



CYFIRMA Research and Advisory Team would like to highlight ransomware trends and insights gathered while monitoring various forums. This includes multiple – industries, geography, and technology – that could be relevant to your organization.
Type: Ransomware
Target Technologies: MS Windows
Introduction
CYFIRMA Research and Advisory Team has found Anomaly Ransomware while monitoring various underground forums as part of our Threat Discovery Process.
Anomaly Ransomware.
Anomaly ransomware, recently identified by researchers, is based on Chaos ransomware.
Once entered into the victim’s system, ransomware encrypts files and appended filenames with a four-character random extension. After completing the encryption process, it altered the desktop wallpaper and delivered a ransom note titled “read_it.txt.”
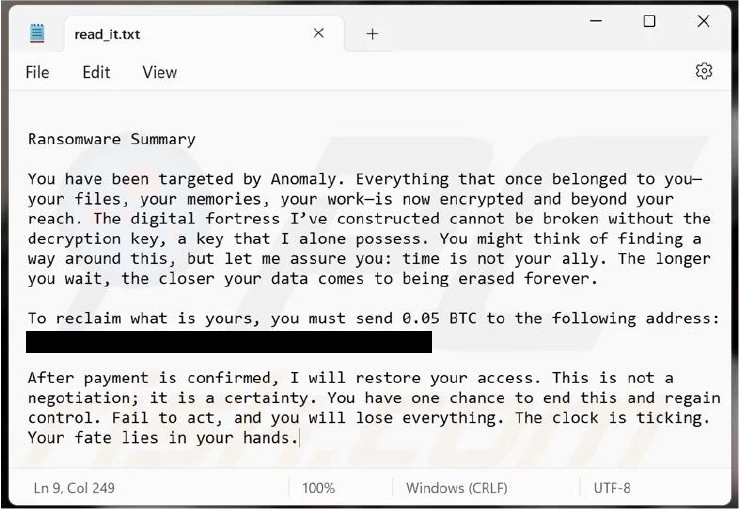
Anomaly’s ransom note informs victims that their files have been encrypted, with recovery possible only by purchasing a decryption key for 0.05 BTC. The note vaguely warns that delays in payment may lead to permanent data loss.

Following are the TTPs based on the MITRE Attack Framework
| Tactic | ID | Technique/ Sub-Technique |
| Execution | T1053 | Scheduled Task/Job |
| Execution | T1059 | Command and Scripting Interpreter |
| Execution | T1106 | Native API |
| Execution | T1129 | Shared Modules |
| Persistence | T1053 | Scheduled Task/Job |
| Persistence | T1176 | Browser Extensions |
| Persistence | T1542.003 | Pre-OS Boot: Bootkit |
| Persistence | T1543.003 | Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service |
| Persistence | T1547.001 | Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder |
| Persistence | T1574.002 | Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Side-Loading |
| Privilege Escalation | T1053 | Scheduled Task/Job |
| Privilege Escalation | T1055 | Process Injection |
| Privilege Escalation | T1543.003 | Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service |
| Privilege Escalation | T1547.001 | Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder |
| Privilege Escalation | T1548 | Abuse Elevation Control Mechanism |
| Privilege Escalation | T1574.002 | Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Side-Loading |
| Defense Evasion | T1014 | Rootkit |
| Defense Evasion | T1027 | Obfuscated Files or Information |
| Defense Evasion | T1036 | Masquerading |
| Defense Evasion | T1055 | Process Injection |
| Defense Evasion | T1070.004 | Indicator Removal: File Deletion |
| Defense Evasion | T1112 | Modify Registry |
| Defense Evasion | T1140 | Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information |
| Defense Evasion | T1202 | Indirect Command Execution |
| Defense Evasion | T1222 | File and Directory Permissions Modification |
| Defense Evasion | T1497 | Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion |
| Defense Evasion | T1542.003 | Pre-OS Boot: Bootkit |
| Defense Evasion | T1548 | Abuse Elevation Control Mechanism |
| Defense Evasion | T1562.001 | Impair Defenses: Disable or Modify Tools |
| Defense Evasion | T1564.001 | Hide Artifacts: Hidden Files and Directories |
| Defense Evasion | T1564.003 | Hide Artifacts: Hidden Window |
| Defense Evasion | T1574.002 | Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Side-Loading |
| Credential Access | T1003 | OS Credential Dumping |
| Credential Access | T1552.001 | Unsecured Credentials: Credentials in Files |
| Discovery | T1010 | Application Window Discovery |
| Discovery | T1012 | Query Registry |
| Discovery | T1033 | System Owner/User Discovery |
| Discovery | T1057 | Process Discovery |
| Discovery | T1082 | System Information Discovery |
| Discovery | T1083 | File and Directory Discovery |
| Discovery | T1087 | Account Discovery |
| Discovery | T1497 | Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion |
| Discovery | T1518.001 | Software Discovery: Security Software Discovery |
| Collection | T1005 | Data from Local System |
| Collection | T1114 | Email Collection |
| Collection | T1115 | Clipboard Data |
| Collection | T1185 | Browser Session Hijacking |
| Command and Control | T1071 | Application Layer Protocol |
| Command and Control | T1105 | Ingress Tool Transfer |
| Impact | T1485 | Data Destruction |
| Impact | T1486 | Data Encrypted for Impact |
| Impact | T1489 | Service Stop |
| Impact | T1490 | Inhibit System Recovery |
| Impact | T1496 | Resource Hijacking |
Relevancy and Insights:
ETLM Assessment:
Based on available data, CYFIRMA assesses that Anomaly ransomware’s high ransom demands and profit-driven motives indicate a likely expansion across industries and regions, focusing on targets capable of meeting their financial demands. Mitigating such threats requires robust cybersecurity measures, including advanced endpoint protection, regular backups, network monitoring, and employee training.
Sigma Rule
title: Delete shadow copy via WMIC threatname:
behaviorgroup: 18
classification: 0 mitreattack:
logsource:
category: process_creation product: windows
detection: selection:
CommandLine:
– ‘*wmic*shadowcopy delete*’ condition: selection
level: critical
(Source: Surface web)
IOCs:
Kindly refer to the IOCs section to exercise controls on your security systems.
STRATEGIC RECOMMENDATION
MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATION
TACTICAL RECOMMENDATION
Type: Loader | Objectives: Data Exfiltration, Stealing Sensitive Information | Target Industries: Electricity, Oil & Gas, Law firms and Legal services | Target Geographies: United States and Europe | Target Technology: Windows OS
CYFIRMA collects data from various forums based on which the trend is ascertained. We identified a few popular malwares that were found to be distributed in the wild to launch cyberattacks on organizations or individuals.
Active Malware of the Week
This week “MintsLoader” is trending
MintsLoader
Researchers have uncovered an ongoing campaign utilizing MintsLoader, a PowerShell- based malware loader, to deliver secondary payloads such as StealC and the Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing (BOINC) client. MintsLoader is distributed through spam emails containing links to Kongtuke/ClickFix pages or JScript files. This malware employs a Domain Generation Algorithm (DGA) that calculates domain names using a seed value derived from the current day and a constant. It also integrates anti- virtual machine (anti-VM) techniques to evade detection by sandboxes and malware analysts. This campaign has notably impacted sectors such as Electricity, Oil & Gas, Law firms and Legal services across the United States and Europe.
Attack Method
The MintsLoader infection starts when a victim clicks a link in a spam email, leading to the download of a JScript file named in a specific format, such as “Fattura” followed by a series of numbers.
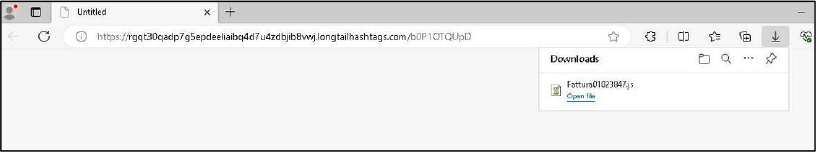
The script introduces a 13-second delay, likely to evade automated detection systems, before initiating a PowerShell command using the curl utility to download the first stage of MintsLoader. To evade detection, the script deletes itself after execution, making it harder for analysts to retrieve. In some cases, the malware is delivered via ClickFix or KongTuke links, using a slightly different method to execute the command. After contacting the command-and-control (C2) server, MintsLoader receives and executes an obfuscated response containing further PowerShell instructions. These scripts begin by decoding information and checking if the system is a virtual machine. This detection process includes examining system properties such as video adapters and cache memory configurations, specifically targeting VMware, Bochs, and other hypervisor environments. If the system is confirmed as a physical machine, the malware continues execution. These steps highlight MintsLoader’s ability to avoid sandbox environments and enhance its effectiveness.
As part of its process, the malware assigns specific values to a variable, which is used throughout its operations and shared with the C2 server. It also employs techniques to differentiate physical machines from virtual ones, ensuring it can bypass sandbox environments or security tools. One of the key features of MintsLoader is its dynamic generation of command-and-control (C2) server addresses. The malware uses a combination of the current day of the month and a constant to create unique domains each day, making detection more difficult for security systems. These domains are used to connect to the C2 server, with the address ending in a “.top” domain.
To construct the C2 URI path, MintsLoader creates a random string of alphanumeric characters and retrieves system details, like the computer name, to build query
parameters. These parameters include the system’s name as an identifier, a unique key, and a pre-set number. Using the curl command, the malware communicates with the C2 server, and the server’s response—also heavily obfuscated—is processed to execute additional stages. However, an attempted bypass of anti-malware protections fails due to flawed coding in the script.
In the final stage, MintsLoader initiates a web request to download its payload from a file- hosting site. One of the key payloads delivered by MintsLoader is StealC, a sophisticated data-stealing malware. While the hosting platform no longer provides the file, its digital signature remains accessible for analysis through security platforms.
StealC
StealC is an information-stealing malware marketed as a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) by its developer, “Plymouth,” on Russian underground forums since January 2023. Built on the framework of the earlier Arkei stealer from 2018, StealC is designed to extract sensitive data from web browsers, extensions, crypto wallets, applications, and email clients. This includes financial information, passwords, and tokens. The malware employs legitimate DLLs, such as sqlite3.dll and nss3.dll, to aid in data collection, which is then sent to its command-and-control (C2) server through HTTP POST requests.
StealC offers threat actors advanced tools, including an admin panel with features like a query builder for sorting stolen data. To evade detection, it uses XOR encryption for its strings, decrypting them during execution and storing the results in memory. The malware also includes several anti-debugging measures, such as exiting if it detects specific
usernames like “JohnDoe,” or systems with certain characteristics like single-core processors, low memory (below 1111 MB), or screen resolutions under 666 pixels. Additionally, it avoids running on systems using Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, Kazakh, or Uzbek language settings.
Before interacting with its C2 server, StealC generates a unique hardware ID (HWID) based on the C:\ drive’s volume serial number, which remains consistent and helps attackers manage stolen data. Initial communications with the C2 involve sending the HWID, followed by requests for base64-encoded configurations. Though its C2 servers are currently offline, the malware previously used HTTP POST requests to exfiltrate stolen files and credentials, while HTTP GET requests fetched third-party libraries like sqlite3.dll.
INSIGHTS
ETLM ASSESSMENT
From the ETLM perspective, CYFIRMA anticipates that MintsLoader’s evolving tactics may cause an increase in the frequency and complexity of cyberattacks, affecting organizations across various sectors. As this malware continues to adapt, it is likely that attackers will find more sophisticated ways to infiltrate networks, making it harder for organizations to detect and mitigate the threat. The use of secondary payloads, like data-stealing malware, could lead to long-term damage, as these threats have the potential to steal sensitive information and disrupt operations. In the future, organizations may find themselves grappling with not only immediate breaches but also the ripple effects of data theft and reputational damage. Employees, too, may face greater risks, as the malware targets human error, using methods such as phishing and deceptive links to gain access. As the attack methods become more refined, organizations will need to stay vigilant and prepared for the evolving nature of these threats, as they could lead to significant financial loss and operational disruption if left unchecked.
IOCs:
Kindly refer to the IOCs Section to exercise controls on your security systems.
STRATEGIC:
MANAGEMENT:
TACTICAL RECOMMENDATIONS
Key Intelligence Signals:
New Star Blizzard spear-phishing campaign targets WhatsApp accounts
Summary
Researchers recently discovered a new tactic employed by the Russian threat group Star Blizard, who have shifted their focus to compromising WhatsApp accounts.
Since November 2024, the group, previously known for targeting government, diplomatic, defense, and Ukraine-related organizations, has adapted its strategy by launching spear-phishing campaigns aimed at infiltrating WhatsApp. This marks a notable shift from their traditional attack methods.
This marks a significant departure from their usual methods, which involved using email attachments and links to steal sensitive information. The attacker’s primary targets have typically been government officials, international relations researchers, and entities involved in aiding Ukraine amid the ongoing conflict. The new campaign began with an email impersonating a U.S. government official, which contained a broken QR code intended to redirect the target to a WhatsApp group discussing Ukraine-related NGO initiatives. The broken code was a strategic move to prompt the target to engage with the email by responding.
Once the target responded, the attacker followed up with a second email containing a malicious link wrapped in a Safe Links-wrapped shortened URL. Clicking the link redirected the victim to a page displaying a legitimate-looking WhatsApp Web QR code, which misled the user into scanning it. Scanning the QR code linked the target’s WhatsApp account to a device controlled by the attacker. This allowed the threat actor to access and exfiltrate messages from the compromised WhatsApp account using browser-based plugins designed for WhatsApp Web. This tactic represents the first instance of the threat actor leveraging WhatsApp as an access vector, signaling a shift in their long-standing tactics and indicating a response to previous exposure and disruptions of their operations.
Although this campaign appeared to wind down by the end of November 2024, it highlights the persistence and adaptability of the threat actor in seeking new ways to gain access to sensitive information.
Relevancy & Insights
Star Blizzard, a Russian threat actor, has a history of targeting entities involved in government, diplomacy, defense policy, and international relations, particularly those with ties to Ukraine or Russia. Their tactics have primarily involved spear-phishing campaigns to exfiltrate sensitive data, often impersonating political figures to increase engagement. From January 2023 to August 2024, they targeted civil society organizations, including journalists, think tanks, and NGOs, to interfere with their activities. Despite being disrupted by coordinated actions from Microsoft and the US Department of Justice in October 2024, Star Blizzard quickly adapted by transitioning to new infrastructure. The November 2024 shift to WhatsApp-based phishing campaigns marks a significant change in their tactics, using QR codes and malicious links to compromise users’ WhatsApp accounts. This shift suggests a response to exposure of their TTPs, showcasing their resilience and adaptability in circumventing detection.
ETLM Assessment:
Star Blizzard, a Russian cyber threat actor, primarily targets individuals and organizations connected to government, diplomacy, defense policy, international relations, and support for Ukraine. Their geographical focus spans globally, with particular attention on countries involved in the Ukraine conflict or with diplomatic ties to Russia. Industries of interest include government entities, NGOs, think tanks, and defense researchers.
Historically, Star Blizzard has employed spear-phishing campaigns leveraging email and malicious links to exfiltrate sensitive information, often impersonating political figures.
Their attacks now include novel tactics, such as targeting WhatsApp accounts via QR code phishing, marking a shift in their techniques. While they have not been known to rely on specific malware consistently, their campaigns leverage various malicious tools to compromise systems and exfiltrate data. Given their adaptability and resilience, including the rapid shift to new domains and attack vectors after disruptions, Star Blizzard poses a persistent threat. Future risks include further evolution of their phishing strategies and expanded use of encrypted communication platforms like WhatsApp.
Strategic Recommendations:
Tactical Recommendations:
Operational Recommendations:
| MITRE FRAMEWORK | ||
| Tactic | ID | Technique |
| Reconnaissance | T1593 | Search Open Websites/Domains |
| Reconnaissance | T1589 | Gather Victim Identity Information |
| Resource Development | T1585.001 | Establish Accounts: Social Media Accounts |
| Resource Development | T1585.002 | Establish Accounts: Email Accounts |
| Resource Development | T1583.001 | Acquire Infrastructure: Domains |
| Resource Development | T1586.002 | Compromise Accounts: Email Accounts |
| Initial Access | T1078 | Valid Accounts |
| Initial Access | T1566.001 | Phishing: Spearphishing Attachment |
| Initial Access | T1566.002 | Phishing: Spearphishing Link |
| Defense Evasion | T1550.004 | Use Alternate Authentication Material: Web Session Cookie |
| Credential Access | T1539 | Steal Web Session Cookie |
| Collection | T1114.002 | Email Collection: Remote Email Collection |
| Collection | T1114.003 | Email Collection: Email Forwarding Rule |
IOCs:
Kindly refer to the IOCs (Indicators of Compromise) Section to exercise controls on your security systems.
Trump Administration postponed TikTok ban, rescinded AI regulation
The U.S. Supreme Court upheld a law set to ban TikTok in the United States starting just before the inauguration of the new US President. However, the outgoing Biden Administration did not enforce the ban, instead leaving the decision to the incoming Trump Administration. Senate Democratic Leader Chuck Schumer revealed on the Senate floor that he had urged Biden to keep the app accessible, stating, “It’s clear that more time is needed to find an American buyer and not disrupt the lives and livelihoods of millions of Americans, including influencers who have built substantial networks of followers.”
President-elect Trump has since walked back his earlier calls to ban TikTok and pledged to find a solution to keep the app operational in the U.S. The new U.S. President Donald Trump signed an executive order extending TikTok’s deadline to remain operational in the United States. He hinted at pursuing a deal in which the
U.S. government would acquire a 50% stake in the company. TikTok briefly went offline in the U.S. late Saturday night before resuming operations on Sunday.
In addition, President Trump rescinded a 2023 executive order issued by President Joe Biden that required AI companies to share safety test results with the U.S. government if their systems posed potential national security risks.
ETLM Assessment
TikTok is only one facet of China’s broader information warfare strategy. The country has inundated American social media platforms with both bots and human- operated accounts aimed at spreading disinformation and fostering division.
In the past two years, China’s campaign has shifted focus from promoting predominantly pro-China narratives to more aggressively targeting U.S. political issues. This effort is part of a larger, multibillion-dollar influence campaign. Using millions of accounts across platforms such as X (formerly Twitter), YouTube, and even fringe platforms like Gab, the campaign seeks to promote pro-China messaging. It has also been a pioneer in adopting advanced techniques like AI-generated profile pictures to enhance credibility and impact.
Over the last five years, researchers monitoring this campaign have observed a consistent evolution in its tactics. These include leveraging video content, automated voiceovers, and, most recently, AI to generate profile images and content designed to exploit and exacerbate societal divisions.
The Space Bears Ransomware Impacts Fukoku Co. Ltd.
Summary
From the External Threat Landscape Management (ETLM) Perspective, CYFIRMA observed in an underground forum that a company from Japan; Fukoku Co. Ltd.(www[.]fukoku-jp[.]com), was compromised by Space Bears Ransomware. Fukoku Co., Ltd. is a Japanese company based in Yanagawa City, Fukuoka Prefecture, specializing in the development and manufacturing of products using non-woven fabrics. The compromised data includes databases, accounting information, sales records, purchasing details, drawings, prototypes, and production cycles.
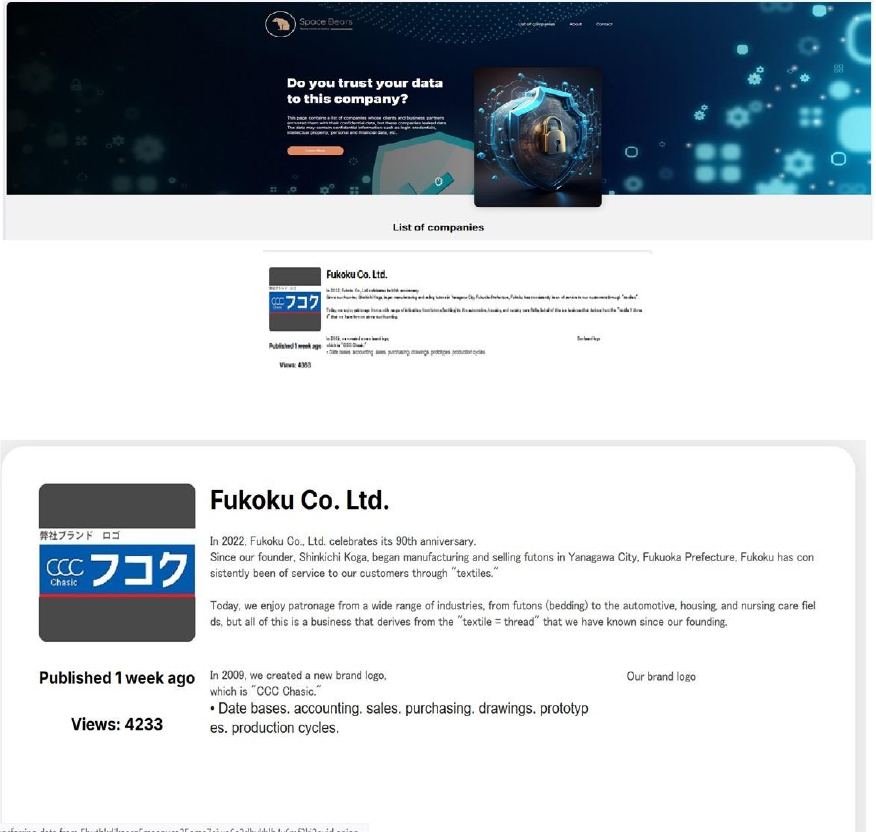
Relevancy & Insights:
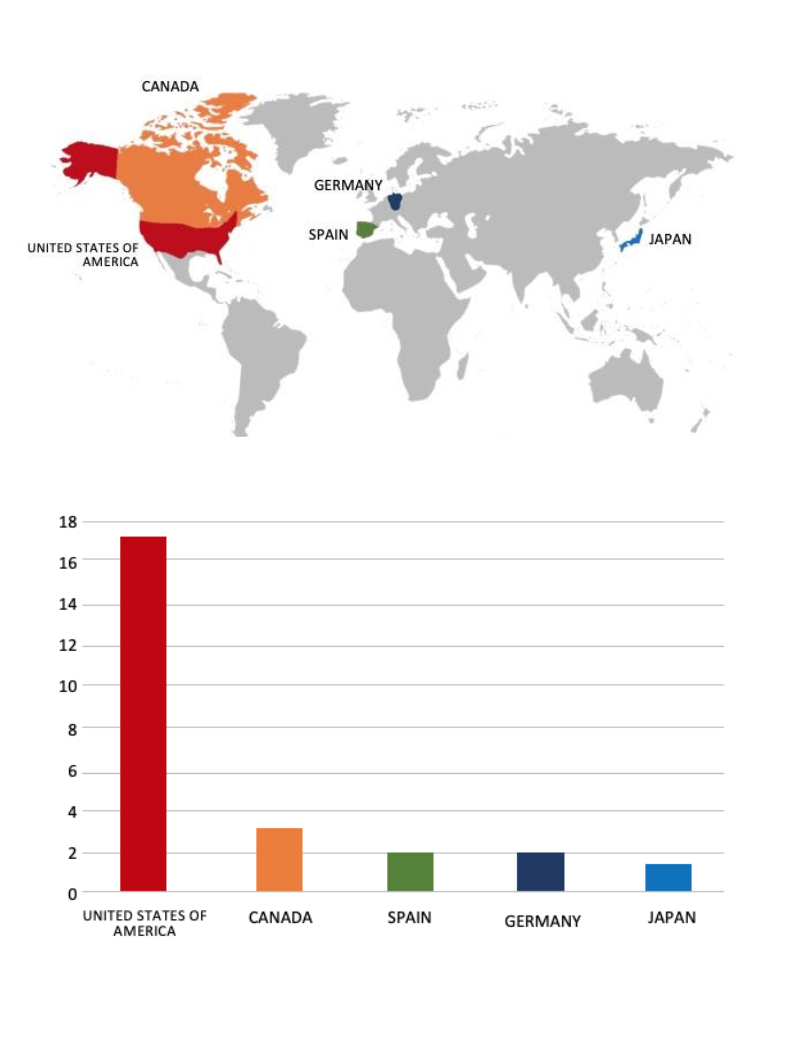
ETLM Assessment:
According to CYFIRMA’s assessment, Space Bears ransomware represents a significant threat in the evolving landscape of cybercrime. With its aggressive tactics, association with established ransomware operations like Phobos, and focus on double extortion, organizations are advised to bolster their cybersecurity measures to mitigate risks associated with such attacks. Continuous monitoring of this group’s activities will be essential for understanding their methods and potential impact on various sectors.
The RansomHub Ransomware Impacts Thai Rotary Engineering Public Co., Ltd. (TREL)
Summary
From the External Threat Landscape Management (ETLM) Perspective, CYFIRMA observed in an underground forum that a company from Thailand; Thai Rotary Engineering Public Co., Ltd. (TREL)(www[.]rotaryeng[.]co[.]th), was compromised by RansomHub Ransomware. Thai Rotary Engineering Public Co., Ltd. (TREL), is a leading engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) company in Thailand. The company specializes in bulk storage terminal projects and offers mechanical fabrication services for the petrochemical and oil & gas industries, serving both local and regional markets. The compromised data consists of confidential and sensitive information related to the organization. The total size of the compromised data is approximately 170 GB.
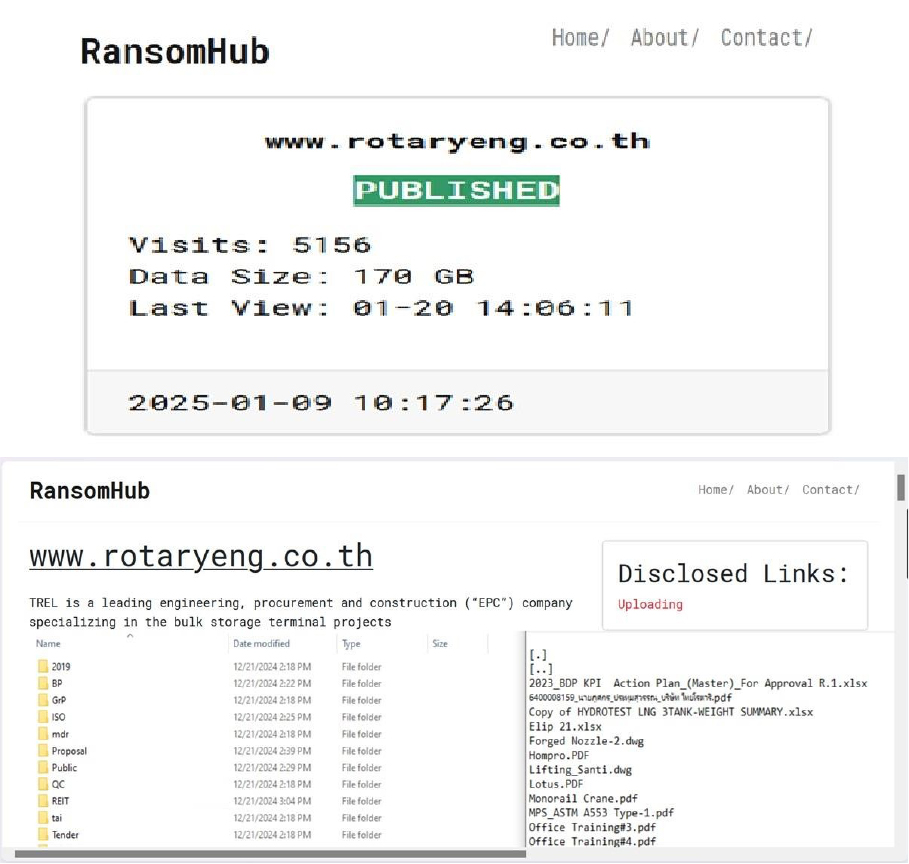
Relevancy & Insights:
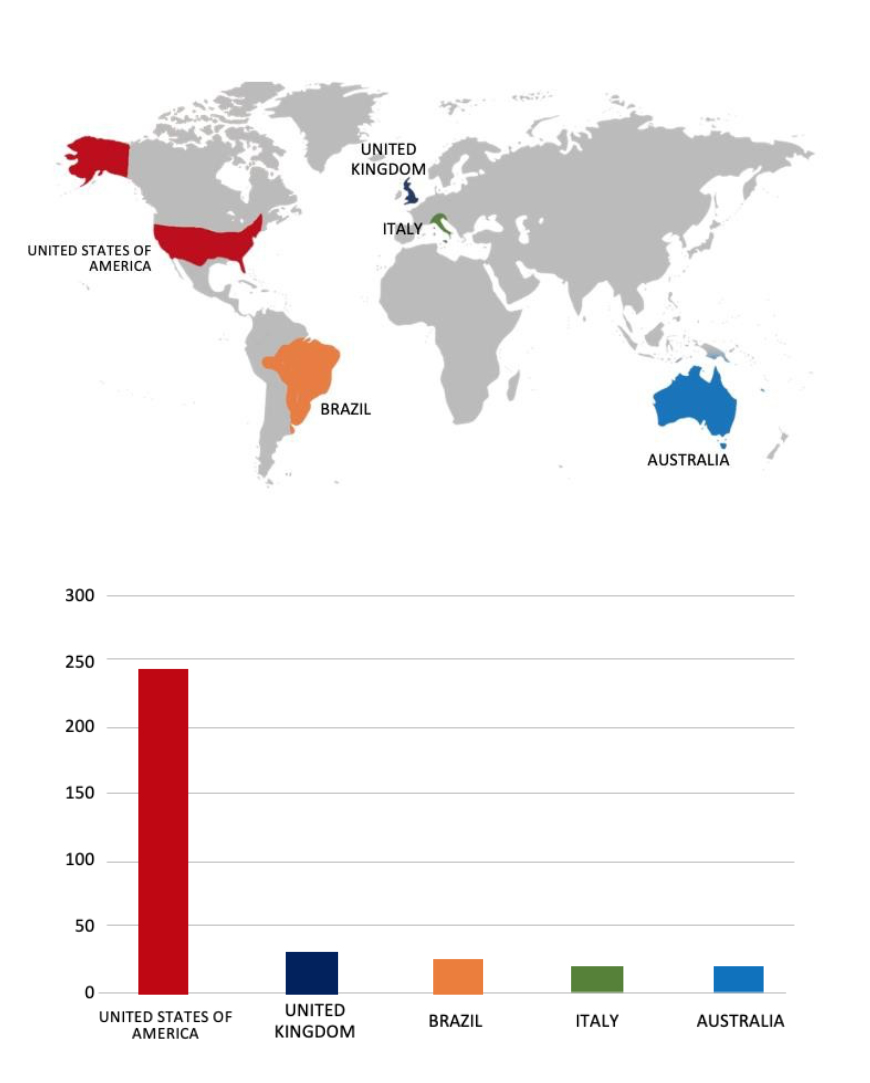
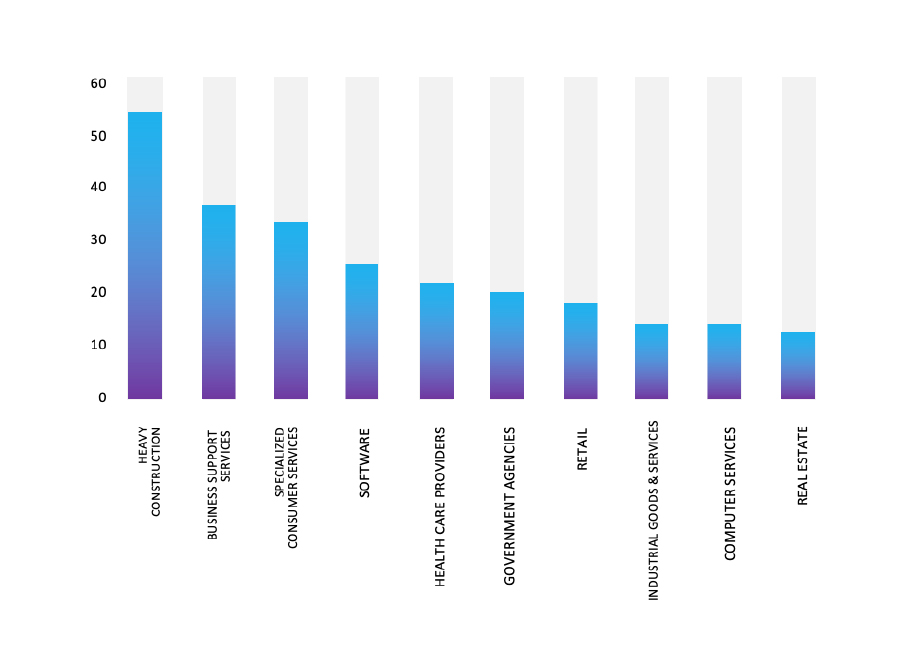
ETLM Assessment:
Based on recent assessments by CYFIRMA, RansomHub ransomware is expected to intensify its operations across various industries worldwide, with a notable focus on regions in the United States, Europe, and Asia. This prediction is reinforced by the recent attack on Thai Rotary Engineering Public Co., Ltd. (TREL), a prominent Engineering, Procurement, and Construction company from Thailand, highlighting RansomHub’s significant threat presence in Southeast Asia.
Vulnerability in Vim
Relevancy & Insights:
The vulnerability exists due to a boundary error when processing untrusted input.
Impact:
A remote attacker can create a specially crafted file, trick the victim into opening it using the affected software, trigger an out-of-bounds write, and execute arbitrary code on the target system.
Affected Products:
https[:]//github[.]com/vim/vim/security/advisories/GHSA-j3g9-wg22- v955
Recommendations:
Monitoring and Detection: Implement monitoring and detection mechanisms to identify unusual system behavior that might indicate an attempted exploitation of this vulnerability.
This week, CYFIRMA researchers have observed significant impacts on various technologies, due to a range of vulnerabilities. The following are the top 5 most affected technologies.
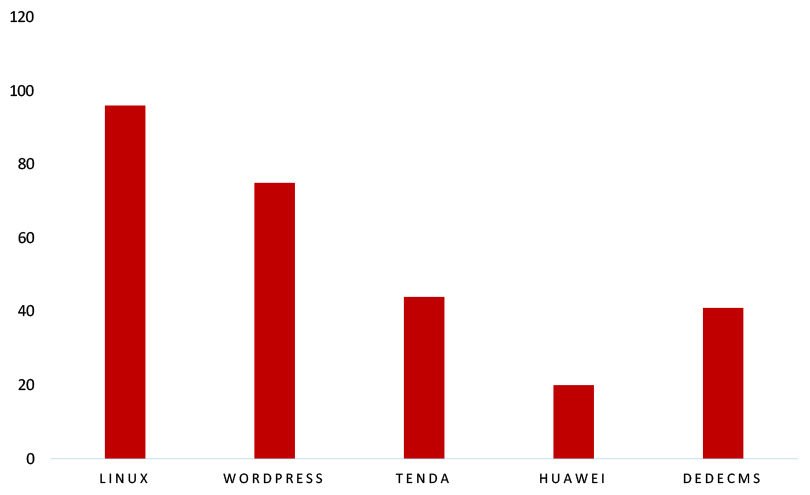
ETLM Assessment
Vulnerability in Vim, a highly configurable text editor, can pose significant threats to user privacy and security. This can impact various industries globally, including technology, finance, healthcare, and beyond. Ensuring the security of Vim is crucial for maintaining the integrity and protection of users’ data worldwide. Therefore, addressing these vulnerabilities is essential to safeguarding text creation and editing processes, particularly in UNIX systems and Apple OS X environments, across different geographic regions and sectors.
Lynx Ransomware attacked and published the data of Jim Thompson
Summary
Recently, we observed that Lynx Ransomware attacked and published the data of Jim Thompson(www[.]jimthompson[.]com) on its dark web website. Jim Thompson is a renowned global lifestyle brand originating from Thailand, celebrated for its exquisite silk products and rich heritage. Jim Thompson ships internationally to several countries, including the USA, Japan, Australia, and various European nations. The ransomware attack resulted in a data leak containing confidential and sensitive organizational information. The total size of compromised data is approximately 230 GB.
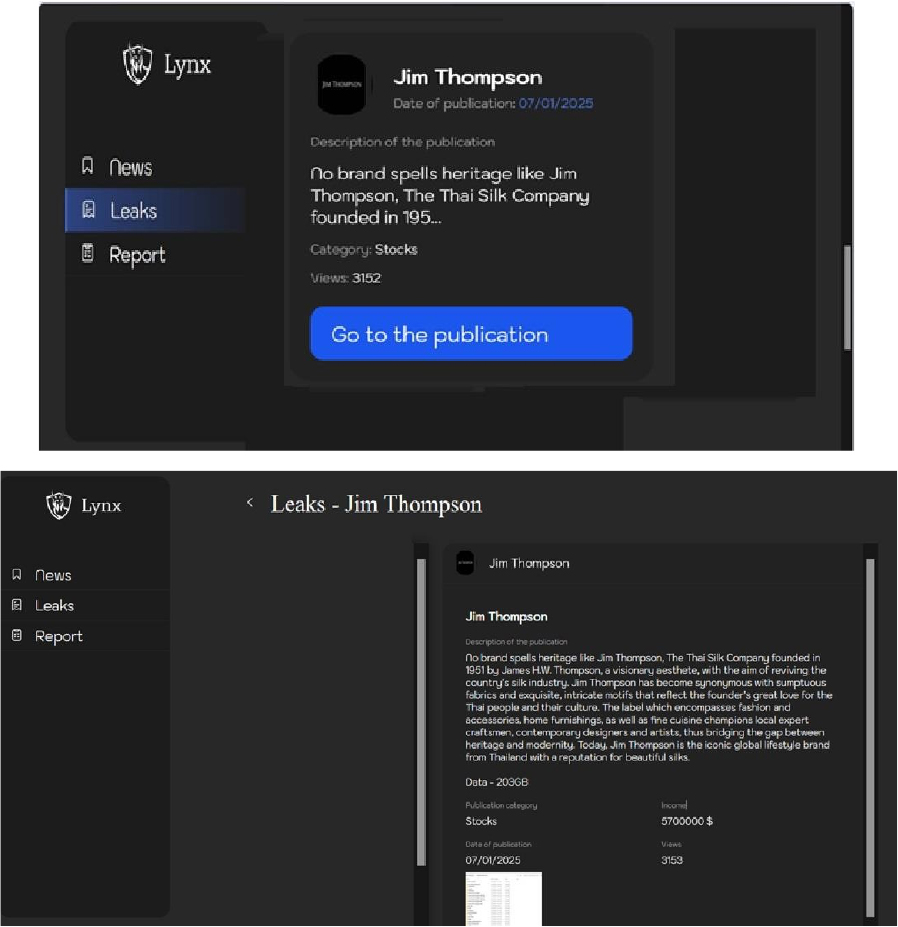
Relevancy & Insights:
ETLM Assessment:
According to CYFIRMA’s assessment, Lynx Ransomware represents a significant threat in the evolving landscape of cybercrime. Its sophisticated techniques and aggressive tactics necessitate robust cybersecurity measures from organizations to mitigate risks associated with ransomware attacks. As this group continues to operate, ongoing monitoring and analysis will be crucial for understanding their methods and developing effective defenses against them.
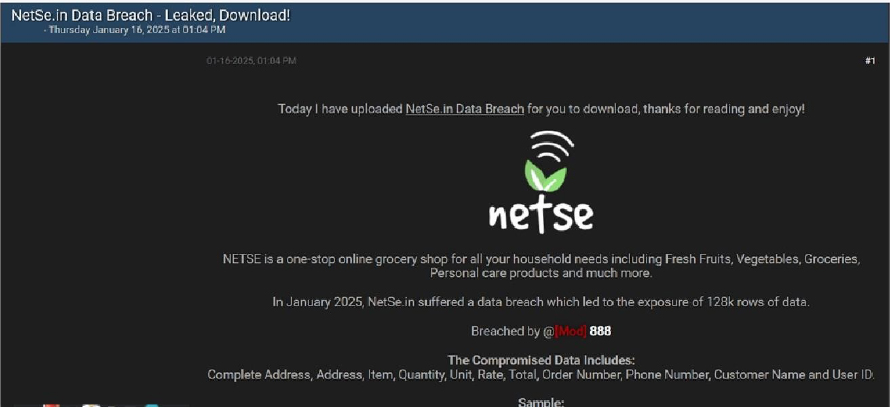
NETSE Data Advertised on a Leak Site
Summary
The CYFIRMA Research team observed a data leak related to NETSE (https[:]//netse[.]in) in an underground forum. NETSE is a one-stop online grocery shop for all household needs including Fresh Fruits, Vegetables, Groceries, Personal care products, and much more. The compromised data includes the complete address, item details (item, quantity, unit, rate, and total), order number, phone number, customer name, and user ID. The breach has been linked to a threat actor identified as “888.”
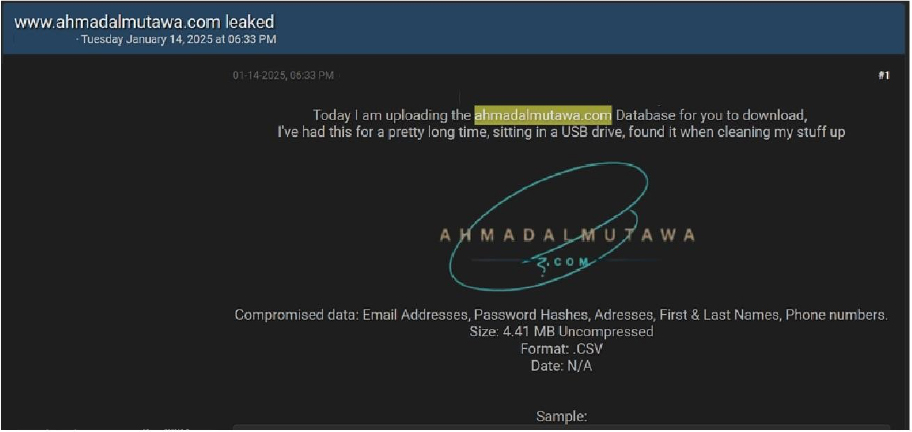
Ahmadalmutawa Data Advertised on a Leak Site
Summary:
The CYFIRMA Research team observed a data leak related to Ahmadalmutawa (https[:]//www[.]ahmadalmutawa[.]com) in an underground forum. The website ahmadalmutawa[.]com is an online platform offering courses, consultations, and resources designed to empower entrepreneurs and business owners. Ahmad Al- Mutawa, the founder, is a seasoned entrepreneur, business coach, and motivational speaker with a focus on supporting small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and fostering personal and professional growth. The compromised data includes email addresses, password hashes, addresses, first and last names, and phone numbers. The total size of the compromised data is 4.41 MB and is stored in CSV format. The breach has been attributed to a threat actor known as “Empathy.”
Relevancy & Insights:
Financially motivated cybercriminals are continuously scouring for exposed and vulnerable systems and applications to exploit. A significant number of these malicious actors congregate within underground forums, where they discuss cybercrime and trade stolen digital assets. Operating discreetly, these opportunistic attackers target unpatched systems or vulnerabilities in applications to illicitly gain access and steal valuable data.
Subsequently, the pilfered data is advertised for sale within underground markets, where it can be acquired, repurposed, and utilized by other malicious actors in further illicit activities.
ETLM Assessment:
The threat actor “888” continues to be active in the cybercrime landscape, making bold claims about breaches while often facing scrutiny regarding the validity of those claims. Organizations are advised to bolster their defenses against potential attacks from this group and similar cybercriminals.
Recommendations: Enhance the cybersecurity posture by:
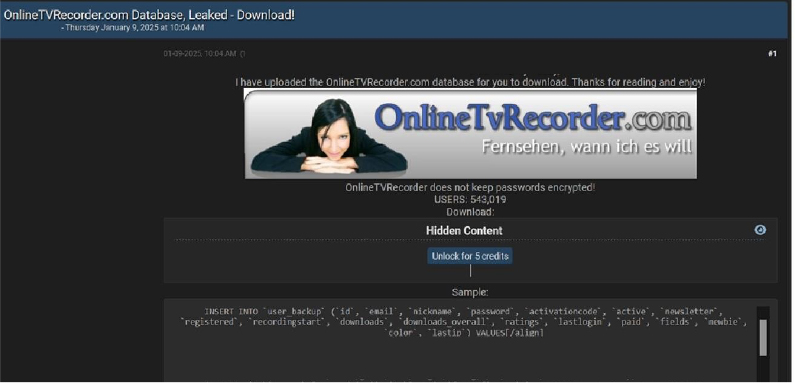
The CYFIRMA Research team observed a data leak related to OnlineTVRecorder (https[:]//www[.]onlinetvrecorder[.]com/) in an underground forum.
OnlineTvRecorder (OTR) is a web-based service that allows users to record television broadcasts from over 100 channels across various countries, including Germany, the USA, the UK, Austria, and Switzerland. OTR functions as a comprehensive media library, enabling users to watch or download films and shows for free. The compromised data includes user IDs, emails, nicknames, passwords, activation codes, newsletter subscriptions, registration details, recording start times, download history, overall downloads, ratings, last login information, paid status, and other sensitive data. The breach has been attributed to a threat actor known as “Ddarknotevil.”
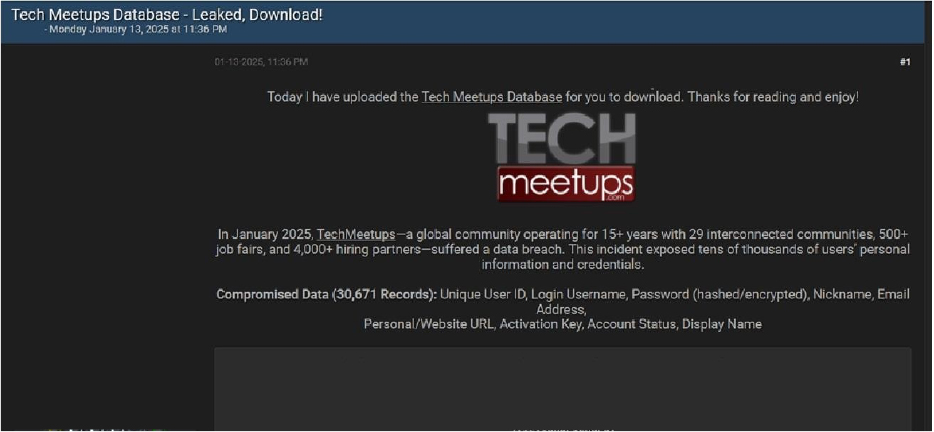
The CYFIRMA Research team observed a data leak related to Tech Meetups (http[:]//www[.]techstartupjobs[.]com) in an underground forum.TechMeetups is a global community operating for 15+ years with 29 interconnected communities, 500+ job fairs, and 4,000+ hiring partners. The compromised data consists of 30,671 records, including a unique user ID, login username, hashed/encrypted password, nickname, email address, personal/website URL, activation key, account status, and display name. The breach has been attributed to a threat actor known as “Rey.
ETLM Assessment:
Threat actor “Ddarknotevil” represents a notable threat within the cybercriminal landscape, particularly through their involvement in high-profile data breaches and sales of stolen information. Organizations are urged to enhance their cybersecurity defenses and remain vigilant against such threats to safeguard their sensitive data and maintain customer trust. Continuous monitoring of threat actors like Ddarknotevil is essential for effective incident response strategies in an evolving cyber threat environment.
STRATEGIC RECOMMENDATIONS
MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS
TACTICAL RECOMMENDATIONS
Please find the Geography-Wise and Industry-Wise breakup of cyber news for the last 5 days as part of the situational awareness pillar
For situational awareness intelligence and specific insights mapped to your organisation’s geography, industry, and technology, please access DeCYFIR.