



Suspected Malware: AvosLocker Malware
Function: Ransomware
Risk Score: 8
Confidence Level: High
Threat actor Associations: Unknown
First Seen: July 2021
Ransomware-as-a-service can cause massive disruption to businesses as well as significant financial impact. Attackers behind these services have developed new techniques and attack patterns and this article provides a technical analysis of the latest malware sample.
The AvosLocker operates ransomware-as-a-service giving malware authors the ability to sell their code to other #cybercriminals and #threatactors. The AvosLocker was first noticed in early July 2021 and continued its operation into 2022. Initially, AvosLocker used to target Windows system and later, expands its operation by including Linux-based variants also. The threat actors use spam or phishing emails as initial vectors to deliver ransomware payload. The group has claimed that AvosLocker’s latest windows variant is one of the fastest available in the market and offers an affiliate program to cyber-criminals.
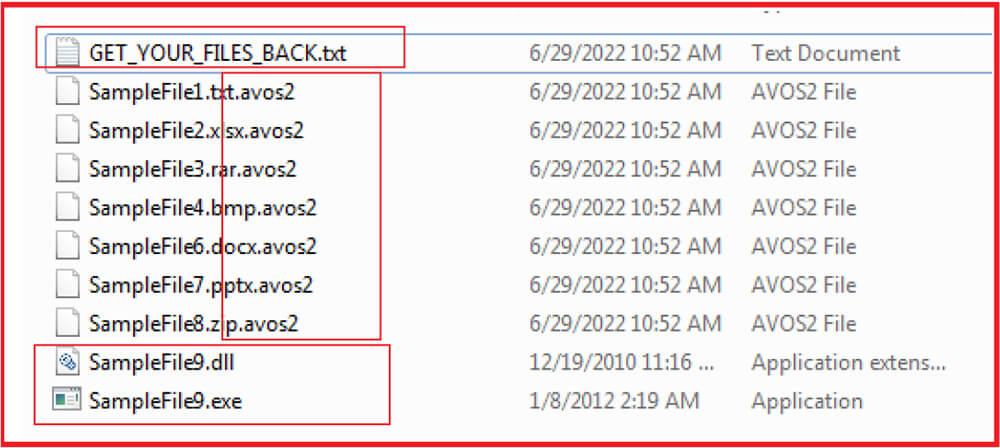
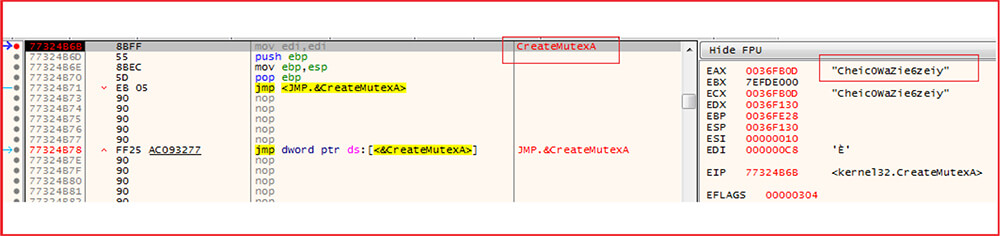
This is how the malware works: Upon execution, it encrypts the files and appends the extension “.avos” to the encrypted file. The updated variants append “.avos2” extension and Linux variants append the extension “.avoslinux” to the encrypted files. The ransomware sample we have analyzed appends the extension “.avos2” to the encrypted file. The sample contains a hard-coded ID and public encryption key. The sample is console-based and provides options to use while executing the sample and shows the status of encrypted or skipped files on the console window. The ransomware drops the ransom note in each folder and desktop with the name “GET_YOUR_FILES_BACK.txt”. The ransomware also creates a mutex with the name “Cheic0WaZie6zeiy” so that only one instance of the ransomware will run at a time.
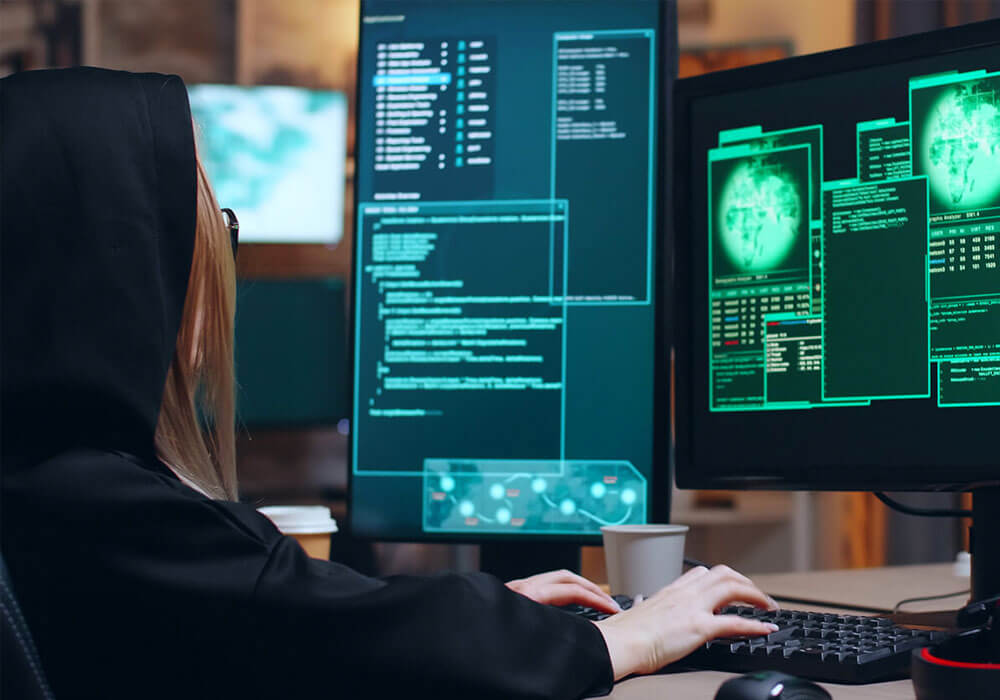
Sample Details:
File Type: Windows PE Executable
Architecture: 32 Bit
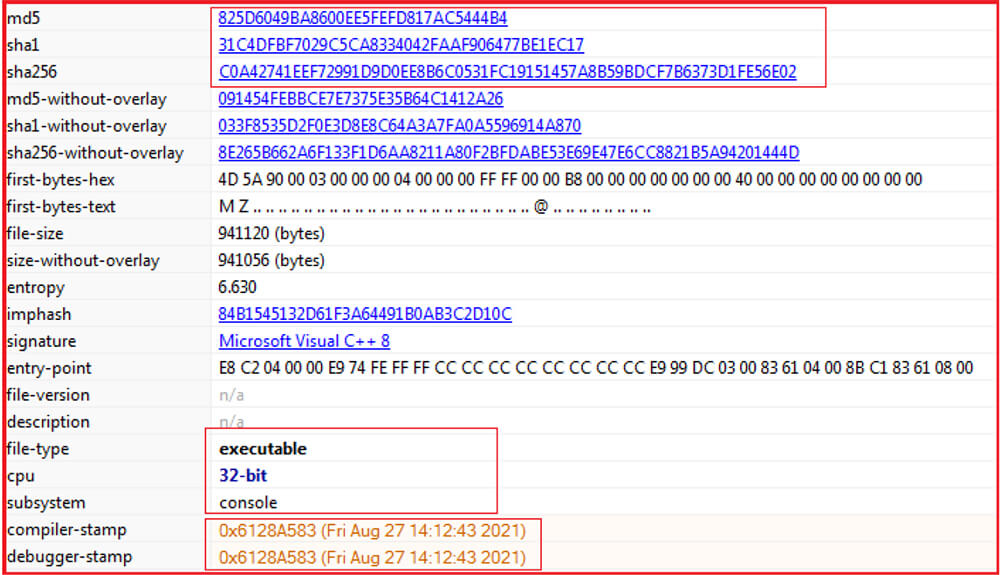
MD5: 825d6049ba8600ee5fefd817ac5444b4
SHA256: c0a42741eef72991d9d0ee8b6c0531fc19151457a8b59bdcf7b6373d1fe56e02
Subsystem: Console
Language: MS Visual C++
Compilation Time: 27 August 2021
The sample malware is Windows PE-32 bit executable having a console subsystem. The binary can be run either through command line or by double-clicking. In both cases, the console window will open and shows the status of files being encrypted.
The below snapshot shows the options available with which the sample can be executed. The options are used to control certain aspects of the functionality like enabling/disabling SMB brute force, maximum concurrent threads, mutex creation, hiding console window, etc. By default, that is without no options, the malware ignores encryption of network drives and SMB share.
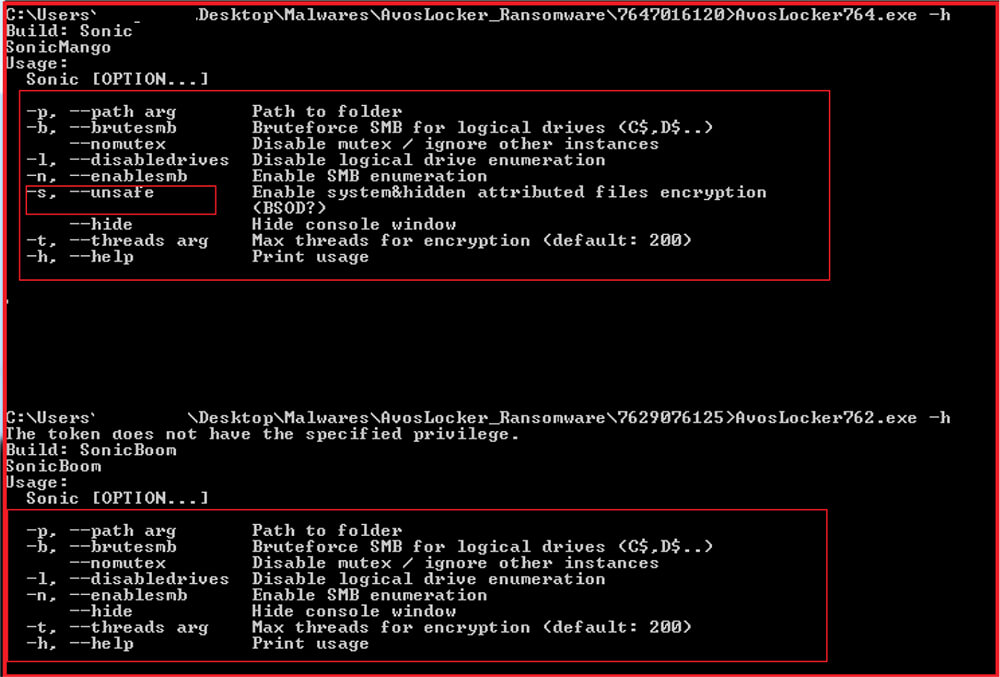
As shown in the above snapshot, our research team checked the options available with two different samples. There is a difference in the options available in both samples as the first sample is recent and another one is a little older. The recent sample has one more option “-s” (–unsafe) available which can be used to enable encryption of system and hidden files also.
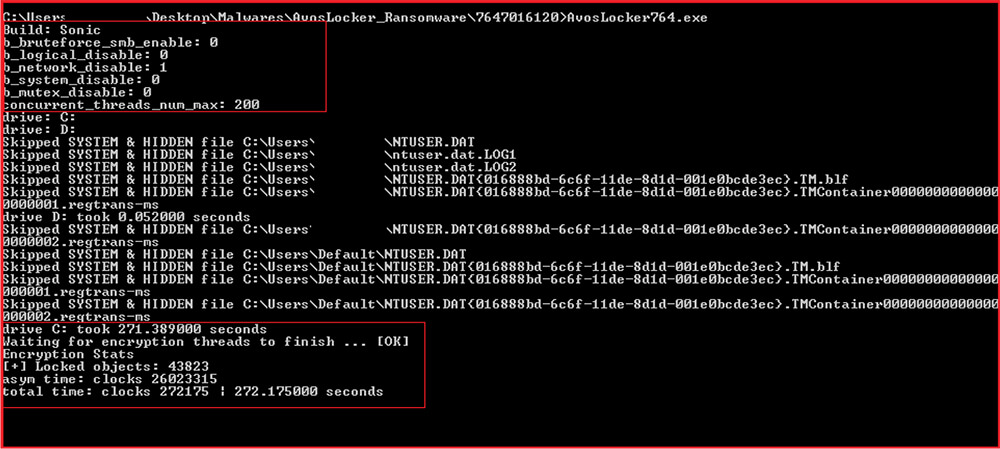
Upon executing the malware sample with no options, it runs with the default option and ignores encryption of SMB share and network drives. It runs 200 concurrent threads for file encryption. During execution, the console window shows progress status. Further, after completion, the console window also displays information regarding a total number of locked objects and the time taken to encrypt.
The AvosLocker encrypts the files and appends “.avos2” extension to the encrypted files. It excludes some of the files with specific extensions like “.exe”, “.dll” and “.avos2”. The ransomware also drops a ransom note in each encrypted folder and Desktop with the name “Get_YOUR_FILES_BACK.txt”.
The ransom note as shown below mentions that the files are encrypted with AES-256 encryption and in order to decrypt the contents, the victim has to pay for the decryption key and application.
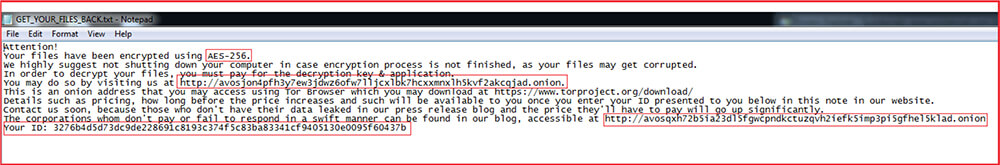
The ransom note also provides two Tor or onion links related to malware authors. The first link is given to contact malware authors with the specified ID mentioned in the ransom note:
http://avosjon4pfh3y7ew3jdwz6ofw7lljcxlbk7hcxxmnxlh5kvf2akcqjad.onion/
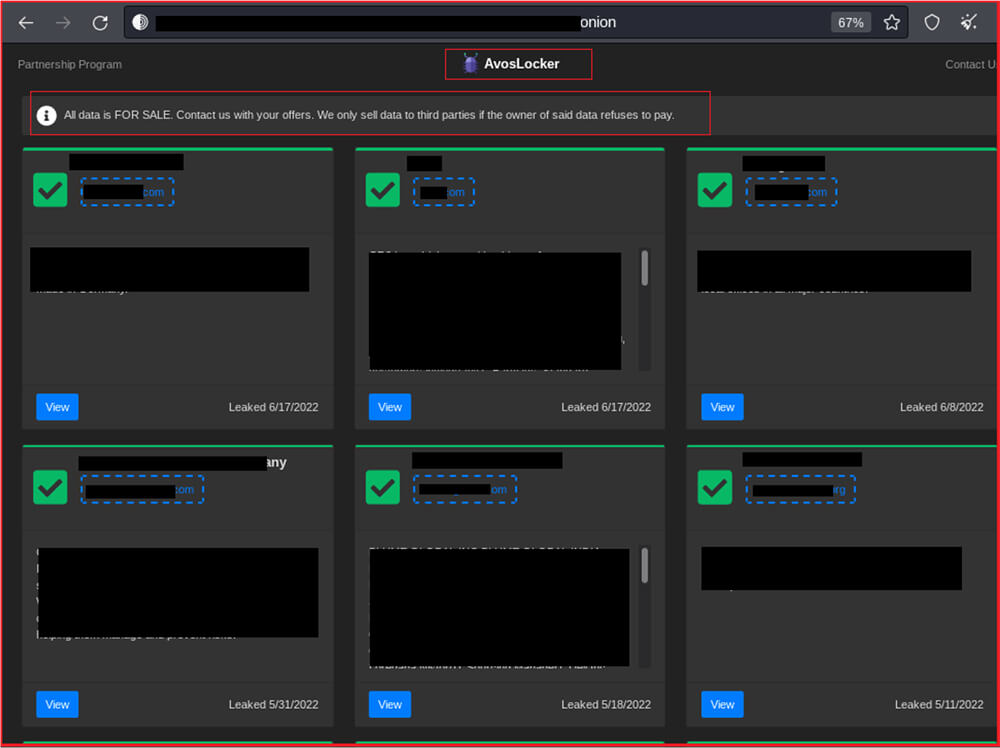
The second link is to the data leak blog of the group which contains the leaked data of the organization who are failed to pay or respond.
http://avosqxh72b5ia23dl5fgwcpndkctuzqvh2iefk5imp3pi5gfhel5klad.onion/
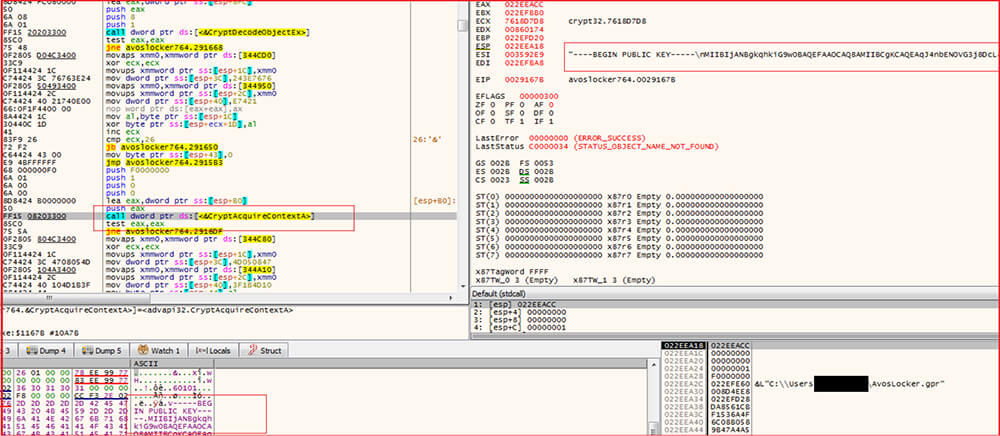
The ID “3276b4d5d73dc9de228691c8193c374f5c83ba83341cf9405130e0095f60437b” mentioned in the ransom-note and the public key used are hard-coded into the malware binary.
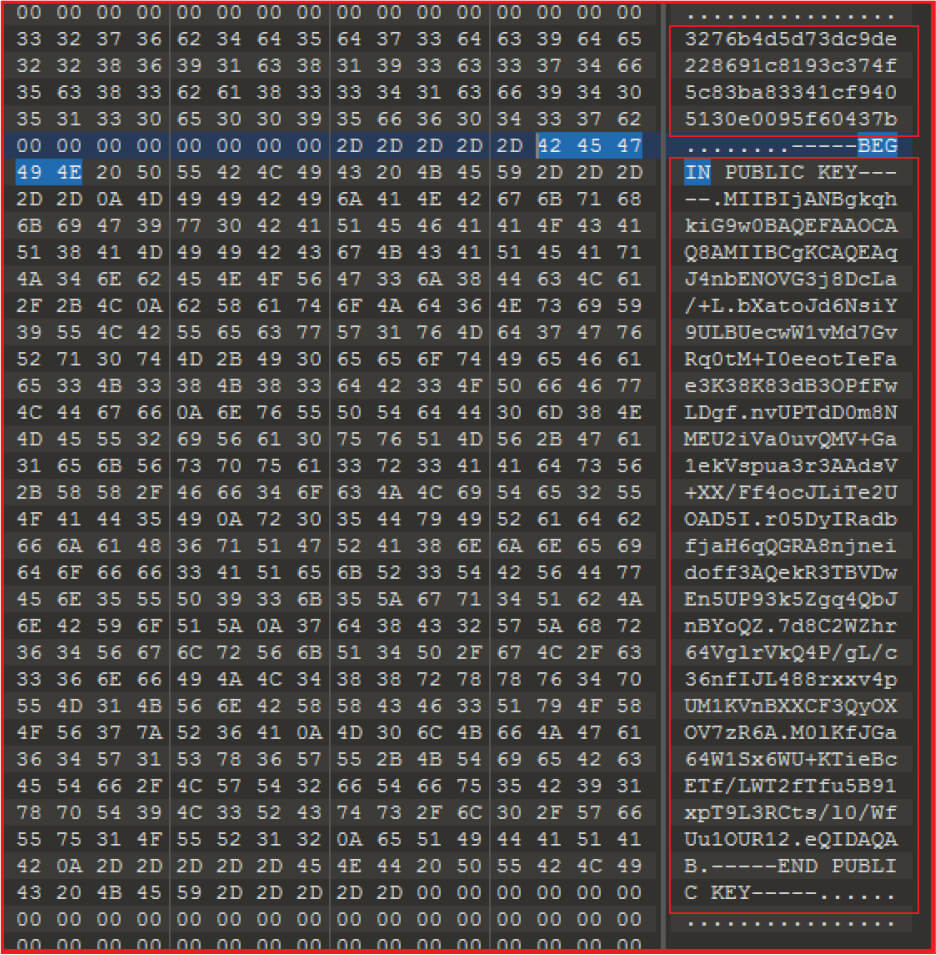
The malware reads the file, encrypts it, and writes the content in the encrypted file with a unique signature that appends to the file. This signature is used to identify whether the file is encrypted or not,
The ransomware collects the command-line options if any passed at the time of binary execution.
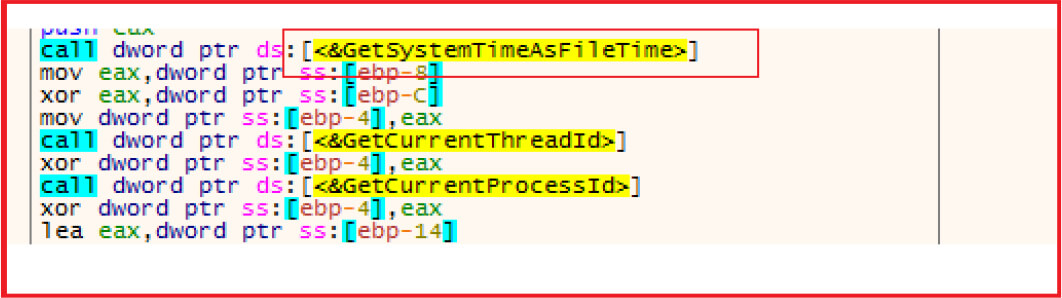
Collecting system information
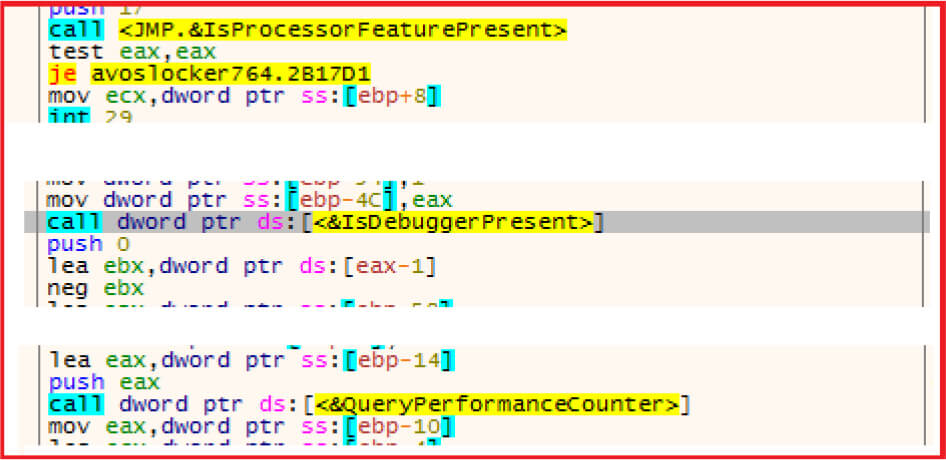
Checking the presence of any debug environment to thwart the analysis process.
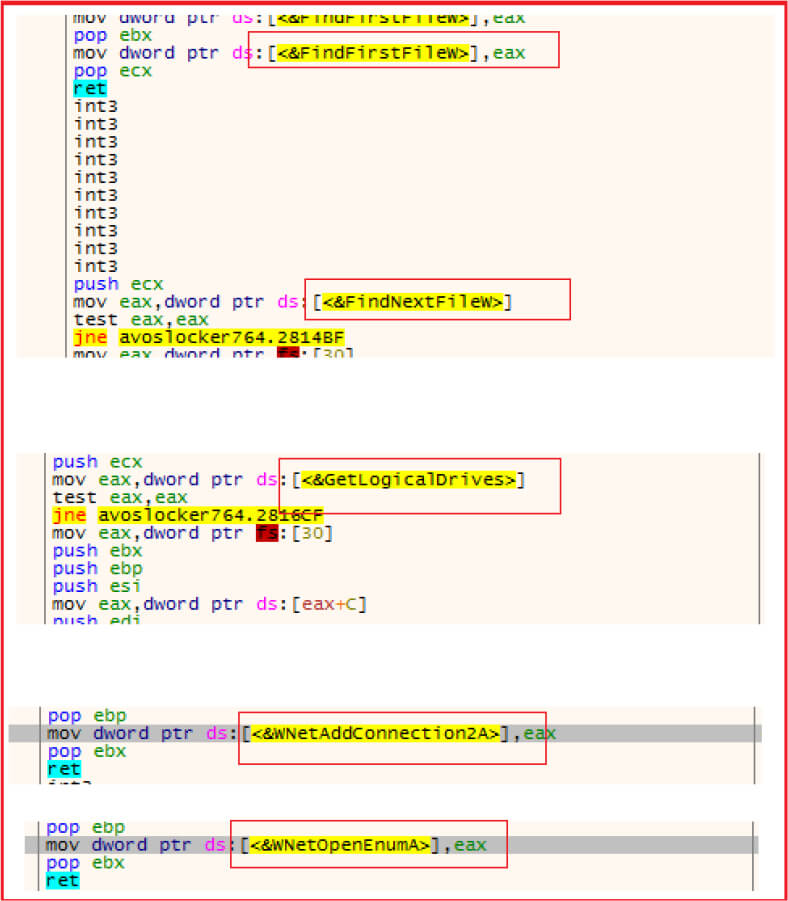
The malware enumerates files, and drives. It also has the capability to enumerate network drives.
The malware creates the mutex with the name “Cheic0WaZie6zeiy” to ensure that only one instance of the malware runs at a time.
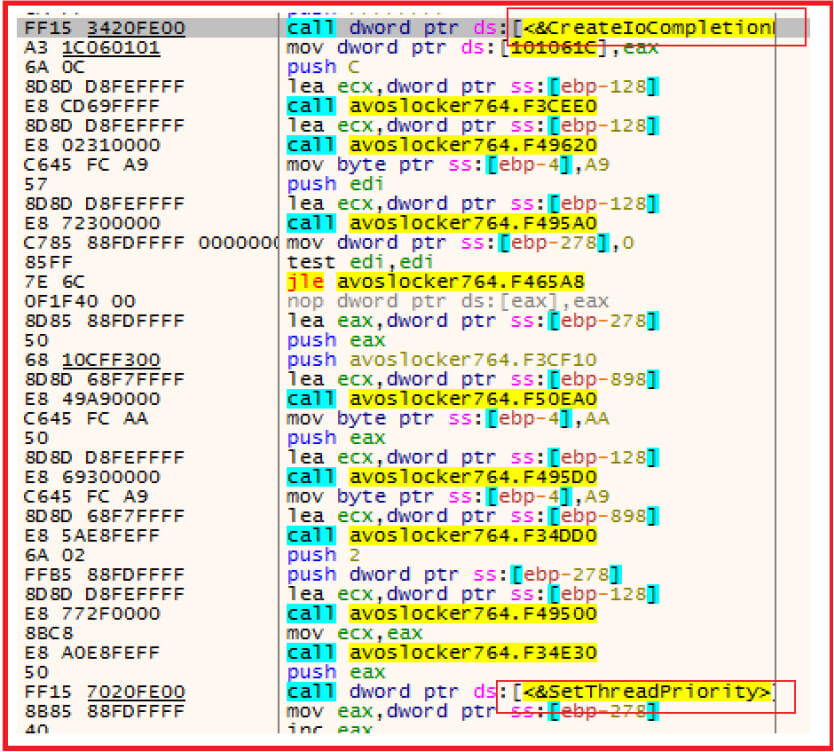
The malware use multi-threading by using APIs CreateIoCompletionPort(), PostQueuedCompletionStatus(), GetQueuedCompletionPort() to handle multiple files concurrently and thread priority is also set to high for quick encryption.
A picture containing a graphical user interface
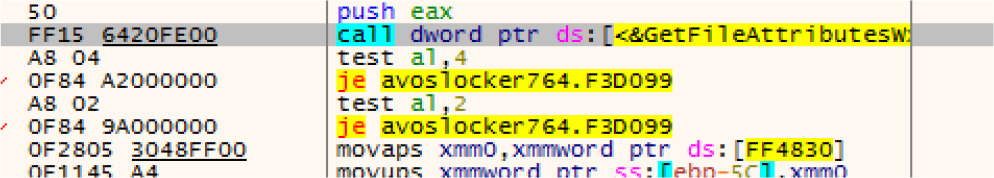
Ransomware checking file attributes before encryption and skip files having “FILE_ATTRIBUTE_HIDDEN” or “FILE_ATTRIBUTE_SYSTEM” attributes.
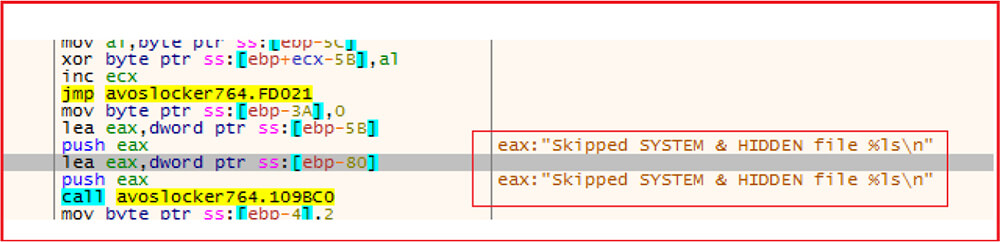
Exclude system and hidden files from encryption. The malware also excludes files having specific extensions like “.exe”, ”.dll”, “avos”, “avos2” etc. and also some folders like “Program Files”, “Program Files (x86)”, “ProgramData” and Windows, etc.
The malware encrypting the files
Appends the extension “.avos2” to encrypted files

For the AvosLocker ransomware victims who failed to pay, the threat actors then leak their data on the site with the organization’s name and information.
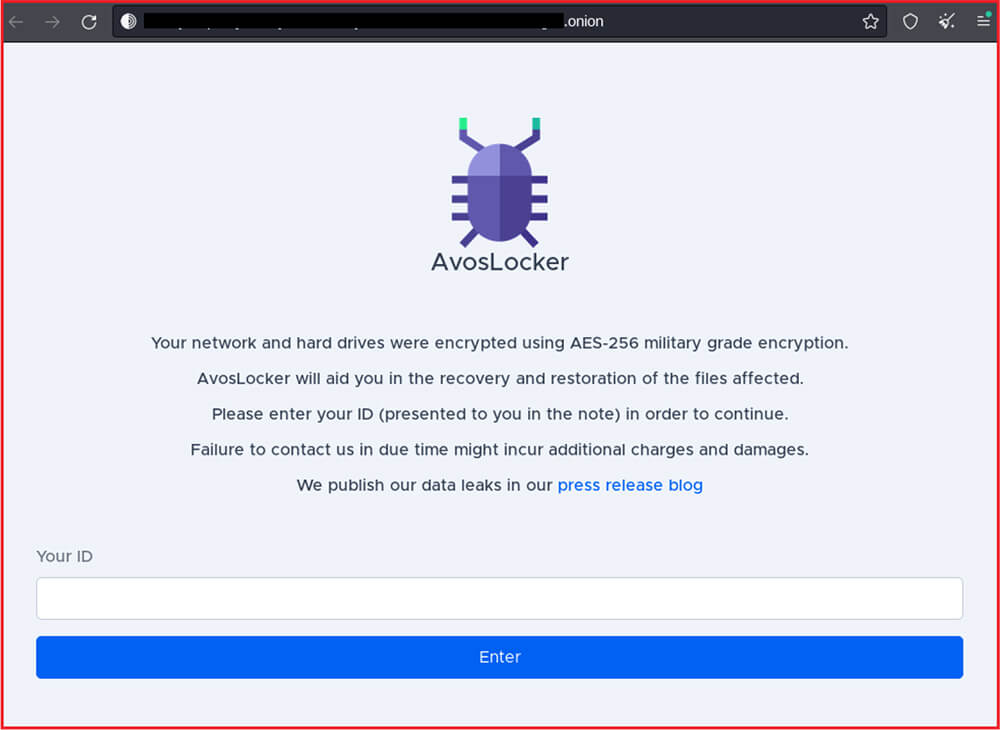
The below-mentioned site where the victim enters the ID mentioned in the ransom-note and it will redirect the victim to the payment page.
The malware has the following capabilities:
AvosLocker ransomware group was first noticed in 2021 and initially targets Windows machines. The newer variants also target the Linux environments. The Avos group is a financially motivated, well-funded group and follows the Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model. Avos group normally uses spam and phishing campaigns for the initial infection vectors. The Linux variants use Proxyshell to exploit vulnerable Microsoft Exchange Servers. The ransomware gets deployed on the victim machine to encrypt data and demand the ransom.
| Sr No. | Indicator | Type | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 825d6049ba8600ee5fefd817ac5444b4 | MD5 | AvosLocker |
| 2 | Cheic0WaZie6zeiy | String | Mutex |
| 3 | 3276b4d5d73dc9de228691c8193c374f5c83ba83341cf9405130e0095f60437b | String | ID |
| 4 | .MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAqJ4nbENO VG3j8DcLa/+L.bXatoJd6NsiY9ULBUecwW1vMd7GvRq0tM+I0eeotIeFae3K38K8 3dB3OPfFwLDgf.nvUPTdD0m8NMEU2iVa0uvQMV+Ga1ekVspua3r3AAdsV+XX/Ff4 ocJLiTe2UOAD5I.r05DyIRadbfjaH6qQGRA8njneidoff3AQekR3TBVDwEn5UP93 k5Zgq4QbJnBYoQZ.7d8C2WZhr64VglrVkQ4P/gL/c36nfIJL488rxxv4pUM1KVnB XXCF3QyOXOV7zR6A.M0lKfJGa64W1Sx6WU+KTieBcETf/LWT2fTfu5B91xpT9L3R Cts/l0/WfUu1OUR12.eQIDAQAB. |
String | Public Key |
| 5 | hxxp[:]//avosqxh72b5ia23dl5fgwcpndkctuzqvh2iefk5imp3pi5gfhel5klad[.]onion | URL | Data Leak Site |
| 6 | hxxp[:]//avosjon4pfh3y7ew3jdwz6ofw7lljcxlbk7hcxxmnxlh5kvf2akcqjad[.]onion | URL | Payment Site |
| Sr No. | Tactic | Technique |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Initial Access (TA0001) | T1566 Phishing |
| 2 | Discovery (TA0007) | T1082 System Information Discovery T1083 File and Directory Discovery |
| 3 | Execution (TA0002) | T1204.002 Malicious File |
| 4 | Defense Evasion (TA0005) | T1027 Obfuscated Files or Information |
| 5 | Collection (TA0009) | T1005 Data from Local System |
| 6 | Impact (TA0040) | T1486 Data Encrypted |