Published On : 2023-05-26
Weekly Attack Type and Trends
Key Intelligence Signals:
- Attack Type: Malware Implants, Spear Phishing, Ransomware Attacks, Vulnerabilities & Exploits, DDoS, Data Leak.
- Objective: Unauthorized Access, Data Theft, Data Encryption, Financial Gains, Payload Delivery.
- Business Impact: Data Loss, Financial Loss, Reputational Damage, Loss of Intellectual Property, Operational Disruption.
- Ransomware – Royal Ransomware | Malware – Sotdas
- Royal Ransomware – One of the ransomware groups.
- Please refer to the trending malware advisory for details on the following:
- Malware – Sotdas
- Behavior –Most of this malware uses phishing and social engineering techniques as its initial attack vector. Apart from these techniques, exploitation of vulnerabilities, defence evasion, and persistence tactics are being observed.
Threat Actor in Focus
Kimsuky Targeting South Korea and Organization Supporting DPRK-Defector
- Suspected Threat Actors: Kimsuky
- Attack Type: Spear Phishing
- Target Geography: South Korea
- Target Industry: NGO and Media Industry
- Objective: Data Exfiltration and Reconnaissance
- Target Technology: Windows
- Business Impact: Data Loss and Operational Disruption
Summary:
In a recent observation, APT Kimsuky, an advanced persistent threat group based in North Korea, was detected conducting a targeted campaign against organizations focused on North Korea-related information services, human rights activists, and support groups for defectors from the DPRK. APT Kimsuky has been active since 2012 and is notorious for its espionage activities, primarily aimed at South Korea. This active campaign by Kimsuky has revealed using of the RandomQuery malware, designed specifically for file enumeration, and stealing sensitive information. The threat actor employed phishing attacks, emails written in the Korean language, disguised as the CEO of Daily NK, a prominent online publication based in Seoul that extensively covers North Korean affairs. The phishing emails manipulate victims to open a Microsoft Compiled HTML Help (CHM) file. Once the CHM file is launched, it triggers the execution of a Visual Basic Script (VBS) that initiates an HTTP GET request to a remote server. This request retrieves the second-stage payload, which is a VBS script responsible for executing the RandomQuery malware. Once the victim’s system is compromised, the malware performs its malicious activity to gather valuable data such as system metadata, running processes, installed applications, and files from various directories. All the stolen information is then transmitted back to the command-and-control (C2) server operated by the attackers.
Insights:
It seems Kimsuky is currently in an aggressive mode. Along with this campaign, Kimsuky was recently detected in another malicious activity. In that attack, the threat actor was observed exploiting a vulnerable and poorly managed Windows IIS server of a Korean construction company and then executing a PowerShell command to download the backdoor for further attacks.
North Korea is very intolerant and known for strictly punishing their citizens, who do not follow rules set by their master. It appears DPRK put their cyberespionage group on the job to gather information and counter internal threats by targeting Defectors in South Korea and punishing them accordingly.
Major Geopolitical Developments in Cybersecurity
Iranian Hackers Possibly Behind Israeli Logistics Industry Attack
- In a recent watering hole attack, at least eight websites linked to Israeli shipping, logistics, and financial services firms were targeted. Researchers have attributed the attacks with low confidence to an Iranian threat actor, tracked as Tortoiseshell, which is also called Crimson Sandstorm (previously Curium), Imperial Kitten, and TA456.
- This APT has been active since at least July 2018, with its initial attacks focusing on Saudi Arabian IT suppliers. Additionally, it has been shown to build up phony employment websites for former members of the US military, in an effort to con them into installing remote access trojans.
- However, this is not the first time that Iranian activity clusters have targeted the Israeli shipping industry with watering hole attacks. The assault technique, also known as “strategic website compromises,” involves infecting a website that is known to be frequently accessed by a certain user group or by people, working in a particular industry, to facilitate the spread of malware.
- An Israeli shipping company’s official login page was used by an Iranian actor in August 2022 to host a watering hole that was intended to send login information to an attacker-controlled domain.
- The most recent intrusions are part of the cyberwar between the two countries that has escalated over the past two years. Although Iranian state-sponsored actors are not as advanced as their Russian and Chinese counterparts, they are enhancing their cyber capabilities every year.
G7 Summit Communique Angers China and Russia
- In a fiery response to statements issued at the recent G7 group’s summit in Hiroshima, Chinese state media have berated the outcome of the meeting and singled out Japan, Great Britain, and the United States in their rhetoric.
- The Group of Seven (G7) declarations issued on Saturday singled out China on issues including Taiwan, non-market policies and practices, malign business, and cyber practices such as illegitimate technology transfer or data disclosure or human rights abuses, underscoring the wide-ranging tensions between Beijing and the group of major industrialized democracies.
- The text calls for increased cooperation with Beijing on issues of global importance and states China is needed as a partner on the international stage, it has also singled out Chinese abuses, which angered Beijing to a degree when the foreign ministry said it firmly opposed the communique and it had summoned Japan’s ambassador to China in a pointed protest to the summit host.
- In terms of attitude to Russia, the communique was way cruel and among other things stated that the G7 countries will deprive Russia of technologies, industrial equipment, and services that serve its war machine. Russia, a close ally of China that was also called out in the G7 statement over its war in Ukraine, said the summit was an “incubator” for anti-Russian and anti-Chinese hysteria and stated the G7 countries are on a path of a dangerous escalation.
- Separately, China’s embassy in Britain urged London to stop slandering China, after British Prime Minister Rishi Sunak said Beijing represents the world’s greatest challenge to security and prosperity. The fiery reactions from Moscow and Beijing are likely to be followed by steps in the fifth domain, which both countries usually utilize in similar situations since they see hacking as a legitimate tool of statecraft. The cyber defenders in the G7 countries should thus be on high alert.
Other Observations
CYFIRMA Research team observed a potential data leak related to Moon Valley Nurseries, (www[.]moonvalleynurseries[.]com). Moon Valley Nurseries is a retailer and wholesaler of garden plants, trees, and plant products. The Company provides products in the categories of desert, citrus, fruit, oak, magnolia, evergreen trees, and palms. The data that has been breached consists of sensitive information, including customer IDs, names, emails, groups, phone numbers, ZIP codes, countries, states/provinces, and other confidential data.
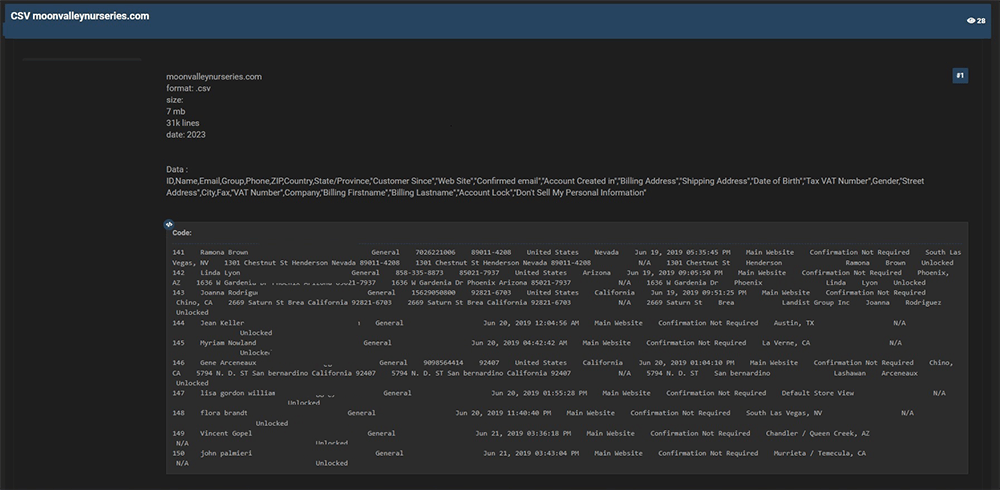
Source: Underground forums
STRATEGIC RECOMMENDATION
- Attack Surface Management should be adopted by organizations, ensuring that a continuous closed-loop process is created between attack surface monitoring and security testing.
- Deploy a unified threat management strategy – including malware detection, deep learning neural networks, and anti-exploit technology – combined with vulnerability and risk mitigation processes.
- Incorporate Digital Risk Protection (DRP) in the overall security posture that acts as a proactive defence against external threats targeting unsuspecting customers.
- Implement a holistic security strategy that includes controls for attack surface reduction, effective patch management, active network monitoring, through next generation security solutions and ready to go incident response plan.
- Create risk-based vulnerability management with deep knowledge about each asset. Assign a triaged risk score based on the type of vulnerability and criticality of the asset to help ensure that the most severe and dangerous vulnerabilities are dealt with first.
MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATION
- Take advantage of global Cyber Intelligence providing valuable insights on threat actor activity, detection, and mitigation techniques.
- Proactively monitor the effectiveness of risk-based information security strategy, the security controls applied and the proper implementation of security technologies, followed by corrective actions remediations, and lessons learned.
- Move beyond the traditional model of security awareness towards improved simulation and training exercises that mimic real attack scenarios, account for behaviours that lead to a compromised, and are measured against real attacks the organization receives.
- Consider implementing Network Traffic Analysis (NTA) and Network Detection and Response (NDR) security systems to compensate for the shortcoming of EDR and SIEM solutions.
- Detection processes are tested to ensure awareness of anomalous events. Timely communication of anomalies and continuously evolved to keep up with refined ransomware threats.
TACTICAL RECOMMENDATION
- Patch software/applications as soon as updates are available. Where feasible, automated remediation should be deployed since vulnerabilities are one of the top attack vectors.
- Consider using security automation to speed up threat detection, improve incident response, increase the visibility of security metrics, and rapid execution of security checklists.
- Build and undertake safeguarding measures by monitoring/ blocking the IOCs and strengthen defences based on tactical intelligence provided.
- Deploy detection technologies that are behavioural anomaly-based to detect ransomware attacks and help to take appropriate measures.
- Implement a combination of security control such as reCAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart), Device fingerprinting, IP backlisting, Rate-limiting, and Account lockout to thwart automated brute-force attacks.
- Ensure email and web content filtering uses real-time blocklists, reputation services, and other similar mechanisms to avoid accepting content from known and potentially malicious sources.




