



CVE-2024-30078 reveals a severe vulnerability in the Wi-Fi drivers across multiple Microsoft Windows versions, potentially enabling threat actors within the Wi-Fi range to remotely execute malicious code on susceptible systems. This issue affects a broad spectrum of Windows versions, with the potential to impact over 1.6 billion active devices worldwide. To mitigate this risk, organizations must take prompt action by applying the patches released by Microsoft and enhancing their security measures to strengthen Windows OS defenses against possible exploits.
CYFIRMA Research has evaluated CVE-2024-30078, a vulnerability causing significant concern in the cybersecurity community due to its critical impact on organizations globally. This flaw affects multiple versions of Microsoft Windows and enables remote code execution (RCE), potentially granting malicious actors unauthorized access to sensitive networks. This highlights the imperative for enhanced cybersecurity measures and proactive threat intelligence to effectively defend against such evolving cyber threats.
Key Takeaways:
CYFIRMA Research recognizes the joint efforts of security researchers and the cybersecurity community in discovering and addressing the CVE-2024-30078 vulnerability.
Vulnerability Type: Remote Code Execution (RCE)
CVE ID: CVE-2024-30078
CVSS Severity Score: 8.8 (High)
Attack Complexity: Low
Attack Vector: Adjacent Network
Availability Impact: High
Confidentiality Impact: High
Integrity Impact: High
User Interaction Required: None
Exploitability Score: 2.8
Impact Score: 5.9
Affected Application: Microsoft Windows Wi-Fi Drivers
Impact: allows unauthenticated attackers to execute malicious code via a critical remote code execution vulnerability.
Severity: critical
Affected Versions: Windows 10 (all versions), Windows 11 (all versions), Windows Server 2008, 2012, 2016, 2019
Patch Availability: yes
Mitigation: Organizations should promptly apply the latest security updates and patches.
CVE-2024-30078 is a high-severity remote code execution vulnerability affecting Microsoft Wi-Fi drivers. This flaw doesn’t require user interaction; attackers can exploit it by sending specially crafted network packets to devices within their Wi-Fi range. It allows attackers to run malicious code on affected systems, compromising multiple Windows operating system versions to gain full control over the compromised devices.
Exploiting CVE-2024-30078 impacts several versions of the Microsoft Windows operating system. When successfully exploited, an attacker can gain complete control over the affected device, potentially leading to serious outcomes, such as unauthorized access, data breaches, manipulation, and compromise of user privacy and data integrity. Additionally, the vulnerability could affect system availability by potentially causing a denial-of-service (DoS) condition.
CVE-2024-30078 affects several versions of the Microsoft Windows operating system. For a detailed list of the specific versions impacted, please refer to the following link here.
Are hackers discussing this vulnerability in the Deep/Dark Web?
As of now, CYFIRMA has observed discussions and potential exploitation of CVE-2024-30078. It is crucial to continuously monitor threat intelligence sources and cybersecurity forums for updates on this activity.
What is the attack complexity level?
The attack complexity level of CVE-2024-30078 is classified as Low. This means that exploiting the vulnerability does not require sophisticated techniques or extensive conditions, making it relatively easier for attackers to exploit.
Is there already an exploit tool to attack this vulnerability?
Currently, there is no known exploit tool specifically targeting CVE-2024-30078, however, the landscape can shift quickly as new tools are developed by both researchers and attackers. It’s important to keep informed through the latest security advisories and threat intelligence to track any emerging exploit tools related to this vulnerability.
Has this vulnerability already been used in an attack?
Yes, according to reports, there have been instances of this vulnerability being exploited in the wild, and while no public proof-of-concept (PoC) was initially available, a PoC was eventually released, and attacks leveraging this vulnerability were subsequently detected.
What are the threat actors associated with this vulnerability?
As of now, there are no specific threat actors publicly associated with CVE-2024-30078. Monitoring security reports and threat intelligence sources is essential to identify any emerging groups or individuals that may exploit this vulnerability.
EXPLOIT AND ANALYSIS
Our analysis found that more than 1.6 billion Microsoft Windows OS are public, and therefore vulnerable to CVE-2024-30078.


Overview:
Authenticated attack (higher difficulty):
Unauthenticated attack (more accessible):
Vulnerability Details:
Location: the vulnerability is in the Dot11Translate80211ToEthernetNdisPacket() function within the Windows native Wi-Fi driver (nwifi.sys).
Exploitation:
To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker must create a very specific type of network data packet designed to interact with the Dot11Translate80211ToEthernetNdisPacket() function. This packet can trigger the vulnerability in the code.
Technical Issue:
In the Link Layer Control (LLC) component of the network stack, a vulnerability arises due to a discrepancy in packet length handling when VLAN (Virtual LAN) is utilized. According to the expected behavior, when a VLAN is set, the packet size should be 8 bytes, with an additional 4 bytes needed if VLAN is present (12 bytes in total). The current implementation incorrectly anticipates a total of 12 bytes, but only receives 10 bytes, leading to an out-of-bounds read and the creation of a 2-byte write vulnerability. This flaw allows for the overwriting of the last two bytes of the sender’s MAC address, which an attacker can exploit by crafting a specially designed data packet. This alteration can compromise network security by tampering with critical address information.
The CVE-2024-30078 vulnerability presents several potential attack scenarios, each with severe implications:
Malware installation: attackers could exploit this vulnerability to deliver and install malware remotely on the targeted system. By gaining unauthorized access through the Wi-Fi driver flaw, they could deploy a variety of malicious payloads, including ransomware, spyware, or trojans, compromising the integrity and security of the system.
Lateral movement: once inside a compromised network, attackers can leverage the vulnerability to move laterally across the network, allowing them to escalate privileges, gain access to additional devices, and spread their attack further within an organization, potentially compromising critical systems and data.
Botnet recruitment: the vulnerability could also be exploited to recruit compromised devices into a botnet. Attackers can control large numbers of affected systems, using them for distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, spamming, or other malicious activities, significantly amplifying the impact of their operations.
Data exfiltration: by exploiting CVE-2024-30078, attackers could gain access to sensitive data on the compromised system or network. They can exfiltrate confidential information, including personal data, intellectual property, and financial records, leading to potential data breaches and severe financial and reputational damage to the affected organization.
Each of these scenarios highlight the critical need for immediate patching and robust security measures to mitigate the risks associated with this vulnerability.
To mitigate this vulnerability, Microsoft released a patch in June 2024 as part of their regular security updates. Users are strongly advised to install updates immediately to protect their system from known vulnerabilities. Wi-Fi security can also be robustly maintained by using complex passwords, encryption protocols, and being aware of rogue access points that could be used to exploit the network. Network firewalls can also be enabled to block unauthorized access and monitor suspicious activity, and organizations should stay informed about the latest security threats and patches.
Target Geography:
CVE-2024-30078, a severe Wi-Fi vulnerability in Windows, has already seen real-world widespread exploitation, impacting regions such as the United States, China, and various parts of Europe. These attacks have been particularly intense in areas with a high density of Windows users.
Target Industry:
CVE-2024-30078 has predominantly impacted sectors heavily reliant on Wi-Fi and extensive Windows deployments. Key affected industries include healthcare, finance, manufacturing, government, and technology/telecommunications. These industries are particularly vulnerable due to the potential for significant operational disruption and exposure of sensitive data.
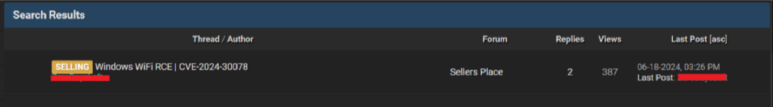
We have identified discussions about selling the CVE-2024-30078 vulnerability on underground forums.


In summary, CVE-2024-30078 presents a severe risk to organizations and users of Microsoft Wi-Fi drivers globally. Immediate action is crucial for those affected, including prompt application of patches and enhanced security measures to counter the risk of unauthenticated remote code execution. Effective defense relies on swift patching, proactive monitoring, and collaboration, guided by insights from CYFIRMA. By acting quickly and working together, organizations can better protect their critical assets from potential exploitation.