



CYFIRMA’s Research team conducted a thorough analysis of the critical security vulnerability, CVE-2023-49103, in OwnCloud’s Graph API. Discovered on November 21, 2023, by OwnCloud, this vulnerability poses a CVSS score of 7.5, indicating its severity. The flaw affects OwnCloud/graphapi, exposing sensitive information to unauthorized users. This vulnerability demands urgent attention, emphasizing the need for prompt mitigation measures across OwnCloud installations. This exploration aims to provide valuable insights into the nature of the vulnerability, its potential impact, and the critical importance of prompt mitigation through patching and proactive security measures.
CVE-2023-49103, disclosed on November 21, 2023, by OwnCloud, represents a critical security threat with a CVSS score of 7.5. This vulnerability, affecting OwnCloud/graphapi versions 0.2.x (before 0.2.1) and 0.3.x (before 0.3.1), exposes sensitive information to unauthorized users. The issue arises from the graphapi app’s reliance on the GetPhpInfo.php library, which, when accessed, reveals PHP environment configuration details, including web server environment variables. In containerized deployments, this may expose critical data such as OwnCloud admin credentials, mail server details, and license keys. Notably, even disabling the graphapi app does not fully mitigate the risk, as phpinfo unveils additional sensitive configuration details exploitable by attackers. Recently CISA has added CVE-2023-49103 to the list of Known Exploited Vulnerabilities, emphasizing the need for immediate action to address and remediate this security threat.
Key Takeaways:
Acknowledgements:
The CYFIRMA Research team acknowledge the security researchers who responsibly disclosed this vulnerability.
Vulnerability Type: Information Disclosure Vulnerability
CVE ID: CVE-2023-49103
CVSS Severity Score: 7.5 (HIGH)
Application: OwnCloud
Impact: Allows unauthenticated attackers information disclosure
Severity: High
Affected Versions: The earliest affected version is OwnCloud 10.13.0 and graphapi 0.2.0 – 0.3.0
Patch Available: Yes
The vulnerability within the “graphapi” is rooted in its dependence on a third-party library that furnishes a URL. Upon accessing this URL, the PHP environment’s configuration details, exposed by the phpinfo function, become visible. This disclosure encompasses all the environment variables of the web server. In containerized deployments, these environment variables may contain sensitive information, including the OwnCloud admin password, mail server credentials, and license key.
The heightened risk associated with the potential exposure of confidential data underscores the critical need to address security concerns promptly. This urgency becomes particularly pronounced in containerized environments, where the impact of such breaches can be more severe. Safeguarding against the exposure of sensitive information in these settings is paramount to ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of critical data.
The earliest affected version is OwnCloud 10.13.0 and graphapi 0.2.0 – 0.3.0
Is there already an exploit tool to attack this vulnerability?
Yes, the availability of public proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code for an Information Disclosure Vulnerability is a serious concern, as it increases the likelihood of malicious actors exploiting the flaw to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. The fact that PoC code is being shared on Telegram channels further exacerbates the situation, as it makes it even easier for attackers to obtain and utilize the exploit.
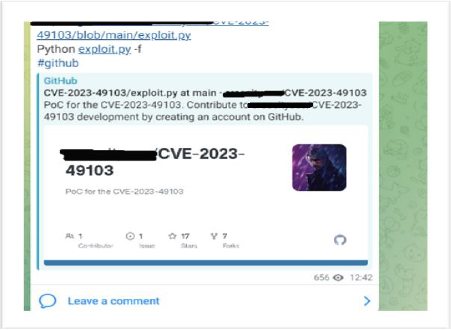
Has this vulnerability already been used in an attack?
Evidence from underground forums indicates active exploitation of the CVE-2023-41903 vulnerability, particularly targeting educational institutions. Researchers have identified 762 IPs involved in exploitation attempts, with 11 unique IPs engaged in these activities over the past 30 days.
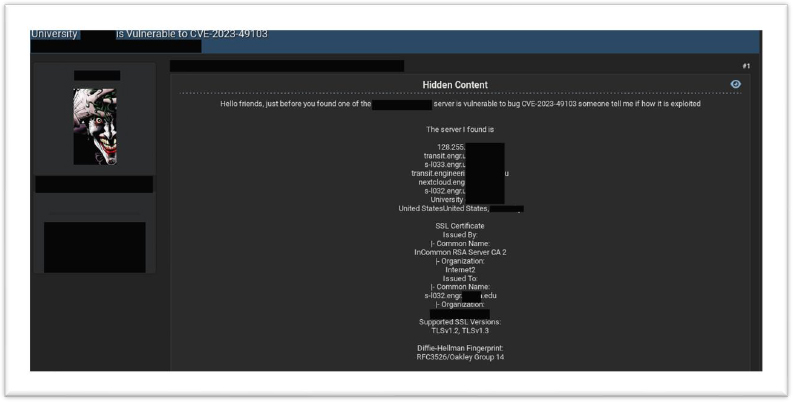
Are hackers discussing this vulnerability in the Deep/Dark Web?
Cybersecurity researchers warn of potential CVE-2023-49103 exploitation chatter on the Deep/Dark Web, originating from diverse locations like the US, Brazil, and France. Continuous monitoring of underground channels remains critical to detect this global threat.
What is the attack complexity level?
The attack complexity level for CVE-2023-49103 in OwnCloud MITRE is assessed as high.
File-transfer services are crucial components of modern business operations, providing trusted access to an organization’s sensitive information, encompassing personal data, financial details, and proprietary intellectual assets. However, as the use of these services grows, so does the potential for exploitation by malicious actors.
Recently, there have been notable instances where threat actors targeted and exploited vulnerabilities in prominent file-transfer services and software. Notable among these are Progress Software’s MOVEit (CVE-2023-34362; CVSS 9.8), Fortra’s GoAnywhere (CVE-2023-0669; CVSS 7.2), and IBM Aspera Faspex (CVE-2022-47986; CVSS 9.8). A more recent addition to this concerning trend is the vulnerability identified in OwnCloud (CVE-2023-49103; CVSS 7.5). Particularly concerning is the active involvement of ransomware groups such as Cl0p and LockBit, which have demonstrated a keen interest in exploiting these vulnerabilities. This also underscores the heightened attention from suspected Russian threat actors like TA505.
Third-party file transfer services can introduce vulnerabilities that not only compromise user data but also open up supply chain attacks. These vulnerabilities can have widespread consequences, affecting organizations from financial institutions to healthcare providers.
In underground forums, CYFIRMA’s Research team has observed that unknown hackers are showing an interest in exploiting organizations, using CVE-2023-49103 within OwnCloud’s Graph API vulnerability. This highlights the possibility of threat actors gaining access to systems and using of double-extortion tactics.
Our investigation into the CVE-2023-49103 vulnerability in OwnCloud revealed a critical unauthenticated information disclosure vulnerability affecting OwnCloud servers. Our research uncovered a staggering 13,862 publicly accessible OwnCloud Webservers that may be vulnerable to this flaw.

Source: OSINT/Surface Web
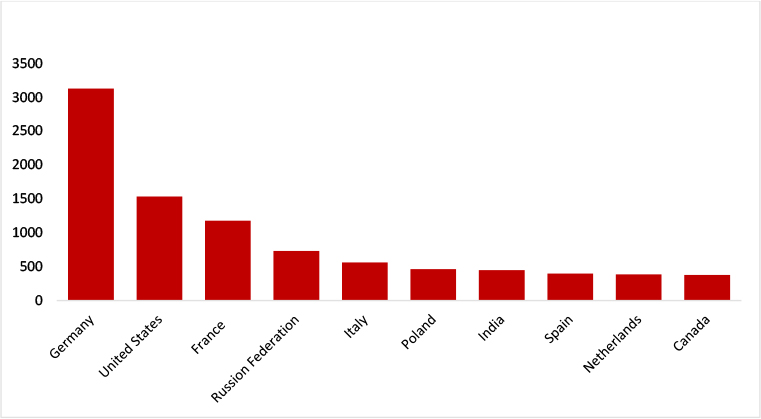
The above graph indicates the top 10 countries that may be potentially vulnerable to CVE-2023-49103.
Vulnerability Overview
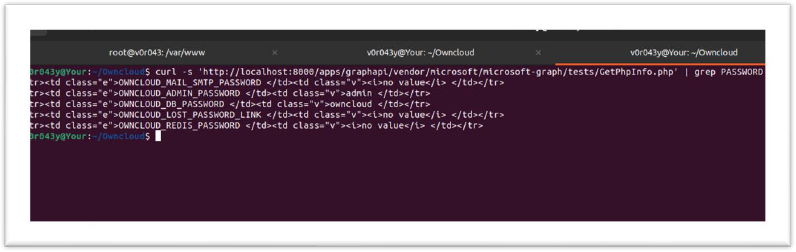
Our teams have configured the testing environment for CVE-2023-49103 vulnerability to assess the public proof-of-concept (POC) on our end. Docker installations are emphasized as particularly vulnerable due to the common practice of passing credentials through environment variables. A Public Proof of Concept (POC) serves as a valuable tool in highlighting the vulnerabilities associated with CVE-2023-49103 within OwnCloud’s Graph API. The POC is designed to effectively demonstrate the inherent security flaw found in the GetPhpInfo.php script, which, when exploited, exposes sensitive information through the phpinfo() function.
This Public POC operates by replicating the steps an attacker might take to exploit the vulnerability. The “check_phpinfo” function systematically inspects each URL by requesting the specified endpoint. If the HTTP status is 200 and the response contains the string ‘OWNCLOUD_ADMIN_’, the URL is flagged as potentially vulnerable.
In terms of practical usage, the Public POC provides a straightforward command-line interface, allowing security professionals to input a list of target URLs and specify the output file for recording vulnerable instances. The POC excels in delivering a clear demonstration of the vulnerability, making it an effective tool for security researchers and practitioners seeking to understand the potential risks associated with OwnCloud instances.
In response to the CVE-2023-49103 vulnerability in OwnCloud’s Graph API, Cyfirma’s research team recommends immediate actions: delete the vulnerable file “owncloud/apps/graphapi/vendor/microsoft/microsoft-graph/tests/GetPhpInfo.php,” disable the phpinfo function in Docker containers, and update sensitive information such as ownCloud admin password, Mail server credentials, Database credentials, and Object-Store/S3 access key. Additionally, apply ongoing hardening measures in future releases, conduct regular vulnerability scans, establish a systematic patch management process, and prioritize the timely deployment of critical security patches for enhanced overall system security. These measures collectively fortify the system against potential threats and align with cybersecurity best practices.
Target Geography: Organizations worldwide deploying OwnCloud’s Graph API falling within the affected versions may potentially be at risk. The impact of CVE-2023-49103 is not restricted by geography but extends to any region where OwnCloud’s Graph API is utilized. Therefore, organizations in regions like Germany, the United States, France, and other areas with significant ownCloud’s Graph API deployments might be exposed to the risk of exploitation.
Target Industry: The CVE-2023-49103 vulnerability in OwnCloud’s Graph API has the potential to affect organizations across a wide spectrum of industries. This includes but is not limited to education, finance, banking, and various other sectors that rely on OwnCloud’s Graph API for Information Disclosure Vulnerability. Threat actors with knowledge of this vulnerability may selectively target industries based on the perceived value of the data or services handled by the OwnCloud’ server. Organizations dealing with sensitive data or those heavily dependent OwnCloud’s Graph API’s capabilities may particularly be attractive targets.
Understanding the potential impact across different geographic regions and, industries is crucial for organizations to evaluate their exposure to CVE-2023-49103 and would provide more specific insights into the nature of the vulnerability and the recommended mitigation measures. Organizations are advised to stay informed through official channels, such as security advisories from relevant authorities or vendors, to obtain the latest and most accurate information.
In conclusion, the identified CVE-2023-49103 vulnerability in OwnCloud’s Graph API poses a significant risk, providing an opportunity for threat actors to exploit various attack vectors. The potential ramifications encompass unauthorized access, data breaches, and system compromise. The urgency of implementing immediate measures, including the removal of vulnerable files, disabling unnecessary functions, and updating critical credentials, cannot be overstated. However, it is imperative to recognize that these actions may only offer temporary relief.
The primary emphasis should be on sustained vigilance, prioritizing the swift deployment of security patches, and implementing robust mitigation strategies. Timely patching is crucial to closing the vulnerability gap and preventing malicious actors from exploiting the system. Organizations must adopt a proactive stance by regularly assessing and fortifying their security posture against evolving threats. By staying ahead of emerging threats through prompt patching and robust mitigation strategies, organizations can effectively safeguard their systems and data from the ever-evolving tactics of threat actors.