



Key Intelligence Signals:
The New Threat Actor Called NewsPenguin Targets Pakistan
Summary:
A new threat actor with name NewsPenguin was recently seen using a sophisticated method to target organizations in Pakistan. The actor is taking advantage of the upcoming Pakistan International Maritime Expo & Conference (PIMEC-2023) to lure victims. The attacker is using targeted phishing emails, with a malicious document attached, which is falsely presented as an exhibitor manual for PIMEC-23 in spear phishing mail. The document employs a remote template injection technique and malicious Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) macro code to deliver the subsequent stage of the attack that ultimately leads to executing the final payload.
The final payload is an advanced espionage tool that uses XOR encryption with a “penguin” encryption key. After the connection between the Command-and-control server and the victim establishes, the server registers the infected system with a unique identifier 12 characters long. This unique identifier is then used for communications between the bot and the server.
Insights:
The threat actor can gain access to information belonging to other military or defense officials from other nations as the target is an international event backed by Pakistan Navy and likely to be attended by different nations.
Researchers have recently reported on the activities of a new nation-state threat actor dubbed “SideWinder.” The SideWinder APT, also known as Rattlesnake or HN2 has been active at least since 2012. It is mainly conducting cyber espionage against governments in the Asia-Pacific region and researchers believe it to have a nexus with the government of India. A new SideWinder.AntiBot.Script tool was discovered in the summer of 2022 being used against Pakistan companies. The list of targeted organizations had over sixty names including the sectors of government, military, financial, law enforcement, political, telecommunications, and media organizations. The targeted countries were Afghanistan, Bhutan, Myanmar, Nepal, and Sri Lanka. Researchers found a lot of similarities between the servers and resources used by SideWinder and the BabyElephant APT organization, raising the possibility that they are one and the same APT.
Hacktivists briefly disrupted a televised speech by President Ebrahim Raisi on the occasion of Revolution Day, a holiday important for the Iranian regime, marking the takeover of power in the country. Domestic dissident hacktivist group Adalat Ali has claimed responsibility for the action. In addition to airing a familiar slogan “Death to Khamenei” (the supreme leader of the clerical regime) the group urged Iranians to withdraw their money from state banks and participate in anti-government protests. The disruption only lasted about a minute but signifies how deeply unpopular the repressive regime is. Authoritarian regimes often lash out both domestically and internationally when under domestic pressure from their own population and thus further worsening of the geopolitical situation in the region is to be expected.
The Byelarusian Cyber-Partisans, dissident hacktivists opposed to both the domestic regime, which is increasingly under pressure from Russia to become a de facto Russian protectorate, and the Russian regime and its war against Ukraine, have released a 335GB dump of emails and other files obtained from Roskomnadzor’s General Radio Frequency Center division. The hacktivists claimed credit on Twitter and promised that more has to come. Further data is promised to contain details on data collection on protests in Ukraine & Kazakhstan for the leadership of the Kremlin by the Russian agency in question.
The U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) will allocate $60 million to Ukraine in support of efforts to protect the country’s infrastructure from cyberattacks. Attempted Russian cyberattacks against infrastructure have not been confined to Ukraine. Researchers have recently reported on a Russian “Chernovite” threat group, which reportedly undertook preparations against roughly a dozen U.S. electrical and natural gas facilities early in Russia’s war against Ukraine. The cyber-attacks have not been executed, but according to the researchers, the attackers have prepared ground, before they were intercepted in a successful public-private cooperation.
CYFIRMA Research team observed that Pepsi Bottling Ventures LLC suffered a data breach caused by a network intrusion that resulted in the installation of information-stealing malware and the extraction of data from its IT systems.
Pepsi Bottling Ventures is the largest bottler of Pepsi-Cola beverages in the United States, responsible for manufacturing, selling, and distributing popular consumer brands. It operates 18 bottling facilities across North and South Carolina, Virginia, Maryland, and Delaware.

Source: Telegram
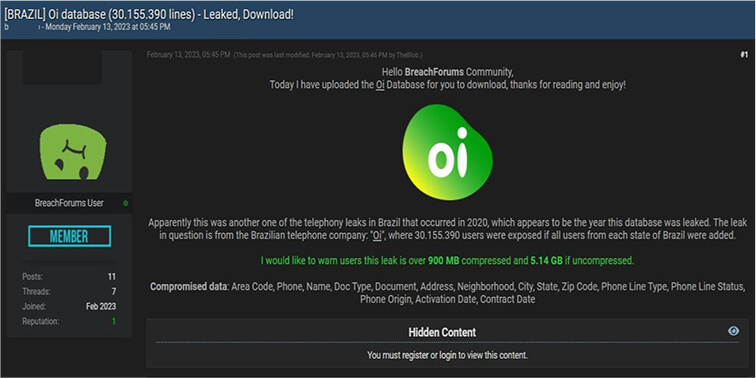
The Team also observed a potential data leak related to www[.]oiinternet [.]com [.]br – Oi is an internet Service Provider, Website Hosting & Internet-related Services in Brazil. This data leak contains area code, phone, name, doc type, address, document, address, neighborhood, city, state, zip code, phone line type, phone line status, phone origin, activation date, contract date
Source: Underground Forums