



This CYFIRMA Monthly Ransomware report analyses ransomware activity in October 2023, covering significant attacks, the top five ransomware families, geographical distribution and evolution of attacks, targeted industries, new ransomware groups, the vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware groups, and trends. Organizations can leverage these insights to enhance their cybersecurity strategies and mitigate ransomware risks.
Welcome to the October 2023 Ransomware Report. This report offers a detailed analysis of significant ransomware events during this period. We explore the top 5 ransomware groups responsible for the highest number of victims and the industries they targeted. Additionally, we investigate the geographical locations that experienced the most ransomware attacks in October 2023. Furthermore, we discuss the evolution of ransomware groups during this month, focusing on emerging actors and vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware groups. The report aims to equip organizations with crucial insights to bolster their cybersecurity measures and combat the evolving ransomware threat landscape effectively.
• In October 2023, the LockBit ransomware group emerged as a significant threat, taking the lead on the chart with 66 victims.
• The manufacturing sector is the primary target of ransomware attacks, experiencing 64 incidents.
• The USA was the most targeted geography, with 151 ransomware incidents.
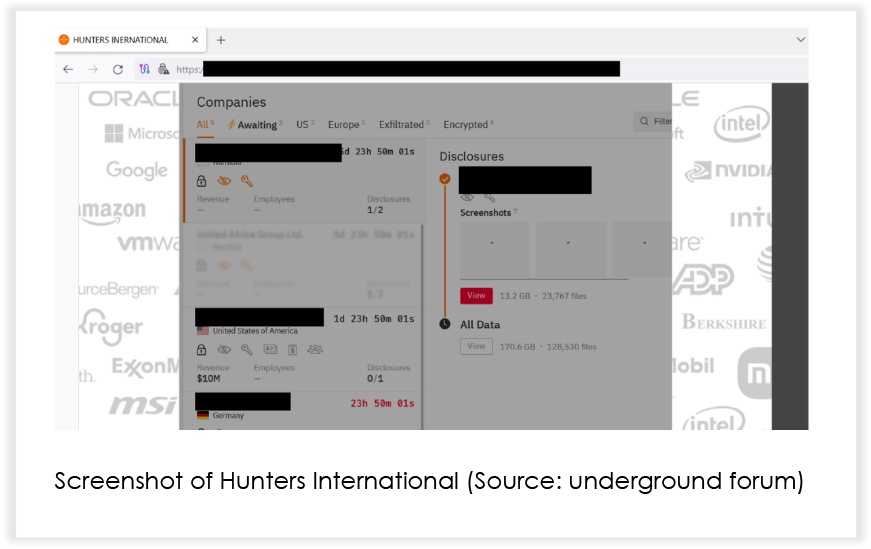
• The ransomware group ‘Hunters International’ emerged as a newly identified threat.
• The number of ransomware victims reduced by 33.34% from September to October 2023.
Multiple ransomware groups were active. Below is a graph showing the top 5 ransomware groups with their victim tallies over September and October 2023.
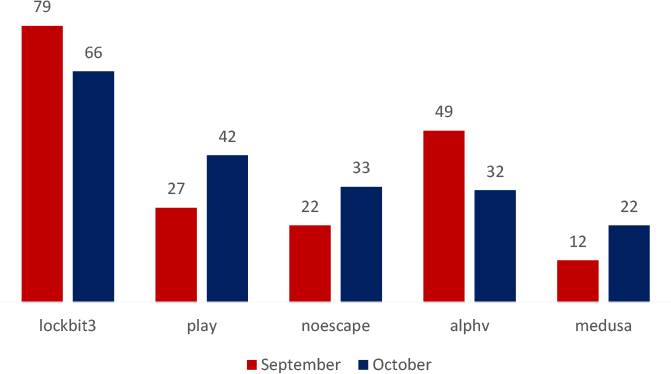
Analyzing the data, there’s a notable reduction in activity related to LockBit and ALPHV, possibly due to effective ransom negotiations, or decreased attacks by these threat actors. Conversely, instances involving Play, NoEscape, and Medusa have risen, indicating a potential surge in their respective ransomware operations among known victims.
INDUSTRIES TARGETED IN OCTOBER 2023
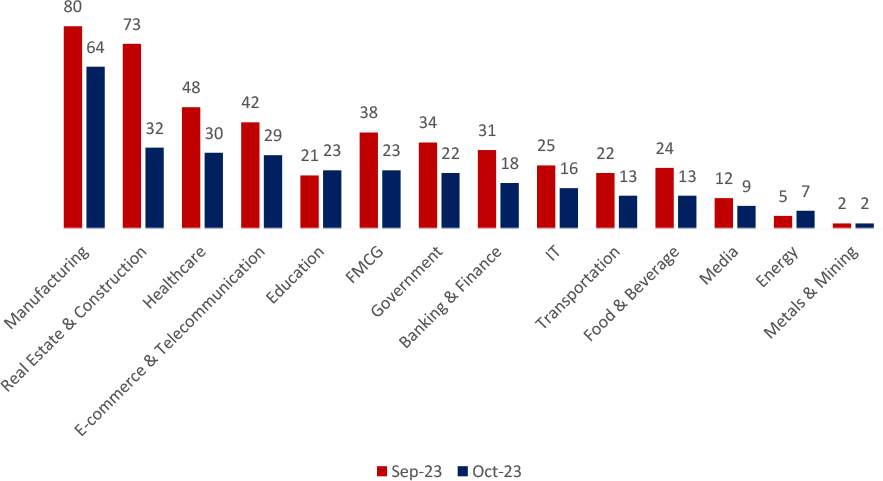
Various industries were targeted, with Manufacturing facing the highest number of attacks (64), followed by Real Estate & Construction (32), and Healthcare (30).
Organizations face a wide range of cyberattacks, driven by various factors such as the value of intellectual property, the potential for financial gain through extortion, or vulnerabilities within specific industries. For instance, e-commerce and telecommunications sectors may be targeted due to their reliance on online transactions, while healthcare is often a prime target due to the sensitivity of patient data. To effectively protect their critical assets, it is crucial for organizations to understand the motivations behind these attacks and implement robust cybersecurity measures.
TRENDS COMPARISON OF RANSOMWARE ATTACKS, 2023 AND 2022
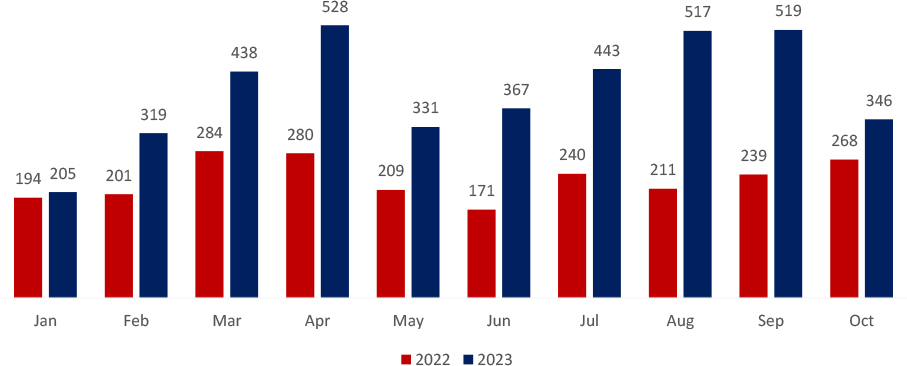
There was a decrease of approximately 33.34% in the number of ransomware victims from September 2023(519 Victims) to October 2023(346 Victims).
Geographical Targets: Top 5 Locations
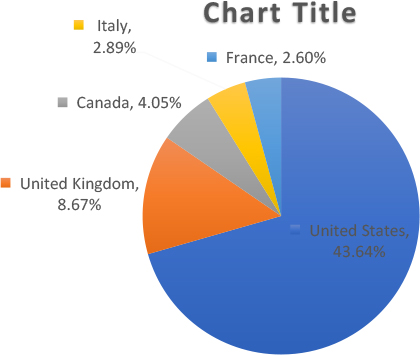
Ransomware attacks spread to more than 50 different locations this October. As seen previously, the United States was most severely impacted, with the largest majority by far (43.64% of those targeted) with the UK as a distant second at 8.67%. Canada stood at 4.05% (14 Victims), Italy at 2.89% (10 Victims), and France at 2.60% (9 Victims).
Cybercriminals often focus their ransomware attacks on the United States, the United Kingdom, and various European nations. These countries, with their strong economies and advanced technological infrastructure, are prime targets.
The appeal lies in exploiting their valuable assets and data, enabling malicious actors to seek substantial financial gains and disrupt critical operations effectively.
BlackCat devises ‘Munchkin’.
The BlackCat/ALPHV ransomware gang has introduced ‘Munchkin,’ a tool that utilizes virtual machines to deploy encryptors on network devices stealthily. Munchkin allows ransomware affiliates to run on remote systems, encrypt network shares, and perform various tasks, making the RaaS more attractive to cybercriminals. The tool uses a customized Alpine OS and provides automated operations, making it easy to adjust for specific targets. The modularity and use of virtual machines make detection and analysis more challenging for security software. BlackCat has evolved with advanced features and notable victims in 2023, including the Florida Circuit Court and MGM Resorts.
EMERGING GROUP
A new player has emerged in the ransomware-as-a-service field, under the name ‘Hunters International’. There are suspicions of a connection to the notorious ‘Hive’ ransomware, as the newly employed encryptor shares significant code similarities (60%). However, ‘Hunters International’ claims to be a newcomer, stating they acquired the code from Hive developers. The encryptor appends the “.LOCKED” extension to encrypted files and provides victims with contact instructions through a “Contact Us.txt” file in each directory.
Rhysida remain aggressive
The Rhysida ransomware group acknowledged their attacks on Portugal’s government and the Dominican Republic’s Migration Agency. Gondomar experienced service disruptions, while Rhysida exposed stolen data. The Dominican Republic agency suffered a data breach involving personal information, with the group demanding a $700,000 ransom to withhold data release.
NoEscape claims the attack on the basketball team.
French basketball team LDLC ASVEL confirmed a data breach by the NoEscape ransomware gang. Stolen data includes players’ personal information, financial documents, and contractual agreements.
Source code of Ransomware leaked.
The source code of the first version of HelloKitty ransomware on a Russian-speaking hacking forum was leaked. The threat actor claims to be working on a new, more potent encryptor.
Ragnar sites got seized.
Data leak sites and Tor negotiation sites of the Ragnar Locker ransomware group have been taken down by Law enforcement agencies from the US, Europe and other nations. Operating since late 2019, Ragnar Locker was known for targeting high-profile organizations and using double-extortion methods. This action marks a significant achievement in the fight against ransomware operations.
Ransomware attack hits the court.
The BlackCat (ALPHV) ransomware group targeted state courts in Northwest Florida, accessing personal data, including Social Security numbers and CVs of employees, including judges. The group claims to have a network map of the court’s systems and service credentials.
Impact Assessment:
Ransomware stands as a grave threat, casting a shadow over organizations and individuals in the external threat landscape. Its destructive nature unfolds through the encryption of data with relentless demands for ransom payments, inflicting financial losses, expenses for data recovery, and business disruptions that include downtime, diminished productivity and reduced trust between the organization and their end users. These attacks can then also trigger regulatory compliance hurdles and legal entanglements, with collateral damage extending to reputation, causing organizations to grapple with public scrutiny and waning market confidence. A steadfast commitment to vigilance and the fortification of robust cybersecurity measures becomes imperative to thwart this escalating menace.
Victimology:
Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting companies holding valuable data such as personal information, financial records, and intellectual property. Industries like manufacturing, real estate & construction, healthcare, FMCG, E-commerce & telecommunication, and finance, and technology are particularly vulnerable due to the richness of their data. These attackers also strategically focus on countries with robust economies and digital infrastructures, as they anticipate higher ransom returns.
While the number of ransomware victims decreased in October, the threat landscape remains fluid and concerning. LockBit’s continued dominance and the Manufacturing sector’s top position among targets underscore the agility of cybercriminals. The emergence of Hunters International adds another dimension of complexity, suggesting a dynamic and ever-changing environment. With the USA facing significant risks, it’s evident that nations with sophisticated infrastructures are strategically targeted. The evolution of BlackCat’s Munchkin tool demonstrates a persistent upward trend in ransomware capabilities. The decline in victim numbers should not lull us into complacency; the need for robust cybersecurity measures remains paramount in the face of constantly evolving tactics and the emergence of new threat actors.