


CVE‑2025‑5777 is a critical information disclosure vulnerability in Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway appliances, caused by unsafe memory handling in the authentication process. The flaw allows unauthenticated remote attackers to perform out-of-bound memory readings, resulting in the leakage of sensitive data, such as session tokens, credentials, and potentially administrative secrets.
This CYFIRMA research investigates the active exploitation of CVE‑2025‑5777, based on observed attacker behavior and available public intelligence. A functional proof-of-concept (PoC) code has been widely circulated across offensive security communities and platforms. Threat actors may exploit this vulnerability by sending malformed HTTP POST requests to exposed authentication endpoints, which may result in the leakage of uninitialized memory content embedded in XML responses.
Immediate mitigation requires applying vendor-issued patches, terminating active user sessions post-upgrade, monitoring for indicators of memory leaks, enforcing strict network segmentation, and deploying WAF rules to detect and block malformed authentication requests.
CVE‑2025‑5777 is a newly disclosed critical vulnerability affecting Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway appliances, widely deployed in enterprise environments to enable secure remote access, VPN connectivity, and application delivery. Classified as an information disclosure vulnerability, CVE‑2025‑5777 allows unauthenticated attackers to exploit a memory management flaw in the authentication process to leak sensitive data from system memory.
The vulnerability arises from improper handling of crafted HTTP POST requests during authentication, which causes uninitialized memory to be returned in server responses. This flaw enables attackers to extract session tokens, usernames, and potentially privileged credentials without needing to authenticate. Given the critical role of NetScaler appliances in remote access and traffic management, exploitation of this vulnerability poses significant risks to enterprise infrastructure.
Critical Information Disclosure Vulnerability: CVE 2025 5777 is a high-severity information disclosure flaw in Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway, allowing unauthenticated attackers to leak sensitive memory contents, including session tokens and credentials.
Memory Leak via Malformed Authentication Requests: The vulnerability results from improper memory handling in the authentication process, where crafted HTTP POST requests return uninitialized memory data in XML responses.
Active Exploitation Confirmed: Public proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits are widely available, and security researchers have observed active in-the-wild exploitation, increasing the urgency for defensive actions.
Widespread Deployment in Remote Access Infrastructure: NetScaler appliances are used across government, financial, healthcare, and enterprise sectors, making this vulnerability a major risk to organizations relying on them for secure access and traffic management.
Immediate Mitigation Essential: Organizations must urgently apply Citrix’s released patches, terminate active sessions, enforce segmentation, deploy WAF signatures to detect malicious authentication traffic, and monitor for indicators of compromise.
CYFIRMA Research acknowledges the collective contributions of cybersecurity researchers, vendors, and the broader security community in identifying and analyzing CVE‑2025‑5777. Their rapid response and responsible disclosure efforts have been critical in accelerating mitigation and helping organizations defend against ongoing exploitation.
Vulnerability Type: Information Disclosure via Memory Leak during Authentication
CVE ID: CVE‑2025‑5777
Application: Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway (VPN/AAA mode)
Impact: Unauthenticated attackers can exploit the vulnerability to leak memory contents, including session tokens and credentials, potentially hijacking sessions and bypassing authentication controls.
Severity: Critical
Affected Versions:
– NetScaler ADC and Gateway 14.1 < 14.1‑43.56
– NetScaler ADC and Gateway 13.1 < 13.1‑58.32
– NetScaler ADC and Gateway 13.1‑FIPS/NDcPP < 13.1‑37.235‑FIPS/NDcPP
– NetScaler ADC and Gateway 12.1‑FIPS < 12.1‑55.328‑FIPS
Patch Available: Yes
Mitigation: Apply the latest Citrix security updates, terminate active sessions post-patch, implement WAF rules for authentication endpoints, and restrict public exposure of affected services.
CVE‑2025‑5777 is a critical information disclosure vulnerability affecting Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway appliances operating in VPN or AAA mode.
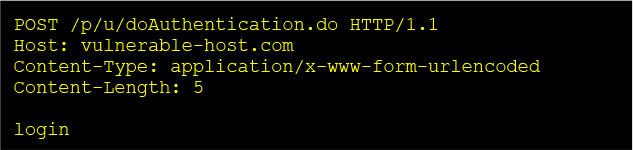
By sending malformed login requests to the authentication endpoint (/p/u/doAuthentication.do), attackers can trigger memory over-read conditions where sensitive data—such as active session tokens, credentials, and internal secrets—are returned within XML response elements. This vulnerability is especially dangerous due to the pre-authentication nature of the attack, allowing external actors to obtain privileged access tokens without valid credentials.
Given the critical role of NetScaler in enterprise and government infrastructure, successful exploitation could lead to session hijacking, MFA bypass, unauthorized access to internal applications, and lateral movement within networks.
Unauthorized Information Disclosure: CVE‑2025‑5777 enables unauthenticated attackers to leak sensitive memory contents, including valid session tokens, usernames, and credentials.
Session Hijacking & MFA Bypass: Extracted tokens can be used to impersonate legitimate users, bypassing multi-factor authentication and gaining privileged access to internal systems.
Lateral Movement Opportunities: Once access is gained, attackers can pivot within the network, potentially targeting additional systems and resources connected through NetScaler.
Credential Theft & Reconnaissance: The vulnerability exposes authentication flows and in-memory secrets that can be weaponized for further attacks or persistent access.
Service Compromise & Abuse: Compromised sessions could allow attackers to disrupt services, reconfigure access policies, or proxy malicious traffic through enterprise gateways.
High Risk Due to Active Exploitation: The availability of public PoC exploits and confirmed in-the-wild abuse significantly raises the risk of widespread exploitation, especially in unpatched environments.
This issue affects Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway appliances operating in VPN or AAA mode in the following versions:
Appliances not configured in VPN or AAA mode are not affected by this vulnerability.
Is there already an exploit tool to attack this vulnerability?
Yes, public proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits for CVE‑2025‑5777 have been released and are actively circulating on platforms such as GitHub, Reddit, and underground cybercrime forums. The exploit involves sending malformed HTTP POST requests to authentication endpoints to extract uninitialized memory, making it relatively easy to replicate.
Has this vulnerability already been used in an attack?
Yes, active exploitation of CVE‑2025‑5777 has been confirmed in the wild.
Are hackers discussing this vulnerability in the Deep/Dark Web?
Yes, the vulnerability has gained attention in underground communities. Discussions and shared PoCs have been observed on dark web forums, significantly raising the potential for automated attacks and mass exploitation campaigns.
What is the attack complexity level?
The attack complexity for CVE‑2025‑5777 is classified as LOW.
Historical Trends and Known Exploits
Memory disclosure vulnerabilities in Citrix NetScaler appliances have previously led to major breaches, as seen in the CitrixBleed (CYFIRMA’S REPORT ON CVE‑2023‑4966) incident. CVE‑2025‑5777 follows a similar pattern, with rapid PoC release, in-the-wild exploitation, and global scanning. Its low complexity and high impact mirror past exploitation trends and demand an urgent organizational response.
Organizations should immediately apply patches, monitor authentication endpoints, terminate all active sessions post-patch, and enforce WAF rules to prevent unauthorized access attempts.
CVE 2025 5777 is a heap memory disclosure vulnerability within the Citrix NetScaler authentication handler. It affects appliances configured with VPN or AAA virtual servers. The issue stems from the improper handling of form parameters in application/x-www-form-urlencoded POST requests processed by the authentication servlet at /p/u/doAuthentication.do.
Root Cause – Authentication Servlet Misbehavior
NetScaler’s backend (like a Java-based Spring or proprietary servlet component) parses incoming POST requests using a deserialization routine that extracts user credentials and initializes internal session objects.
In vulnerable versions, when a POST request contains a parameter without an associated key-value assignment — for instance, login with no = or value — the server:
The InitialValue XML field is constructed using StringBuilder.append() or a similar function that wraps byte buffers directly into a string without proper zeroization or bounds checking. Consequently, raw heap data—often remnants of session memory, credential strings, or previous request payloads—gets embedded within the <InitialValue> tag of the server’s response.
This behavior indicates a likely flaw in the low-level parameter parsing logic (HttpServletRequest.getParameterMap() or a custom parser) that fails to validate or sanitize malformed keys during binding and response serialization.
Request Structure and Flow
Triggering Request:
Leaking Response Example:
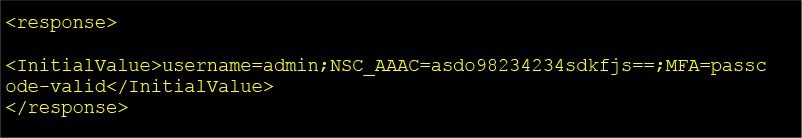
Depending on the heap state, the leaked memory may contain:
Technical Conditions for Exploitation
Post-Leak Abuse
Once a valid NSC_AAAC token is captured from a memory leak:
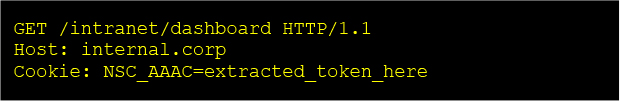
The NetScaler backend validates the session as authenticated, skipping MFA and user login. This grants full access to the VPN, web SSO applications, or administrative interfaces mapped behind the gateway.
To mitigate the risks associated with CVE 2025 5777, organizations are strongly advised to take the following technical measures immediately:
Upgrade to Patched Builds:
Apply the latest Citrix security updates to NetScaler ADC and Gateway appliances. Ensure firmware versions are updated to:
Terminate All Active Sessions: After applying patches, explicitly terminate all existing VPN and user sessions to prevent reuse of any leaked tokens using commands such as:
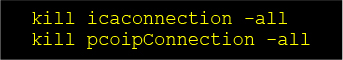
Enforce Strong Authentication Policies: Enable session binding (IP, device fingerprint) and reauthentication mechanisms to reduce the risk of token replay attacks. Implement time-based expiration of session tokens.
Deploy a Web Application Firewall (WAF): Use WAF rules to detect and block malformed POST requests to authentication endpoints (/p/u/doAuthentication.do). For example, block requests where form parameters do not follow a valid key=value structure.
Limit Public Exposure: Restrict access to NetScaler management and authentication interfaces using IP allowlists, internal-only network zones, and strong ACLs. Do not expose authentication endpoints to the open internet if not absolutely required.
Monitor and Analyze Logs: Actively monitor NetScaler logs for anomalous activity, including:
Enable Rate Limiting and Session Throttling: Configure rate limits for authentication endpoints to detect and block enumeration, memory leak harvesting, or abuse patterns.
Implement Deep Packet Inspection (DPI): Deploy IDS/IPS or DPI tools to analyze inbound HTTP traffic for attack signatures and unauthorized API calls targeting authentication workflows.
Network Segmentation and Zero Trust Principles: Isolate NetScaler devices from production workloads and internal management networks. Apply the principle of the least privilege of lateral communication between systems.
Conduct Proactive Threat Hunting: Investigate internal authentication flows and audit privileged user sessions created during the exposure window to detect any signs of compromise.
Target Geography
The impact of CVE‑2025‑5777 is global in scope, with vulnerable Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway appliances identified across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Middle East. As these devices are often deployed at the edge of enterprise networks to manage secure remote access and authentication, publicly exposed instances are being actively scanned and exploited by threat actors worldwide.
Target Industry
Industries most at risk include telecommunications, financial services, government, and healthcare sectors that depend on Citrix infrastructure for secure connectivity and identity management. These environments often host sensitive data and mission-critical systems behind NetScaler Gateways, making successful exploitation highly impactful. Service providers and managed security vendors using Citrix for multi-tenant infrastructure are also prime targets due to the potential for cascading compromise.
Target Technology
Technologically, the vulnerability affects Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway appliances operating in VPN or AAA mode, specifically in versions prior to the security-fixed firmware releases. These systems manage core authentication workflows and issue session tokens that can be hijacked once leaked. As these appliances are integrated with identity providers, internal apps, and virtual desktop environments, exploitation of CVE‑2025‑5777 can compromise broader trust architectures and backend systems.
Currently, threat actors are actively discussing the vulnerability. However, the CYFIRMA Research team is continuously monitoring for new developments or discussions.
The case of CVE‑2025‑5777 underscores the severe consequences of improper input handling in authentication workflows within critical network infrastructure. This vulnerability highlights the urgent need for organizations to implement proactive security practices, including prompt patching, robust session management, and strict segmentation of publicly exposed services like Citrix NetScaler.
As exploitation continues in the wild, this incident serves as a stark reminder that even mature and widely adopted platforms remain susceptible to subtle but dangerous flaws. Continuous security assessments, threat intelligence integration, and rapid incident response readiness are essential to mitigating the evolving risks posed by targeted exploitation of authentication and access control layers.