Published On : 2023-06-16
Weekly Attack Type and Trends
Key Intelligence Signals:
- Attack Type: Malware Implants, Ransomware Attacks, Vulnerabilities & Exploits, DDoS, Data Leak.
- Objective: Unauthorized Access, Data Theft, Data Encryption, Financial Gains, Payload Delivery.
- Business Impact: Data Loss, Financial Loss, Reputational Damage, Loss of Intellectual Property, Operational Disruption.
- Ransomware – LockBit 3.0 Ransomware | Malware – Stealth Soldier
- LockBit 3.0 Ransomware – One of the ransomware groups.
- Please refer to the trending malware advisory for details on the following:
- Malware – Stealth Soldier
- Behavior –Most of this malware uses phishing and social engineering techniques as its initial attack vector. Apart from these techniques, exploitation of vulnerabilities, defence evasion, and persistence tactics are being observed.
Threat Actor in Focus
APT32 Uses New Powerful Malware to Target Vietnamese Public Company
- Suspected Threat Actors: APT32 aka OceanLotus
- Attack Type: Malware Implant
- Objective: Data Theft
- Target Technology: Windows
- Target Geographies: Vietnam
- Target Industries: Public Sector and Agriculture
- Business Impact: Data Loss
Summary:
Recently, attacks against Vietnamese public companies and agribusiness have been linked to the threat actor known as REF2754, which shares similarities with the Vietnamese threat group APT32, Canvas Cyclone, Cobalt Kitty, and OceanLotus and is active since 2014. There are very limited details about the target industry and attack method, however, so far, we know it was the agribusiness and public sector companies that were targeted by employing new malware. One of the malwares is known by the name SPECTRALVIPER. SPECTRALVIPER is a highly obfuscated x64 backdoor that possesses various functionalities, including PE loading and injection, file upload and download, and directory manipulation, as well as token impersonation capabilities. During the defense evasion process, the malware SPECTRALVIPER employs extensive obfuscation techniques, such as breaking down each function into multiple layers of dummy functions that encapsulate the original logic. Additionally, the control flow of these functions is obfuscated using control flow flattening. This technique rearranges program blocks within a loop and utilizes a switch statement to control the flow of the program, effectively eliminating clear program structures. Meanwhile, another malware that was spotted during investigations is P8LOADER, it is a recently uncovered x64 Windows loader designed to execute a PE file either from a file or from memory. This malicious software possesses the capability to redirect the output of the loaded PE to its logging system and employs hooking techniques to log import calls within the PE. Another malware called Powerseal, is a PowerShell runner designed specifically for offensive security purposes. It draws inspiration from numerous open-source offensive security tools, injecting their features into a cohesive package that offers streamlined offensive capabilities while incorporating built-in defense evasion techniques.
Insights:
- It is important to note that APT32 resurfaced after a period of inactivity of approximately two years, and it is not the first instance of the group carrying out attacks within their own territory. In the past, the APT targeted NGOs located in Vietnam, and the motive behind those attacks remains unclear.
- The REF2754 victim is a significant agribusiness enterprise that holds critical importance within Vietnam’s food production and distribution supply chains. The ongoing campaign targeting this entity has resulted in unauthorized access to its financial transaction records. Examining these compromised records in conjunction with the national strategic food safety policy for REF2754 can yield valuable insights into various aspects, including management competency, corruption, foreign influence, and price manipulations. These insights surpass the limitations of traditional regulatory reporting, offering unique perspectives otherwise unattainable through standard procedures.
Major Geopolitical Developments in Cybersecurity
France Thwarts Russian disinformation campaign
- The French authorities have publicly identified a digital disinformation campaign against several European countries, including France, since September, involving state entities or entities affiliated with the Russian government that has been amplifying false information.
- According to France’s foreign affairs ministry, French authorities thwarted a campaign in which malicious actors attempted to plant and amplify disinformation using, in part, spoofed pages, misrepresenting themselves as major news outlets in a coordinated campaign. The campaign involved the creation of fake web pages impersonating French media, including 20 Minutes, Le Monde, Le Parisien, and Le Figaro, and government sites, as well as the creation of fake accounts on social networks. According to the ministry, the campaign involved Russian embassies and cultural centers, as well as Russian companies, in an attempt to undermine Western support for Ukraine, in its defense to Russian aggression. French officials stated that the campaign was detected in advance, with protective and preventive measures being already taken and other technical steps still underway. The Ministry for Europe and Foreign Affairs also stated that it has dodged an attempt at identity theft on its website.
Hacktivist collective claims to have damaged Russian telecom provider’s infrastructure.
- The Cyber Anarchy Squad, a hacktivist collective which states it organizes itself to support Ukraine in defending itself against Russia, claimed to have hit and severely damaged Russian telecommunications provider Infotel JSC and its hardware. The targeted organization confirmed the attack and acknowledged that some of its network equipment was damaged.
- The Central Bank of Russia is one of Infotel JSC’s many clients in the financial industry. Its infrastructure is crucial for connecting the Central Bank to other financial service providers and online retailers. According to the hacktivist collective, their attack has made it difficult, if not impossible, for banks to carry out normal transactions.
Other Observations
CYFIRMA Research team observed a potential data leak related to CARA, (www[.]cara [.]com[.]my). CARA is a creative technology service provider, founded in 2005 in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. The company thrives on its passion for leveraging technology to creatively solve business challenges. The data that has been exposed consists of a diverse array of sensitive and confidential information in SQL format, with a total size of 7.3 GB.
Source: Underground forums
New Stealer Malware was announced in a well-known underground forum
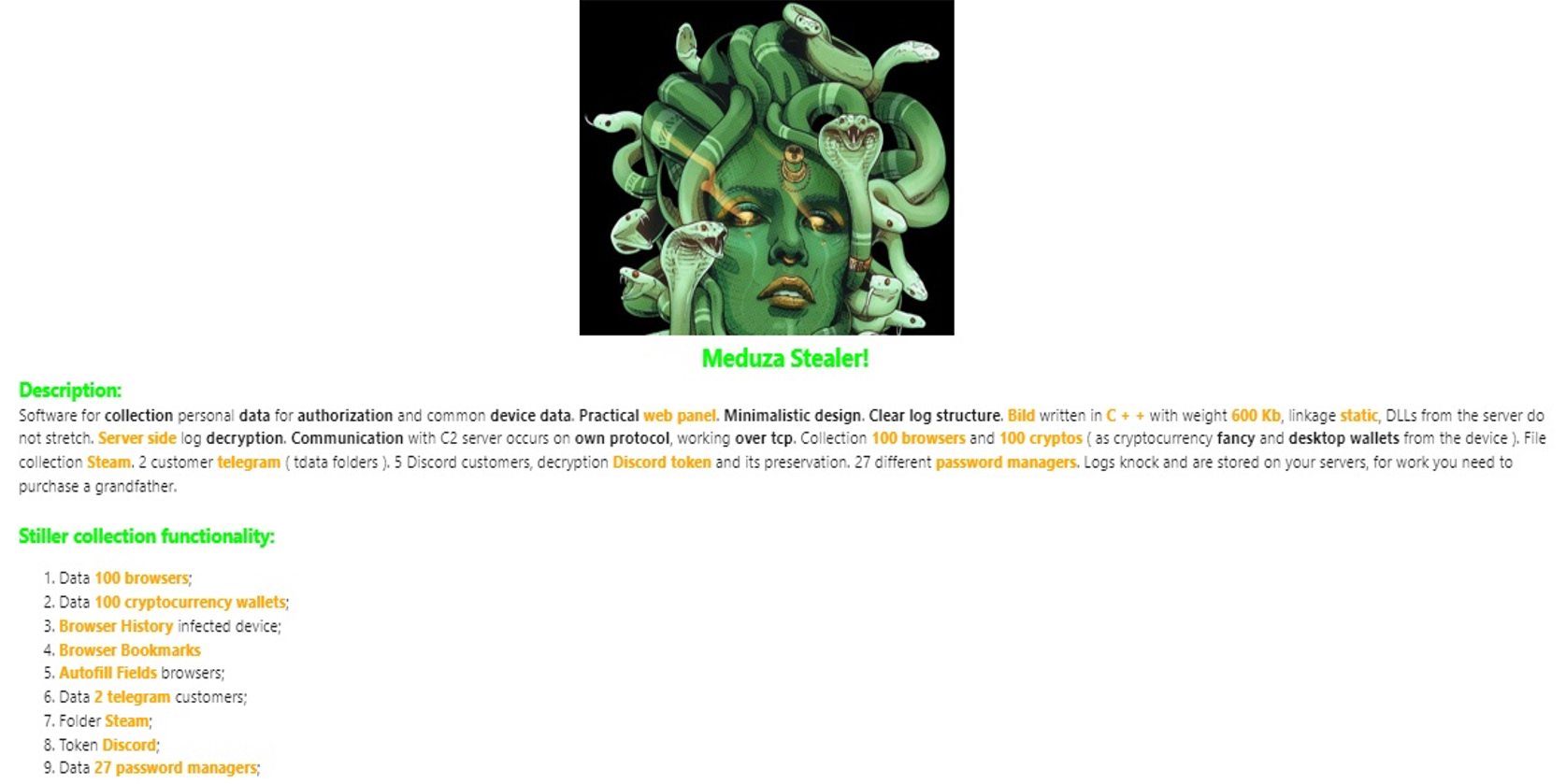
Source: Underground forums
CYFIRMA Research team observed threat actor Meduza releasing a new and untested malware named Meduza Stealer. Meduza Stealer is software designed to gather personal data for authentication purposes and capture general device information. It features a practical web panel with a minimalist design and a clear log structure. The build, written in C++, has a compact size of 600 KB and utilizes static linking, without requiring DLLs from the server. Server-side log decryption ensures data security. Communication with the C2 server occurs through a proprietary TCP-based protocol. Meduza Stealer can collect data from 100 web browsers, 100 crypto wallets (including cryptocurrency extensions and desktop wallets), and Steam files. It also targets Telegram clients (data folders) and Discord clients, enabling Discord token decryption and saving. Additionally, it supports 27 different password managers. Collected logs are securely stored on dedicated servers, necessitating the purchase of a dedicated server for operational purposes.
Stealer Collection Functionality:
- Data Collection from 100 web browsers.
- Data Collection from 100 cryptocurrency wallets.
- Capture of Browser History from infected devices.
- Capture of Browser Bookmarks from infected devices.
- Gathering of Autofill Fields from supported browsers.
- Data Collection from Telegram clients.
- Retrieval of Steam folder contents.
- Extraction of Discord Tokens.
- Data Collection from 27 password managers.
Panel Functionality:
- Secure Login Page: A protected entry point to the panel, utilizing multiple encryption algorithms.
- Loglist: Provides a comprehensive list of logs with general information for each log.
- Dashboard: An intuitive and informative page displaying weekly statistical information for easy monitoring and analysis.
- File Pumper: Enables users to increase the size of any file directly within the web panel for specific purposes.
The Meduza group is a newly established threat actor specializing in custom software development. Their services include creating phishing and landing pages, developing bots for messaging platforms, designing software for automation purposes, building optimized backends, crafting user-mode malware for Windows and Android, working with blockchain and smart contracts, and creating graphic and console applications for desktop and mobile devices. The group possesses a diverse technology stack and expertise in programming languages such as C/C++, Java, JavaScript/TypeScript, Kotlin (JVM), and Python.
STRATEGIC RECOMMENDATION
- Attack Surface Management should be adopted by organizations, ensuring that a continuous closed-loop process is created between attack surface monitoring and security testing.
- Deploy a unified threat management strategy – including malware detection, deep learning neural networks, and anti-exploit technology – combined with vulnerability and risk mitigation processes.
- Incorporate Digital Risk Protection (DRP) in the overall security posture that acts as a proactive defence against external threats targeting unsuspecting customers.
- Implement a holistic security strategy that includes controls for attack surface reduction, effective patch management, active network monitoring, through next generation security solutions and ready to go incident response plan.
- Create risk-based vulnerability management with deep knowledge about each asset. Assign a triaged risk score based on the type of vulnerability and criticality of the asset to help ensure that the most severe and dangerous vulnerabilities are dealt with first.
MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATION
- Take advantage of global Cyber Intelligence providing valuable insights on threat actor activity, detection, and mitigation techniques.
- Proactively monitor the effectiveness of risk-based information security strategy, the security controls applied and the proper implementation of security technologies, followed by corrective actions remediations, and lessons learned.
- Move beyond the traditional model of security awareness towards improved simulation and training exercises that mimic real attack scenarios, account for behaviours that lead to a compromised, and are measured against real attacks the organization receives.
- Consider implementing Network Traffic Analysis (NTA) and Network Detection and Response (NDR) security systems to compensate for the shortcoming of EDR and SIEM solutions.
- Detection processes are tested to ensure awareness of anomalous events. Timely communication of anomalies and continuously evolved to keep up with refined ransomware threats.
TACTICAL RECOMMENDATION
- Patch software/applications as soon as updates are available. Where feasible, automated remediation should be deployed since vulnerabilities are one of the top attack vectors.
- Consider using security automation to speed up threat detection, improve incident response, increased the visibility of security metrics, and rapid execution of security checklists.
- Build and undertake safeguarding measures by monitoring/ blocking the IOCs and strengthen defences based on tactical intelligence provided.
- Deploy detection technologies that are behavioural anomaly-based to detect ransomware attacks and help to take appropriate measures.
- Implement a combination of security control such as reCAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart), Device fingerprinting, IP backlisting, Rate-limiting, and Account lockout to thwart automated brute-force attacks.
- Ensure email and web content filtering uses real-time blocklists, reputation services, and other similar mechanisms to avoid accepting content from known and potentially malicious sources.





