



CVE-2024-7593 is a critical vulnerability identified in Ivanti Virtual Traffic Manager (vTM) and has recently been included in CISA’s Known Exploitable Vulnerabilities (KEVs) catalogue. This vulnerability, which carries a CVSS score of 9.8, allows unauthenticated attackers to gain administrative access to the vTM system. Such access opens the door to a range of serious risks, including data theft, unauthorized deployment of malware, and complete loss of control over the network infrastructure. Organizations using vTM are strongly urged to address this vulnerability promptly to mitigate the potential for exploitation and safeguard their critical systems.
CVE-2024-7593 is a critical authentication bypass vulnerability affecting vTM. This flaw allows remote attackers, without prior authentication, to create an administrator account, granting them full control over the system. Exploiting the vulnerability requires access to the vTM management interface. Although no active exploitation has been reported, the availability of public exploit code significantly raises the risk. Ivanti has released patches to address the issue, and organizations must secure their systems immediately to prevent potential breaches.
Key Takeaways:
Acknowledgements:
The CYFIRMA Research team acknowledges security researchers who responsibly disclosed this vulnerability.
Vulnerability Type: Remote unauthenticated attacker to bypass authentication
CVE ID: CVE-2024-7593
CVSS Severity Score: 9.8 (Critical)
Application: Ivanti Virtual Traffic Manager
Impact: Allowing authentication bypass, and creation of an administrator user.
Severity: CRITICAL
Affected Versions: Ivanti Virtual Traffic Manager 22.2 through 22.7R1
Patch Available: Yes
CVE-2024-7593 allows an unauthenticated, remote attacker to access the vTM management interface and create an administrator account, effectively gaining full control over the system. Exploiting this vulnerability could lead to serious consequences, such as unauthorized access to sensitive data, system manipulation, and disruption of network operations. While no active exploitation has been observed, the existence of publicly available exploit code significantly elevates the risk of attacks. Ivanti has issued patches to address this vulnerability, and immediate remediation is advised to mitigate potential threats.
Exploiting CVE-2024-7593 allows an unauthenticated attacker to gain administrative access giving attackers the potential to assume full control of the system, leading to unauthorized access, data theft, and the deployment of malware. Additionally, they could disrupt network operations, potentially launching DDoS attacks or manipulating critical network traffic. The public availability of exploit code further increases the likelihood of exploitation, making it essential for organizations to immediately apply patches and mitigate the threat to prevent severe operational and security impacts.
CVE-2024-7593 affects several versions of Ivanti vTM, specifically 22.2, 22.3, 22.3R2, 22.5R1, 22.6R1, and 22.7R1. Organizations utilizing any of these versions are strongly advised to apply the available patches promptly to safeguard against exploitation of this critical authentication bypass vulnerability.
Is there already an exploit tool to attack this vulnerability?
Yes, there is a publicly available exploit code for CVE-2024-7593. While Ivanti has stated that no known exploitation has been observed, the existence of exploit tools increases the risk that attackers could leverage this vulnerability to gain unauthorized access to Ivanti vTM systems. Organizations should prioritize applying patches and implementing security measures to mitigate potential threats.
Has this vulnerability already been used in an attack?
As of now, there have been no reported instances of CVE-2024-7593 being actively exploited in attacks. However, Ivanti has emphasized that a publicly available exploit code exists, which raises concerns about the potential for future attacks. Organizations are encouraged to take immediate action by applying patches and enhancing security measures to prevent any possible exploitation.
Are hackers discussing this vulnerability in the Deep/Dark Web?
Yes, hackers are discussing CVE-2024-7593 in the Deep and Dark Web, and they are sharing PoC exploits related to this vulnerability. This activity heightens the urgency for organizations to address the vulnerability promptly, as the availability of PoC exploits can facilitate potential attacks. Companies must implement the necessary patches and security measures to protect against exploitation.
What is the attack complexity level?
The attack complexity level for affecting Ivanti vTM is assessed as critical.
Our analysis has identified vulnerable, internet-exposed instances of this critical flaw, enabling remote unauthenticated attackers to bypass authentication mechanisms, which could lead to the compromise of entire systems.
The provided PoC exploit showcases a critical authentication bypass vulnerability, CVE-2024-7593, in Ivanti vTM.
The PoC begins by checking if the curl command-line tool is installed, essential for executing HTTP requests. If curl is not found, the script outputs an error message and aborts, ensuring that the user has the necessary tools for the exploit to function properly.
Next, the script utilizes command-line options to capture the target host and port specified by the user. This is accomplished using a while loop with getopts, allowing the user to provide inputs in a structured manner. If either the host or port is missing, the script calls a usage function, which would typically display the correct command usage and then exits to prevent further execution.
After ensuring that the required parameters are provided, the script prompts the user to enter a new username and password for the administrative account. The password input is secured using the -s flag with the read command, which hides the input from being displayed on the terminal, enhancing security during credential entry.
With the new credentials collected, the script constructs the URL for the vTM management portal using the specified host and port. It prepares the HTTP POST request parameters by setting the section of the management interface to “Access Management: LocalUsers” and assembling the necessary data fields for creating a new user account. The data includes the new username, password, and a confirmation of the password.
The core of the PoC involves sending the crafted POST request to the vTM management interface using curl. The request is sent to the endpoint responsible for user account management, with the constructed parameters and data passed as part of the request. The -s flag suppresses the progress output from curl, while the -k flag allows connections to SSL sites without requiring certificate verification, which can be useful for testing against systems with self-signed certificates.
After the request is executed, the script evaluates the server’s response to determine whether the user account creation was successful. It does this by checking for a specific HTML title tag in the response content, which indicates a successful operation. If the exploit is successful, the script prints a message displaying the new username and password, informing the attacker that they can now log in with the newly created credentials. If the account creation fails, the script outputs an error message indicating that it was unable to create the new user.
This PoC effectively demonstrates how an attacker could exploit the CVE-2024-7593 vulnerability to gain unauthorized administrative access to the vTM system. Such access could have severe implications, including the potential for data breaches, traffic manipulation, or the deployment of malware within the network.
To mitigate the risks this presents, organizations should promptly apply the available patches for affected versions and restrict access to the management interface through firewall rules and VPN usage. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) is crucial to enhance security, while regular security audits and reviews of user access controls will help identify and remediate vulnerabilities. Monitoring for suspicious activity, including logging and analysing access attempts, will facilitate early detection of potential breaches. Additionally, providing security awareness training to personnel and ensuring they are prepared to respond to incidents are essential steps. Staying informed about security advisories and engaging with the cybersecurity community can further bolster an organization’s defenses against this critical vulnerability.
Target Geography:
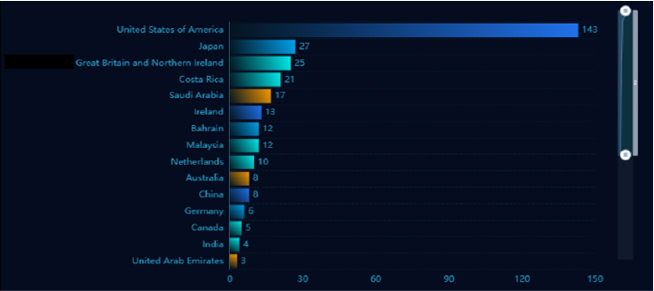
The target geography for CVE-2024-7593 encompasses regions with high internet exposure and utilization of Ivanti vTM, particularly in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. These regions often host critical infrastructure and data centers that may be vulnerable to remote attacks due to inadequate security measures or delayed patching.
Target Industry:
Industries that are particularly at risk include financial services, telecommunications, healthcare, and government sectors. These industries rely heavily on traffic management systems for operational efficiency and often handle sensitive data, making them attractive targets for attackers seeking unauthorized access or data theft.
Target Technology:
The target technology includes Ivanti vTM. Organizations using these versions are susceptible to exploitation through the authentication bypass vulnerability. Additionally, the attack vectors may involve HTTP/S protocols and management interfaces that are improperly secured or exposed to the internet. Organizations utilizing cloud-based infrastructures or hybrid environments are also at heightened risk, as misconfigurations can lead to increased exposure.
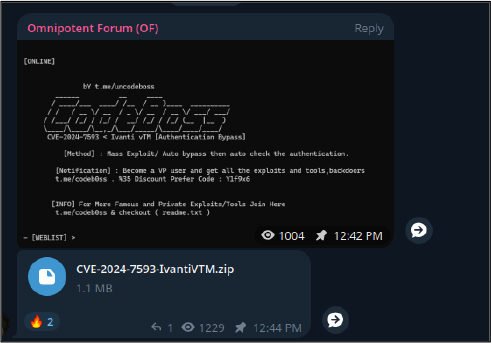
Malicious actors have been witnessed on underground forums, sharing exploits, technical details, and proof-of-concepts (PoCs) related to this vulnerability. This increased attention highlights the seriousness of the issue and the potential risks for organizations, emphasizing the need for stronger security measures.
In conclusion, CVE-2024-7593 represents a critical vulnerability in Ivanti Virtual Traffic Manager that could allow unauthenticated attackers to gain administrative access and potentially compromise sensitive systems. Given the high CVSS score of 9.8, organizations must prioritize the immediate application of patches and adopt robust security measures to mitigate the risk of exploitation. Implementing strategies such as access restrictions, multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, and continuous monitoring can significantly enhance defenses against unauthorized access. Furthermore, fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness and staying updated on emerging threats is essential for maintaining a resilient security posture. By taking these proactive steps, organizations can protect their infrastructure and safeguard against the potential ramifications of this severe vulnerability.