



Key Intelligence Signals:
Blind Eagle Back with New Wave of Attack Against Multiple Nations
Summary: The threat actor Blind Eagle also known as APT-C-36, is a South American cyber espionage group, that has been targeting financial and governmental entities in Latin America for the past few years, they especially focus on Colombia as their primary target. The group usually uses a PDF attachment sent by email as the initial vector for infection. The threat actor uses Blind Carbon Copy (BCC) field instead of the “To:” field to evade spam filters and successfully deliver their phishing mail. The PDF attachment contains a URL that redirects the user to a malicious website, which downloads a second-stage payload from the public service Discord. In a recent campaign, the threat actor the masked link in the email, which redirected to dian.server[.]tl. DIAN is Colombia’s Directorate of National Taxes and Customs and, dian.server[.]tl was a fake website that impersonated DIAN’s website. The threat actor manipulated the victim into believing the webpage is the real DIAN website. The fake DIAN website page reflected a download button that lets victims view PDFs. Clicking the download button initiates the download of a malicious file from the Discord content delivery network (CDN), which the attackers are abusing in this phishing scam. Upon further research on payload deployment, it was learned that attacks also included Ecuador, Chile, and Spain.
Insights: Previously in the month of January, Blind Eagle was seen targeting by impersonating the ministry of foreign affairs from the Columbian government. The threat actor is targeting the victim in the same manner, but the impersonation part is different.
The threat actor is observed of expanding its attack surface to European nations in addition to targeting nations in Latin America.
The largest Western Europe-led cyber exercise has taken place in Tallinn, Estonia with 34 teams taking part in a live-fire cyber battle. The exercise had been led by a team of cyber specialists from the British Army and was the culmination of more than 12 months of training for more than 750 cyber specialists, including defense, government, and industry personnel from 11 countries including Ukraine.
Hosted in Tallinn, Estonia, the exercise saw teams from across the world respond to common and complex simulated cyber threats including attacks to networks, industry control systems, and unmanned robotic systems – simulating some of the tactics Russia used to disrupt Ukrainian cyberspace in the early days of the invasion one year ago. The exercise participants were judged in a competition on the effectiveness and speed of their response and how quickly they identify and adapt to new threats – which is a vital way of training needed for developing war-fighting skills for cyberspace in 21. century.
Russia’s Internet watchdog Roskomnadzor has banned nine foreign-based messaging apps from use by the Russian government. The agency singles out the apps as providing a way for users to communicate directly with one another with no possibility for public mediation of the content, which seems to be a problem for the Russian government. Rozkomnadzor’s statement makes no specific accusation of subversion or direct complicity with any foreign powers trying to disrupt the Russian government, in contrast to earlier bans on Facebook and Instagram. The apps that fall under the new restrictions include Discord, Microsoft Teams, Skype for Business, Snapchat, Telegram, Threema, Viber, WhatsApp, and WeChat.
Researchers have observed a Chinese cyberespionage operation that’s targeting government entities in several Southeast Asian countries, including Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia. A new version of the SoulSearcher loader is being used by the threat actor to distribute the Soul malware. The researchers come to the conclusion that one or more APTs based in China are using the malware, even though the Soul framework was previously unattributed.
Although the operation bears similarities to earlier campaigns run by the Chinese APT “Sharp Panda,” the researchers note that specific attribution remains a problem because sharing unique tools or operational techniques is very common among threat actors operating out of China.
According to US Cyber Command and NSA chief General Paul Nakasone, who has recently testified in front of the US Senate Armed Services Committee, Russia remains a very capable adversary in cyberspace. The general has also assured the Senators that US Cyber Command was monitoring the Russian war against Ukraine very carefully. Other Cyber Command and NSA officials made similar comments to the media, noting that the agencies anticipate that Russian cyber activities may become bolder and look at broader targets, outside of Ukraine and that there is a chance that Russia will be increasingly brazen in its cyberattacks on civilian infrastructure.
According to US Cyber Command and NSA chief General Paul Nakasone, who has recently testified in front of the US Senate Armed Services Committee, Russia remains a very capable adversary in cyberspace. The general has also assured the Senators that US Cyber Command was monitoring the Russian war against Ukraine very carefully. Other Cyber Command and NSA officials made similar comments to the media, noting that the agencies anticipate that Russian cyber activities may become bolder and look at broader targets, outside of Ukraine and that there is a chance that Russia will be increasingly brazen in its cyberattacks on civilian infrastructure.
The White House has released the National Cybersecurity Strategy, which newly refocuses roles, responsibilities, and resource allocations in the digital ecosystem, with a five-pillar approach. Two primary goals of the strategy shared in a press release are to rebalance the responsibility to defend cyberspace, by shifting the burden of cybersecurity away from individuals and onto specialized organizations in the sector, as well as to realign incentives to favor long-term investments by balancing threat defense with smart planning and investment. The strategy has five core tenets: Defend critical infrastructure, disrupt and dismantle threat actors, shape market forces to drive security and resilience, invest in a resilient future, and forge international partnerships to pursue shared goals.
CYFIRMA Research team observed a potential data leak related to www[.]matalan [.]co[.]uk- Matalan provides the retailing of men, women, and children’s clothing and accessories. Their headquarters are located in Liverpool, United Kingdom. This data leak contains the name, email address, and address.
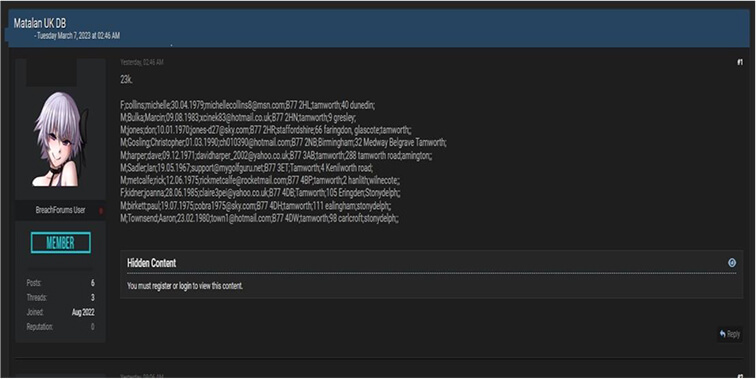
Source: Underground Forums
The Team also observed a potential data leak related to www[.]adata[.]com – ADATA is a technology manufacturing and selling company that focuses on complete memory solutions. It is headquartered in New Taipei City, Taiwan. This data leak contains sensitive data of approximately 1.5TB.
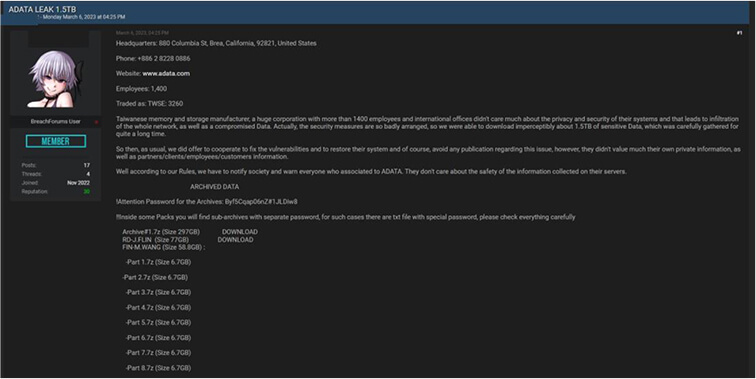
Source: Underground Forums