



The CYFIRMA Industry Report delivers original cybersecurity insights and telemetry-driven statistics of global industries, covering one sector each week for a quarter. This report focuses on the automotive industry, presenting key trends and statistics in an engaging infographic format.
Welcome to the CYFIRMA infographic industry report, where we delve into the external threat landscape of the automotive industry over the past three months. This report provides valuable insights and data-driven statistics, delivering a concise analysis of attack campaigns, phishing telemetry, and ransomware incidents targeting the automotive industry.
We aim to present an industry-specific overview in a convenient, engaging, and informative format. Leveraging our cutting-edge platform telemetry and the expertise of our analysts, we bring you actionable intelligence to stay ahead in the cybersecurity landscape.
CYFIRMA provides cyber threat intelligence and external threat landscape management platforms, DeCYFIR and DeTCT, which utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning to ingest and process relevant data, complemented by manual CTI research.
For the purpose of these reports, we leverage the following data from our platform. These are data processed by AI and ML automation based on both human research input and automated ingestions.
While this report contains statistics and graphs generated primarily by automation, it undergoes thorough review and enhancement for additional context by CYFIRMA CTI analysts to ensure the highest quality and provide valuable insights.
Advanced Persistent Threat Attack Campaigns
Automotive organizations featured in 1 out of the 9 observed campaigns, which is a presence in 11% of campaigns.
Observed Campaigns per Month

The monthly chart shows a single observed campaign in August and underscores a significant drop in active observed campaigns since the spike observed in July.
Suspected Threat Actors

FIN11 and FIN7 are suspected threat actors behind August attack campaign.
GEOGRAPHICAL DISTRIBUTION
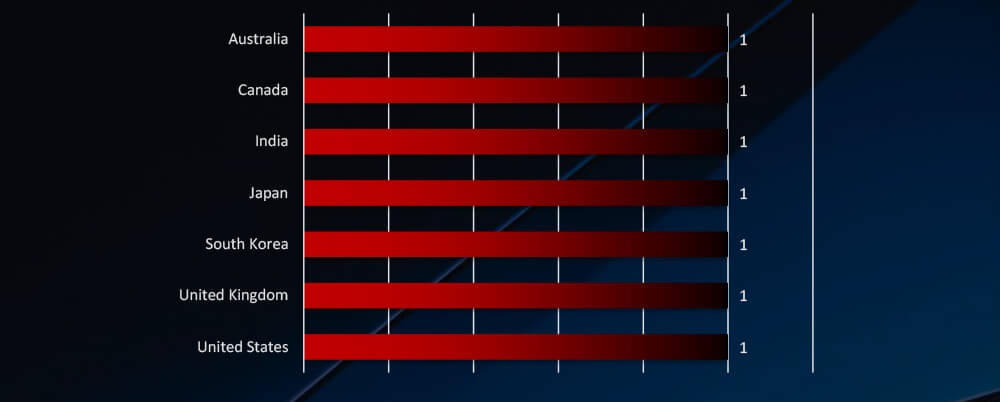

Victims of the same attack campaign were recorded in 7 different countries.
TOP ATTACKED TECHNOLOGY

Attack campaign focused on attacking application infrastructure and database software.
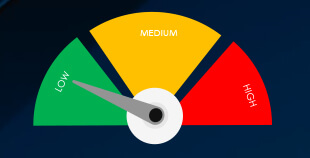
Risk Level Indicator: Low
Monthly activity has witnessed a significant decline since the surge in the summer attributed to North Korean and Chinese threat actors. Subsequently, only 9 new campaigns have been uncovered in the past 90 days. Long-term data reveals a cyclical pattern in which the discovery of new Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) leads to a surge in campaign identification, followed by a period of relative calm. However, we presume that threat actors remain active, potentially in a state of temporary withdrawal or employing as-yet-undetected TTPs.
When it comes to suspected threat actors targeting automotive organizations, financially motivated threat actors dominate over the nation-state APTs. Specifically notorious large ransomware groups such as FIN7 and FIN11.The single observed campaign in the last 90 days is attributed to threat actors with known links to Cl0p and BlackBasta ransomware groups.
In terms of geographical impact, it is hard to draw any insight from only one observed campaign, however, long-term data from the previous 90-day report suggest an obvious correlation with countries known for strong automotive industries, including growing interest in the Indian booming automotive industry.
Application infrastructure and open-source database software were the two targeted technologies in the automotive victims.
Over the past 3 months, CYFIRMA’s telemetry recorded no phishing campaigns out of a total of 218,820 that impersonated the automotive industry.
Since there are consistently no wider phishing attack campaigns impersonating automotive sector, it is not tracked as a category.
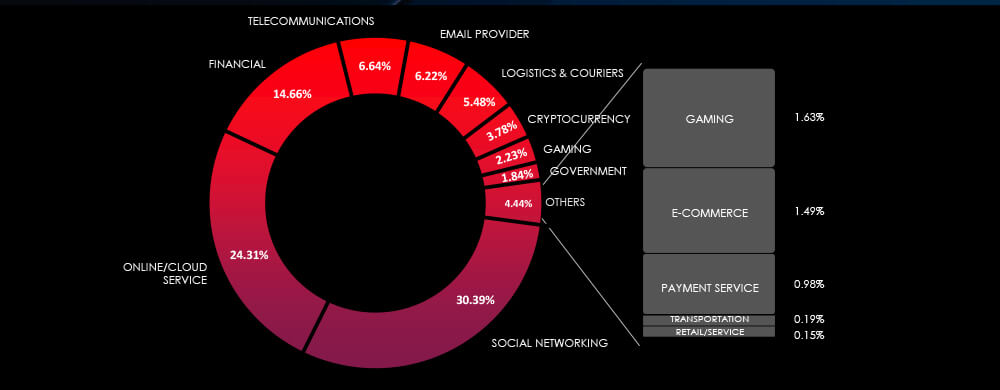
Global Distribution of Phishing Themes per Sector
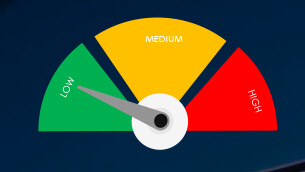
Risk Level Indicator: Low
Along the same lines as general manufacturing and excluding spear-phishing attacks by geopolitically motivated APTs and ransomware affiliates, the automotive industry is not considered an attractive lure or target for phishing campaigns for several reasons. Primarily, the analogue nature of their operations results in a lack of easily monetizable data to target. Automotive companies typically have less direct access to high-value personal or financial information that cybercriminals typically target, such as credit card data or social security numbers.
Simultaneously, the complex machinery and technologies involved in the automotive industry are hard to understand. Therefore, cybercriminals prefer to focus on other industries with greater rewards for less work and more straightforward ways to monetize.
In the past 90 days, CYFIRMA has identified 67 verified ransomware victims within the automotive industry sectors. This accounts for 3.8% of the overall total of 1,766 ransomware incidents during the same period.
The Monthly Activity Chart

Monthly trends show consistent numbers across months
Breakdown of Monthly Activity by Gang
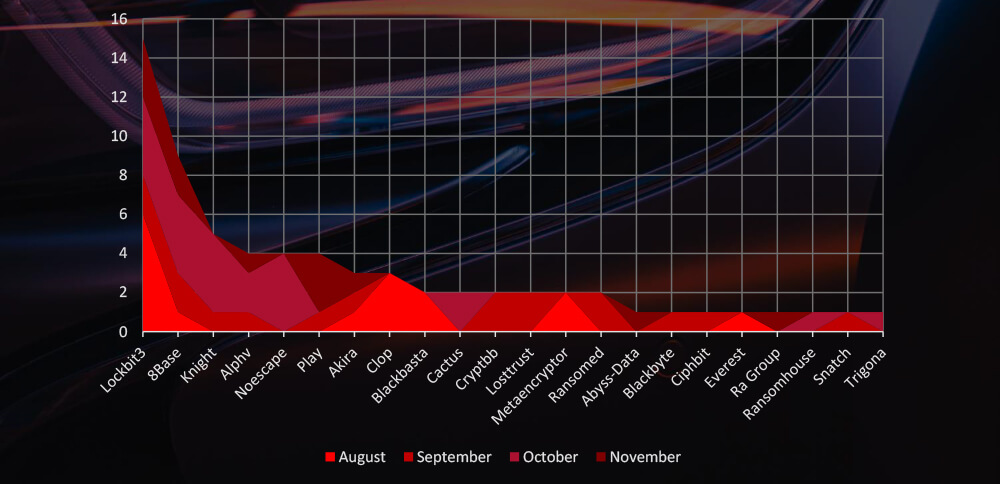
A breakdown of the monthly activity provides insights per group activity. For example, Cl0p gang recording victims only in August, whereas Lockbit3 has been consistently active.
Ransomware Victims in Automotive Industry per Group
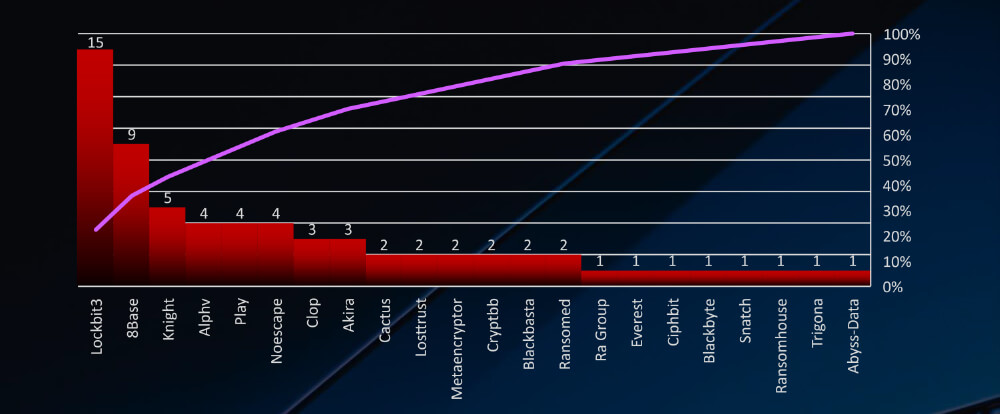
In total 22 out of 55 groups recorded automotive organization victims in the past 90 days. The top 4 are responsible for half of them.
Comparison to All Ransomware Victims by Group (Top 25)
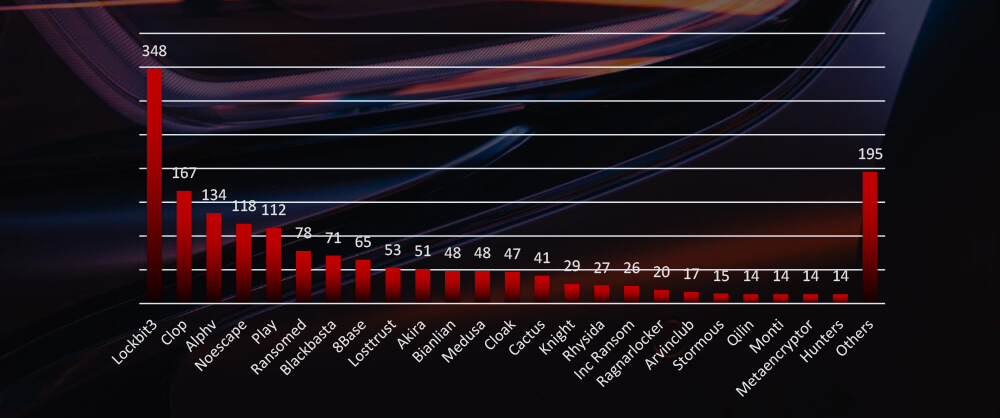
Compared to all recorded victims in the same time period, some groups like 8base and Knight have a comparatively higher share of automotive victims, suggesting higher interest.
Geographic Distribution Of Victims
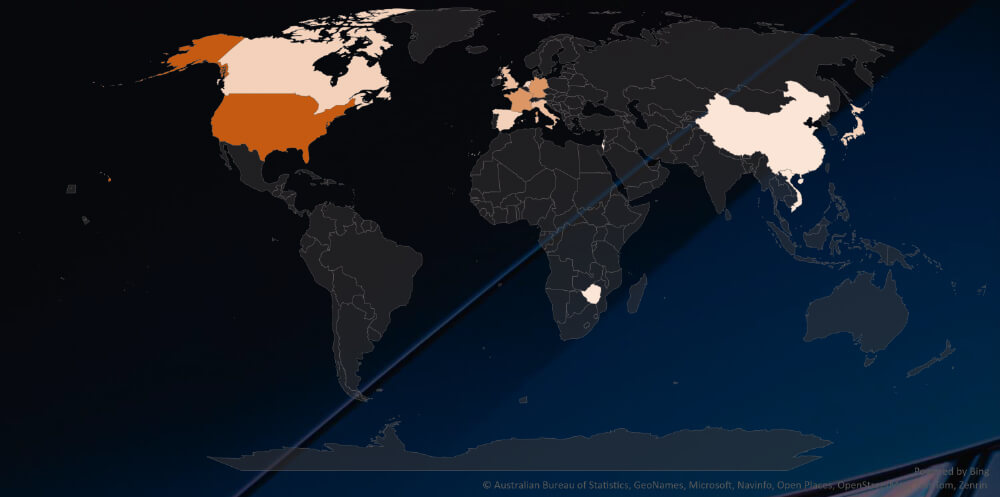
The heatmap of geographic distribution illustrates the global reach of ransomware across continents and is considerably correlated with economies known for automotive industry.
Total Victims per Country
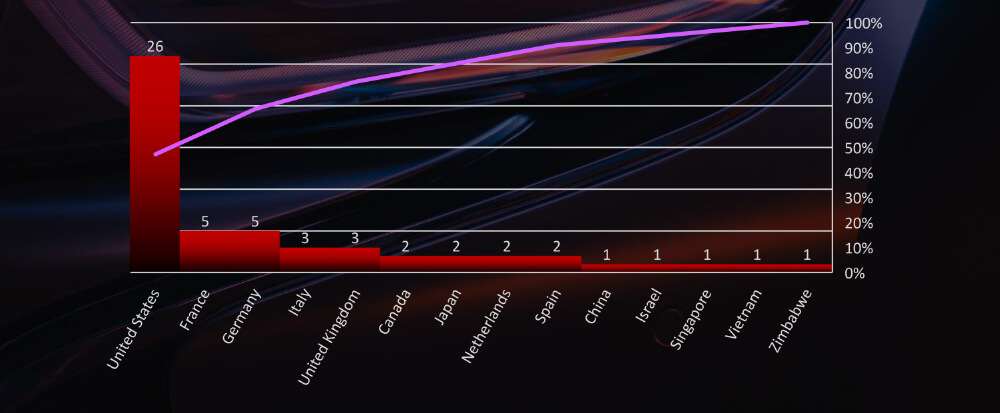
In total 14 countries recorded automotive industry ransomware victims with the US alone accounting for 47% of all.
Sectors Distribution
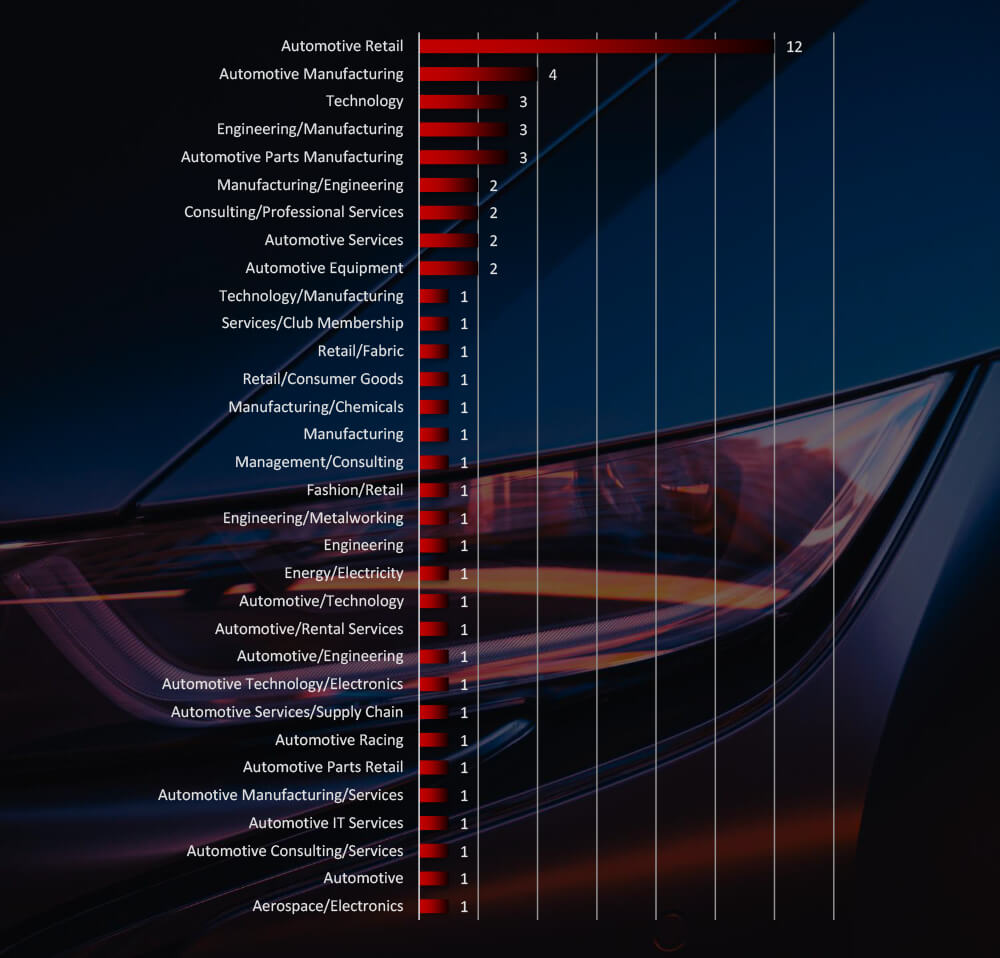
Listing all sectors matched under the automotive industry umbrella shows victims across sectors, including many niches.
Risk Level Indicator: High
The automotive industry is among the most targeted sectors for ransomware attacks. Although the total numbers may not rival those of other industries, its narrow focus results in a notably high percentage of victims. Monthly cyberactivity consistently reveals significant volumes of attacks. A closer examination of responsible groups highlights the August rampage of the Cl0p gang, while Lockbit3, 8base, and ALPHV demonstrate sustained interest and a high number of victims.
Data regarding the total number of victims per group indicates that the automotive industry is primarily targeted by larger gangs. However, a new group (appeared in August 2023) named ‘Knight’ recorded the third-highest number of victims, surpassing well-known entities like ALPHV or Noescape.
Of the 55 identified victims across 14 different countries, the United States emerges as the most affected, with 26 recorded incidents, followed by France, Germany, and Italy. This trend strongly correlates with the presence of renowned automotive powerhouses in these regions.
For a comprehensive, up-to-date global ransomware tracking report on a monthly basis, please refer to our new monthly “Tracking Ransomware” series here.
In assessing the cybersecurity landscape within the automotive industry, the threat of ransomware remains notably high, with larger gangs showing sustained interest and the emergence of new mid-sizes gangs . Geographically, the United States and prominent European countries stand as primary targets, aligning with their robust automotive presence.
Conversely, the risk posed by phishing campaigns within the industry is low. The analog nature of operations and the complexity of automotive technologies serve as deterrents for cybercriminals, who find other sectors more lucrative and easier to exploit.
While recent months indicate a decline in APT campaign activity, potentially signalling a temporary pause in known tactics, financially motivated threat actors—particularly those associated with major ransomware groups like FIN7 and FIN11—remain significant concerns. Geographical correlations reinforce ransomware trends, linking campaigns to countries known for robust automotive industries, including a burgeoning interest in India’s automotive sector.