



The CYFIRMA Research team delves into the critical cybersecurity landscape surrounding the Citrix Bleed vulnerability, marked by CVE-2023-4966. This flaw, impacting Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway, has become a focal point of global concern, as evidenced by targeted attacks on government networks and financial institutions. The vulnerability, dubbed Citrix Bleed, allows threat actors to exploit session tokens, potentially leading to unauthorized access and data compromise.
One of the largest global banks, ICBC, recently experienced a security breach, likely attributed to a potential failure in addressing the “Citrix Bleed” vulnerability through patching.
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the emergence of critical vulnerabilities demands a heightened level of attention and swift response from organizations. Among these, CVE-2023-4966, colloquially known as Citrix Bleed, has surfaced as a substantial threat to the integrity of Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway deployments.
This vulnerability, assigned a severity score of 9.8 out of 10, poses the risk of unauthorized access, potential data breaches, and system compromise. Its critical nature necessitates immediate action to secure systems and protect against potential exploitation.
As we delve into the intricacies of CVE-2023-4966, it becomes apparent that its implications extend beyond the immediate affected software, potentially compromising broader technological ecosystems. This exploration aims to provide valuable insights into the nature of the vulnerability, its potential impact, and the critical importance of prompt mitigation through patching and proactive security measures.
Key Takeaways:
Acknowledgements:
CYFIRMA Research acknowledges the collaborative efforts of security researchers, and cybersecurity community in identifying and addressing CVE-2023-4966. The Citrix team’s prompt response and mitigation efforts are commendable, highlighting the significance of coordinated security research in safeguarding digital ecosystems.
Vulnerability Type: Session Token Leakage
CVE ID: CVE-2023-4966
CVSS Severity Score: 9.8
Application: Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway
Impact: Unauthorized access, potential data breaches, system compromise, session token leakage
Severity: Critical
Affected Versions: Multiple Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway are Vulnerable – here.
Patch Available: Yes
The Citrix Bleed vulnerability (CVE-2023-4966) represents a critical security flaw in Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway. Exploiting this vulnerability allows attackers to gain unauthorized access, posing a significant threat to the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information. Cybercriminals have swiftly capitalized on this weakness, orchestrating attacks on government networks and financial institutions globally.
The impact of the Citrix Bleed vulnerability is severe, encompassing potential data breaches, unauthorized access, and compromise of critical systems. The session token leakage opens avenues for malicious actors to gain remote access to devices within the periphery of the organization’s firewall without generating any logs. Threat actors will likely use this access to exfiltrate sensitive information from various servers within the compromised network.
Multiple Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway are affected by CVE-2023-4966, check here.
Is there already an exploit tool to attack this vulnerability?
Yes, a known public exploit tool for CVE-2023-4966 in Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway, commonly known as Citrix Bleed, is accessible.
Has this vulnerability already been used in an attack?
Yes, Specific information confirming exploitation of CVE-2023-4966 is available. Researchers have observed over 250 distinct IPs trying to exploit this vulnerability in the last 30 days.
Are hackers discussing this vulnerability in the Deep/Dark Web?
As observed by CYFIRMA, hackers are actively discussing or potentially exploiting CVE-2023-4966 in the Deep/Dark Web. Regular monitoring of underground forums and channels is essential to stay informed about emerging discussions or potential threats.
What is the attack complexity level?
The attack complexity level for CVE-2023-4966 in Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway is currently assessed as LOW. What makes it more dangerous is that the initial exploit string is not logged on to the device being exploited. This is the reason many organizations who have not patched, are currently compromised, and have no clue about it.
Historical Trends and Known Exploits:
Historically, threat actors have exploited vulnerabilities in similar software products. Given this pattern, it is vital to acknowledge that threat actors may attempt to exploit CVE-2023-4966 in Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway, potentially leading to unauthorized access, data breaches, or network compromise. Organizations should take this risk seriously and promptly apply patches or updates to secure their systems.
While our analysis found that more than 38000 Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateways are public, and which can be vulnerable to CVE-2023-4966. Refer fig 1.0

At the heart of this security matter is a clever sequence of actions that an unauthorized actor could take to exploit vulnerabilities in Citrix ADC/Gateway. An attacker initiates a series of carefully crafted GET requests, exploiting a weakness in the “/oauth/idp/.well-known/openid-configuration” endpoint. The manipulation involves a precise “Host” header, leveraging a repetition of the character ‘24,812 times. This subterfuge is designed to induce a specific condition within Citrix ADC/Gateway, providing an initial foothold.
Below is the malicious HTTP request:
GET /oauth/idp/.well-known/openid-configuration HTTP/1.1
Host: a <repeated 24812 times>
Connection: close
The response to the above HTTP request contains leaked system memory data, containing session tokens for unauthorized remote access, bypassing authentication, including multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Having gained access, the attacker’s focus shifts to valuable artifacts—session tokens. These tokens, identified by distinct patterns (either 65 or 32 characters long hexadecimal strings), act as authentication passes. The attacker systematically extracts these tokens, ensuring they possess the necessary credentials for subsequent maneuvers.
Armed with session tokens, the attacker proceeds to test their validity by sending POST requests to the “/logon/LogonPoint/Authentication/GetUserName” endpoint. This phase mimics the real-world scenario of an adversary probing different entry points within the system.
To facilitate understanding, the attacker incorporates a “verbose mode.” This feature offers detailed insights, including hex dump output, providing a comprehensive overview of the memory dump process.
The successful execution of this exploit not only allows unauthorized access but also introduces the potential for data breaches and systemic compromise. Once inside, the attacker could navigate through sensitive information, posing threats to data confidentiality and integrity.
This revelation serves as an urgent call to action for organizations relying on Citrix ADC/Gateway. Prompt attention to this matter is crucial to prevent potential unauthorized access, data breaches, or other compromises to digital infrastructure.
To mitigate the Citrix Bleed vulnerability, organizations must promptly apply the patches provided by Citrix. Timely implementation of these patches is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and potential data breaches. Additionally, organizations should conduct thorough security assessments to identify any signs of exploitation and monitor for unusual activities. It’s advisable to reinforce cybersecurity measures, including robust access controls, network segmentation, and regular security audits. Heightened user awareness and education on phishing and social engineering attacks are essential components of an effective mitigation strategy. Collaboration with cybersecurity experts and the adoption of proactive threat detection tools can further enhance the organization’s resilience against potential exploits related to the Citrix Bleed vulnerability.
Target Geography:
Organizations worldwide that have deployed Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway instances, falling within the affected versions may potentially be at risk.
The impact of CVE-2023-4966 is not limited by geography but instead extends to any region where Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway are deployed. As such, organizations in regions such as North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and other areas with a significant presence of Citrix NetScaler installations could be exposed to the risk of exploitation.
Target Industry:
The CVE-2023-4966 vulnerability in Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway has the potential to affect organizations across diverse industries. This includes but is not limited to healthcare, finance, government, telecommunications, and various other sectors that rely on Citrix NetScaler for secure application delivery and access.
Threat actors with knowledge of this vulnerability may selectively target industries based on the perceived value of the data or services handled by Citrix NetScaler instances. Organizations dealing with sensitive information or those heavily dependent on Citrix NetScaler for secure application delivery may be particularly attractive targets.
Target Technology:
The CVE-2023-4966 vulnerability is specific to Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway, critical components for secure application delivery and remote access. While the immediate impact is on NetScaler instances, it is crucial to recognize that the ramifications of successful exploitation can extend beyond the NetScaler environment.
A successful exploitation of this vulnerability can result in unauthorized access to sensitive data, potentially compromising the broader technological ecosystem. This includes servers, applications, and interconnected systems integrated with Citrix NetScaler, amplifying the potential impact on an organization’s technology infrastructure.
Understanding the potential impact on different geographic regions, industries, and technologies helps organizations assess their exposure to the CVE-2023-4966 vulnerability. It underscores the importance of promptly addressing the issue through patching, proactive security measures, and vigilant monitoring to mitigate the risks associated with this critical vulnerability.
CYFIRMA’s Research team has observed unknown hackers selling initial access to organizations compromised using Citrix Bleed Exploits. We can expect to see the use of double-extortion tactics by ransomware groups after gaining footholds on target organizations using this vulnerability.
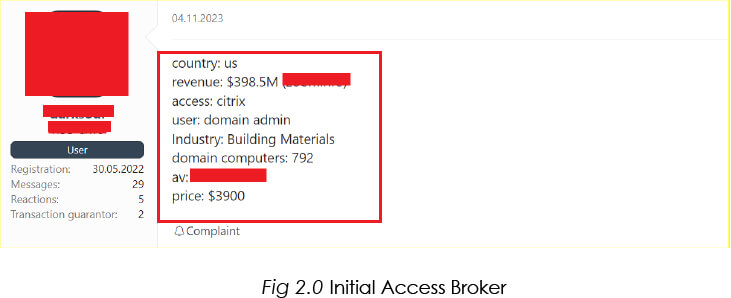
In conclusion, the identification of CVE-2023-4966 exposes a critical vulnerability in Citrix ADC/Gateway, emphasizing the urgency for organizations to address this issue promptly. The exploitation, involving precise manipulations and unauthorized access, not only jeopardizes the security of sensitive data but also underscores the need for proactive measures. Security professionals must act swiftly to fortify defenses, implement patches, and conduct thorough assessments to prevent potential unauthorized access and mitigate the risks of data breaches. The severity of this vulnerability necessitates immediate attention to ensure the continued integrity and confidentiality of digital infrastructure. CYFIRMA’s observations on hacker discussions in the Deep/Dark Web underscore the urgency of the situation. Active discussions or potential exploitation in these forums heighten the risk, necessitating continuous monitoring and proactive measures.