



A recent joint advisory by the National Security Agency (NSA), the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), and the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) describes how Chinese state-sponsored threat actors continue to exploit publicly known vulnerabilities to build a broad infrastructure of compromised systems. These threat actors attack a wide variety of targets including public and private sector organizations worldwide. The advisory detailed vulnerabilities associated with network devices routinely exploited by the attackers as early as 2020. The figure illustrates these publicly known vulnerabilities:
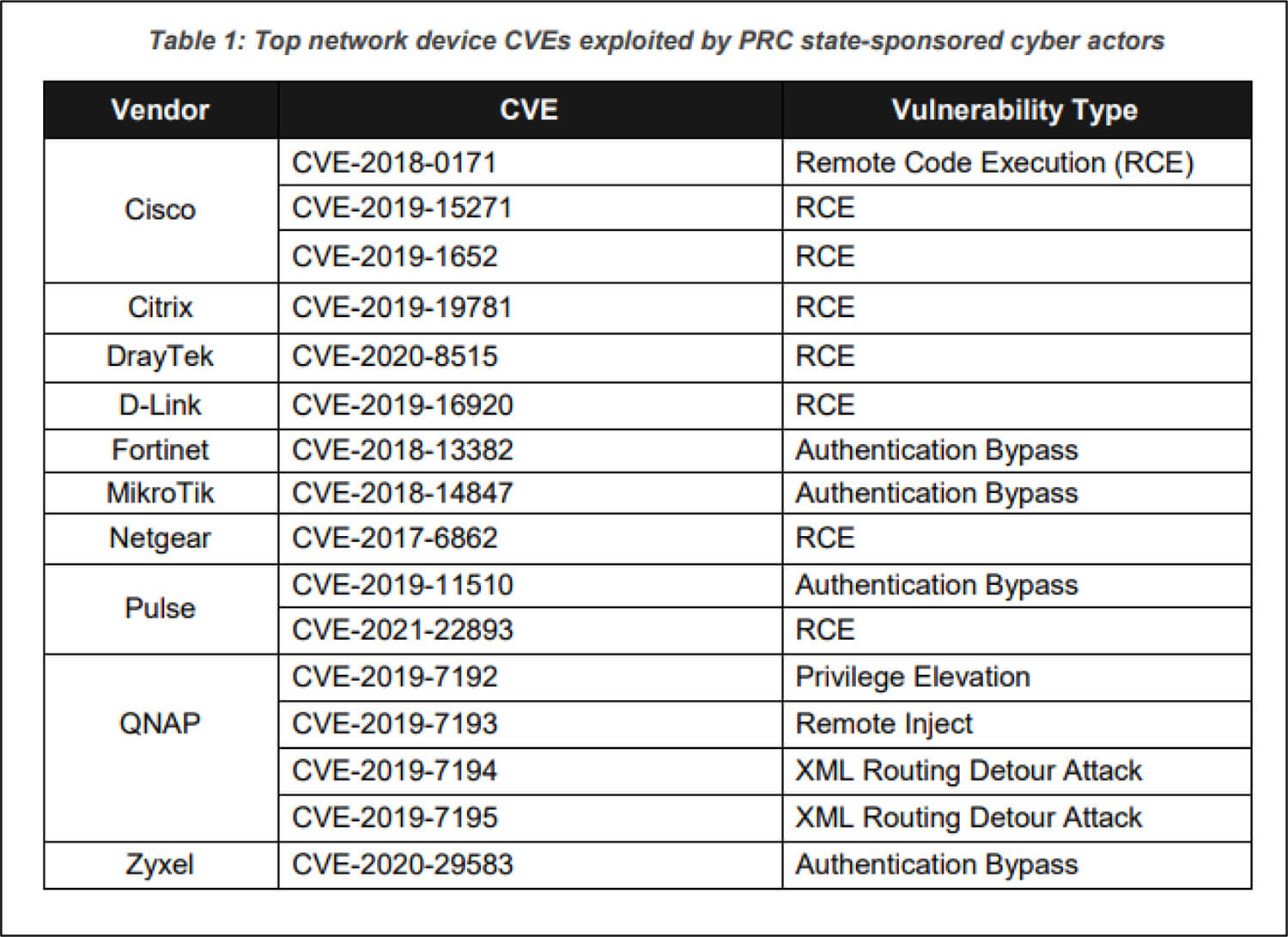
Source: Surface Web
The Chinese state-sponsored threat actors frequently take the help of open-source exploitation frameworks and tools such as RouterSploit and RouterScan for reconnaissance and vulnerability scanning. This type of activity allows them to identify make, model, as well as known vulnerabilities for further exploitation. In one such incident, after gaining initial access into the network of a telecommunications organization/ network service provider, the threat actors identified critical users and infrastructure, in this case, they identified a critical Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) server and later went onto compromise and dump credential from the underlying Structured Query Language (SQL) database which contained both cleartext and hashed passwords for user and administrative accounts.
The agencies highlight that these attackers are also consistent in evolving and adapting tactics to bypass defenses. They observed the state-sponsored actors monitored “accounts and actions” of network defenders, and then went on to modify their ongoing campaign accordingly to remain under the radar. They modified their infrastructure and toolsets as soon as information related to their ongoing campaigns become public. The Chinese state-sponsored threat actors were often found mixing their customized toolset with tools available publicly to obscure their activity in noise or normal activity of a network.
In a joint action by The Justice Department, IRS, and FBI, the popular SSNDOB Marketplace used by cybercriminals to acquire stolen Social Security numbers and other sensitive personal information has been seized and shut down. According to the DOJ, the marketplace was generating over USD19 million in sales revenue. The seizure orders were executed against several domains associated with SSNDOB which included ssndob.ws, ssndob.vip, ssndob.club, and blackjob.biz. The cybercriminals behind SSNDOB would advertise their services in other dark web forums known to be frequented by cybercriminals, offer support to their customers, use servers in various geographic locations, and require payment in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
SSNDOB Marketplace seemed to be associated with another popular stolen credential marketplace called Joker’s Stash which was shut down in January 2021.
On May 30, 2022, a Security Researcher reported a reflected XSS vulnerability in the Download Manager – a WordPress plugin that is installed on over 100,000 websites. The vulnerability has been assigned identifier CVE-2022-1985. One feature of the Download Manager plugin gives the ability to embed files and other assets in a page or post by using shortcode. This particular function was found by researchers vulnerable to reflected XSS. The vulnerability exists due to a lack of proper input sanitization and escaping the user-supplied inputs. Due to the vulnerability, JavaScript can be invoked to manipulate the page, hijack the forms, and trick the site administrator to divulge sensitive information.
Researchers state that the vulnerability may also lead to more specialized attacks where hackers would acquire administrator access, install a backdoor and compromise the site entirely.
According to WordPress security analysts, users with Free, Premium, Care, and Response, are protected from exploitation of this vulnerability due to Wordfence Firewall’s built-in Cross-Site Scripting protection. Regardless of the protection, the vendor has recommended upgrading to the latest patched instance.
MD5 : 140F716E974CD7483EEAA380A9C4FD82
SHA1 : 4D5B17CA34D8D15FBAE65AB637919E13E72A3476
SHA256 : 4DCED4DDB2FFA1E0E1E9C2F6A2D4B1302CEBCA59E7D340ADA0F2E421288B54FE
Motivation : Steal user credentials
Recently, the CYFIRMA research team has observed an active phishing campaign to steal victims’ credentials. The email contains a malicious attachment in .html format with an embedded JavaScript which upon execution will bring the user to a fake Sharepoint login page. The objective is to steal credentials and redirected the user to other malicious URLs.
Access the full technical analysis here.