



This CYFIRMA Monthly Ransomware report thoroughly analyses ransomware activity in February 2024, covering significant attacks, the top five ransomware families, geographical distribution, targeted industries, evolution of attacks, and trends. Organizations can leverage these insights to enhance their cybersecurity strategies and mitigate ransomware risks.
Welcome to the February 2024 Ransomware Report. This report offers a detailed analysis of ransomware events during this period. We explore the top 5 most active ransomware groups and the industries they targeted, as well as the locations that experienced the most attacks. We also discuss the evolution of ransomware groups and vulnerabilities exploited, intending to equip organizations with crucial insights to bolster their cybersecurity measures and combat the evolving threat landscape effectively.
In February 2024, multiple ransomware groups were active. Below, we outline trends concerning the top 5 ransomware groups.
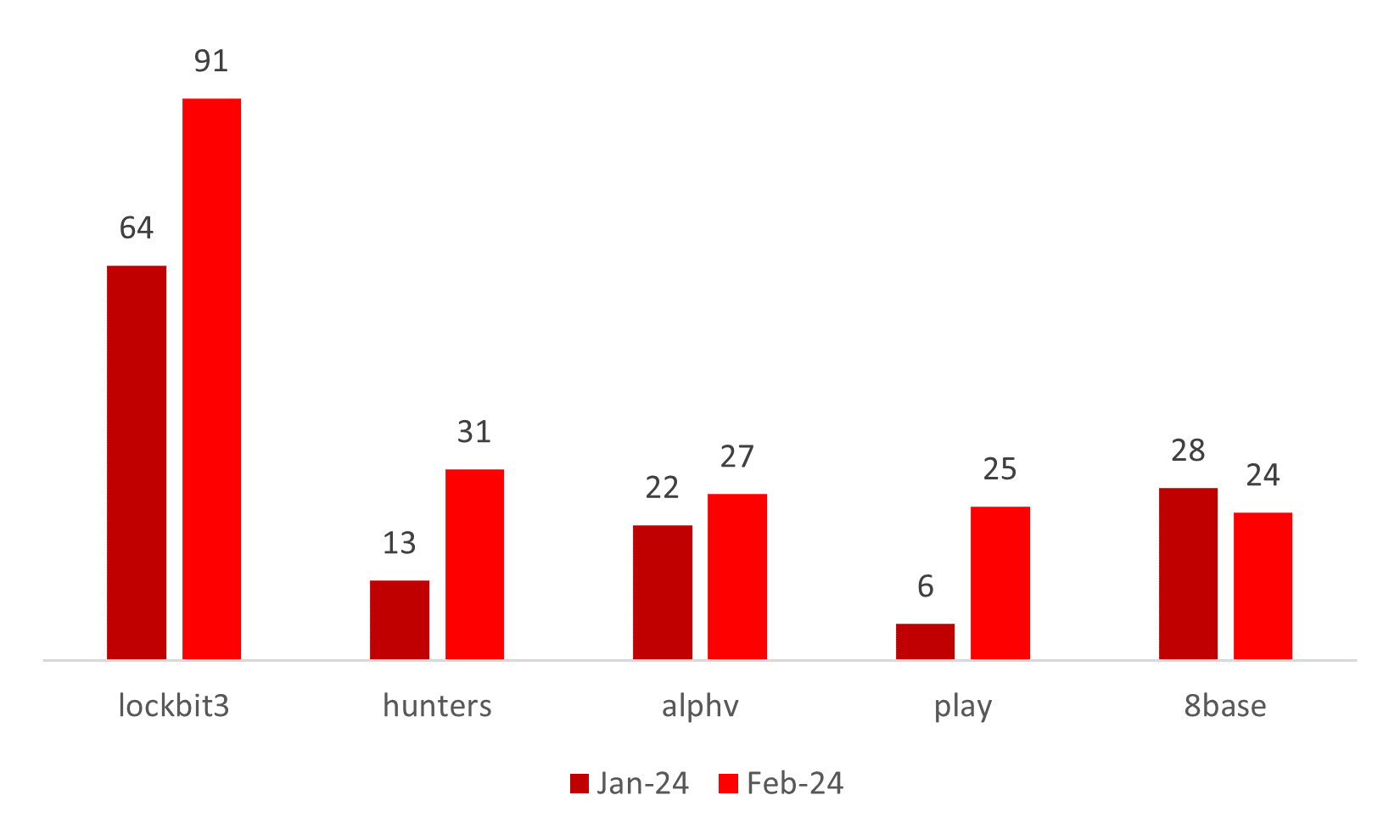
From January 2024 to February 2024, LockBit3 saw a 42.2% increase in victims, while Hunters experienced a substantial rise of 138.5%. Alphv and Play exhibited modest increases of 22.7% and 316.7%, respectively. The increase in count may be a result of failed ransom negotiations. In contrast, 8Base witnessed a 14.3% decrease in victim count, which can be attributed to successful negotiations or a decrease in its function.
LOCKBIT
Despite law enforcement actions, LockBit quickly bounced back, registering the highest number of victims this month. This underscores the group’s technical prowess and resilience in the face of challenges.
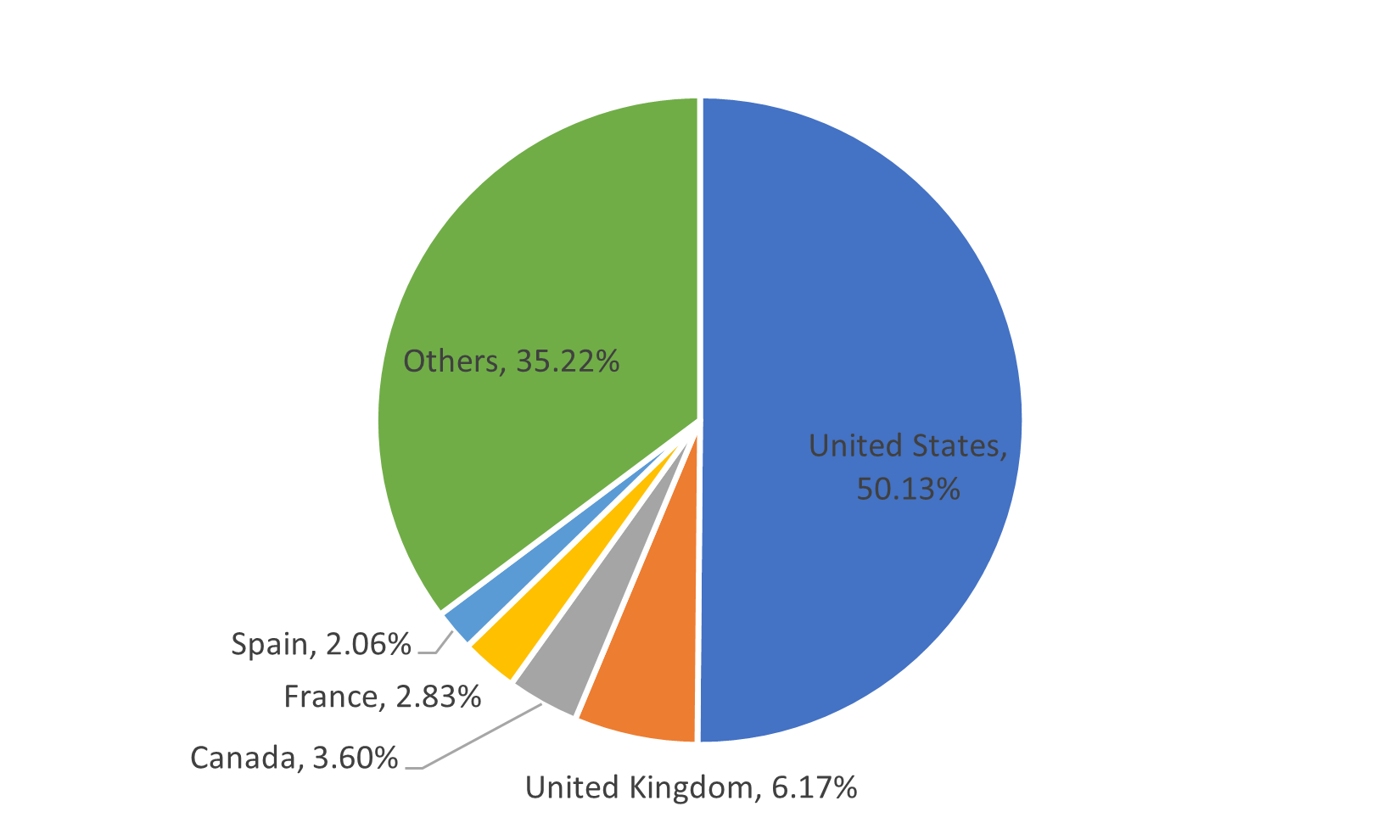
Manufacturing emerged as the primary target, with the United States being LockBit’s focal nation.
Interestingly, the impacted companies had revenues ranging from $5 million to $15.9 billion, meaning LockBit affected a wide range of businesses, not just specific financial tiers.
The group’s persistent dominance in victim count remains noteworthy, often attributed to the exploitation of the ConnectWise ScreenConnect vulnerability.
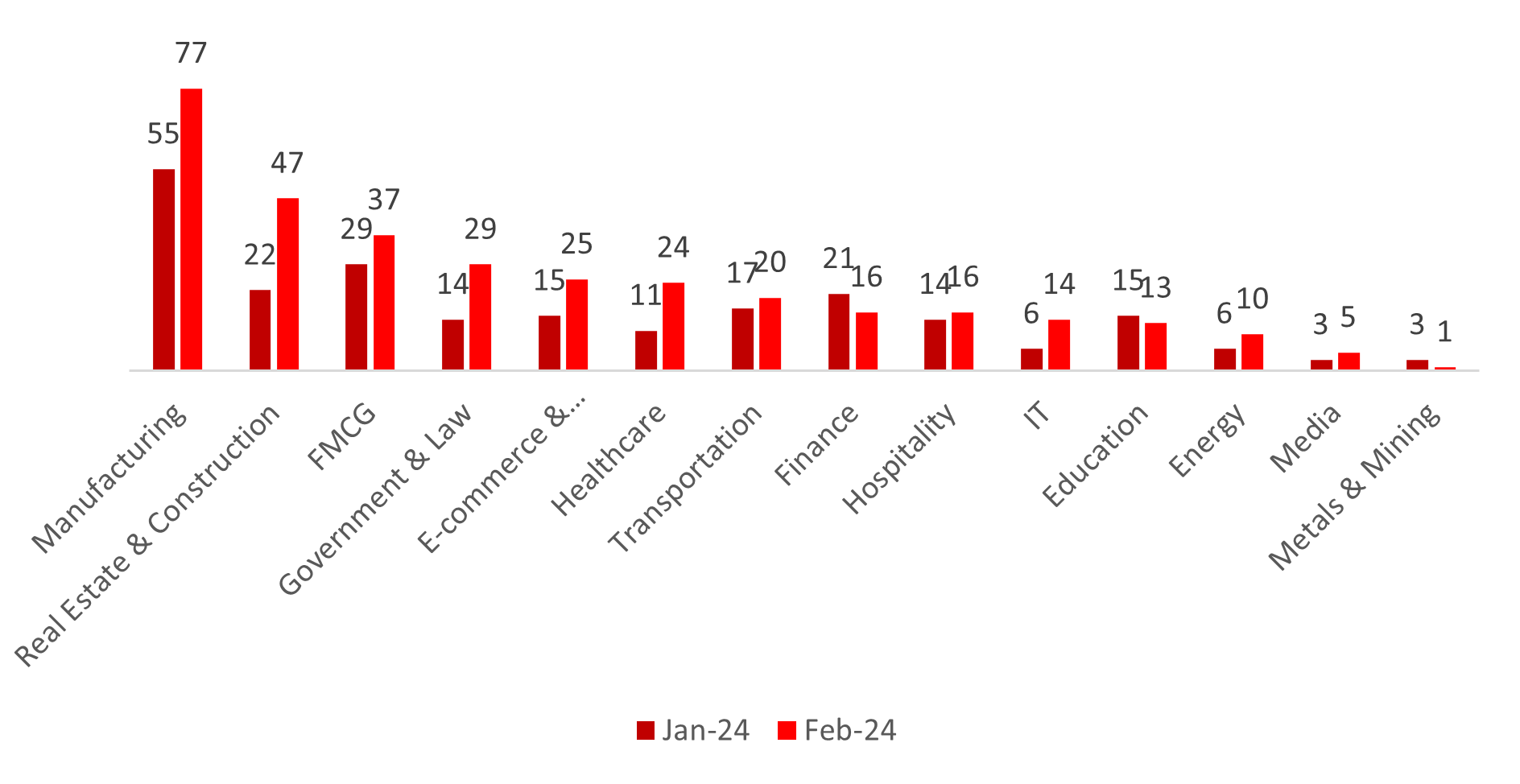
In February 2024, the manufacturing sector saw a 40% increase in ransomware victims, as compared to January, reflecting a concerning trend. Real Estate & Construction, FMCG, and Government & Law also experienced notable rises of 113.6%, 27.6%, and 107.1%, respectively. E-commerce & Telecommunications, Healthcare, and Transportation witnessed increases of 66.7%, 118.2%, and 17.6%, respectively. Meanwhile, the Finance sector faced a 23.8% decline.
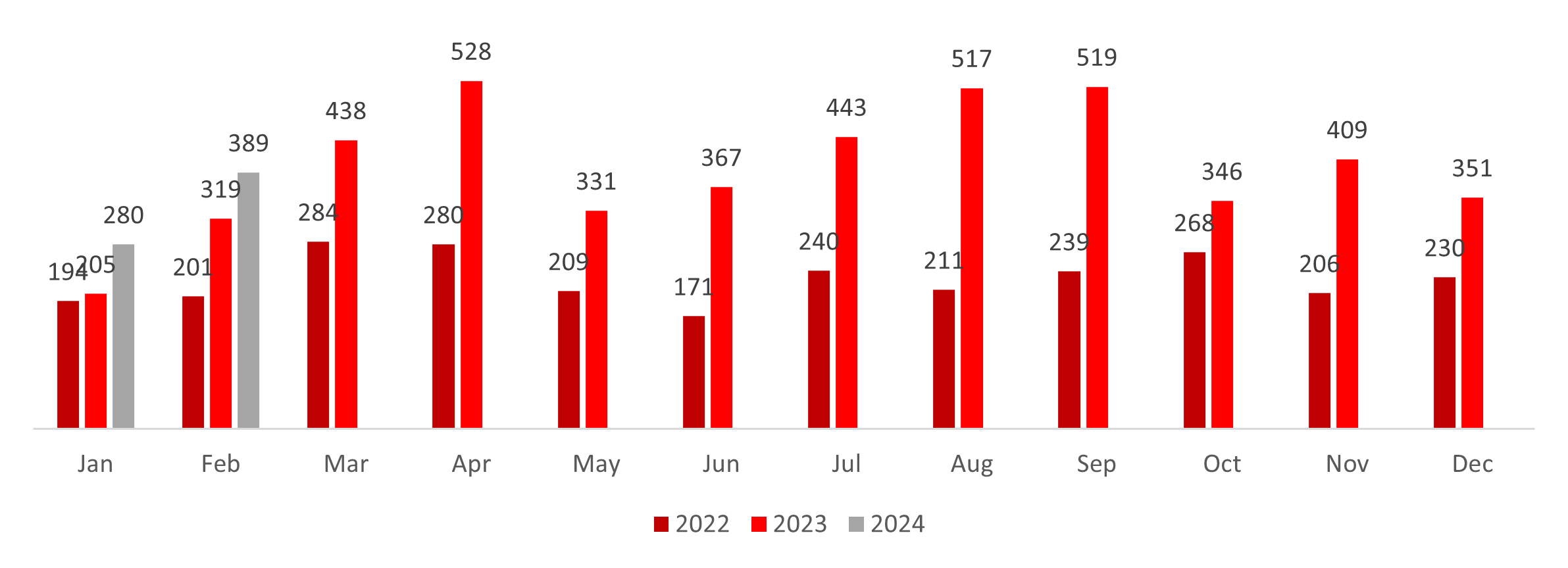
The ransomware attack trend has been on the rise over the years, particularly in February, which consistently experienced growth. Notably, there was a 58.71% increase from 2022 to 2023 and a subsequent 22% rise from 2023 to 2024, indicating sustained growth.
In February, the number of victims surged by approximately 38.9% compared to January, highlighting a significant uptick in incidents within that period.
| Sr No | CVE ID | CVSS Score | NAME | Affected Product | Associated Ransomware |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CVE-2024-1709 | 10 | ConnectWise ScreenConnect Authentication Bypass Vulnerability | ScreenConnect 23.9.7 and prior | Black Basta, Bl00dy Ransomware, LockBit, Blackcat |
| 2 | CVE-2024-1708 | 8.4 | Path-Traversal Vulnerability | ScreenConnect 23.9.7 and prior | Black Basta, Bl00dy Ransomware, LockBit |
LockBit has promptly resumed its ransomware operations on a restructured infrastructure, employing upgraded encryption tools and rerouting ransom notes to new servers, all achieved within a week post a law enforcement breach. The group is escalating its threats, particularly focusing on increased targeting of government entities.
RansomHouse group introduces ‘MrAgent’; a tool automating VMware ESXi attacks, aiming to streamline data encryption on multiple hypervisors simultaneously. It identifies the host system, disables the firewall, and deploys ransomware with custom configurations received from the command-and-control server. MrAgent aims to maximize impact by targeting all reachable VMs at once, posing severe security implications.
Alpha
Recently escalating its operations, Alpha (distinct from Alphv), is a ransomware that surfaced in February 2023. Its latest activities indicate a growing sophistication, marked by the addition of an 8-character alphanumeric extension to encrypted files and updated ransom notes, instructing victims to contact the threat actor through messaging services. The ransom demand varies from 0.272 BTC to $100,000. Researchers found a connection between Alpha and the defunct Netwalker ransomware, suggesting a potential revival or the reuse of Netwalker’s code by a new threat group.

Source: Underground Forum
Blackout
A recent addition to the ransomware landscape is the emergence of Blackout; a new group that has reportedly claimed two victims as indicated on their Onion site. The CYFIRMA Team will provide further updates as more information about the group becomes available during the report drafting process.
Source: Underground Forum
Source code of Knight Ransomware up for Sale.
A cybercriminal is reportedly selling the purported source code for the third version of the Knight ransomware on a hacker forum. Knight ransomware, which emerged in July 2023, succeeded the Cyclops operation, functioning on Windows, macOS, and Linux/ESXi systems. Notably, it offered info-stealers and a ‘lite’ encryptor for lower-tier affiliates targeting smaller organizations.
Also, the members of the ransomware group have been inactive since December 2023.
Hyundai Motor hit by Black Basta.
Hyundai Motor Europe was hit by Black Basta Ransomware Attack, Threat Actors claim theft of 3TB of Corporate Data
Warning Issued on Blackcat Ransomware Attacks.
The FBI, CISA, and HHS issued a warning on ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware targeting U.S. healthcare. Responsible for numerous breaches and $300 million in ransoms, BlackCat intensified attacks on healthcare, since December 2023. The recent cyberattack on UnitedHealth Group’s Optum is attributed to BlackCat, possibly exploiting a ScreenConnect vulnerability. The advisory stresses cybersecurity measures for critical infrastructure and healthcare. FBI offers up to $10 million in rewards for identifying or locating BlackCat leaders.
Akira hits Sweden Municipality
Bjuv, a municipality in Sweden faces a threat from the Akira ransomware group, which vows to expose almost 200GB of pilfered data. The dark web message details the compromised information, encompassing confidential documents and personal HR files.
Arrests of three suspected SugarLocker members.
Russian authorities have arrested three members of the SugarLocker ransomware group, operating under the guise of tech company, Shtazi-IT. The arrests coincide with a broader international operation against the LockBit ransomware group. SugarLocker, active since 2021, operates on a ransomware-as-a-service model, receiving a percentage of profits from victims. The group primarily uses Remote Desktop Protocol for attacks. The arrested individuals face charges of creating, using, and distributing malicious computer programs, potentially leading to up to four years in prison.
Based on available public reports, approximately 31% of enterprises are compelled to halt their operations, either temporarily or permanently, in the aftermath of a ransomware onslaught. The ripple effects extend beyond operational disruptions, as detailed by additional metrics:
Impact Assessment
Ransomware represents a formidable threat, presenting challenges for both companies and individuals by pilfering critical data and subsequently demanding payment for its release. The aftermath of these attacks often leads to substantial financial losses, whether incurred through ransom payment or investments in cybersecurity solutions for restoration. Moreover, financial setbacks extend to disrupted services, diminished customer trust, and the emotional distress inflicted upon affected entities. Beyond immediate financial concerns, such incidents can breach data regulation laws, impacting reputation, consumer trust, and market confidence. Consequently, addressing ransomware emerges as a paramount priority for businesses and government organizations alike to fortify financial stability and public trust.
Victimology
Currently, threat actors focus on targeting businesses possessing valuable data, including personal details, financial information, and intellectual property. Industries such as Manufacturing, Real Estate, Healthcare, FMCG, E-commerce, Finance, and Technology are particularly susceptible due to their data abundance. Cybercriminals strategically choose countries with robust economies and advanced digital infrastructures to maximize ransom returns. Their objective is evident: identify vulnerabilities, encrypt data, and demand substantial ransoms for release, all with the aim of securing significant profits.
In February 2024, ransomware continued to pose significant threats, with LockBit emerging as the dominant force despite law enforcement efforts. LockBit’s resurgence, marked by its technical sophistication and resilience, underscored its ability to target a wide range of industries. The surge in ransomware attacks across various sectors, coupled with the exploitation of vulnerabilities like ConnectWise ScreenConnect, highlights the urgent need for enhanced cybersecurity measures. Additionally, the emergence of new ransomware groups like Blackout and Alpha further complicates the landscape. Despite notable arrests and warnings, ransomware attacks persist, emphasizing the necessity for collaborative efforts among law enforcement, cybersecurity professionals, and businesses to mitigate future threats and protect critical infrastructure.