In September 2025, the global cyber threat environment remained guarded yet volatile, marked by a steady cadence of state-sponsored espionage, ransomware evolution, and geopolitical cyber manoeuvring. China and Russia intensified espionage and hybrid operations across Europe and Asia, while Iran and North Korea sustained financially and politically motivated campaigns targeting defense, finance, and infrastructure sectors. Manufacturing emerged as the month’s most targeted industry, with ransomware groups like Play and Akira driving disruptive attacks and exploiting third-party dependencies. Dark Web chatter shifted toward AI-enhanced phishing, Initial Access Broker collaboration, and pre-positioning for Q4 campaigns, highlighting the convergence of criminal and state ecosystems. Simultaneously, vulnerability exploitation accelerated, with active abuse of Fortinet and Apache flaws and weaponization timelines shrinking to mere days. Amid rising AI weaponization, supply-chain infiltration, and geopolitical tensions, organizations face a complex and adaptive threat landscape demanding sustained vigilance, rapid patching discipline, and intelligence-led defense strategies.
The Global threat level remains at GUARDED. While activity across APT, ransomware, and hacktivist fronts persists, no strategically significant escalation warrants an increase. Cross-domain coordination between state and criminal ecosystems is rising, suggesting elevated vigilance heading into Q4.

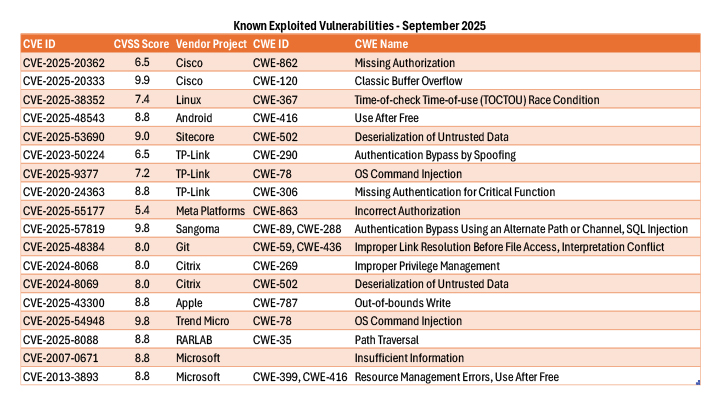
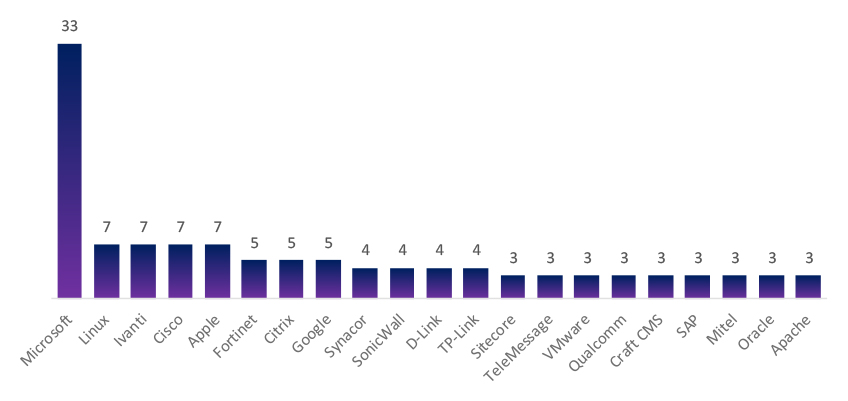
Unlike earlier months dominated by Microsoft, September’s KEVs span Cisco, Linux, Sitecore, TP-Link, Meta, Git, Citrix, and Trend Micro. This diversification signals a broadening threat surface targeting network appliances, web platforms, and developer tools.
Remains elevated. Qilin and Play exploit RMM/VPN flaws; Fog leverages Google GC2 for persistence; SafePay and Anubis pivot to data-first extortion and destructive payloads.
The Israel–Iran conflict fuels DDoS and data leaks, but has a limited infrastructure impact. Europe’s digital sovereignty shift introduces temporary exposure, while Russia’s hybrid warfare continues to shape global cyber posture.
Increased IAB collaboration and AI-powered phishing discussions. Surge in Southeast Asia network access sales and ransomware affiliate recruitment.
Global cyber activity remains volatile but stable. Ransomware, AI weaponization, and state-aligned espionage sustain a GUARDED posture, with heightened monitoring recommended through year-end.
Adversaries aggressively target manufacturing because the consequences extend beyond data loss to physical disruption and economic devastation. Motivations center on crippling critical production and stealing proprietary advantage.
We observed evidence of Chinese state-sponsored activity focusing on the sector in Asia. A new variant of the PlugX backdoor, attributed with medium confidence to the Naikon cyber espionage group, was identified targeting the manufacturing and telecommunications sectors in Central and South Asian countries. This activity seeks to compromise systems for intellectual property theft.
September was defined by high-impact operational incidents across the automotive and industrial base:
The manufacturing industry remains the hardest hit business sector for ransomware. September saw 66 confirmed incidents globally, reflecting an elevated threat level.
Third-Party and Supply Chain Risk: Attacks continue to exploit weaknesses in the software supply chain. The Salesforce/Salesloft/Drift compromise (attributed to ShinyHunters/UNC6395) impacted multiple organizations, including Stellantis, demonstrating how external SaaS vendors are exploited to reach major manufacturers. Additionally, the ransomware attack that crippled Collins Aerospace’s check-in system caused major delays at European airports, highlighting risks to the broader industrial supply base.
ERP/Zero-Day Extortion: Threat actors affiliated with CL0P initiated a large-scale extortion campaign targeting executives regarding alleged data theft from Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) environments. EBS systems are critical to manufacturing operations (ERP systems), and the zero-day exploitation likely began in August 2025.
Lack of Insurance: Critically, JLR reportedly had no active cyber insurance coverage at the time of its devastating attack, necessitating an unprecedented £1.5 billion UK government loan guarantee to manage the crisis.
As of late 2025, global APT activity remains elevated, driven by intensifying geopolitical tensions and rapid cyber-capability expansion among major powers. China-aligned actors continue wide-scale espionage across government, telecom, and critical infrastructure, increasingly targeting Europe and APAC. Russia-linked groups sustain aggressive campaigns in Ukraine and Europe, mixing cyber-sabotage with disinformation and credential theft. Iranian operators focus on Israel and Western assets, conducting espionage and influence operations, while North Korea pursues financially motivated and espionage-driven attacks using supply-chain infiltration and malware implants. The Middle East and Asia-Pacific remain hotspots, with critical infrastructure, defense, and research sectors facing persistent intrusion attempts. Overall, APT operations are becoming more coordinated, stealthy, and hybrid, blurring lines between espionage, crime, and warfare, and posing ongoing risks to global digital stability.

China continues to leverage zero-day and n-day vulnerabilities for intelligence collection and strategic espionage, maintaining persistent access to government and critical infrastructure networks.

North Korean APT groups maintained a dual focus on cyber espionage and financial theft, sustaining a key funding channel for the regime’s strategic programs.

Russia-linked threat actors sustained hybrid cyber operations blending espionage, sabotage, and influence campaigns, primarily targeting Europe and NATO-aligned nations.

CURRENT THREAT POSTURE
STATE-LINKED THREAT CLUSTERS
Victim Industry Landscape
Financial Services,
Defense and Aerospace,
Government and Policy Institutes,
Telecommunications,
Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Target Area
Sensitive Data, Credentials, Endpoints.
Operational Drivers
Financial Gain (crypto theft, ransomware),
Intelligence Collection (espionage on defense and policy entities),
Geopolitical Influence and Strategic Advantage.
Tooling and Infrastructure
North Korean groups maintain high operational discipline, combining custom malware development, social engineering, and supply-chain infiltration. They display adaptive TTPs with a strong focus on financial gain to support state programs.
Recent Intrusions of Note
Espionage operations observed against the Japanese Defense Intelligence Headquarters and the South Korean MoD, over $45M in cryptocurrency losses linked to Lazarus and BlueNoroff campaigns in Q3 2025.
CURRENT THREAT POSTURE
STATE-LINKED THREAT CLUSTERS
Victim Industry Landscape
Financial Services,
Defense and Aerospace,
Government and Policy Institutes,
Telecommunications,
Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Target Area
Sensitive Data, Credentials, Endpoints.
Operational Drivers
Strategic Intelligence Collection, Regional Political/Ideological Objectives, Disruption & Denial,
Financial Gain / Fundraising.
Tooling and Infrastructure
Iranian groups demonstrate
moderate-to-high operational capability: proficient in social engineering, custom and commodity malware, wiper and extortion tooling, and exploitation of internet-exposed devices.
Recent Intrusions of Note
Multiple credential-harvesting campaigns targeting Israeli media and cybersecurity professionals, reported compromises of regional payment processors and associated data exposures.
STEADY ACTIVITY, SHARPER PRECISION
Ransomware volumes held steady through September, but the operational profile shifted to fewer opportunistic hits, more targeted, high-value breaches emphasizing disruption over scale.
SECTOR EXPANSION BEYOND MANUFACTURING
Manufacturing remains the year’s most affected sector, but September saw growth in attacks on government, business services, retail, and healthcare, signaling a pivot toward sectors with sensitive data and weaker segmentation controls.
ACCESS AND PERSISTENCE AT THE CORE
VPNs, identity services, and hypervisors are the dominant entry points. The shift toward MFA theft and ESXi exploitation highlights the erosion of perimeter-based defenses and the growing importance of identity and virtualization security.
GEOPOLITICAL AND REGIONAL FOCUS
Europe (Germany, France, UK, Spain, Italy) remained the main theater of activity, with sustained secondary targeting in South Korea, Australia, and the Middle East, reflecting both economic incentives and affiliate reach.
Evolving Tradecraft and Innovation
Major groups demonstrated technical escalation:
Strategic Implication
The ransomware ecosystem is professionalizing, adopting AI-assisted payload generation, firmware persistence, and modular loaders. Organizations must evolve beyond patching cycles to integrate identity resilience, hardware integrity checks, and rapid recovery readiness as core business risk controls.
SHIFT FROM “ATTACKS” TO “ACCESS AND MONETIZATION.”
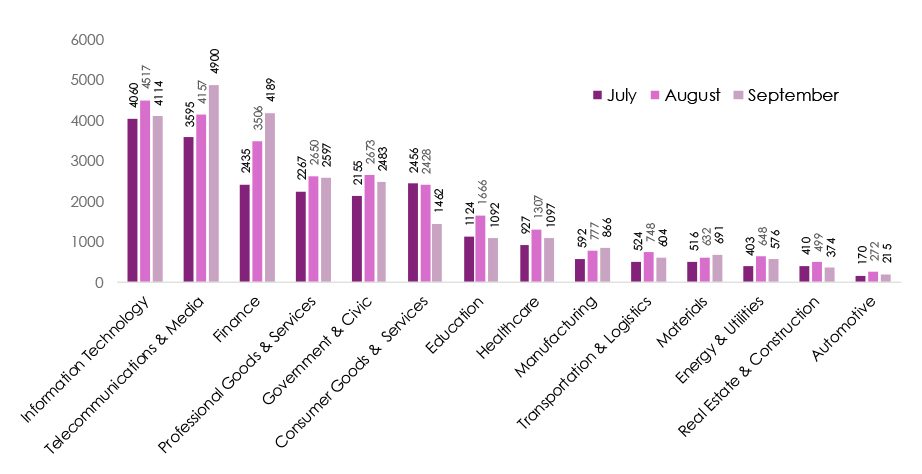
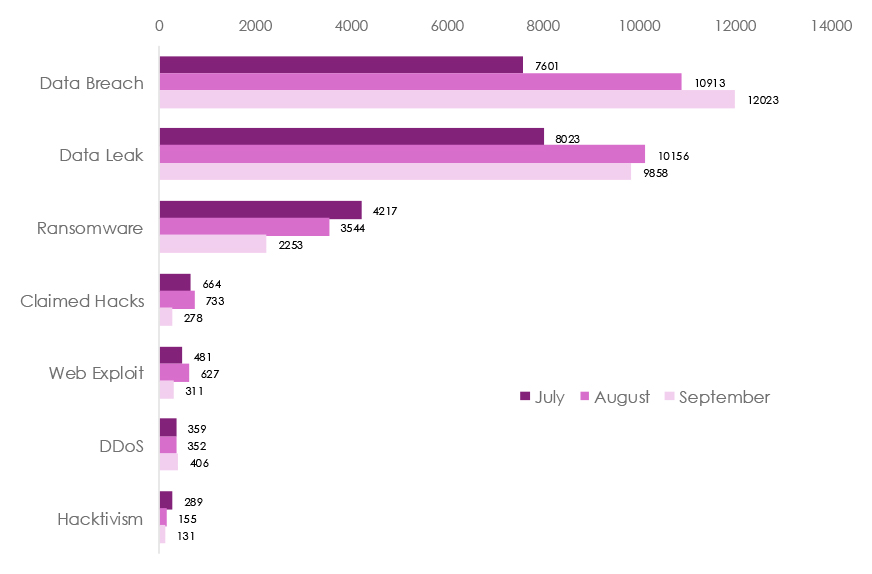
Mentions of data breaches and leaks surged (up 58% since July), while overt attack chatter like ransomware promotions, claimed hacks, and web exploits declined. Threat actors are moving toward quiet data monetization, signaling a maturing, profit-driven underground economy.
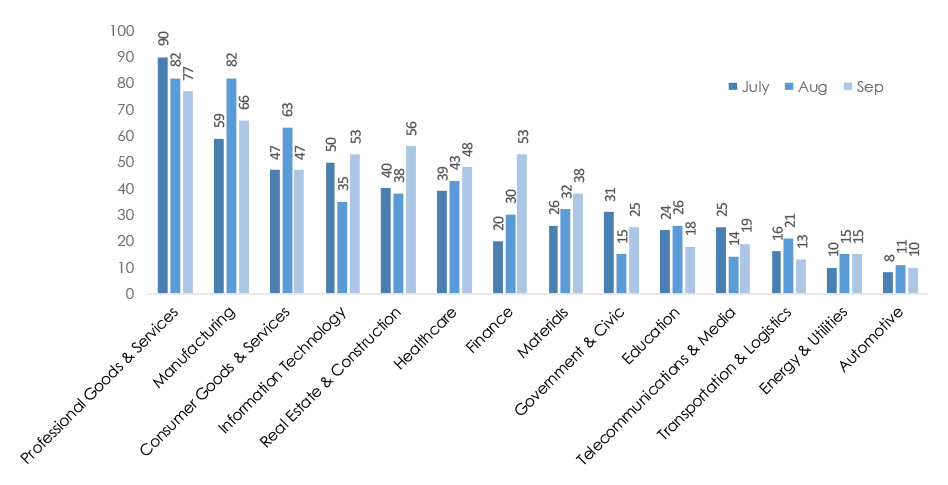
FINANCE AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS REMAIN PRIME TARGETS.
Chatter around Finance (4,189 posts) and Telecom & Media (4,900) continued rising—reflecting sustained targeting of data-rich, high-interconnectivity sectors. Both are essential entry points for lateral attacks across partner ecosystems.
RANSOMWARE NARRATIVES PERSIST BUT ARE MORE COVERT.
Ransomware mentions persist, yet most discussions now occur within data sale and negotiation threads instead of public leak sites—evidence of a shift to private extortion models emphasizing stealth and operational discretion.
INITIAL ACCESS BROKERS (IABS) DOMINATE ECOSYSTEM CHATTER.
The growth in breach/leak discussions corresponds with increased IAB activity selling VPN, SSO, and RDP access across critical sectors. This is a leading indicator of future ransomware and espionage campaigns, often preceding attacks by weeks.
Strategic Implication
Cybercriminal operations are transitioning from “public disruption” to data commoditization and stealth access trade. Organizations must strengthen identity governance, data loss monitoring, and third-party oversight, treating Dark Web chatter as an early-warning signal, not an after-incident reflection.
POLITICAL
NATO strengthens defenses on satellites, cables, and supply chains. Adversaries will shift to targeting human systems, zero-days, cloud, and third-party services. As NATO moves more assertively in cyber (or treats cyber as warfare), adversaries may respond more aggressively, increasing state-on-state cyber conflict. The increase in investment in cyberspace could cause economic strains on smaller allies, which could delay implementations, creating temporary vulnerabilities.
World Economic Forum’s report, influenced by international dialogues at Davos, highlights geopolitical turmoil as a driver for cyber risks, with one-third of CEOs citing espionage as a top concern. Drives regulatory harmonization, expanding cyberspace governance, but complicating compliance for global firms. If unaddressed, it could lead to a 35% rise in cyber claims as predicted by insurers, fueling a broader “cyber arms build-up.”
TECHNOLOGICAL
Europe’s push for digital sovereignty continues to accelerate amid escalating US-EU trade tensions under the Trump administration, including 145% tariffs on Chinese imports affecting global supply chains and heightened fears of US data access via laws like the CLOUD Act. Several EU entities and coalitions are advancing divestment from U.S. hyperscalers (Microsoft Azure, AWS, Google Cloud) toward open-source and European-native alternatives. Adversaries may try to exploit gaps during transition, target open-source tools for zero-day exploits, and increase reconnaissance.
Widespread adoption of LLMs and agentic AI frameworks (e.g., multi-tool orchestrators, like elizaOS) continues to transform both enterprise automation and threat actor operations. Ransomware groups, including Akira, BlackCat, and LockBit, increasingly deploy LLM-assisted negotiation bots, phishing generators, and data-leak extortion scripts to enhance efficiency in double-extortion campaigns.
U.S. Rotations: October 10, 2025, marks a pivotal day in global conflicts, with a U.S.-brokered ceasefire in Gaza triggering Israeli troop withdrawals and U.S. deployments, while Russia’s drone-missile barrage on Ukraine escalates hybrid warfare. These movements—de-escalatory in the Middle East but intensifying in Eastern Europe—amplify cyber threats by straining logistics, exposing C4ISR systems, and fueling state-sponsored hacktivism. Globally, insured cyber claims linked to these theaters rose 28% YoY in Q3 2025, driven by supply chain vulnerabilities and disinformation ops.
Proxy and Hacktivist Surges: Iranian/Ukrainian proxies exploit movements for DDoS/ICS hits; EU data sovereignty push (Sep Data Act) fragments defences.
THREAT VOLUME STABLE, SEVERITY ELEVATED
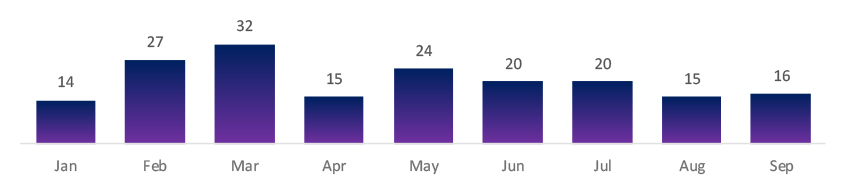
While the number of exploited vulnerabilities dropped to 16 in September (below the annual average), nearly half were rated high to critical (CVSS ≥8.0). Attackers are focusing on high-impact, easily automated flaws rather than volume.
DIVERSIFIED VENDOR EXPOSURE
Unlike earlier months dominated by Microsoft, September’s KEVs span Cisco, Linux, Sitecore, TP-Link, Meta, Git, Citrix, and Trend Micro. This diversification signals a broadening threat surface targeting network appliances, web platforms, and developer tools.
RECURRING WEAKNESS PATTERNS
Exploited CVEs clustered around four persistent classes: Missing/Incorrect Authorization (CWE-862/863), Command Injection (CWE-78), Deserialization (CWE-502), and Race Conditions/Link Resolution flaws (CWE-367/436). These remain the most reliable and reusable exploit vectors across industries.
EDGE AND WEB INFRASTRUCTURE AT HIGH RISK
KEVs tied to TP-Link, Citrix, and Sitecore highlight ongoing exploitation of perimeter and web application layers, key enablers of lateral movement, data theft, and ransomware staging.
LEGACY AND SUPPLY-CHAIN EXPOSURE PERSIST
The reappearance of a 2007 Microsoft CVE and newly exploited Git and Linux flaws emphasize the need to manage legacy systems and developer environments as active attack surfaces, not background noise.
Strategic Implication:
Patch velocity, particularly for internet-facing and development infrastructure, remains the single most effective control. September’s KEVs confirm that attackers are refining exploitation of familiar weaknesses faster than defenders are patching them.
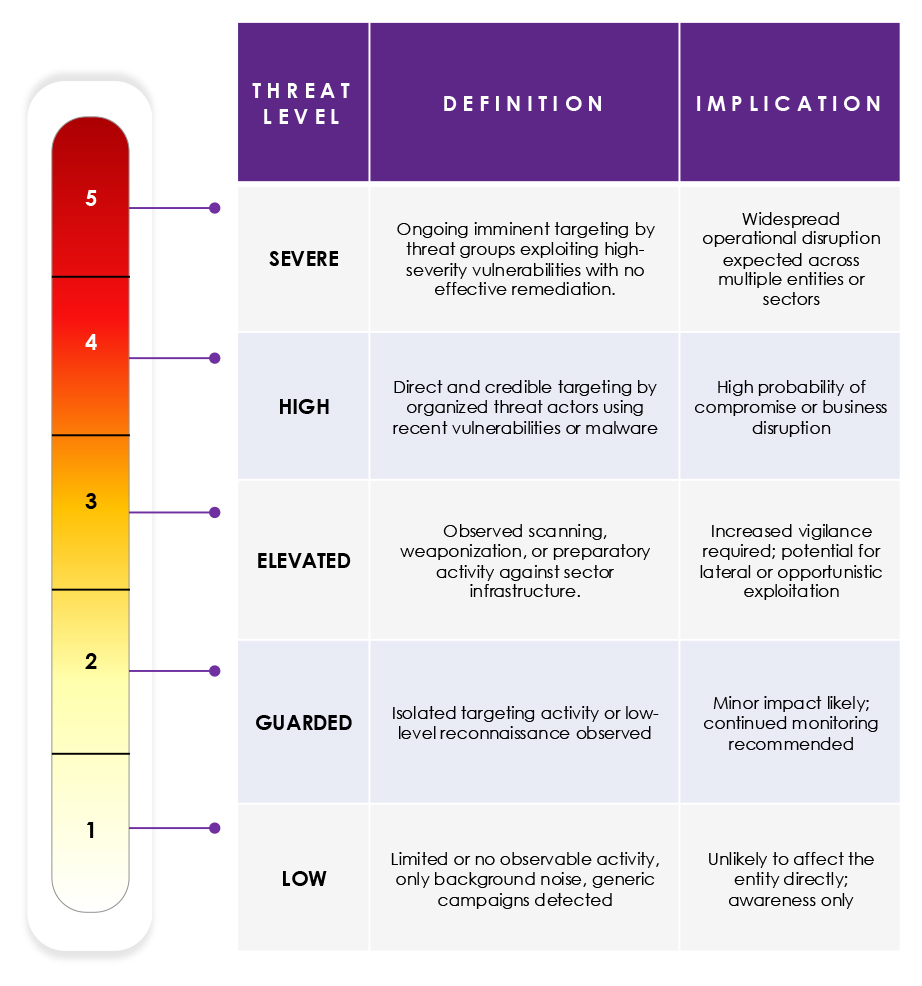
CYFIRMA applies a five-tier model to assess the likelihood and potential impact of threat activity. Each level reflects a fusion of actor intent, capability, and exploitation opportunity, assessed through multi-source intelligence correlation and vulnerability telemetry.