jasmin ransomware |
RA Group To RA World
The RA World ransomware group, previously known as RA Group, has rapidly evolved its tactics since emerging in April 2023, expanding its attacks globally across various industries. Initially leveraging Babuk ransomware’s source code, it has customized its approach, employing sophisticated multistage attacks, including GPO manipulation and double extortion tactics, while evading detection.
StopCrypt; the extensively distributed ransomware, undergoes evolution to bypass detection measures.
A new variant of StopCrypt ransomware has emerged, utilizing a multi-stage execution process to evade security measures. Initially targeting consumers through malvertising and adware bundles, it employs process hollowing and scheduled tasks for persistence. Despite low ransom demands, its widespread impact underscores a concerning trend in cybercrime.
GhostLocker Evolved
GhostLocker 2.0, a more advanced version of the GhostLocker ransomware by GhostSec, encrypts files with “.ghost” extension and features a modified ransom note. It connects to a C2 panel for tracking and offers customization options. Written in GoLang, it enhances encryption key length and selectively targets files for encryption. Ransomware demonstrates refined evasion tactics, emphasizing the persistent threat of ransomware attacks.
Qilin Getting More Dangerous.
Researchers have identified the latest evolution of the Qilin/Agenda ransomware, signifying a notable advancement with its Rust-based variant aimed at VMware vCenter and ESXi servers. This version showcases heightened sophistication, incorporating new functionalities and stealth mechanisms. Infection initiates through the delivery of the ransomware binary via Cobalt Strike or RMM tools, utilizing a PowerShell script for propagation. Subsequently, it alters the root password on all ESXi hosts, uploads malicious payloads via SSH, and introduces new commands for privilege escalation and the disabling of virtual machine clusters. Notably, attackers now have the capability to print ransom notes for psychological impact. Employing a shell for command execution, Agenda leaves minimal traces. To circumvent detection, it employs a BYOVD tactic, exploiting vulnerable SYS drivers.
Donex ransomware
Donex ransomware was discovered in the beginning of March 2024. This ransomware encrypts data, adds a unique victim ID extension to filenames, and leaves a ransom note named “Readme.[victim’s_ID].txt” demanding payment for decryption.

Kill Security
A recently emerged ransomware group, dubbed Kill Security, has listed six new victims on its leak site during the drafting of this report. Limited information is currently available about this ransomware group. Stay tuned for updates from CYFIRMA.
Qilin Strikes UK
The Big Issue; a newspaper in the United Kingdom renowned for empowering the homeless by employing them as vendors, faces a cyber incident after being targeted by the Qilin ransomware gang. The group claims to have stolen 550 gigabytes of confidential data.
NHS Scotland Hit by INC Ransomware
An incident has occurred where the INC Ransom extortion gang stole three terabytes of alleged data by breaching the National Health Service (NHS) of Scotland. The cybercriminals posted medical details and demanded a ransom, posing a serious threat to Scotland’s public health system, which encompasses primary care, hospital care, dental care, pharmaceuticals, and long-term care services.
Rhysida Continues to Target Health Care
The Rhysida ransomware targeted Lurie Children’s Hospital in Chicago, a prominent pediatric care institution serving over 200,000 children annually. The cyberattack disrupted medical services, forcing the hospital to take IT systems offline, impacting communication and patient care. Rhysida claims to have stolen 600 GB of data from the hospital.
Nissan confirms Ransomware Attack
Nissan Oceania disclosed a data breach affecting 100,000 individuals, following a cyberattack in December 2023 attributed to the Akira ransomware group. The attack targeted Nissan’s regional division handling operations in Australia and New Zealand, impacting areas such as distribution, marketing, sales, and services.
Based on available public reports, approximately 31% of enterprises are compelled to halt their operations, either temporarily or permanently, in the aftermath of a ransomware onslaught. The ripple effects extend beyond operational disruptions, as detailed by additional metrics:
Impact Assessment
Ransomware poses a significant threat, creating hurdles for both organizations and individuals by stealing vital data and demanding payment for its return. The consequences of these attacks often result in substantial financial damages, whether through ransom payments or investments in cybersecurity measures for recovery. Additionally, financial losses extend to disrupted operations, diminished customer confidence, and the emotional toll on affected parties. Furthermore, such incidents can lead to breaches of data regulations, affecting reputation, consumer trust, and market stability. As a result, tackling ransomware becomes a critical imperative for businesses and government bodies to safeguard financial security and public confidence.
Victimology
Presently, threat actors concentrate on targeting businesses harboring valuable data, encompassing personal details, financial information, and intellectual property. Industries like Manufacturing, Real Estate, Healthcare, FMCG, E-commerce, Finance, and Technology face heightened susceptibility due to their wealth of data. Cybercriminals strategically select countries with robust economies and advanced digital infrastructures to optimize ransom returns. Their objective is clear: identify vulnerabilities, encrypt data, and demand substantial ransoms for release, all aimed at securing significant profits.
The ransomware landscape in March 2024 showcased dynamic shifts in the activities of prominent ransomware groups and their evolving tactics. While some groups experienced fluctuations in their victim counts, others demonstrated resilience and adaptability, continuing their operations despite law enforcement interventions. Manufacturing, Real Estate & Construction emerged as primary targets, reflecting the diverse interests of ransomware actors. Notably, the emergence of new ransomware variants and groups, such as Donex ransomware, underscores the persistent threat posed by ransomware attacks. The exploitation of vulnerabilities like CVE-2024-27198 in JetBrains TeamCity highlights the importance of timely patching and robust cybersecurity measures. As ransomware threats continue to evolve and expand globally, organizations must remain vigilant and prioritize proactive defense strategies to mitigate risks and safeguard their digital assets.