


CVE-2026-23760 represents a severe authentication bypass vulnerability in SmarterTools SmarterMail email server software. The flaw exists in the password reset API endpoint (force-reset-password), which permits unauthenticated requests and critically fails to verify existing passwords or reset tokens when resetting system administrator accounts.
An unauthenticated remote attacker can exploit this vulnerability by sending a crafted HTTP POST request to the vulnerable endpoint containing only a target administrator username and a new password. The application accepts this request and resets the administrator password without requiring the existing password or a valid reset token. Once authenticated with the newly set credentials, the attacker gains access to built-in administrative functionality that permits direct execution of operating system commands, effectively providing SYSTEM-level (Windows) or root-level (Linux) access to the underlying host.
The vulnerability is under active exploitation in the wild. Security researchers have identified more than 10000+ potentially vulnerable instances globally as of late January 2026. Evidence of active exploitation emerged on January 17, 2026—just 2 days after SmarterTools released the patch. Multiple security organizations, including CISA (U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency), added this vulnerability to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog on January 26, 2026.
SmarterTools SmarterMail is an enterprise-grade email server solution widely deployed across organizations globally for handling business email communications. The software provides comprehensive email server functionality, including webmail access, calendar management, file storage, and administrative features.
CVE-2026-23760 stems from a fundamental security design flaw in the authentication service’s password reset functionality. The ForceResetPassword method in the SmarterMail.Web.Api.AuthenticationController class permits anonymous access via the [AuthenticatedService(AllowAnonymous = true)] attribute. While anonymous access to password reset endpoints is common practice, the critical failure lies in the code’s conditional branching based on the user-controlled IsSysAdmin Boolean parameter.
When processing administrator account password resets (triggered by IsSysAdmin=true), the application completely bypasses validation of the existing password despite accepting an OldPassword parameter in the request. This represents a catastrophic authentication control failure, as the system trusts user-supplied data to determine whether to enforce security controls. Ironically, the regular user password reset flow correctly validates the existing password, making this a privilege-specific vulnerability that affects only the most powerful accounts in the system.
Key Takeaways:
Acknowledgements:
CYFIRMA Research acknowledges the collective contributions of cybersecurity researchers, vendors, and the broader security community in identifying and analyzing CVE-2026-23760. Their rapid response and responsible disclosure efforts have been critical in accelerating mitigation and helping organizations defend against ongoing exploitation.
The vulnerability exists in the ForceResetPassword method of the AuthenticationService class within the SmarterMail web API. The code implements two distinct execution paths based on the value of the user-controllable IsSysAdmin Boolean parameter received in the JSON request body:
The administrator-specific code path retrieves the administrator account details using the supplied username, validates the new password against password complexity requirements, but critically omits validation of the OldPassword field. Despite accepting this parameter in the API request structure, the application never checks whether it matches the current administrator password. The code then proceeds to create a new password hash and updates the database directly.
Technical Impact
Successful exploitation of CVE-2026-23760 results in complete compromise of the SmarterMail server and underlying host system:
| Impact Category | Description | Severity |
| Confidentiality | Complete access to all email communications, user credentials, calendar data, file storage, and system configuration | HIGH |
| Integrity | Ability to modify/delete emails, create backdoor accounts, alter system settings, inject malware, modify application code | HIGH |
| Availability | Complete control over email service availability, potential for ransomware deployment, DoS capabilities | HIGH |
| Privilege Escalation | Direct escalation from unauthenticated network access to SYSTEM/root privileges on the host operating system | CRITICAL |
| Lateral Movement | Compromised email server can be used as a pivot point for attacks against internal network resources | HIGH |
| Persistence | Attackers can establish multiple persistence mechanisms, including backdoor accounts, scheduled tasks, and system-level implants | HIGH |
Business Impact
The business consequences of a successful attack extend far beyond technical compromise:
All versions of SmarterTools SmarterMail prior to Build 9511 are vulnerable to CVE-2026-23760. The vulnerability was patched in Build 9511, released on January 15, 2026, with additional security improvements in Build 9518, released on January 22, 2026.
| Version Status | Build Number | Release Date | Vulnerability Status | Recommendation |
| Vulnerable | All builds < 9511 | Before Jan 15, 2026 | VULNERABLE | UPGRADE IMMEDIATELY |
| Patched | Build 9511 | January 15, 2026 | PATCHED | Minimum acceptable version |
| Recommended | Build 9518+ | January 22, 2026 | PATCHED | Includes additional security fixes |
Version Identification
Organizations can identify their current SmarterMail version through:
| Indicator | Status | Details |
| Exploit Availability | YES | Public PoC available; Nuclei template released; GitHub repositories contain working exploits |
| Active Attacks | YES | Confirmed exploitation since Jan 17, 2026 (2 days post-patch); Shadowserver detecting active scanning |
| Dark Web Chatter | HIGH | Vulnerability discussed in underground forums; Patch diffing tutorials shared |
| Attack Complexity | LOW | Single HTTP request required; No authentication needed; Predictable admin usernames |
| Weaponization | YES | Integrated into automated scanning tools and exploitation frameworks |
| CISA KEV Status | LISTED | Added to KEV catalog Jan 26, 2026; Federal remediation deadline Feb 16, 2026 |
| EPSS Score | 29.55% | Estimated probability of exploitation in next 30 days (significantly elevated) |
| Ransomware Usage | UNKNOWN | CISA indicates unknown ransomware campaign usage; High likelihood given exploit characteristics |
Exploit Chain Walkthrough
The complete attack sequence demonstrates the critical nature of this vulnerability:
Attacker identifies SmarterMail instance via:
Attacker confirms vulnerability presence by attempting a benign authentication check or analyzing version information against known vulnerable builds.
Attacker crafts and delivers an exploit payload:
Proof of Concept (PoC) Code
The following HTTP request demonstrates the authentication bypass vulnerability:
Source: watchTowr Labs – PoC Code
Successful Exploitation Response
Upon successful exploitation, the server responds with:
The success: true response confirms that the administrator password has been successfully reset to the attacker-controlled value.
Post-Exploitation: Remote Code Execution
Once authenticated as a system administrator, the attacker proceeds to RCE via the Volume Mounts feature:
In the “Volume Mount Command” field, the attacker enters an arbitrary operating system command. For example:
When configuration is saved, SmarterMail executes the command with elevated privileges:
Technical Specifics: API Request Structure
The ForceResetPasswordInputs object structure that enables the bypass:
The fundamental design flaw: the application trusts the client-supplied IsSysAdmin value to determine whether to enforce security controls. When set to true, the code bypasses password validation entirely, relying solely on username existence and new password complexity checks.
Upgrade to SmarterMail Build 9511 or later immediately. Build 9518 (released January 22, 2026) is recommended as it includes additional security improvements, including NTLM relay attack mitigations.
Patch Implementation Steps
Step 1: Pre-Upgrade Preparation
Take a full backup of the SmarterMail installation, database, and configuration files. Document the current version and configuration settings. Schedule maintenance window with user notification.
Step 2: Download Patch
Download Build 9518 or later from the official SmarterTools website: https://www.smartertools.com/smartermail/downloads
Step 3: Apply Upgrade
Follow vendor upgrade procedures for your platform (Windows/Linux). Verify application starts successfully, and all services are operational post-upgrade.
Step 4: Verify Patch
Confirm build number in Settings → About. Assess that exploitation attempts fail with the “Invalid input parameters” error message.
Step 5: Post-Patch Forensics
Conduct a comprehensive security assessment to identify potential prior compromise.
Target Geography
With approximately 10000+ vulnerable SmarterMail instances identified through internet-wide scanning. Significant concentrations have been observed in the United States, Western Europe (notably Germany, the United Kingdom, and France), Asia-Pacific business hubs, and parts of Latin America. Given that SmarterMail deployments are typically internet-facing for webmail and API access, exposed systems are actively scanned and targeted by threat actors worldwide, with exploitation activity observed shortly after patch disclosure.
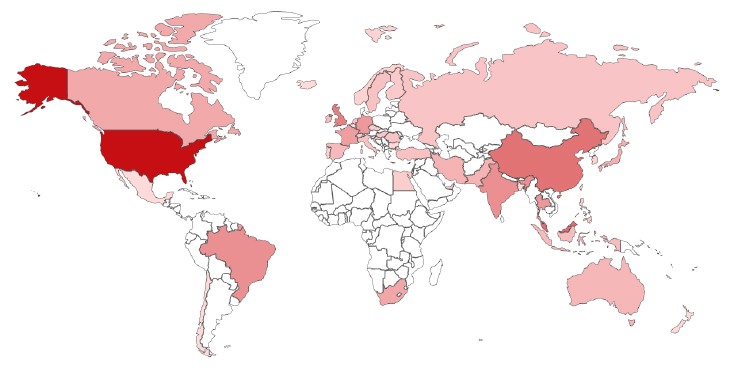
Target Industry
The vulnerability primarily impacts small-to-medium businesses, managed service providers, educational institutions, healthcare organizations, and government entities. These sectors rely heavily on email infrastructure for operational continuity, identity workflows, and sensitive communications. Managed service providers represent particularly high-value targets due to multi-tenant exposure, where a single compromise can affect multiple downstream customers. Successful exploitation may result in mailbox compromise, credential harvesting, data exfiltration, and potential ransomware deployment.
Target Technology
CVE-2026-23760 affects internet-exposed, on-premises SmarterMail email server deployments running unpatched versions. It is part of a broader cluster of critical vulnerabilities disclosed in January 2026, including CVE-2025-52691 and CVE-2026-24423, both involving remote code execution vectors. The clustering of high-severity flaws indicates systemic security weaknesses within the application. Exploitation enables remote code execution, unauthorized mailbox access, persistence establishment, and potential lateral movement across connected enterprise systems.
Currently, threat actors are actively discussing the vulnerability. However, the CYFIRMA Research team is continuously monitoring for more new developments or discussions.
CVE-2026-23760 represents a critical security vulnerability with severe real-world impact. The pre-authentication nature, low attack complexity, and direct path to SYSTEM/root-level compromise make this vulnerability exceptionally dangerous. The rapid weaponization and active exploitation within 48 hours of patch release demonstrate that threat actors are actively monitoring and exploiting SmarterMail vulnerabilities.