



NAVIGATING THE CYBER TSUNAMI OF 2024

In 2024 and beyond we will witness a tidal wave of change in the cybersecurity landscape. Advancements in technology, a shifting geopolitical climate, and the ever-evolving ingenuity of cybercriminals converge to create a perfect storm demanding our immediate attention. This thought leadership paper examines ten pivotal predictions that will define the cyber terrain of 2024 and beyond.
From the rise of the AI-powered “digital adversary” to the weaponization of misinformation in election campaigns, the threats we face are diverse and dynamic. Yet within this turbulence, opportunities for collaboration and innovation are abundant.
This paper presents ten critical cyber predictions for the remainder of 2024, exposing threat actors and the proactive measures we must take. Awareness is the first line of defense, so brace yourselves, for a treacherous voyage through the ever-shifting currents of the cybersecurity realm.
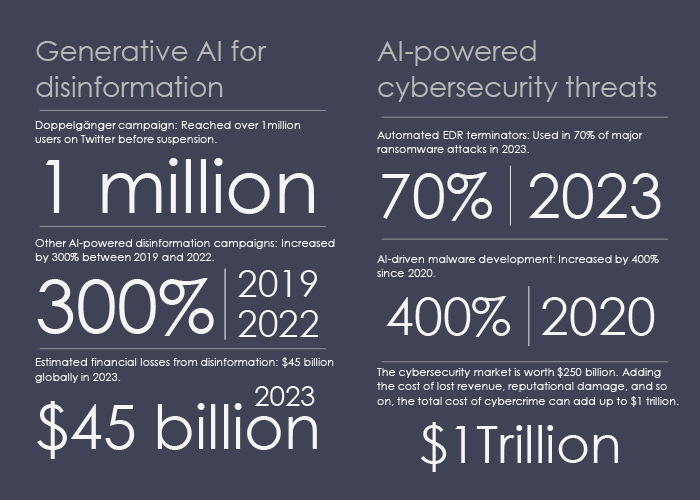
Adversaries are leveraging AI-driven capabilities for intricate digital assaults. For instance, the Russian influence network Doppelgänger’s use of generative AI in propaganda showcases a pivotal advancement, highlighting the ability of AI-powered adversaries to exploit information vulnerabilities and spread disinformation.

Additionally, the development of techniques like Tree of Attacks with Pruning (TAP) reveals vulnerabilities in large language models. This enables adversaries to manipulate even carefully crafted AI systems, boasting a success rate of over 80% in bypassing state-of-the-art LLMs. These advancements suggest an imminent reality where AI-driven adversaries exploit AI systems themselves, breaching established boundaries and generating harmful content (for instance through the deployment of automated EDR terminators used by certain ransomware gangs).
This trend forecasts the rise of AI-powered digital adversaries that can navigate AI defenses and manipulate information with agility and precision, with significant societal and cybersecurity implications.
STATISTICS – THE RISE OF BOT INTERACTIONS AND CONFLICTS


With nations across the world moving towards protectionism, the remainder of 2024 could witness an increase in state-sponsored cyber-attacks on major industries, organizations, and government entities.

Since the pandemic and the growing turbulence of the geopolitical threat landscape, most nations have started moving towards protectionist economy policies to boost their GDP and create jobs.
This has the potential to derail the international sharing of intellectual property (IP), as well as blueprints, source codes, and technology.
This leads nation-state actors to rely on economic espionage/cyber-attacks to boost their own economy or cripple a target nation’s economy leaving no footprints of possible attack sources.
Such cyber-attacks seek to illegally influence a country’s economic policy or steal critical technologies or sensitive data, by attacking critical systems, such as financial assets, OT systems, and power grids.
The costs of cybercrimes include damage and destruction of data, loss of money, decreased productivity, theft of intellectual property, personal and financial data, embezzlement, fraud, post-attack interruption to the normal course of business, forensic investigation, restoration & deletion of hacked data and systems, and reputational damage.
Last year, we witnessed increasing trends of nation-state actors targeting financial institutions, government entities, critical infrastructure against the nation, and public and private organizations to attempt to impact the economy.
State-sponsored threat actors rely on legitimate services, open sources, and supply chains as preferred channels of attack as they can evade detection successfully. Additionally, these channels would require low investment and provide high returns financially and in terms of information theft.

Cybercrime/Cyberattacks could reach 10.5 Trillion USD by 2025 starting from 3 Trillion USD in 2015, and 8 Trillion USD in 2023, an increase by 250% approx. since 2015

Cybercriminals would be looking to target a huge goldmine of 200 zettabytes of data (approx) by 2025.
Nation-state actors will leverage deep fake technology to influence, misinform, and socially engineer campaigns to diminish trust, intensify polarization, and erode the global social fabric.
Brace for a bigger impact in 2024, as all necessary elements for widespread attacks are ready for deployment – even by the most unsophisticated cybercriminals.

THE PROLIFERATION OF DEEPFAKES IN 2024 and beyond: A RISING TIDE OF DECEPTION
In the latter half of 2024, deepfakes – powered by artificial intelligence – are set to become more widespread. Synthetic media will manipulate videos, audio, or images, create deceptive illusions of individuals engaging in actions, or make statements they never did. Their versatility means that they are increasingly being utilized for social engineering attacks, with the ability to manipulate individuals into divulging sensitive information.
Deepfakes are likely to act as a prominent tool for both state and non-state actors. Indeed, as the use of cyberwarfare has become an established fact, we believe that 2024 and beyond will witness the start of a new chapter, with deepfakes used for potent psychological warfare to destabilize governments and manipulate opinions. This trend is exemplified by the previous circulation of a deepfake video, depicting Ukrainian President Zelenskyy, instructing soldiers to surrender. This points towards a more aggressive future, where deepfakes could be deployed to incite violence, destabilize governments, and provoke conflicts.
Malicious actors will exploit deepfakes to erode trust in institutions and public figures, amplifying misinformation and propaganda through AI and social media platforms. These convincing fakes can fabricate actions or statements, fueling discord and undermining effective governance: notably, a manipulated video of President Biden in February 2023 falsely announced offensive actions against transgender women.
The rise of AI and accessible deepfake tools also enhances the threat landscape for fraud and identity theft. Compromised data, leaked business information and personal details will allow malicious actors to create convincing emails, social media messages, or phone calls that appear to come from legitimate sources. The accessibility of these tools will present an ever-heightened risk, tricking individuals into disclosing personal information and therefore falling victim to further, more sophisticated cyber-attacks.
The synthetic media market is witnessing a concerning trend, whereby the non-consensual creation and circulation of fake nude images and videos of women have been observed on platforms like Telegram, facilitated by a network of bots for sharing, trading, selling, and advertising deepfake content services. This unsettling market is anticipated to expand due to the growing demand for such content in the coming year, exerting a considerable impact on women in particular, and in certain instances, children.
While deepfakes have inherent risks, they also have valuable applications. For instance, in healthcare, AI can help ALS patients communicate, while medical education can benefit from the creation of interactive simulations.
Despite the benefits of technological advancement, the increasing malicious threat posed by AI prompts a call for stringent laws, global regulations, and investments in deepfake detection technologies. China has already implemented laws mandating disclosure of deepfake use, with regulations prohibiting distribution without a clear disclaimer. Similar laws are also likely to emerge in countries like India later this year, reflecting a global trend toward safeguarding against harmful repercussions of deepfakes.

Although global, the increase in deepfake use was more substantial in North America, where it rose 1740% in 2023 compared with 2022, and in Asia-Pacific (APAC), which saw a 1530% surge over the same period.
Deepfake use for identity fraud purposes
Increased by:
Deepfakes, AI Will Drive
USD 10 Trillion
Experts fear in 2024
Viral undetectable deepfakes will have a calamitous impact
This trend will leapfrog multi fold In Financial Fraud and Crime On elections
In the coming year, ransomware attacks are poised to evolve, prioritizing speed over subtlety. Forensic incident investigations reveal a shift where ransomware groups are opting for rapid execution rather than meticulous concealment. Interestingly, they’re even leaving behind operational guidelines, emphasizing speed over stealth.

Expect a surge in ransomware coded in GO and RUST languages, known for their speed and adaptability across platforms. This versatility will widen the range of potential targets, heightening the threat.
Additionally, ransomware is likely to incorporate automation and machine learning into various stages of its lifecycle. This includes using these technologies for victim profiling, automated decryption post-payment, and negotiations. Incorporating EDR terminators before encryption aims to bypass obstacles, and the rise of RDDOS as a triple extortion tactic adds pressure on victims.
Anticipate a significant decrease in attacker dwell time, dropping from days to hours, highlighting the urgency and efficiency of ransomware operations.
Finally, an increasing preference for Chacha20 encryption algorithms over conventional AES signifies a deliberate move towards quicker encryption processes at the heart of malicious activities.
In the upcoming year and beyond, behavioral data will emerge as a critical focal point within cybersecurity, particularly in the context of threat actors’ strategies. This form of data, encompassing user habits and digital interaction patterns, will significantly escalate in value for malicious threat actors seeking to both steal behavioral data and develop their own collection. Threat actors will strategically leverage behavioral data to personalize and refine social engineering tactics, crafting sophisticated phishing attempts that mirror individual communication styles or interests identified through online behavior.
Moreover, they will exploit behavioral insights to predict potential weaknesses within networks, facilitating targeted attacks or unauthorized access to sensitive information. Analyzing behavioral patterns will aid threat actors in efficiently navigating networks for data exfiltration or lateral movement, intensifying the impact of their exploits.
The acquisition of behavioral data will occur through various means, including exploiting system vulnerabilities for data collection, perpetrating breaches to access databases housing such data, manipulating individuals via social engineering to divulge behavioral insights, or acquiring information from illicit sources on the dark web.”
We will witness a seismic increase in behavioural driven cyber adversary attacks, reiterating the need to shift towards behavioural threat hunting
LIMITATIONS OF TACTICAL INTELLIGENCE (E.g. IOCS) LEADS ONTO BEHAVIOURAL DETECTION
2023
There was an unparalleled increase in the sharing of threat intelligence that integrated behavioural attributes. Like CISA’s advisories around ransomware groups to FBI’s collaborative Cybersecurity Advisories – the emphasis has been around providing all-inclusive behavioural insights into threat actors.
2024 and Beyond
The focus area must be around Behavioural Threat Hunting Cyber risks have become one of the main issues for global security and Behavioural based cyber-attacks and adversary action are leading the way. The associated annual cost is estimated to exceed $200 billion globally.
2024 will be a year when the world goes to the ballot box; nearly 80 countries will hold national elections, including many with large but damaged democracies, such as India, Indonesia, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Russia, and Mexico. Geopolitical trends, social media – further weaponized with artificial intelligence – will play an outsized and destructive role.

Disinformation and propaganda have been documented since the Roman empire, but rapid technological innovations in this area arguably have the potential to cause disastrous consequences.
Evolutions in digital publishing and AI have enabled perpetrators to mimic the output of mainstream media outlets, pushing their agendas widely, inexpensively, and effectively, as the target audience is unable to differentiate between fake and legitimate reporting.
Russia used this technique on social media to a great effect to disseminate a fabrication about US aid to Ukraine being diverted to buy superyachts for President and Mrs. Zelenskyy: even though it was rapidly debunked, the damage was already palpable as reservations were voiced in Congress about the renewal of US aid to Ukraine.
Elections in Argentina were also marked by generative AI use, targeting candidates with humiliating, fabricated content (often of a sexual nature). It was further used to generate political ads, and to support candidates’ campaigns and outreach activities in India, the United States, Poland, Zambia, and Bangladesh, resulting in a global climate of distrust towards synthetic media in political settings.
We have observed an increase of 50% of disinformation in the Taiwan Strait region. In 2024, we expect the spread of mis and disinformation to rise as the Chinese Community Party (as Russia has historically done with Ukraine) continues to use Taiwan as a testbed for manipulation campaigns.
We predict the use of generative AI to become more prevalent, complex, and effective. Meta recently took down more than seven thousand accounts linked to a Chinese influence operation in the largest-known operation of its kind, indicating that the extent of disinformation surrounding the Taiwanese elections will be greater and more insidious than previously witnessed, with more state and non-state actors watching and eager to adopt these measures themselves.
Russia – and increasingly China – are also exporting digital ‘packages’ to the developing world to aid domestic digital repression, making fact-checking all the more challenging.
Since 2017, the Meta has disclosed more than two hundred coordinated inauthentic behavior operations on its platforms, across more than one hundred countries. Meta has close to four billion monthly active users across its platforms, including Facebook, WhatsApp, and Instagram.

The remaining months of 2024 are anticipated to witness a surge in threat actors exploiting zero-day or N-Day vulnerabilities within third-party and supply chain relationships. This trend is fueled by the expanding global reach of supply chains, the integration of numerous third-party entities, and the growing complexity of interconnected systems. The objectives encompass revenue generation and espionage, with a focus on the theft of advanced technologies spanning diverse sectors.

We believe that while the typical association with supply chains often involves nation-state-backed groups engaging in cyber espionage or critical infrastructure disruption, it’s essential to acknowledge that recent supply chain attacks go beyond this exclusive domain. Financially motivated cybercriminals and other cyber-criminal groups have embraced this tactic to further their nefarious objectives, and this trend will continue.
Malicious Open-Source Repositories: Attackers inject malicious code into legitimate open-source software, distributing it through trusted repositories like GitHub. This code can unknowingly integrate into software applications developed by organizations.
Exploiting Third-Party Vendors: Attackers target organizations by exploiting vulnerabilities in third-party software, hardware, or services integrated into their systems. Access to these vendors’ systems becomes a springboard for attacking the actual targets.
Supply chain attacks can have devastating consequences, including data breaches, disruption of critical operations, and significant financial losses. Some prominent 2023 attacks highlight the severity of the issue:
3CX Supply Chain Attack (March 2023): Targeting the 3CX Desktop App, attackers exploited a compromised third-party library to insert malicious code, potentially leading to data theft, communication disruption, and ransomware installation.
MOVEit Supply Chain Attack (May 2023): The Cl0p ransomware group targeted Progress Software’s file-transfer service, affecting over 2,550 organizations. The attack led to data exfiltration, ransom demands, and financial losses surpassing $2.9 million.
JetBrains TeamCity Supply Chain Attack (Sept 2023): Exploiting a critical vulnerability, attackers infiltrated systems globally, emphasizing the need for proactive security measures in software supply chains.
KEY TAKEAWAYS AND FUTURE TRENDS
In the coming year, cyber attackers are poised to heighten their focus on exploiting vulnerabilities within interconnected third-party networks and supply chains. Weak links in these chains serve as gateways for hackers, enabling them to breach multiple entities through a single compromise.
The intricate nature of modern supply chains presents difficulties in securing every component, offering hackers opportunities to exploit trust relationships between entities. Software dependencies and compromised vendors remain primary targets, facilitating the distribution of malware through widely used applications.
Hackers will employ sophisticated tactics like watering hole attacks to indirectly breach high-value targets via less secure third parties. Furthermore, ransomware attacks directed at supply chains will increase, affecting multiple entities simultaneously and compelling affected organizations to comply with ransom demands.
Securing the entirety of the supply chain against cyber threats remains a formidable challenge, exacerbated by regulatory complexities. Strengthening security measures and fostering resilient relationships within the supply chain will be crucial in mitigating these evolving cyber risks.
| SR NO. | ATTACK | YEAR | GLOBAL COST VALUE APPROXIMATE | PERCENTAGE INCREASE FROM LAST YEAR |
| 1 | Supply Chain Attack | 2022 | Approx $39 Billion | Baseline |
| 2 | Supply Chain Attack | 2023 | Approx $43 Billion | 10.26 percent increase from 2022 |
| 3 | Supply Chain Attack | 2024 | Approx $52 Billion | 20.92 percent increase from 2023 |
The EV market has brought changes in the automotive industry. However, this rapid digital revolution has opened the door to a new wave of cyber threats and vulnerabilities. As electric vehicles become increasingly reliant on advanced vehicle technology, connected software, and pay-to-unlock features, cybercriminals are increasingly targeting electric vehicle infrastructure.
EV SALES PROJECTIONS FOR 2024
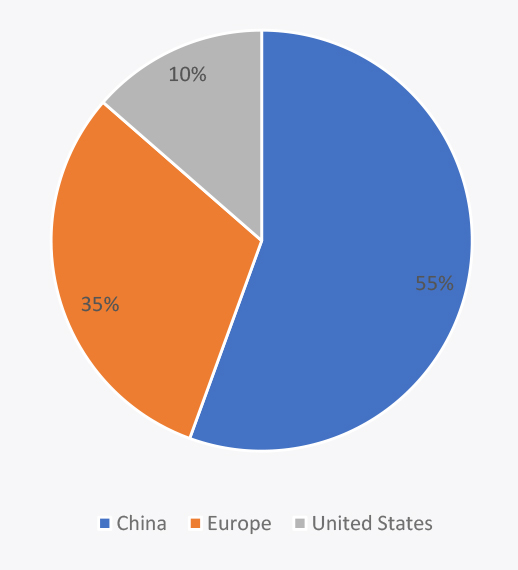
In 2024 and beyond, electric vehicles (EVs) will constitute an average of 27% of car sales across China, Europe, and the United States. In China, EVs will represent 55% of all cars sold, showcasing the country’s significant adoption rate. Europe will see EVs making up 35% of its total car sales, while in the United States, EVs will account for 10% of all cars sold.
SURGE IN CYBER INCIDENTS
There has been a 300% surge in cyber incidents targeting electric vehicle components. This alarming increase underscores the growing vulnerability of electric vehicles to cyberattacks, emphasizing the need for enhanced cybersecurity measures to protect these advanced systems.
EV CHARGING VULNERABILITIES
Reported EV charging vulnerabilities are expected to double by 2024 from 2022 levels (2x). This increase highlights the growing security challenges in the electric vehicle ecosystem, emphasizing the need for robust cybersecurity measures to protect against potential threats.
EV CHARGING MARKET GROWTH
The EV charging market is expected to reach $28.6 billion by 2030, growing at an impressive 18.5% CAGR from $6.1 billion in 2021. This significant growth underscores the increasing demand for electric vehicle infrastructure and the expanding market opportunities in the sector.
RISING COSTS OF CYBERATTACKS
The average cost of cyberattacks in the automotive sector is expected to rise by 180%. System downtime costs have already reached up to $1.99 billion, highlighting the severe financial impact of cybersecurity breaches on the industry.
DATA BREACHES
30% of electric vehicle companies have experienced a data breach. A prominent electric and hybrid propulsion systems developer’s website, which serves as a platform for industry updates and product/service promotion, has recently suffered a data breach. Confidential information, including IDs, user IDs, names, CPFs, emails, phone numbers, and additional details, has been compromised and is now available for purchase on the dark web for $4000. This incident highlights the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures within the industry.
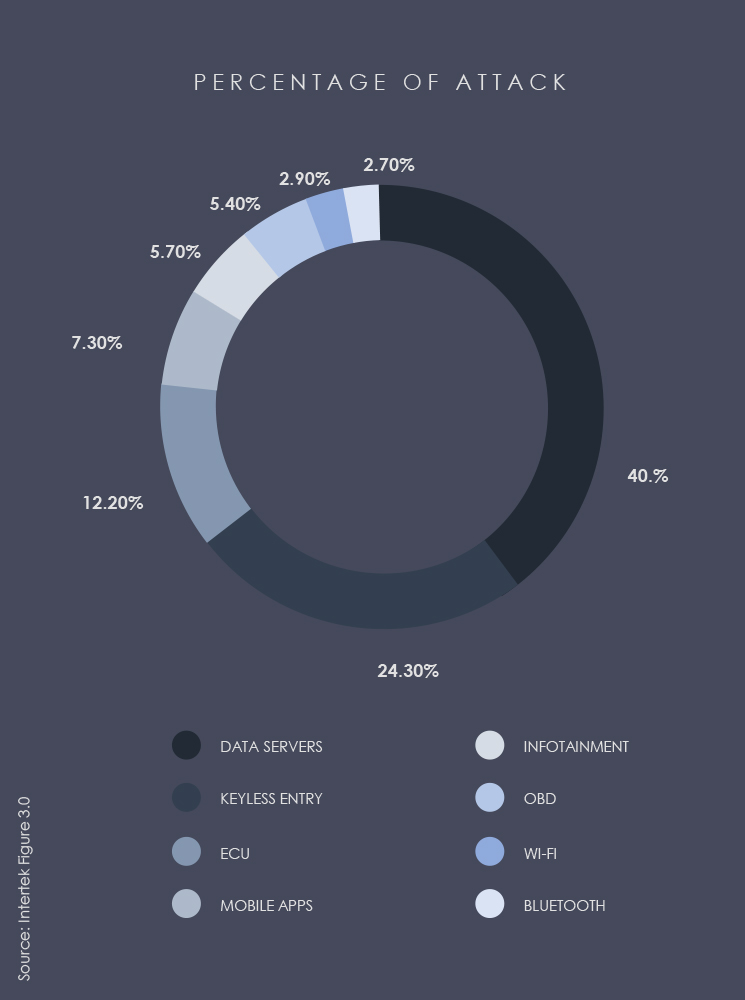
Looking ahead to the cybersecurity landscape in 2024, a significant shift is imminent. Cloud, IoT, and IIoT are not just potential targets; they are becoming sophisticated tools in the hands of threat actors. Recent incidents, like the discovery of critical flaws in popular cloud databases, emphasize the vulnerability of interconnected systems. This poses a real risk to data integrity and security in cloud infrastructures.
The forecast anticipates a new Mirai botnet variant, V3G4, adept at exploiting vulnerabilities targeting Linux and IoT devices. The healthcare sector is a distinct target, with cybercriminals capitalizing on vulnerabilities in medical devices, from drug-infusion pumps to pacemakers, creating opportunities for data harvesting, ransom, and potential harm to patients.

The emphasis on legacy systems as a strategic approach is not widely adopted by threat actors. This is mainly due to the necessity for specialized knowledge about older systems and their vulnerabilities, which may not be extensively documented or widely known. CYFIRMA believes that this trend will increase in 2024 and beyond, where they target legacy systems, infrastructure or out-of-life devices, particularly among state-sponsored actors equipped with the resources and motivation to engage in thorough reconnaissance and craft customized exploits.
Current trends show a worrying shift – we’re moving from mostly nation-state-directed cyber-attacks to more widespread mass exploitation campaigns. This trend is raising concerns in the industry. As ‘mass cybercrime market’ threat actors hone their skills in navigating the intricate languages and protocols of Industrial Control Systems (ICS), the risk is going up significantly. Their improved skills pose a real threat, especially because it allows non-affiliated attackers to offer ‘as-a-service’ ICS exploitation. Which in turn is likely to be leveraged by nation-state threat actors as we have seen with boutique spyware, like the infamous ‘Pegasus’.
The rapid growth of IoT, including devices like fitness trackers, smart refrigerators, and virtual assistants, is opening up new opportunities for cybercriminals. With an expected 64 billion IoT installations globally by 2026, this surge is driven by the increasing popularity of remote work, expanding the potential targets for cyber-attacks. Unlike laptops and smartphones, IoT devices often have limited processing and storage capabilities, making it difficult to establish robust security measures, such as firewalls and antivirus software. Consequently, we anticipate a significant rise in IoT attacks in 2024, exposing multiple entry points for cybercriminals in the evolving landscape of connected devices.
In the healthcare sector, cybercriminals focus on obtaining valuable personal data, particularly patient records that are lucrative on the black market. The convergence of interconnected devices and Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) complicates the landscape. Cyberattacks pose risks of data harvesting, ransom, and potential harm to patients. The increased usage of pacemakers and wearable medical devices has led to recent incidents of exploitation, and in 2024, this trend is expected to intensify with the greater incorporation of such devices.
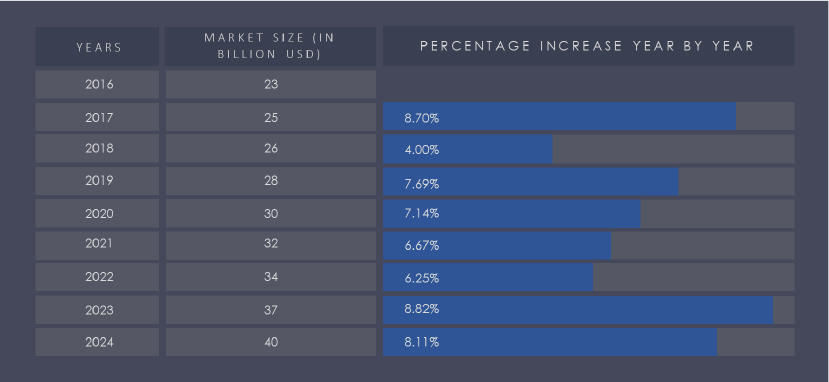
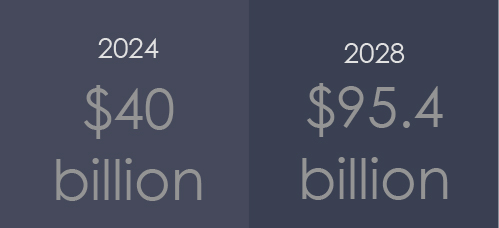
The global smart electronic health records market in the year 2024 is estimated to reach $40 billion and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 23.7%, reaching $95.4 billion by 2028.
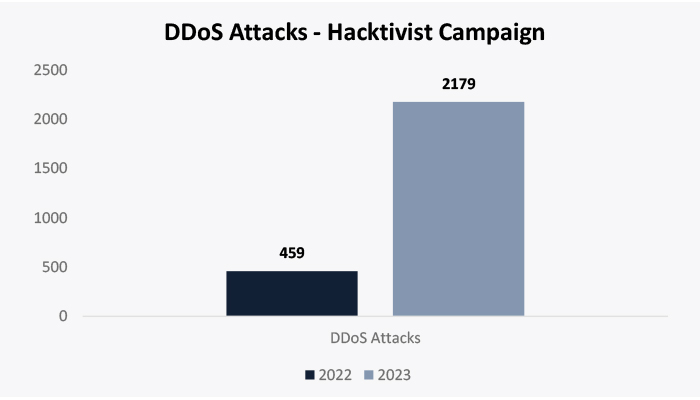
The evolving threat landscape, particularly in regions like Ukraine, has seen the rise of hacktivist groups leveraging DDoS as a tool of ideological warfare. The trajectory of these groups suggests a potential shift towards more sophisticated and damaging RDDoS campaigns in the future. We suspect that DDoS hacktivists who gained knowledge of conducting DDoS operations eventually turn RDDoS campaigners, once the purpose of the actual campaign is over or diluted. With learning and enhancements in DDoS tools, RDDoS will have destructive impacts on companies globally in the coming days.
AN EVOLUTIONARY PERSPECTIVE
RDDoS, an evolution of traditional DDoS attacks with a ransomware twist, has gained traction due to its dual-threat nature. Originating from the late 1990s, RDDoS has seen a resurgence, especially with a 67% YoY increase in reported incidents in 2022. The fusion of DDoS capabilities with ransomware functionalities intensifies the threat landscape, creating challenges for targeted organizations.
Simplicity and Accessibility
RDDoS attacks are growing in accessibility, as attackers exploit common web applications and take advantage of affordable botnet rentals. This ease of use is compounded by an abundance of readily available botnets, including an increasing number of IoT devices still being compromised from the mass log4j vulnerability and others. Furthermore, the low skill gap required for RDDoS attacks, thanks to the absence of the need to breach the target network and establish persistence, contributes to its attractiveness for malicious actors.
Financial Incentives
Despite extensive efforts by various international organizations and nation-states advocating against paying ransoms as the primary approach to combat ransomware, many victims continue to pay the ransom. Recognizing this as a vulnerability, RDDoS attacks seek to exploit it. Spending significantly less effort to capitalize on the prevailing willingness of certain entities to fulfil ransom demands.
Cybercriminal Innovations
Ransomware groups such as BlackCat, LockBit, and AvosLocker are exploring RDDoS as a means to amplify pressure on victims. The integration of DDoS with ransomware creates a multifaceted threat, increasing the complexity of response and mitigation efforts.
Operational Disruption
RDDoS attacks targeting organizations, already compromised by ransomware can paralyze critical operations, hampering response and recovery efforts. The simultaneous impact of ransomware and DDoS exacerbates the operational challenges, creating a perfect storm for targeted entities.
Financial Implications
The combined effect of ransomware and DDoS can result in significant financial losses due to downtime, lost revenue, and potential ransom payments. The financial strain enhances the leverage of cybercriminals, increasing the likelihood of ransom payments to mitigate the extended impact of the attack.
Reputational Damage
Beyond operational and financial implications, RDDoS attacks can inflict lasting reputational damage on targeted organizations. The exposure of sensitive information and the public perception of vulnerability can erode trust and credibility, affecting long-term viability and stakeholder relationships.
In summary, the emergence of RDDoS represents a pivotal shift in the cyber threat landscape, combining the disruptive power of DDoS with extortion capabilities. As hacktivist groups evolve and cybercriminals innovate, organizations globally must prepare for the escalating RDDoS threat. Proactive defense strategies, robust incident response capabilities, and stakeholder collaboration are crucial to mitigating the risks and minimizing the impact of RDDoS attacks in the coming days.