



The CYFIRMA Industries Report delivers original cybersecurity insights and telemetry-driven statistics of global industries, covering one sector each week for a quarter. This report focuses on the healthcare industry, presenting key trends and statistics in an engaging infographic format.
Welcome to the CYFIRMA infographic industry report, where we delve into the external threat landscape of the healthcare industry over the past three months. This report provides valuable insights and data-driven statistics, delivering a concise analysis of attack campaigns, phishing telemetry, and ransomware incidents targeting the healthcare industry.
We aim to present an industry-specific overview in a convenient, engaging, and informative format. Leveraging our cutting-edge platform telemetry and the expertise of our analysts, we bring you actionable intelligence to stay ahead in the cybersecurity landscape.
CYFIRMA provides cyber threat intelligence and external threat landscape management platforms, DeCYFIR and DeTCT, which utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning to ingest and process relevant data, complemented by manual CTI research.
For the purpose of these reports, we leverage the following data from our platform. These are data processed by AI and ML automation, based on both human research input and automated ingestions.
Finally, we acknowledge that many victims are never listed as they are able to make a deal with the attackers to avoid being published on their blogs.
While this report contains statistics and graphs generated primarily by automation, it undergoes thorough review and enhancement for additional context by CYFIRMA CTI analysts to ensure the highest quality and provide valuable insights.
Healthcare organizations featured in 1 out of the 11 observed campaigns, which is a presence in 9% of all campaigns.
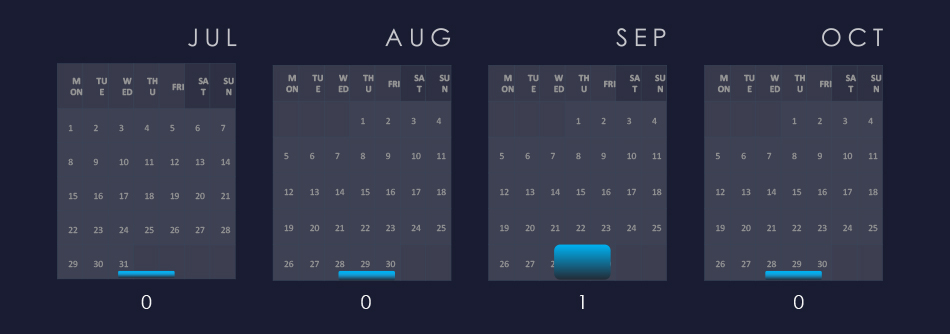
A single campaign with recorded victims in the healthcare industry was observed during September.
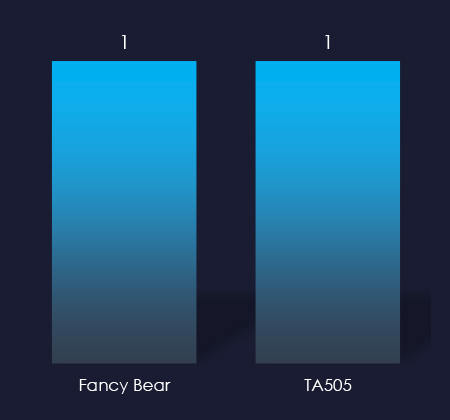
Attributed threat actors behind the campaign are both nation-state-sponsored Russian Fancy Bear and cybercrime syndicate TA505. It is an established fact that Russian cybercrime often cooperates with Russian intelligence.
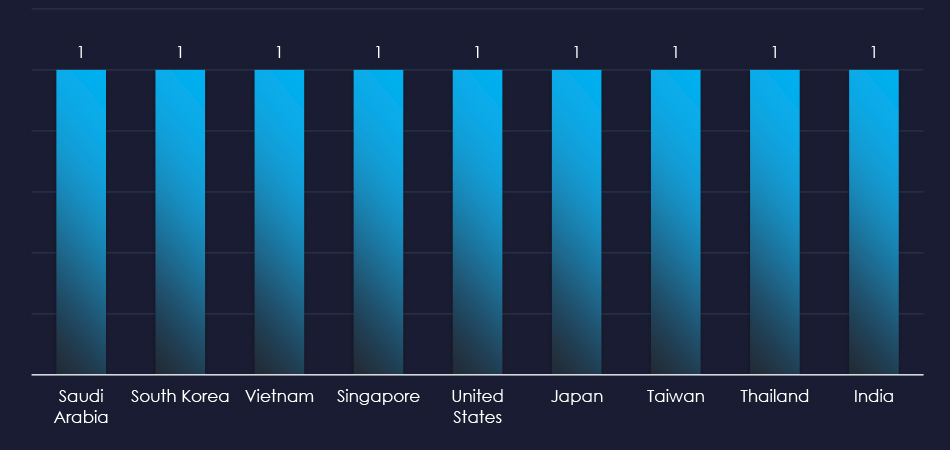
Recorded victims of the observed campaign span 9 different countries. The main focus appears to be Asia and India, but victims were recorded in Saudi Arabia and the US as well.

Web applications continue to be the most targeted technology across industries.

Risk Level Indicator: Low
In the past 90 days, healthcare organizations have not been significantly impacted by advanced persistent threat (APT) campaigns. Only 1 out of 11 observed APT campaigns recorded healthcare industry victims.
Monthly Trends
A single relevant campaign was observed during September.
Key Threat Actors
Threat actors attributed to the one observed campaign are both nation-state-sponsored Fancy Bear and cybercrime syndicate TA505 from Russia. Collaboration between Russian intelligence agencies and cybercrime has been known for many years now.
Geographical Impact
The campaigns impacted 9 countries mostly from East Asia.
Targeted Technologies
Web applications remain the most frequently targeted technology.
Over the past 3 months, CYFIRMA’s telemetry detected only 73 phishing campaigns themed around healthcare out of a total of 222,447.
The chart below illustrates the global distribution of observed themes. Observed healthcare accounts for 0.03% of all captured phishing attempts and is mostly related to insurance. Therefore, it is not being tracked as its own category.
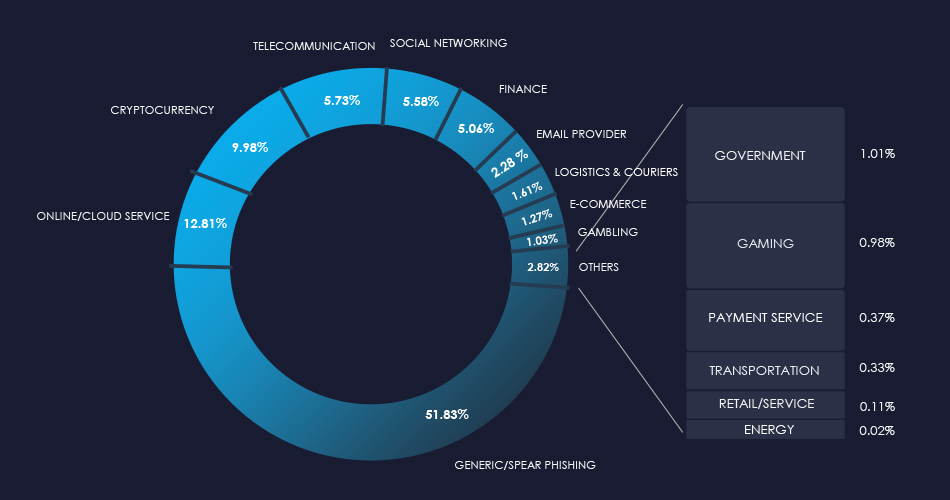
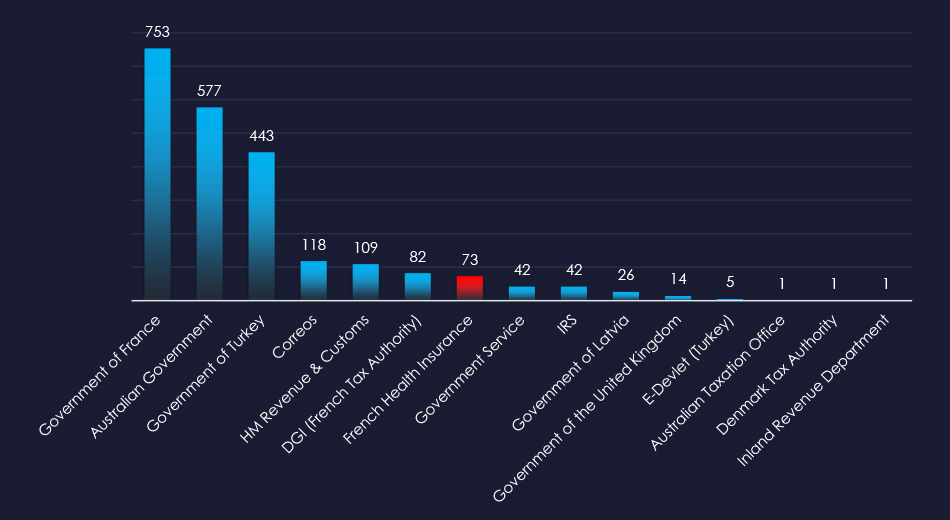
Showing the chart for entire government-themed phishing where French Health Insurance was observed.
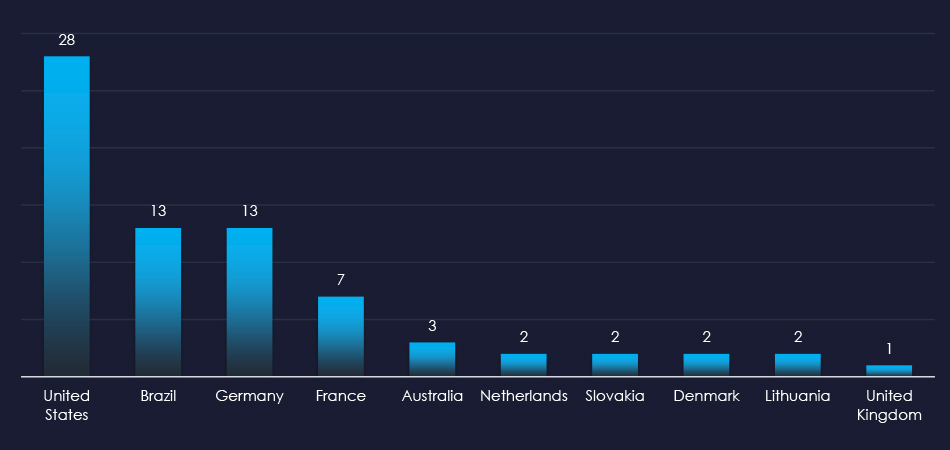
The US is a leading source of most phishing, despite the French organization being impersonated. In total this campaign was sent from 10 different countries.

Risk Level Indicator: Low
The healthcare sector is not a popular phishing theme due to the highly fragmented nature of the industry and the lack of direct monetization avenues for threat actors. There is also no simple way to craft a campaign for a widespread “spray and pray” type of phishing campaign.
However, it is certainly used for spear-phishing to target specific persons or organizations.
Overall, the only healthcare-related organization impersonated was the French Health Insurance, which is more financial than a healthcare organization.
ASN-origin data reveals that the United States is the leading source of phishing emails. And given the French institution impersonation, Brazil was the second most frequent country of origin.
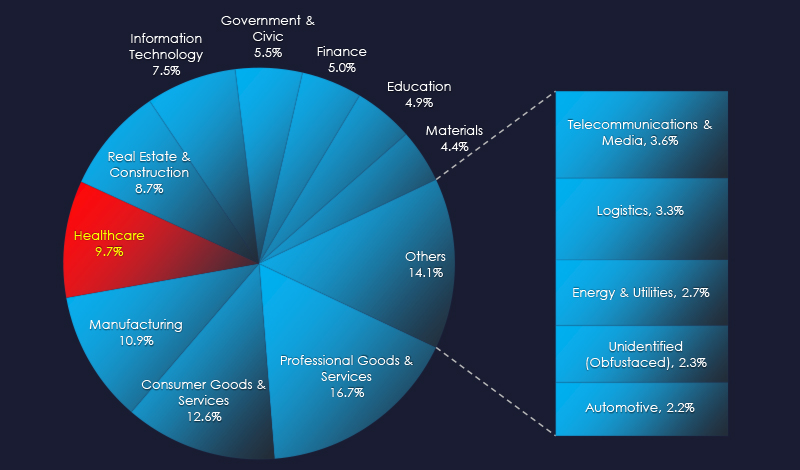
In the past 90 days, CYFIRMA has identified 133 verified ransomware victims in the healthcare industry. This accounts for 9.7% of the overall total of 1,377 ransomware victims during the same period, placing healthcare industry as the 4th most frequent victim of ransomware.
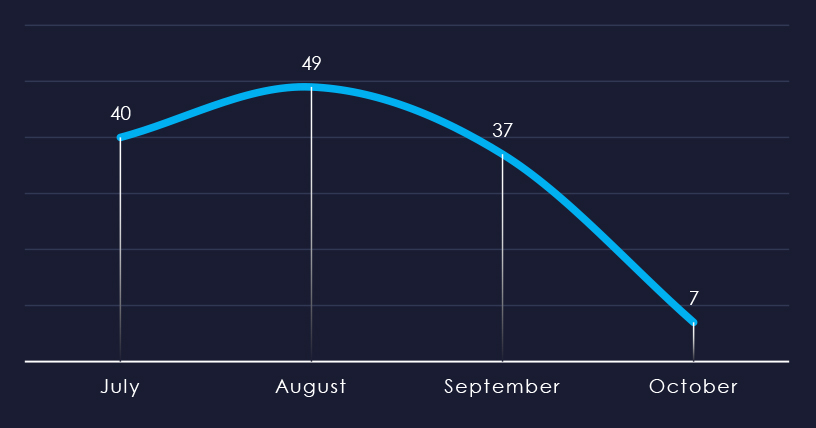
Considering just a few days of October, we can see sustained numbers of victims with a spike during August.
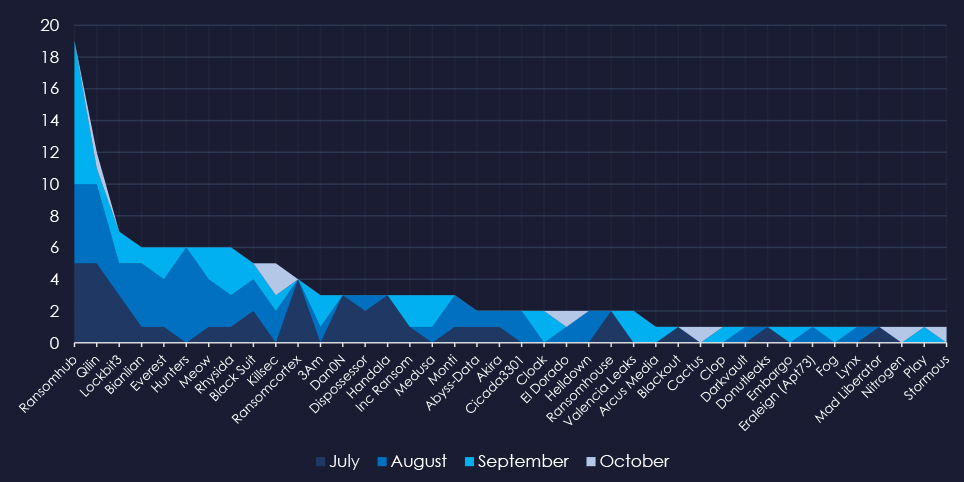
A breakdown of the monthly activity provides insights into which gangs were active each month. For example, RansomHub was active across months and Hunters during August.
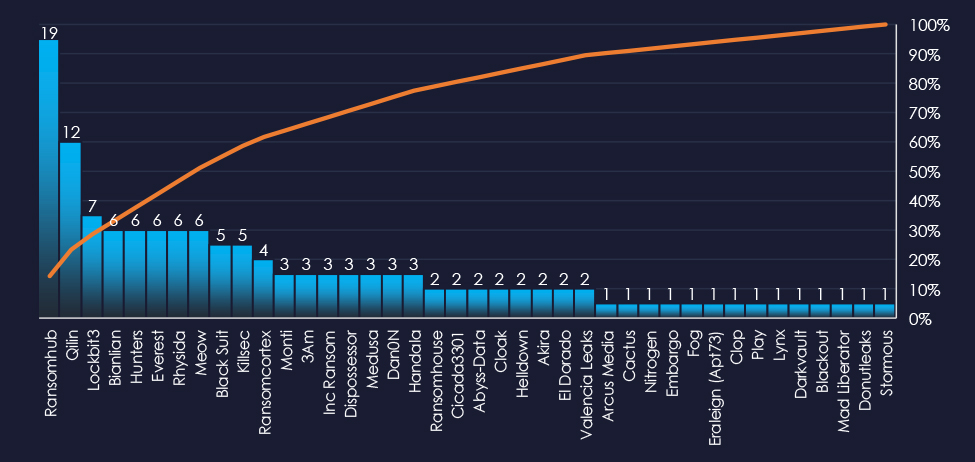
In total 40 out of 59 active groups recorded healthcare organizations victims in the past 90 days. Notable is a relatively even distribution among large number of groups in this period.
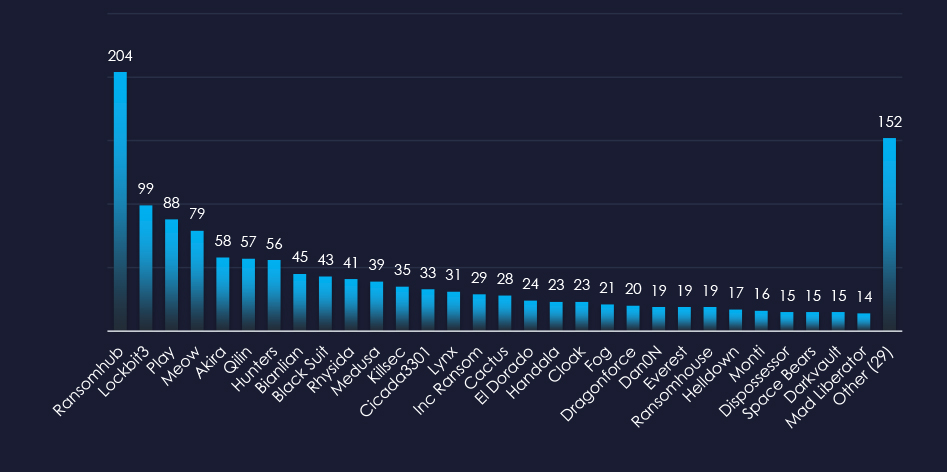
Comparing the healthcare industry to all recorded victims, Qilin stands out with a high percentage of victims in this industry recording 12 out of 57 (21%) victims in the healthcare industry, implying a focus on this industry.
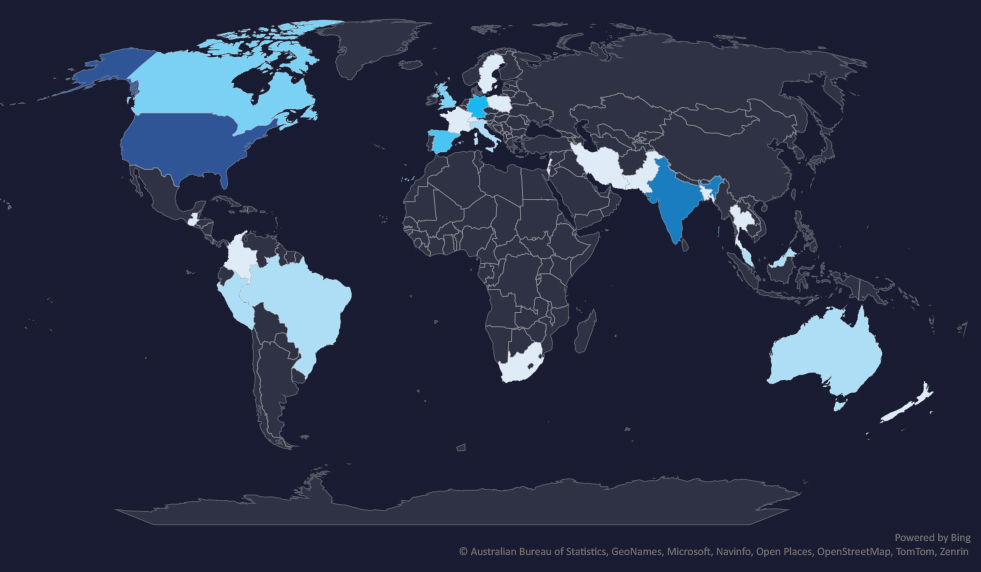
The geographic distribution heatmap underscores the widespread impact of ransomware, highlighting the countries where victims in this industry have been recorded.
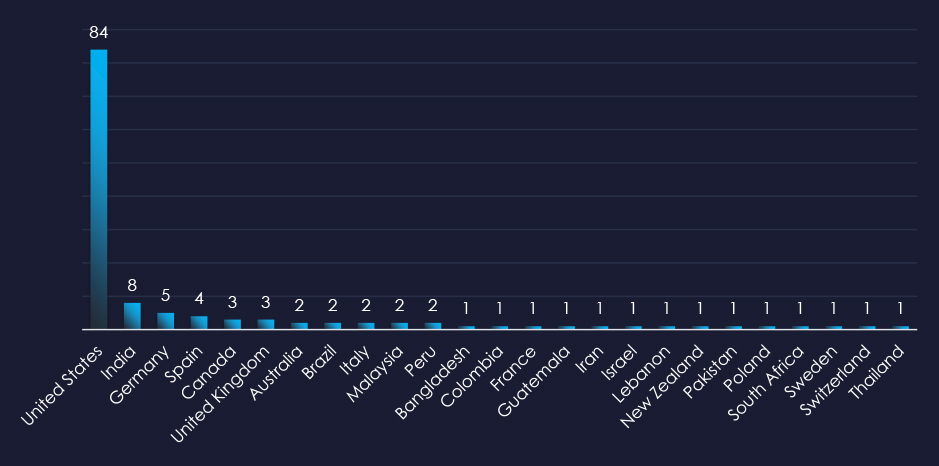
In total 25 countries recorded ransomware victims with the US alone accounting for ~64% of all victims with identified geography.

Risk Level Indicator: Moderate*
The healthcare industry is placed as the 4th most frequent victim. It faces a sustained ransomware threat, with attacks affecting a wide range of sub-sectors, however highly focused on the US. Therefore, the US warrants a high-risk factor, whereas the rest of the world is moderate.
Monthly Activity Trends
Ransomware activity in the healthcare industry recorded a mild spike during August.
The RansomHub group was the most across all months. Hunters group recorded all their victims in August, contributing to the mild spike.
Ransomware Gangs
A total of 40 out of 59 active ransomware groups targeted the healthcare industry in the past 90 days:
Qilin: 21% of their victims were from the healthcare industry (12 out of 57 victims).
Ransomhub: Only 9.3% of their victims were from the healthcare industry (19 out of 204 victims). However, they replaced Lockbit3 as the most prominent RaaS group and the sheer volume of attacks puts them on the top with the most victims in the Healthcare industry.
The relatively even distribution among many groups indicates high interest in this industry, especially in the US.
Geographic Distribution
The geographic distribution of ransomware victims in the healthcare industry reflects the industry’s nature. Meaning in most countries there is public healthcare, often not well funded. But in the US healthcare is privatized and a very profitable business, therefore it is highly targeted.
64% of all victims with identified geography are located in the US.
In total, 25 countries recorded ransomware victims in the healthcare industry.
For a comprehensive, up-to-date global ransomware tracking report, please refer to our new monthly “Tracking Ransomware” series here.
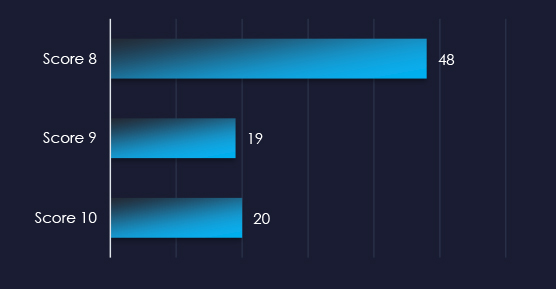
Over the past 3 months, CYFIRMA’s DECYFIR platform recorded 5,711 reported vulnerabilities with a score higher than 8. This is out of a total of 16,063 reported vulnerabilities.
Filtered by vendors, we have observed 137 vulnerabilities related specifically to the Healthcare industry out of which 87 have a score of 8 or higher. 4 of the reported vulnerabilities have a known exploit.
| Title | NIST Link |
| CVE-2019-0708 : A remote code execution vulnerability exists in Remote Desktop Services formerly known as Terminal Services when an unauthen… | https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2019-0708 |
| CVE-2017-0143 : The SMBv1 server in Microsoft Windows Vista SP2; Windows Server 2008 SP2 and R2 SP1; Windows 7 SP1; Windows 8.1; Windows Ser… | https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2017-0143 |
| CVE-2021-44228 : Apache Log4j2 2.0-beta9 through 2.15.0 (excluding security releases 2.12.2 2.12.3 and 2.3.1) JNDI features used in config… | https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2021-44228 |
| CVE-2017-0144 : The SMBv1 server in Microsoft Windows Vista SP2; Windows Server 2008 SP2 and R2 SP1; Windows 7 SP1; Windows 8.1; Windows Ser… | https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2017-0144 |
In the past 90 days, Healthcare organizations have faced moderate to high risk across monitored categories.
APT campaigns The healthcare sector experienced a minimal impact from APT campaigns, with only 1 out of 11 observed campaigns affecting the industry, occurring in September. Threat actors involved were Russia’s Fancy Bear (nation-state sponsored) and TA505 (cybercrime syndicate). The campaigns impacted nine countries, mostly in East Asia, targeting web applications.
Phishing The healthcare sector is not a popular target for phishing due to its fragmented nature and lack of direct monetization avenues. Only one healthcare-related organization, French Health Insurance, was impersonated, which functions more as a financial institution. Phishing attacks primarily originated from the United States and Brazil.
Ransomware The healthcare industry is the 4th most frequent victim of ransomware attacks, facing a moderate risk globally but a high risk in the United States due to its profitable privatized healthcare system. A mild spike in activity was observed in August, with RansomHub being the most active group. Out of 59 active ransomware groups, 40 targeted healthcare, indicating high interest—especially in the U.S., where 64% of the victims are located. Attacks were recorded in 25 countries overall.
Vulnerabilities Over the past three months, 5,711 high-severity vulnerabilities were reported out of 16,063 total. Specifically, 137 vulnerabilities related to the healthcare industry were identified, with 87 scoring 8 or higher and four with known exploits, representing potential risks that require immediate attention.