


At Cyfirma, we are dedicated to providing you with up-to-date information on the most prevalent threats and tactics used by malicious actors to target both organizations and individuals. In this report, we will explore the nefarious practice of SEO Poisoning, uncovering its insidious nature, potential consequences, and recommended prevention strategies. SEO poisoning is a malicious technique employed by threat actors to manipulate search engine results and drive users to their malicious websites. This technique relies on various methods, including typosquatting and blackhat SEO tactics, to deceive users and expose them to risks such as credential theft, malware infections, and financial losses. By staying informed and proactive, you can safeguard yourself against this pervasive threat and mitigate its detrimental effects.
As the usage of search engines continues to increase, SEO poisoning has emerged as a significant and often overlooked security threat. Exploiting the trust placed in top search results, threat actors employ deceptive tactics to manipulate search engine rankings, leading unsuspecting users to malicious websites. This comprehensive report delves into the depths of SEO poisoning, unravelling its complex workings, techniques, and potential ramifications.
By shedding light on this pervasive threat, organizations and individuals can better understand the risks at hand and take proactive measures to safeguard their digital presence and sensitive information. With a focus on detection, prevention, and mitigation strategies, this report equips readers with the knowledge needed to combat SEO poisoning’s insidious influence.
SEO poisoning, also known as search engine poisoning, is a malicious technique employed by threat actors to manipulate search engine results and increase the visibility of their malicious websites. It is a form of blackhat SEO tactics used to deceive search engines and users, leading them to click on compromised or malicious links. SEO poisoning can have detrimental effects, including credential theft, malware infections, and financial losses.
There are various techniques and methods used in SEO poisoning, each with the aim of tricking search engine algorithms and exploiting user behavior. Here are some of the key techniques employed:
Typosquatting: Typosquatting involves registering domain names that are similar to legitimate ones, but with intentional typos or misspellings. Threat actors take advantage of users’ typos when typing URLs or clicking on links, redirecting them to malicious websites instead of the intended legitimate ones. For example, a user searching for “team viewer” might click on a typosquatted domain that appears in the search results, leading them to a fake website, where malware-infected files are offered for download. For more details on “Typosquatting” technique, associated threats, and recommended mitigation approaches, explore Cyfirma’s detailed report here.
Link Manipulation: Threat actors may manipulate links to improve their website’s search engine ranking and visibility. This can involve creating a network of backlinks from unrelated websites, known as private link networks, to give the impression of authority and relevance to search engines. By artificially boosting the number of backlinks, attackers attempt to trick search engines into ranking their malicious websites higher in search results.
Keyword Stuffing: Keyword stuffing is the practice of cramming irrelevant or excessive keywords into webpage content, meta tags, or other parts of a website. The intention is to manipulate search engine algorithms into giving the website a higher ranking for those keywords. However, this technique often results in poor user experience and can lead to penalties from search engines, if detected.
Content Cloaking: Content cloaking involves presenting different content to search engine crawlers than what is displayed to users. By doing so, threat actors can deceive search engines into ranking their websites higher, based on the content shown to crawlers, while displaying unrelated or malicious content to users. This technique aims to manipulate search engine rankings by presenting favourable information to crawlers, while hiding the true nature of the website from users.
Malicious Advertising (Malvertising): Malvertising is another method used in SEO poisoning campaigns. It involves placing malicious advertisements on legitimate websites or in search engine results. When users click on these ads, they may be redirected to malicious websites that distribute malware or attempt to steal sensitive information.
Threat actors continually evolve their techniques to make SEO poisoning campaigns more effective and difficult to detect. They may target specific user groups, such as IT administrators, by employing spear-phishing tactics. By customizing attacks and creating sophisticated traps, threat actors increase the chances of users falling victim to their malicious schemes.
In recent years, the increasing sophistication of AI and natural language processing technologies has not only benefited legitimate applications but also posed new challenges in the realm of cybersecurity. Attackers are now leveraging AI and ChatGPT-like models to enhance the effectiveness of their SEO poisoning attacks.
By utilizing AI-powered tools, threat actors can automate and streamline various stages of their campaigns. AI algorithms can help them identify popular search queries and trending topics to optimize their malicious content for maximum visibility. They can generate convincing and contextually relevant content, enabling them to create websites and articles that appear legitimate and trustworthy to search engines and users.
Here are some examples of how AI and ChatGPT are used by threat actors for advance SEO poisoned attacks:
These examples highlight the ways in which AI and ChatGPT can be employed to enhance the effectiveness and sophistication of SEO poisoned attacks. By leveraging AI technology, attackers can increase their chances of deceiving users, manipulating search engine rankings, and successfully distributing malware or stealing sensitive information.
From an external threat landscape perspective, SEO poisoning attacks pose significant risks to organizations. Here are three key points to consider:
Heightened Malware Distribution: SEO poisoning attacks have become a favoured method for distributing malware to unsuspecting users. By manipulating search engine rankings and luring users to malicious websites, threat actors can exploit vulnerabilities, infect systems with malware, and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. The increasing sophistication of these attacks makes it imperative for organizations to be vigilant in protecting their networks and systems.
Targeted Exploitation: Threat actors can employ targeted SEO poisoning techniques to tailor their attacks to specific audiences, making them more challenging to identify and defend against. By leveraging spear-phishing tactics and personalized content, attackers can trick high-value targets, such as IT administrators or executives, into accessing malicious websites or downloading infected files. Organizations must be aware of these targeted threats and implement robust security measures accordingly.
Reputational and Financial Consequences: SEO poisoning attacks not only compromise the security of organizations but also have severe reputational and financial consequences. If an organization’s website or brand name is associated with malicious activities due to SEO poisoning, it can result in reputational damage and loss of customer trust. Moreover, financial losses can arise from legal liabilities, remediation costs, and potential lawsuits. Organizations must prioritize the prevention and detection of SEO poisoning to safeguard their reputation and financial stability.
In 2023, there have been several reported incidents of SEO poisoning campaigns that have targeted users with the intention of distributing malware and stealing sensitive information. Here are a couple of notable examples:
For instance, attackers utilized poisoned Google Ads to drop a Python-based malware that specifically targeted browsers, aiming to steal information such as browser passwords and cryptocurrency wallets. The fake installers were designed to mimic legitimate software, such as OBS Studio or Notepad++, to deceive users into downloading and executing the malware.
These latest campaigns provide us a clear indication that SEO poisoning continues to pose a significant threat.
Underground and Dark Web Forums: Hub for Cybercriminals Selling SEO Poisoning Attack Services and Tools:
Further, as shown in below screen shots, the cybercriminals are also selling SEO poisoning attack services and tools on underground and dark web forums:
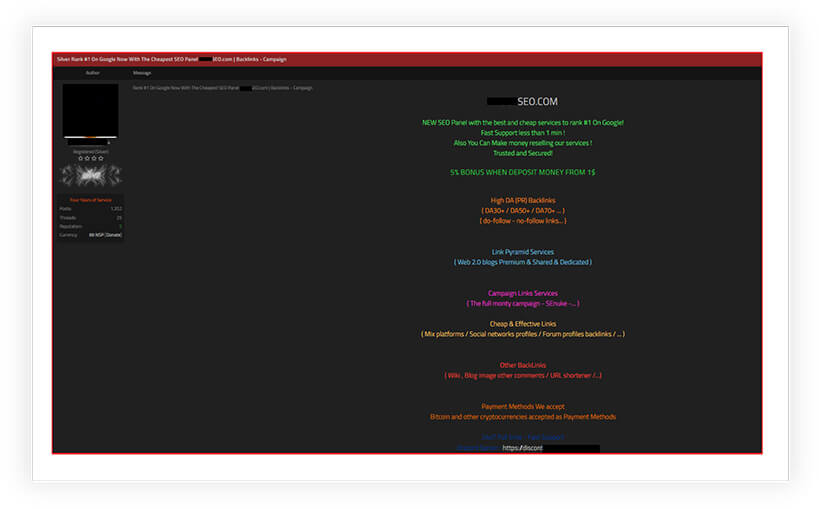
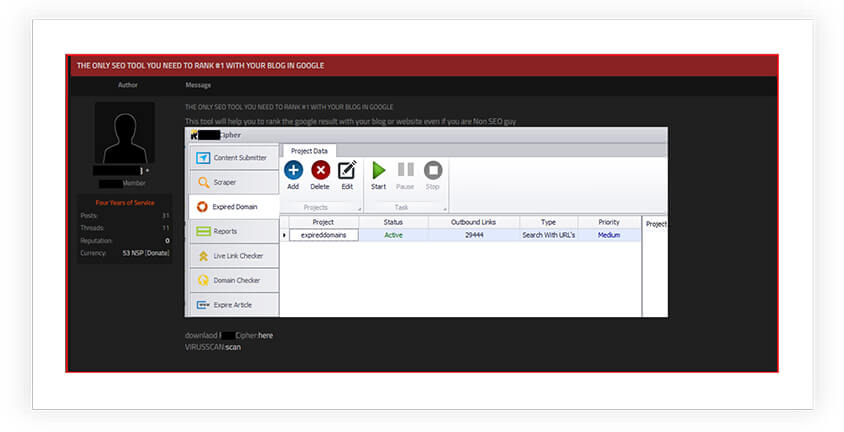
Screen shots obtained from these illicit forums reveal a thriving market, where individuals and cybercriminals can purchase ready-made solutions or hire skilled attackers to carry out SEO poisoning campaigns.
By understanding the external threat landscape surrounding SEO poisoning attacks, organizations can better comprehend the importance of implementing proactive security measures and staying abreast of emerging threats in order to safeguard their digital assets and maintain a strong security posture.
Volume and Scale: The sheer volume of websites and web pages on the internet makes it challenging to monitor and identify all instances of SEO poisoning. Detecting every malicious or compromised website in search engine results is a daunting task, and manual monitoring is impractical due to the scale involved.
Legitimate Websites Compromised: SEO poisoning attacks often involve compromising legitimate websites and injecting malicious content. Identifying whether a website has been compromised and is actively participating in SEO poisoning can be complex, as distinguishing between legitimate and malicious content becomes more challenging.
Evolving Techniques: Cybercriminals constantly adapt their SEO poisoning techniques, making it challenging for detection systems to keep up with the latest tactics. As attackers employ new methods and obfuscation techniques, traditional detection mechanisms may struggle to identify and classify malicious websites accurately.
Polymorphic Malware: SEO poisoning campaigns often involve the distribution of malware. However, cybercriminals frequently utilize polymorphic malware, which can change its code structure and characteristics to evade detection by antivirus or endpoint protection solutions. This makes it difficult to detect and mitigate the malware payload associated with SEO poisoning.
SEO poisoning attacks have emerged as a significant and evolving threat in the digital landscape, exploiting the widespread use of search engines and the trust placed in top search results. This report has provided a comprehensive examination of SEO poisoning, encompassing its techniques, recent campaigns, the complexities involved in detection, and the recommended prevention strategies. It has highlighted the critical role played by AI and ChatGPT-like models in enhancing the effectiveness of these attacks.
To prevent SEO poisoning, organizations can adopt measures such as typosquatting detection procedures, the use of Indicators of Compromise (IOC) lists, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to enhance their detection capabilities and mitigate the impact of these attacks. Organizations must prioritize user security training and awareness programs, establish a solid internal security posture, and regularly disclose abnormal SEO results to their security teams. By educating staff and customers, implementing robust security measures, and staying vigilant against emerging threats, organizations can minimize the risks associated with SEO poisoning attacks.
From an external threat landscape perspective, organizations face a heightened risk of malware distribution, targeted exploitation, and severe reputational and financial consequences. As the threat landscape continues to evolve, it is crucial for organizations to remain proactive, adaptable, and informed. By understanding the techniques employed by threat actors, organizations can better protect themselves, their stakeholders, and their digital assets from the far-reaching consequences of SEO poisoning attacks.
Recommendations to Prevent SEO Poisoning Attacks: