



CVE-2023-34468 is a critical security vulnerability affecting the Apache NiFi project; a data integration and automation tool. The vulnerability was disclosed through multiple sources, including the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) and Apache’s security advisory. It allows remote code execution via malicious H2 database connection strings. The issue was reported in Apache NiFi’s Jira tracker and has gained attention in the cybersecurity community.
The Apache NiFi project, a popular data integration tool, has been found vulnerable to CVE-2023-34468, revealing a potential avenue for remote code execution. CYFIRMA Research conducted an in-depth analysis, uncovering the implications of this vulnerability. This report outlines the key details, potential impacts, affected versions, and mitigation strategies for organizations utilizing Apache NiFi.
Key Takeaways:
Acknowledgements:
CYFIRMA Research acknowledges the collaborative efforts of security researchers, Apache NiFi contributors, and the wider cybersecurity community in identifying and addressing this vulnerability. The Apache Software Foundation’s prompt response and mitigation efforts are commendable, highlighting the significance of coordinated security research in safeguarding digital ecosystems.
Vulnerability type: Remote Code Execution (RCE) CVE ID: CVE-2023-34468
CVSS Severity Score: 8.8 [High]
Application: Apache NiFi
Impact: Remote code execution, unauthorized access, data breaches, server compromise
Affected Versions: Apache NiFi – 0.0.2 through 1.21.0
Patches Available: Yes
CVE-2023-34468 is a security vulnerability discovered in Apache NiFi, an open-source data integration and automation tool used by organizations to process and distribute data. The flaw allows for remote code execution by exploiting specially crafted H2 database connection strings. H2 is an embedded Java-based database commonly used in Apache NiFi configurations.
Attackers could potentially take advantage of this vulnerability to execute arbitrary code on vulnerable Apache NiFi instances. This could lead to unauthorized access, data theft, or system compromise.
The impact of this vulnerability is severe, as it grants attackers the ability to gain unauthorized access to systems, exfiltrate sensitive data, and execute malicious code remotely. An attacker could exploit this flaw to compromise data integrity, disrupt operations, and potentially cause financial and reputational damage.
This vulnerability affects Apache NiFi versions up to the reported issue. Organizations using these versions are at risk and should take immediate action. Check here.
Is there already an exploit tool to attack this vulnerability? As of the available information, there is a known public exploit tool for CVE-2023-34468 in Apache NiFi.
Has this vulnerability already been used in an attack? There is no specific information confirming whether CVE-2023-34468 in Apache NiFi has been exploited. However, given its Critical severity, organizations should remain vigilant and actively monitor their systems for signs of compromise.
Are hackers discussing this vulnerability in the Deep/Dark Web? As per CYFIRMA observation, hackers are actively discussing or exploiting CVE-2023-34468 in the Deep/Dark Web. Continuous monitoring of underground forums and channels is necessary to stay updated on any emerging discussions or potential threats.
What is the attack complexity level? The attack complexity level for CVE-2023-34468 in Apache NiFi is LOW.
Historical Trends and Known Exploits: Threat actors have historically exploited vulnerabilities in similar software products. Given the pattern of exploiting such vulnerabilities, it is important to acknowledge that threat actors may attempt to exploit CVE-2023-34468 in Apache NiFi. This could lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, or network compromise. Organizations should take this risk seriously and apply patches or updates to secure their systems.
The exploration and analysis of the CVE-2023-34468 vulnerability in Apache NiFi involved a comprehensive investigation into the vulnerability’s core mechanics, potential attack vectors, and the steps required to compromise vulnerable systems.
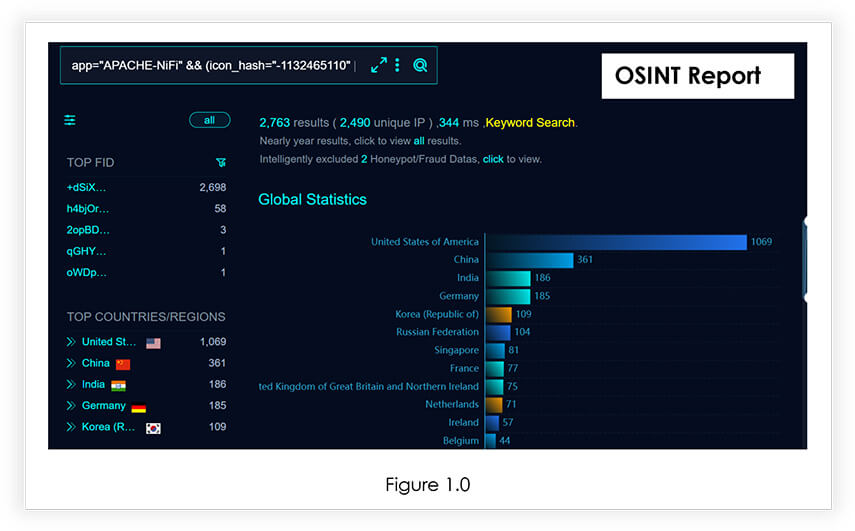
While we were researching, we also found that almost 2700 Apache Nifi are publicly available which may be vulnerable to CVE-2023-34468 vulnerability.
The Metasploit Module CYFIRMA Researchers examined here provides a lens into the vulnerability exploitation, demonstrating its potential for both defenders and adversaries. The Exploit Code can be found here.
Module Workflow: The journey of this module unfolds in several critical phases:
To mitigate the risk associated with CVE-2023-34468, Apache NiFi users should take the following actions:
Target Geography: Organizations worldwide that have deployed Apache NiFi instances, falling within the affected versions may potentially be at risk. Apache NiFi is used globally, making the vulnerability relevant to organizations across different geographical regions.
The impact of this vulnerability is not limited by geography but instead extends to any region where Apache NiFi is used. As such, organizations in regions such as North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and other areas with a significant presence of Apache NiFi installations could be exposed to the risk of exploitation.
Target Industry: The CVE-2023-34468 vulnerability in Apache NiFi has the potential to affect organizations across a wide spectrum of industries. This includes but is not limited to healthcare, finance, government, telecommunications, and various other sectors that rely on Apache NiFi for data integration and automation.
Threat actors with knowledge of this vulnerability may selectively target industries based on the perceived value of the data or services handled by Apache NiFi instances. Organizations dealing with sensitive data or those heavily dependent on Apache NiFi’s capabilities may particularly be attractive targets.
Target Technology: The CVE-2023-34468 vulnerability is specific to Apache NiFi, a data integration and automation tool widely adopted by organizations for managing data flows and processing. While the immediate impact is on Apache NiFi instances, it is crucial to recognize that the ramifications of successful exploitation can extend beyond the Apache NiFi environment.
A successful exploitation of this vulnerability can result in unauthorized code execution, potentially compromising the broader technological ecosystem. This includes servers, applications, and interconnected systems integrated with Apache NiFi, amplifying the potential impact on an organization’s technology infrastructure.
Understanding the potential impact on different geographic regions, industries, and technologies helps organizations assess their exposure to the CVE-2023-34468 vulnerability. It underscores the importance of promptly addressing the issue through patching, proactive security measures, and vigilant monitoring to mitigate the risks associated with this vulnerability.
From underground forums, CYFIRMA Research team has observed that unknown hackers are selling Apache NiFi Exploits.
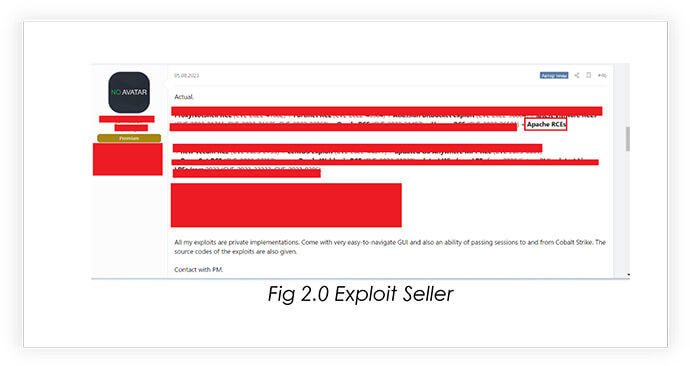
In conclusion, the CVE-2023-34468 vulnerability in Apache NiFi demands swift and decisive action from organizations and individuals using this data integration and automation tool. It is paramount that organizations promptly apply available security patches, update their Apache NiFi installations, and maintain continuous vigilance through network monitoring.
The collaborative sharing of threat intelligence within the cybersecurity community is still essential to anticipate and respond to emerging threats effectively.
The CYFIRMA Research team continues its unwavering commitment to contribute to the collective efforts aimed at bolstering cybersecurity resilience. Our dedication is still steadfast in protecting digital assets in the face of evolving cyber threats and vulnerabilities, ensuring that organizations remain well-prepared to address and mitigate security challenges effectively.