



Key Intelligence Signals:
Mustang Panda Deploys PlugX against Europe.
Summary:
Mustang panda is China’s state-sponsored cyber espionage group active since the year 2012. The threat actor is known for doing their operations in Europe and Asia. In the attack, the threat actor targeted a European entity using a spear phishing attack. The phishing was part of a campaign discussing the effect EU sanctions against Russia will have on the European Union. The threat actor was found to be using PlugX malware delivered through an attached ISO file to the email. The ISO file was decoyed as a document with the name “draft letter to European Commission RUSSIAN OIL PRICE CAP sg de.doc”. This is not yet clear to whom they have targeted but researchers have only published technical details behind the attack. The ISO file contains an LNK file which then contains a command line argument that can be triggered by user execution to start the PlugX malware to come into action.
Insights:
Mustang Panda has been very active from last December targeting European Public Sector and Private sector entities.
The threat is implementing new bypass methods and introducing new loader to drop Plugx malware. These technical skills keep them under the radar of the threat intel community.
Researchers have noted new patterns in state-sponsored actors’ online behavior that have emerged during the last year. Geopolitically driven actors have a history of taking advantage of the software supply chain, but it now seems that their attention is on the supply chain’s IT services. Although they are frequently not the end targets, hostile actors find cloud solutions and managed service providers (MSPs) to be interesting targets because of their broad use and their links to customers in sectors including critical infrastructure, government, and policy. Nation-state actors are increasingly investing in their capabilities and exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities more and more. Researchers also note that “cyber-mercenaries”, “privateers” and other cyber criminals for hire are becoming more significant. They are very active in the field of “surveillance as a service”, and so they pose a particular threat to dissidents, human rights campaigners, journalists, supporters of civil society, and other ordinary citizens, while typical APTs are mainly focusing on targets in which their government-sponsors are interested for political reasons.
The United States, the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, Morocco, and Israel announced a formal expansion to the Abraham Accords recently. The accords, an international treaty signed in 2020, which has normalized relations among Israel and several nations in the Middle East, are now being expanded to newly include knowledge sharing on cyber security, as also open the possibility for joint cyber exercises. According to the US Department of Homeland Security, the agreement will address several common challenges in cyberspace, including ransomware, cybercrime, and the rising threat of Iran. The accords are coming in time of heightened activity of Iranian hackers and increasing tension between Israel and Iran, which resulted in bombing of Iranian military research facilities recently, in an attack attributed to Israel by the US. Both Israel and the US are considered cyber superpowers and are likely to share their extensive knowledge of Iranian state-backed hackers in order to create a broader coalition to contain increasingly hostile Iran.
Last week senior officials from the United States and India held the first meeting of the Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET) initiative. Through this relationship, government organizations, private companies, and academic institutions will collaborate more closely on defense innovation and technology. During the conference, the two nations identified biotechnology, advanced materials, and rare earth processing technologies as potential areas of future cooperation and discussed the creation of “innovation bridges” in these industries. Jake Sullivan, national security advisor to President Biden, highlighted “the backdrop of geopolitical competition with China” as a facet of the ongoing alliance between the United States and India.
CYFIRMA Research team observed that Order Express – a USA-based money transfer service company and offers plane tickets and car services, that the 43M lines were advertised for sale which includes the addresses, names, and phone numbers, orders made (SSN 32M lines in total), ID’s, DL payment info and much more.
Total file size: Customer Data 6GB; Company data 87GB.
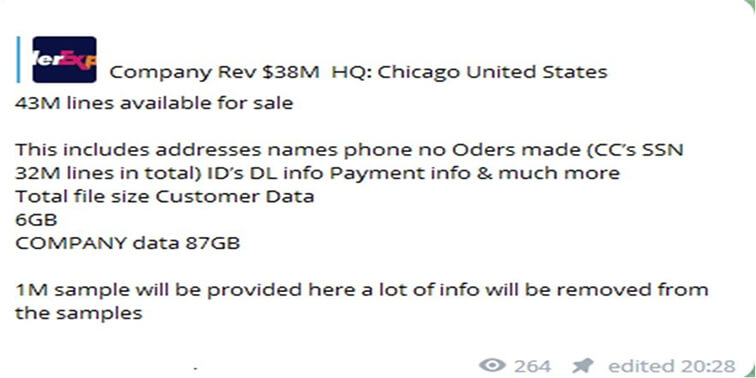
Source: Telegram
The Team also observed a potential data leak related to www[.]egypt [.]gov[.]eg -The Egyptian Government which maintains data of all citizens of Egypt. This data leak contains the citizens names, date of birth, Id number, family members info and residence info.
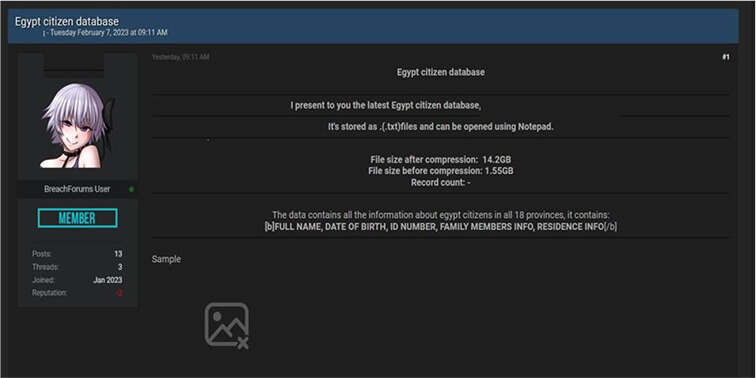
Source: Underground Forums