


CYFIRMA Threat Intelligence has observed an ongoing malicious campaign leveraging the domain ‘telegrampremium[.]app’, which fraudulently mimics the official Telegram Premium platform. This domain hosts a downloadable executable file ‘start.exe’ containing a newly identified variant of the Lumma Stealer malware, a sophisticated information-stealing trojan. The malware is capable of exfiltrating a wide range of sensitive data, including browser-stored credentials, cryptocurrency wallet details, and system information. Critically, the payload is delivered automatically upon accessing the URL, without requiring user interaction, thereby significantly elevating the threat level. This operation highlights the adversaries’ continued use of brand impersonation and social engineering techniques to facilitate large-scale malware distribution.
CYFIRMA strongly recommends the immediate blocking of the domain, comprehensive endpoint scanning, and prompt credential rotation to mitigate potential impact and prevent further compromise.
In the evolving cyber threat landscape, financially motivated threat actors are increasingly employing deceptive methods to distribute infostealer malware. CYFIRMA has identified a malicious campaign utilizing a spoofed Telegram Premium website to deliver a new variant of the Lumma Stealer. Upon visiting the site, a malicious executable is automatically downloaded, which, when executed, exfiltrates browser credentials, cryptocurrency wallet information, and system data. This campaign exemplifies the use of brand impersonation and drive-by download techniques, underscoring the critical need for robust endpoint security, domain reputation monitoring, user awareness initiatives, and continuous threat intelligence.
| Target Technologies | Windows Operating System |
| Threat Type | Website Mimic |
| Written In | C/C++ |
| File Types | PE (Portable Executable) |
| Key Malware Identifiers | Start.exe |
| Observed First | 2025-07-20 |
| Impact | Credential Harvesting, Data Exfiltration |
| MD5 Hashes | 86170725074de3b8edcd7671afa9b69d |
The entropy value of the file start.exe exceeds 7, suggesting that it is likely packed using a Cryptor. This level of entropy is indicative of obfuscation techniques commonly used to hinder reverse engineering and complicate static analysis, thereby evading detection by traditional security tools.
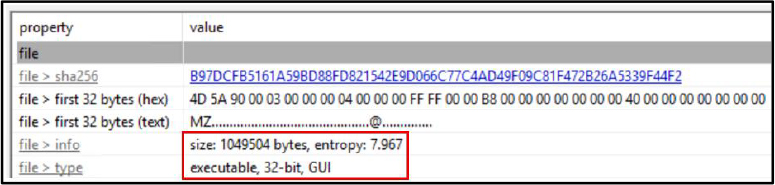
Malware imports a broad set of Windows API functions to enable comprehensive system interaction. These include:
These functions collectively enable the malware to read, write, and modify files; access and manipulate the system registry and clipboard; execute additional payloads; and blend into user workflows suggesting capabilities aligned with persistence, data theft, and system manipulation.
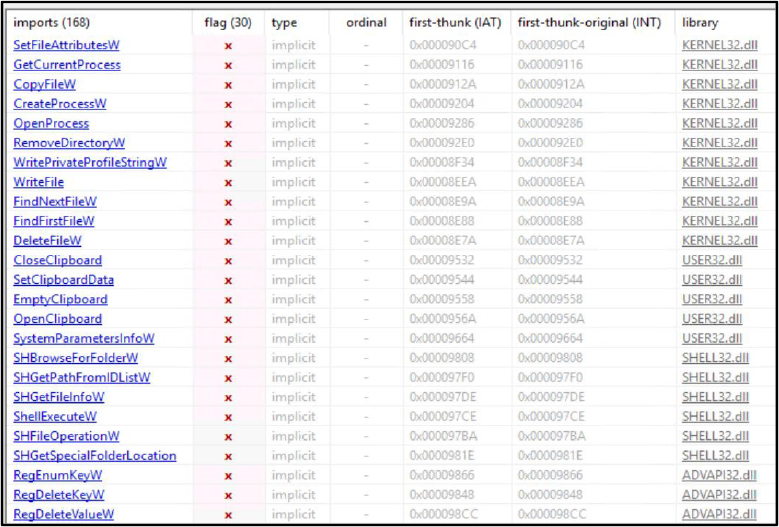
The domain telegrampremium[.]app was registered on July 13, 2025, through Web Commerce Communications Limited (WebNic.cc) and is scheduled to expire on July 12, 2026. With a domain age of only 17 days and a recent update recorded on July 21, 2025, it is indicative of a newly created domain potentially intended for short-term malicious activity. The domain resolves to the IP address 87[.]120[.]126[.]213, hosted by H2NEXUS Ltd in Germany, under ASN215730, and is currently shared with five other domains. The minimal changes in IP and hosting history further support the assessment that this domain may be part of a targeted, short-duration threat campaign.
Upon further investigation, it was revealed that the executable file was built using the C/C++ programming language.
Execution:
CreateThread starts a new thread for execution; CloseHandle releases system resource handles. Both are often used in malware for executing and managing code.
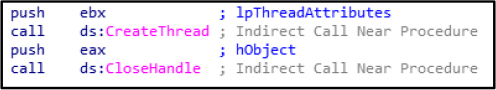
The ShellExecuteW function is used to launch secondary payloads, enabling further execution of the malware.
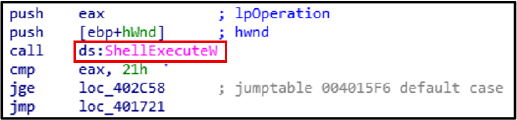
Defense Evasion:
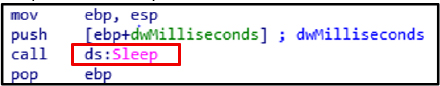
The Sleep function suspends execution. Malware leverages this to delay operations, evade dynamic analysis, and avoid detection mechanisms.
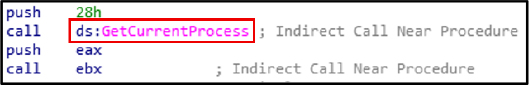
The malware uses GetCurrentProcess for process control, privilege escalation, code injection, and anti-analysis.
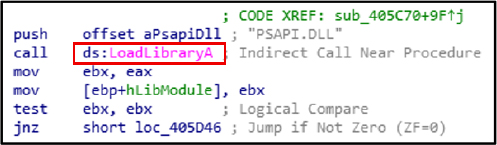
The LoadLibraryExW API to dynamically load DLLs at runtime, enabling stealthy execution and evasion of static analysis. This technique is commonly used for modular loading, process injection process, and fileless malware behavior.
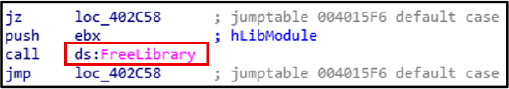
The FreeLibrary function is used to unload DLLs from memory, helping malware clean up and reduce forensic traces after executing malicious code
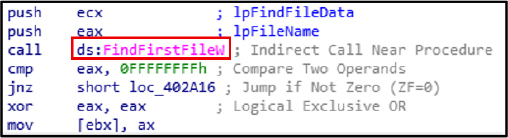
Data Discovery:
FindNextFileExW is utilized to enumerate directory files for data exfiltration purposes
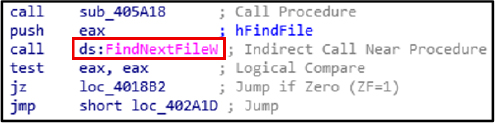
FindNextFileW continues file enumeration initiated by FindFirstFileExW
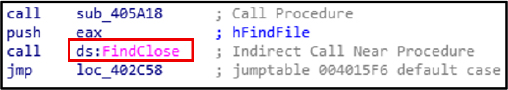
FindClose is used to release the handle obtained from FindFirstFileExW
GetFileAttributesW retrieves the attributes of a specified file or directory, while SetFileAttributesW modifies those attributes.
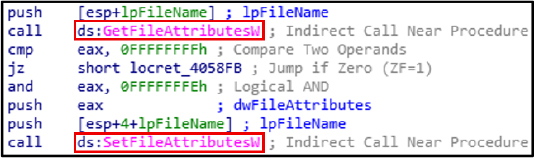
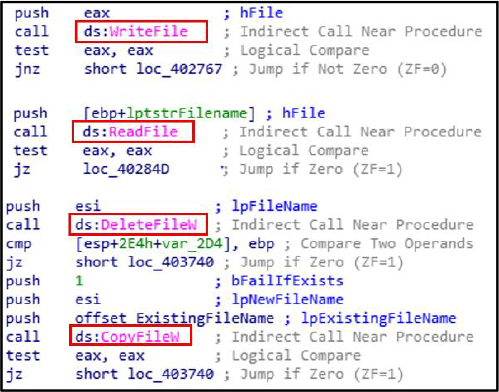
Input/Output (I/O) operations:
WriteFile, ReadFile, DeleteFile, and CopyFile are Windows API functions used to write to, read from, delete, and copy files, respectively.
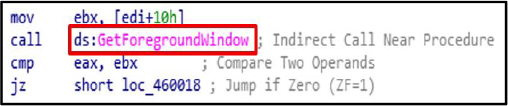
Credential Access:
The GetForegroundWindow function is used to identify the currently active window, often to capture user activity
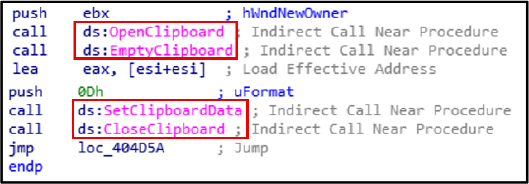
OpenClipboard, EmptyClipboard, SetClipboardData, and CloseClipboard are Windows APIs used to access, clear, modify, and release the clipboard, respectively.
Registry Modification
RegCreateKeyExW, RegSetValueExW, RegQueryValueExW, RegDeleteValueW, RegEnumKeyW, and RegCloseKey are Windows APIs for managing registry keys and values, commonly used by malware for persistence and configuration.
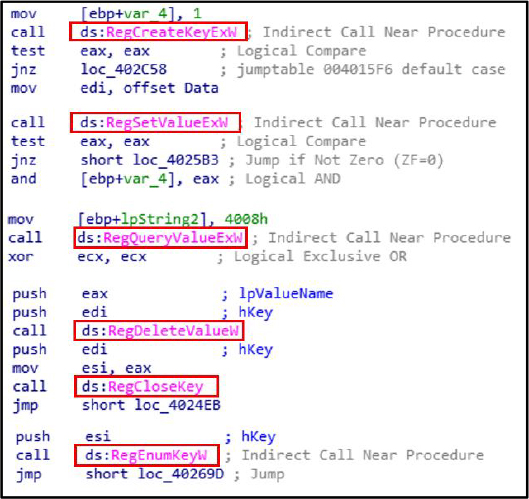
Malware Behaviors
Upon execution, the malware drops multiple .jpg files into the %TEMP% directory; however, these are not legitimate image files but instead contain encrypted payload data disguised with a .jpg extension
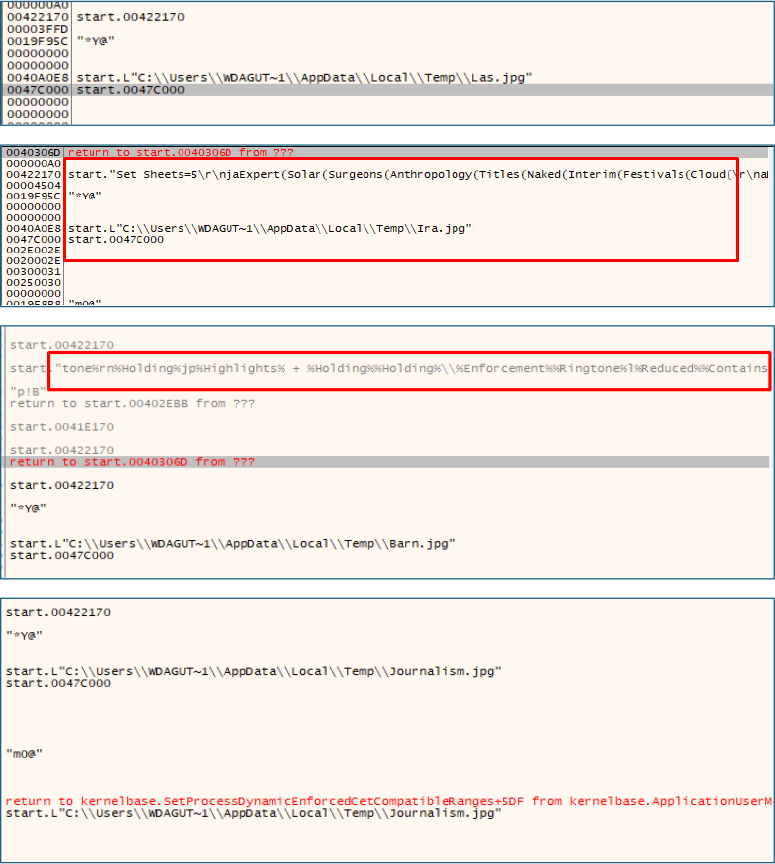
Several files dropped in Temp folder
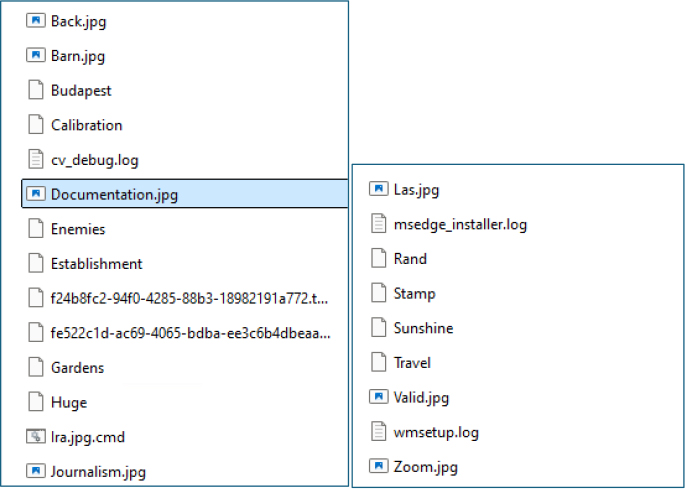
Later, lra.jpg is renamed to lra.jpg.cmd, an obfuscated batch script designed to delete the original malware.
Network Communication: During the investigation, multiple DNS queries were observed originating from a host identified as Arcade.com. These queries were directed to Google’s public DNS server (8.8.8.8) over port 53, indicating that the malware is deliberately circumventing internal DNS mechanisms to ensure reliable and unmonitored domain resolution.
The domains queried can be classified into two categories:
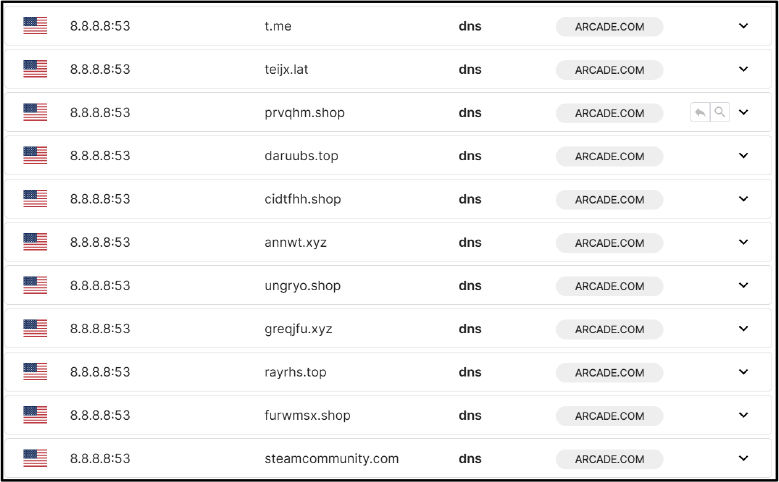
The overall DNS behavior is indicative of malware attempting to establish external communications for purposes such as data exfiltration, retrieval of secondary payloads, or execution of remote instructions. The use of a public DNS resolver in conjunction with DGA-based domain queries underscores the threat actor’s intent to evade detection, bypass enterprise security controls, and maintain persistence within the compromised environment.
An executable file impersonating Telegram Premium was observed on July 20, 2025, highlighting the growing trend of brand impersonation and drive-by downloads used in credential theft and data exfiltration campaigns.
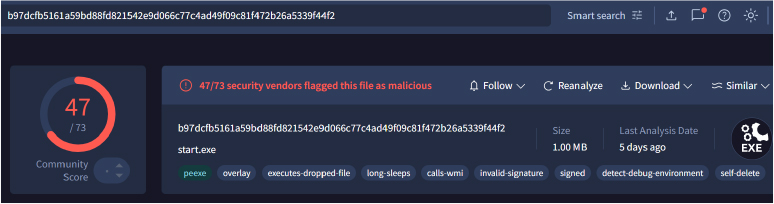
Threat actors behind this campaign hosted a malicious file, start[.]exe, on the domain telegrampremium[.]app, a fake Telegram Premium site. Once accessed, the file is automatically downloaded without user interaction, representing a significant increase in threat severity. The malware identified is a new variant of Lumma Stealer, a sophisticated information-stealing trojan capable of exfiltrating browser credentials, cryptocurrency wallets, and system metadata.
| Tactic | Technique ID | Technique Name |
| Execution | T1047 | Windows Management Instrumentation |
| T1059 | Command and Scripting Interpreter | |
| T1129 | Shared Modules | |
| Persistence | T1112 | Modify Registry |
| T1198 | Trust Provider Hijacking | |
| T1547 | Boot or Logon AutoStart Execution | |
| T1547.009 | Shortcut Modification | |
| Privilege Escalation | T1055 | Process Injection |
| Defense Evasion | T1006 | Direct Volume Access |
| T1027 | Obfuscated files or Information | |
| T1027.002 | Software Packing | |
| T1036 | Masquerading | |
| T1036.001 | Invalide Code Signature | |
| Discovery | T1010 | Application Window Discovery |
| T1012 | Query Registry | |
| T1057 | Process Discovery | |
| T1063 | Security Software Discovery | |
| T1082 | System Information Discovery | |
| Collection | T1115 | Clipboard data |
| T1125 | Video Capture | |
| Command And control | T1071 | Application layer Protocol |
| T1573 | Encrypted Channel | |
| Impact | T1485 | Data Destruction |
| T1529 | System Shutdown/Reboot |
CYFIRMA Threat Intelligence has uncovered a malware campaign using a fake Telegram Premium site to distribute a new Lumma Stealer variant. The malware uses drive-by downloads, system and registry manipulation, clipboard access, and dynamic APIs to maintain persistence, evade detection, and steal sensitive data, including credentials and cryptocurrency wallets. The campaign’s domain impersonation and evasive network tactics highlight growing threats to Windows systems.
Network and Endpoint Security
Access Control and Authentication
Infrastructure and Threat Intelligence Monitoring
Incident Response Preparedness
Stay engaged with CYFIRMA’s threat intelligence platform to stay informed on emerging TTPs and strengthen defenses against evolving threats. Regularly update your SIEM with YARA rules and IOCs provided by CYFIRMA to improve detection and response capabilities.
Kindly refer to the IOCs section to exercise controls on your security systems.
| Type | Indicator | Remarks |
| SHA256 | b97dcfb5161a59bd88fd821542e9d066c77c4ad49f09c81f472b26a5339f44f2 | Block |
| Domain | Telegrampremium[.]app | Block |
| IP | 87[.]120[.]126[.]213 | Block |
| Domain | Teijx[.]lat | Monitor |
| Domain | Prvqhm[.]shop | Monitor |
| Domain | Daruubs[.]top | Monitor |
| Domain | Cidtfhh[.]shop | Monitor |
| Domain | Annwt[.]xyz | Monitor |
| Domai | Ungryo[.]shop | Monitor |
| Domain | Greqjfu[.]xyz | Monitor |
| Domain | Rayrhs[.]top | Monitor |
| Domain | Furwmsx[.]shop | Monitor |
| SHA-1 | 9a5f72502fd9be56226716e6435888a43ff43154 | Monitor |
| SHA-1 | fc0e3ff066427316bcb001d05b3ac5692093d6a3 | Monitor |
| SHA-1 | 7a77f579c6a4bda83d659be4e39ddfd7b7e2f73c | Block |
| SHA-1 | 3921ba3ad9ace63827a8ad2d70c1c4a79d462f24 | Monitor |
| SHA-1 | 8c893331a5e01e0c99a7ad0f7f1cbb9418a86d4a | Monitor |
| SHA-1 | 0736ccd4920e227ebae3b0ded4950c01f663af6a | Monitor |
| SHA-1 | 888e33a919d5dda152a539aed3f5a3b7840937bc | Monitor |
rule LummaStealer_TelegramPremium_Variant
{
meta:
description = “Detects Lumma Stealer variant delivered via telegrampremium[.]app”
author = “CYFIRMA Threat Research”
date = “2025-07-30”
hash_sample = “b97dcfb5161a59bd88fd821542e9d066c77c4ad49f09c81f472b26a5339f44f2”
malware_family = “Lumma Stealer”
strings:
$domain1 = “telegrampremium.app”
$domain2 = “teijx.lat”
$domain3 = “prvqhm.shop”
$domain4 = “daruubs.top”
$domain5 = “cidtfhh.shop”
$domain6 = “annwt.xyz”
$domain7 = “ungryo.shop”
$domain8 = “greqjfu.xyz”
$domain9 = “rayrhs.top”
$domain10 = “furwmsx.shop”
$ip1 = “87.120.126.213”
$hash1=
“b97dcfb5161a59bd88fd821542e9d066c77c4ad49f09c81f472b26a5339f44f2”
condition:
(any of ($hash*) and any of ($domain*) and any of ($ip*))
}